How can I help you?
Getting Started with WPF TreeGrid (SfTreeGrid)
12 Aug 202524 minutes to read
The WPF TreeGrid (SfTreeGrid) is a data oriented control that displays the self-relational and hierarchical data in tree structure with columns. The data can be loaded on-demand also.
Assembly Deployment
The following list of assemblies needs to be added as reference to use SfTreeGrid control in any application,
| Required assemblies | Description |
|---|---|
| Syncfusion.Data.WPF | Syncfusion.Data.WPF assembly is dependent assembly for Syncfusion.SfGrid. WPF |
| Syncfusion.SfGrid.WPF | Syncfusion.SfGrid.WPF assembly contains classes that handles all UI operations of SfTreeGrid. SfTreeGrid control present in Syncfusion.UI.Xaml.TreeGrid namespace. This namespace also added in http://schemas.syncfusion.com/wpf Syncfusion WPF schema. |
| Syncfusion.Shared.WPF | Syncfusion.Shared.WPF contains various editor controls (such as IntegerTextBox, DoubleTextBox and etc) which are used in SfTreeGrid. |
In order to use export to excel and export to PDF functionalities of SfTreeGrid control, add the reference to following assemblies,
| Optional Assemblies | Description |
|---|---|
| Syncfusion.SfGridConverter.WPF | Syncfusion.SfGridConverter.WPF contains static extension classes for exporting SfTreeGrid to excel and PDF in Syncfusion.UI.Xaml.TreeGrid.Converter namespace. |
| Syncfusion.XlsIO.Base | Syncfusion.XlsIO.Base contains fundamental and base classes for creating and manipulating excel files. |
| Syncfusion.Pdf.Base | Syncfusion.Pdf.Base contains fundamental and base classes for creating PDF. |
Creating simple application with SfTreeGrid
In this walk through, you will create WPF application with SfTreeGrid control.
- Creating project
- Adding control via Designer
- Adding control manually in XAML
- Adding control manually in C#
- Binding self-relational data in SfTreeGrid
- Binding nested collection with SfTreeGrid
- Populate SfTreeGrid in on-demand
- Defining Columns
- Selection
- Sorting
- Editing
- Filtering
Creating the project
Create new WPF project in Visual Studio to display SfTreeGrid with data objects.
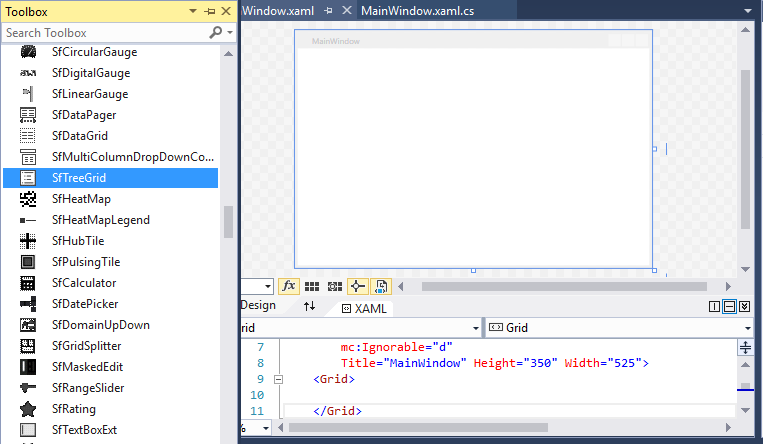
Adding control via Designer
WPF TreeGrid (SfTreeGrid) control can be added to the application by dragging it from Toolbox and dropping it in Designer view. The required assembly references will be added automatically.
Adding control manually in XAML
In order to add control manually in XAML, do the below steps,
- Add the below required assembly references to the project as shown in the below image,
- Syncfusion.Data.WPF
- Syncfusion.SfGrid.WPF
- Syncfusion.Shared.WPF
- Import Syncfusion® WPF schema http://schemas.syncfusion.com/wpf or SfTreeGrid control namespace Syncfusion.UI.Xaml.TreeGrid in XAML page.
-
Declare SfTreeGrid control in XAML page.
<Window x:Class="WpfApplication1.MainWindow" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:syncfusion="http://schemas.syncfusion.com/wpf" Title="MainWindow" Width="525" Height="350"> <Grid> <syncfusion:SfTreeGrid x:Name="treeGrid" /> </Grid> </Window>
Adding control manually in C#
To add control manually in C#, do the below steps,
- Add the below required assembly references to the project,
- Syncfusion.Data.WPF
- Syncfusion.SfGrid.WPF
- Syncfusion.Shared.WPF
- Import SfTreeGrid namespace Syncfusion.UI.Xaml.TreeGrid.
-
Create SfTreeGrid control instance and add it to the Page.
using Syncfusion.UI.Xaml.TreeGrid; namespace WpfApplication1 { public partial class MainWindow : Window { public MainWindow() { InitializeComponent(); SfTreeGrid treeGrid = new SfTreeGrid(); Root_Grid.Children.Add(treeGrid); } } }
Binding self-relational data in SfTreeGrid
WPF TreeGrid (SfTreeGrid) supports to bind self-relational data by setting SfTreeGrid.ParentPropertyName and SfTreeGrid.ChildPropertyName properties where tree structure is formed based on these two properties.
SfTreeGrid.ParentPropertyName – Denotes the property in data object which is used to identify the root nodes.
SfTreeGrid.ChildPropertyName - Denotes the property in data object which is used identify its parent by matching the property value with ParentPropertyName property value of other data objects.
The data objects which has unique property value in SfTreeGrid.ParentPropertyName or the data objects which has the property value as in SfTreeGrid.SelfRelationRootValue are root nodes.
Creating Data Model for self-relational collection
SfTreeGrid is a data-bound control. So, before binding to the control, you must create data model for application.
-
Creating data object class named
EmployeeInfoand declare properties as shown below,public class EmployeeInfo { int _id; string _firstName; string _lastName; private string _title; double? _salary; int _reportsTo; public string FirstName { get { return _firstName; } set { _firstName = value; } } public string LastName { get { return _lastName; } set { _lastName = value; } } public int ID { get { return _id; } set { _id = value; } } public string Title { get { return _title; } set { _title = value; } } public double? Salary { get { return _salary; } set { _salary = value; } } public int ReportsTo { get { return _reportsTo; } set { _reportsTo = value; } } }
NOTE
If you want your data object (EmployeeInfo class) to automatically reflect property changes, then the object must implement INotifyPropertyChanged interface.
-
Create a
ViewModelclass with Employees property and Employees property is initialized with several data objects in constructor.public class ViewModel { public ViewModel() { this.Employees = this.GetEmployees(); } private ObservableCollection<EmployeeInfo> _employees; public ObservableCollection<EmployeeInfo> Employees { get { return _employees; } set { _employees = value; } } private ObservableCollection<EmployeeInfo> GetEmployees() { ObservableCollection<EmployeeInfo> employeeDetails = new ObservableCollection<EmployeeInfo>(); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Ferando", LastName = "Joseph", Title = "Management", Salary = 2000000, ReportsTo = -1, ID = 2 }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "John", LastName = "Adams", Title = "Accounts", Salary = 2000000, ReportsTo = -1, ID = 3 }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Thomas", LastName = "Jefferson", Title = "Sales", Salary = 300000, ReportsTo = -1, ID = 4 }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Andrew", LastName = "Madison", Title = "Marketing", Salary = 4000000, ReportsTo = -1, ID = 5 }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Ulysses", LastName = "Pierce", Title = "HumanResource", Salary = 1500000, ReportsTo = -1, ID = 6 }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Jimmy", LastName = "Harrison", Title = "Purchasing", Salary = 200000, ReportsTo = -1, ID = 7 }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Ronald", LastName = "Fillmore", Title = "Production", Salary = 2800000, ReportsTo = -1, ID = 8 }); //Management employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Andrew", LastName = "Fuller", ID = 9, Salary = 1200000, ReportsTo = 2, Title = "Vice President" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Janet", LastName = "Leverling", ID = 10, Salary = 1000000, ReportsTo = 2, Title = "GM" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Steven", LastName = "Buchanan", ID = 11, Salary = 900000, ReportsTo = 2, Title = "Manager" }); //Accounts employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Nancy", LastName = "Davolio", ID = 12, Salary = 850000, ReportsTo = 3, Title = "Accounts Manager" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Margaret", LastName = "Peacock", ID = 13, Salary = 700000, ReportsTo = 3, Title = "Accountant" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Michael", LastName = "Suyama", ID = 14, Salary = 700000, ReportsTo = 3, Title = "Accountant" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Robert", LastName = "King", ID = 15, Salary = 650000, ReportsTo = 3, Title = "Accountant" }); //Sales employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Laura", LastName = "Callahan", ID = 16, Salary = 900000, ReportsTo = 4, Title = "Sales Manager" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Anne", LastName = "Dodsworth", ID = 17, Salary = 800000, ReportsTo = 4, Title = "Sales Representative" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Albert", LastName = "Hellstern", ID = 18, Salary = 750000, ReportsTo = 4, Title = "Sales Representative" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Tim", LastName = "Smith", ID = 19, Salary = 700000, ReportsTo = 4, Title = "Sales Representative" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Justin", LastName = "Brid", ID = 20, Salary = 700000, ReportsTo = 4, Title = "Sales Representative" }); //Back Office employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Caroline", LastName = "Patterson", ID = 21, Salary = 800000, ReportsTo = 5, Title = "Receptionist" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Xavier", LastName = "Martin", ID = 22, Salary = 700000, ReportsTo = 5, Title = "Mail Clerk" }); //HR employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Laurent", LastName = "Pereira", ID = 23, Salary = 900000, ReportsTo = 6, Title = "HR Manager" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Syed", LastName = "Abbas", ID = 24, Salary = 650000, ReportsTo = 6, Title = "HR Assistant" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Amy", LastName = "Alberts", ID = 25, Salary = 650000, ReportsTo = 6, Title = "HR Assistant" }); //Purchasing employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Pamela", LastName = "Ansman-Wolfe", ID = 26, Salary = 600000, ReportsTo = 7, Title = "Purchase Manager" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Michael", LastName = "Blythe", ID = 27, Salary = 550000, ReportsTo = 7, Title = "Store Keeper" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "David", LastName = "Campbell", ID = 28, Salary = 450000, ReportsTo = 7, Title = "Store Keeper" }); //Production employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Jillian", LastName = "Carson", ID = 29, Salary = 600000, ReportsTo = 8, Title = "Production Manager" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Shu", LastName = "Ito", ID = 30, Salary = 550000, ReportsTo = 8, Title = "Production Engineer" }); employeeDetails.Add(new EmployeeInfo() { FirstName = "Stephen", LastName = "Jiang", ID = 31, Salary = 450000, ReportsTo = 8, Title = "Production Engineer" }); return employeeDetails; } }
Binding to Data
To bind the SfTreeGrid to data, set SfTreeGrid.ItemsSource property to an IEnumerable of implementation and to form tree structure from self-relational data, set SfTreeGrid.ParentPropertyName and SfTreeGrid.ChildPropertyName properties. Each row is SfTreeGrid is bound to an object in ItemsSource and each column is bound to a property in data object.
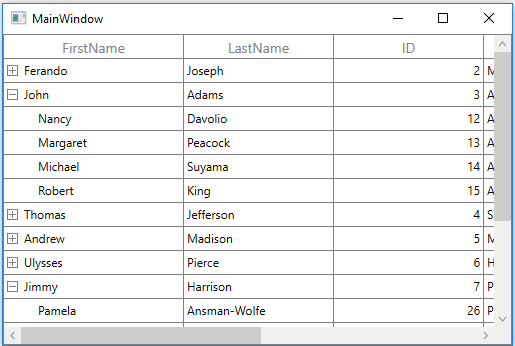
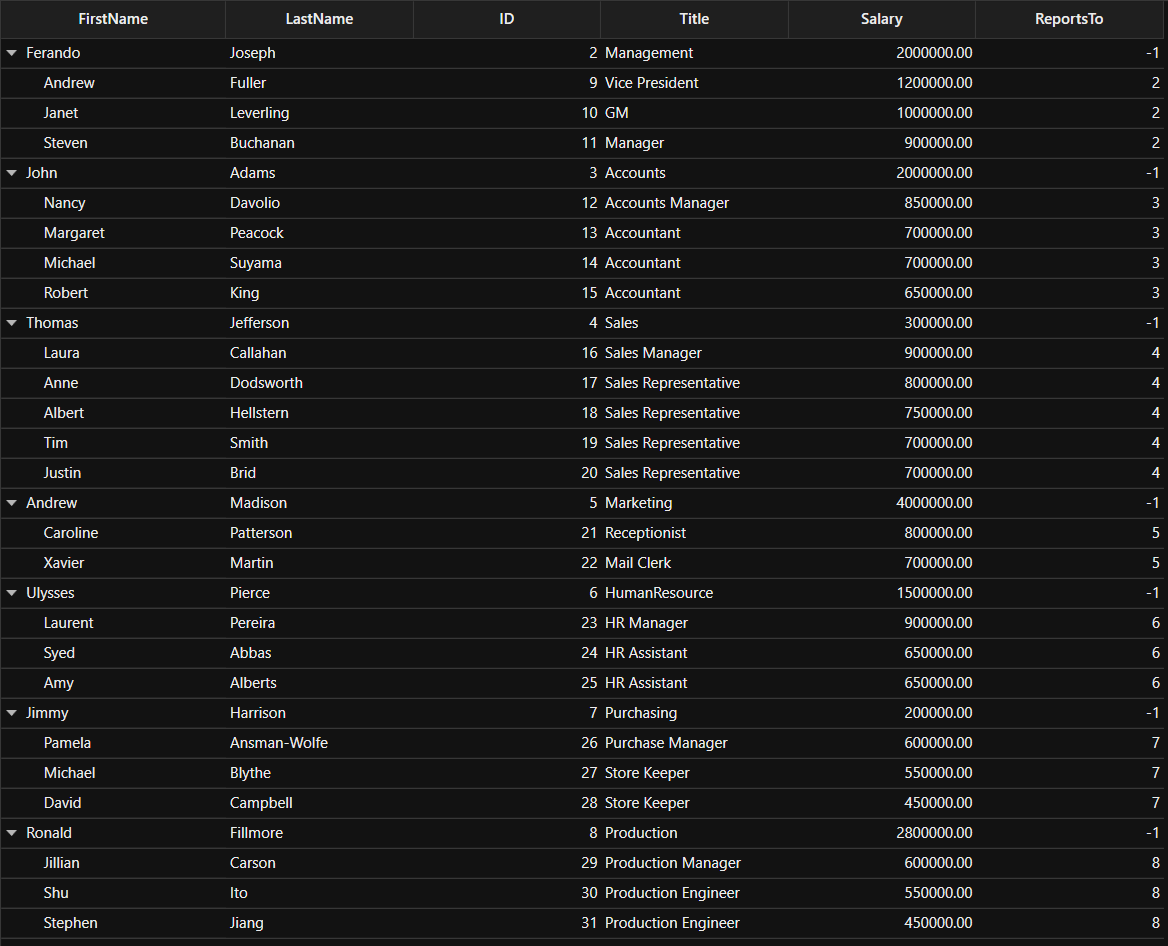
Bind the self-relations collection created in the previous step to SfTreeGrid.ItemsSource property and set ParentPropertyName as ID and ChildPropertyName as ReportsTo to form the tree structure as shown below,
<Window x:Class="GettingStarted.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:GettingStarted"
xmlns:syncfusion="http://schemas.syncfusion.com/wpf"
Title="MainWindow"
Width="525"
Height="350">
<Window.DataContext>
<local:ViewModel />
</Window.DataContext>
<Grid x:Name="Root_Grid">
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid Name="treeGrid"
ChildPropertyName="ReportsTo"
ItemsSource="{Binding Employees}"
ParentPropertyName="ID"
SelfRelationRootValue="-1" />
</Grid>
</Window>using Syncfusion.UI.Xaml.TreeGrid;
namespace GettingStarted
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfTreeGrid treeGrid = new SfTreeGrid();
ViewModel viewModel = new ViewModel();
treeGrid.ParentPropertyName = "ID";
treeGrid.ChildPropertyName = "ReportsTo";
treeGrid.SelfRelationRootValue = -1;
treeGrid.AutoExpandMode = AutoExpandMode.RootNodesExpanded;
treeGrid.ItemsSource = viewModel.Employees;
Root_Grid.Children.Add(treeGrid);
}
}
}
Binding Nested collection with SfTreeGrid
WPF TreeGrid (SfTreeGrid) supports to bind nested or hierarchical collection (where each data object has hierarchy within) by setting the property name to SfTreeGrid.ChildPropertyName which holds the child collection.
Creating Data Model for nested collection
-
Create data object class named
PersonInfoand declare properties as shown below,public class PersonInfo { private string _firstName; private string _lastName; private bool _available; private double _salary; private ObservableCollection<PersonInfo> _children; public string FirstName { get { return _firstName; } set { _firstName = value; } } public string LastName { get { return _lastName; } set { _lastName = value; } } public bool Availability { get { return _available; } set { _available = value; } } public double Salary { get { return _salary; } set { _salary = value; } } public ObservableCollection<PersonInfo> Children { get { return _children; } set { _children = value; } } } -
Create a
ViewModelclass with PersonDetails property and PersonDetails property is initialized with several data objects in constructorpublic class ViewModel { public ViewModel() { this.PersonDetails = this. CreatePersonData(); } private ObservableCollection<PersonInfo> _personDetails; public ObservableCollection<PersonInfo> PersonDetails { get { return _personDetails; } set { _personDetails = value; } } private ObservableCollection<PersonInfo> CreatePersonData() { var personList = new ObservableCollection<PersonInfo>(); ObservableCollection<PersonInfo> childCollection1 = new ObservableCollection<PersonInfo>(); childCollection1.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Andrew", LastName = "Fuller",Availability=true, Salary = 1200000 }); childCollection1.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Theodore", LastName = "Hoover",Availability=true, Salary = 1200000 }); childCollection1.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Harry", LastName = "Nixon",Availability=false, Salary = 1200000 }); ObservableCollection<PersonInfo> childCollection2 = new ObservableCollection<PersonInfo>(); childCollection2.Add(new PersonInfo { FirstName = "Ronald", LastName = "Fillmore", Availability = false, Salary = 23000 }); childCollection2.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Steven", LastName = "Buchanan", Availability = true, Salary = 340000 }); childCollection2.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Robert", LastName = "King", Availability = true, Salary = 32000 }); personList.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Obama", LastName = "bosh",Availability=false, Salary = 2000000, Children = childCollection1 }); personList.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "John", LastName = "Adams",Availability=true, Salary = 2000000, Children = childCollection2 }); personList.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Thomas", LastName = "Jefferson",Availability=true, Salary = 300000, Children = childCollection1 }); personList.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Andrew", LastName = "Madison",Availability=false, Salary = 4000000, Children = childCollection2 }); personList.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Ulysses", LastName = "Pierce",Availability=true, Salary = 1500000, Children = childCollection1 }); personList.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Jimmy", LastName = "Harrison",Availability=false, Salary = 200000, Children = childCollection2 }); personList.Add(new PersonInfo() { FirstName = "Ronald", LastName = "Fillmore", Availability=false,Salary = 2800000, Children = childCollection1 }); return personList; } }
Binding to Data
To bind the SfTreeGrid to data, set ItemsSource property to an IEnumerable of implementation and to form tree structure from nested collection data, set SfTreeGrid.ChildPropertyName. Each row in SfTreeGrid is bound to an object in ItemsSource and each column is bound to a property in data object.
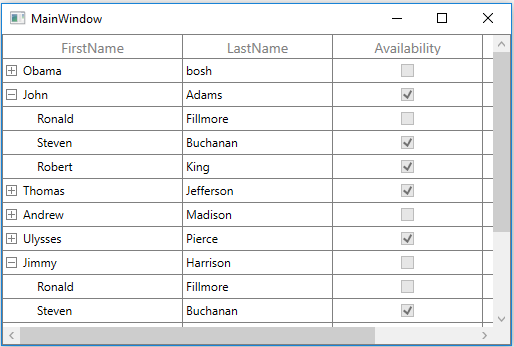
Bind the nested collection created in the previous step to SfTreeGrid.ItemsSource property and set ChildPropertyName as Children to form the tree structure as shown below,
<Window x:Class="NestedCollectionDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:NestedCollectionDemo"
xmlns:syncfusion="http://schemas.syncfusion.com/wpf"
Title="MainWindow"
Width="525"
Height="350">
<Window.DataContext>
<local:ViewModel />
</Window.DataContext>
<Grid x:Name="Root_Grid">
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid Name="treeGrid"
ChildPropertyName="Children"
ItemsSource="{Binding PersonDetails}" />
</Grid>
</Window>using Syncfusion.UI.Xaml.TreeGrid;
namespace NestedCollectionDemo
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfTreeGrid treeGrid = new SfTreeGrid();
ViewModel viewModel = new ViewModel();
treeGrid.ItemsSource = viewModel.PersonDetails;
treeGrid.ChildPropertyName = "Children";
Root_Grid.Children.Add(treeGrid);
}
}
}
Defining Columns
By default, the WPF TreeGrid (SfTreeGrid) control generates the columns automatically when value assigned to SfTreeGrid.ItemsSource property. The type of the column generated depends on the type of data in the column and the attribute of the property the column bound with.
The following table lists the column types and its constraints for auto column generation.
| Generated Column Type | Data Type / Attribute |
|---|---|
| Property of type String and any other type apart from below specified cases. | |
| Property of type Int or Double | |
| Property of type DateTime | |
| Property of type Bool | |
| Property with Currency DataType attribute. [DataType(DataType.Currency)]. | |
|
Property with PhoneNumber DataType attribute. [DataType(DataType.PhoneNumber)]. |
|
| Property of type Uri |
When columns are auto-generated, you can handle the SfTreeGrid.AutoGeneratingColumn event to customize or cancel the columns before they are added to the SfTreeGrid.
You can prevent the automatic column generation by setting SfTreeGrid.AutoGenerateColumns property to false. When SfTreeGrid.AutoGenerateColumns property is false, you should define the columns to be displayed as below,
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid Name="treeGrid"
AutoExpandMode="AllNodesExpanded"
AutoGenerateColumns="False"
ChildPropertyName="Children"
ItemsSource="{Binding PersonDetails}">
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.Columns>
<syncfusion:TreeGridTextColumn HeaderText="First Name" MappingName="FirstName" />
<syncfusion:TreeGridTextColumn HeaderText="Last Name" MappingName="LastName" />
<syncfusion:TreeGridTextColumn HeaderText="ID"
MappingName="Id"
TextAlignment="Left" />
</syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.Columns>
</syncfusion:SfTreeGrid>Below is the list of column types provided in SfTreeGrid.
| Column Type | Comments |
|---|---|
| Represents SfTreeGrid column that hosts textual content in its cells. | |
| Represents SfTreeGrid column that hosts control in its cells which is used to format and display Numeric values. | |
| Represents SfTreeGrid column that hosts control in its cells which is used to display and format DateTime values. | |
| Represents SfTreeGrid column that hosts `ComboBox`control in its cells. | |
| Represents SfTreeGrid column that hosts `CheckBox` control in its cells. | |
| Represents SfTreeGrid column that hosts `MaskedTextBox` control in its cells which is used to display textual content by applying Mask. | |
| Represents SfTreeGrid column that hosts control in its cells which is used to display numeric values with currency format. | |
| Represents SfTreeGrid column that hosts control in its cells which is used to display numeric values with percent format. | |
| Represents SfTreeGrid column that hosts `HyperLink` control in its cells. | |
| Represents SfTreeGrid column that hosts template-specified content in its cells |
Selection
By default, the entire row is selected when a user clicks a cell in a SfTreeGrid. You can set the SfTreeGrid.SelectionMode property to specify whether a user can select single row or cell, or multiple rows or cells.
You can handle the selection operations with the help of SfTreeGrid.SelectionChanging and SfTreeGrid.SelectionChanged events.
Sorting
By default, you can sort columns in a SfTreeGrid by clicking the column header. You can configure the sorting by setting SfTreeGrid.SortColumnDescriptions property.
You can customize sorting by handling the SfTreeGrid.SortColumnsChanging and SfTreeGrid.SortColumnsChanged events. To cancel the default sort, set the Cancel property to true in SfTreeGrid.SortColumnsChanging event.
Editing
Editing can be enabled by setting SfTreeGrid.AllowEditing property to True. You can customize the editing operations by handling SfTreeGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit and SfTreeGrid.CurrentCellEndEdit events.
Filtering
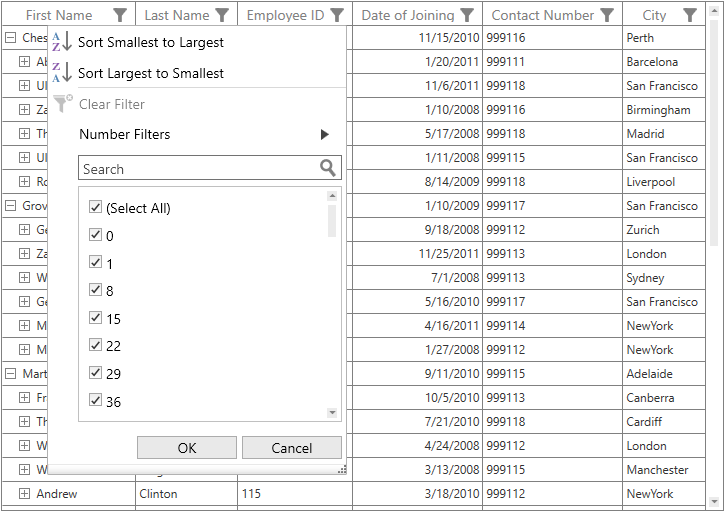
Filtering can be enabled by setting the SfTreeGrid.AllowFiltering property to true, where advanced filter UI can be opened by clicking the filter icon in column header to filter the nodes in SfTreeGrid. The filtering operations can be customized by handling the SfTreeGrid.FilterChanging and SfTreeGrid.FilterChanged events.
Theme
SfTreeGrid supports various built-in themes. Refer to the below links to apply themes for the SfTreeGrid,
NOTE
You can refer to our WPF TreeGrid feature tour page for its groundbreaking feature representations. You can also explore our WPF TreeGrid example to know how to render and configure the treegrid.