How can I help you?
Relations and Hierarchy in Windows Forms GridGrouping
21 Jan 202524 minutes to read
GridGroupingControl can display nested tables in a hierarchy using master-detail configuration. In a hierarchical view, all the tables in the data source are inter-connected via relations. Generally a relation between any two tables can take any of the following forms: 1:1, 1:n, n:1 or n:n.
A GridGroupingControl can automatically detect DataRelations in a dataset for display. By default, Relation is created for each relation found in dataset. Hence, the data relations defined in a dataset are sufficient enough for the grid to form relations. No additional code is required in this case.
With nested tables, each record in the parent table will have an associated set of records in the child table. Every record in the relation is provided with a +/- button called RecordPlusMinus that can be expanded (as well as collapsed) to bring the underlying records in the child table into view. The number of tables that can be nested with relations using a grid is unlimited.
Adding Relations
The relations of the table can be defined by adding it to the TableDescriptor.Relations collection. By default the GridGroupingControl will create a relation (RelatedMasterDetails) for each DataRelation found in a DataSet. Relations can either be related foreign key tables or nested child tables that can be expanded and collapsed. Each entry in this collection is owned byRelationDescriptor that stores details of a relation. All the RelationDescriptors for a given table is managed by RelationDescriptor Collection which is returned by TableDescriptor.Relations property.
TableDescriptor.RelationChildColumns collection is internally initialized and contains child key fields of the RelationDescriptor.RelationKeys collection of a RelationKind.RelatedMasterDetails relation. You should not modify this collection.
TableDescriptor.PrimaryKeyColumns collection defines fields that form a unique primary key for the table. By default, PrimaryKeyColumns collection is initialized from the child key fields of the RelationDescriptor.RelationKeys collection of a RelationKind.ForeignKeyReference relation. If the table is not a foreign table and UniqueConstraint for a data table is present, the collection is initialized with fields from that UniqueConstraint. Users can also manually modify the collection. If the table is the foreign table of a RelationKind.ForeignKeyReference relation, the parent table uses the fields that are defined in the PrimaryKeyColumns collection to look-up and identify records in the foreign table.
Adding Relations through Designer
After binding the hierarchical dataset to the grid, user could find that TableDescriptor.Relations collection is populated with values. These values represent the relationship between the parent and child tables.
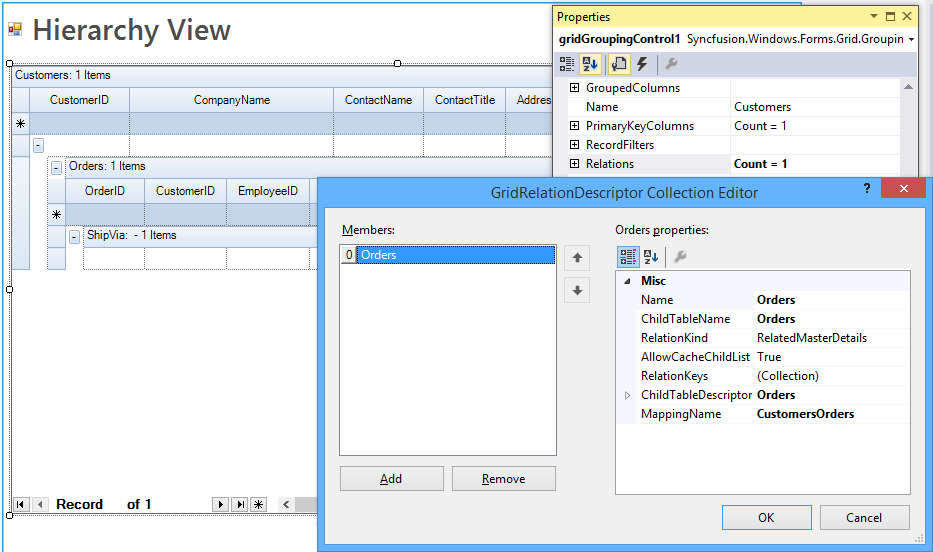
The following GridRelationDescriptor properties are used to set up the relations in GridGroupingControl.
Name - Specifies the relation name.
ChildTableName - Specifies the name of the ChildTable.
RelationKeys - Defines the mapping between the parent and child columns in a master-detail relation.
MappingName - Specifies the name of the PropertyDescriptor in the parent table that contains the details about the relation.
RelationKind - Specifies the type of the relation. This options includes the follows.RelatedMasterDetails, ForeignKeyReference, ForeignKey KeyWords, UniformChildList, ListItemReference.
AllowCacheChildList - Indicates whether the ChildList associated with a view can be cached. Used with UniformChildList relation.
ChildTableDescriptor - Specifies the table schema of Child Table.
Supported Relations
The following are the types of relations supported by the GridGroupingControl,
Related Master Details Relation
It is a Master-Details relation where matching keys in a columns of the parent and child tables define a relationship between two tables. This is a 1:n relation where each record in the child table can only belong to one parent record.
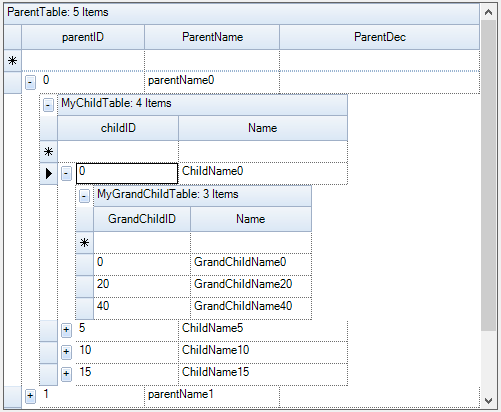
This section demonstrates how to manually specify master-detail relations between three independent tables that have primary key and foreign key column in common.
-
Setup three data tables that have primary and foreign key columns in common.
private int numberParentRows = 5; private int numberChildRows = 20; private int numberGrandChildRows = 50; //Creates Parent Table. private DataTable GetParentTable() { DataTable dataTable = new DataTable("ParentTable"); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("parentID")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("ParentName")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("ParentDec")); for (int i = 0; i < numberParentRows; i++) { DataRow dataRow = dataTable.NewRow(); dataRow[0] = i; dataRow[1] = string.Format("parentName{0}", i); dataRow[1] = string.Format("parentName{0}", i); dataTable.Rows.Add(dataRow); } return dataTable; } //Creates Child Table. private DataTable GetChildTable() { DataTable dataTable = new DataTable("ChildTable"); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("childID")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Name")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("ParentID")); for (int i = 0; i < numberChildRows; i++) { DataRow dataRow = dataTable.NewRow(); dataRow[0] = i.ToString(); dataRow[1] = string.Format("ChildName{0}", i); dataRow[2] = (i % numberParentRows).ToString(); dataTable.Rows.Add(dataRow); } return dataTable; } //Creates Grand Child Table. private DataTable GetGrandChildTable() { DataTable dataTable = new DataTable("GrandChildTable"); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("GrandChildID")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Name")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("ChildID")); for (int i = 0; i < numberGrandChildRows; i++) { DataRow dataRow = dataTable.NewRow(); dataRow[0] = i.ToString(); dataRow[1] = string.Format("GrandChildName{0}", i); dataRow[2] = (i % numberChildRows).ToString(); dataTable.Rows.Add(dataRow); } return dataTable; }Private numberParentRows As Integer = 5 Private numberChildRows As Integer = 20 Private numberGrandChildRows As Integer = 50 'Creates Parent Table. Private Function GetParentTable() As DataTable Dim dataTable As New DataTable("ParentTable") dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("parentID")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("ParentName")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("ParentDec")) For i As Integer = 0 To numberParentRows - 1 Dim dataRow As DataRow = dataTable.NewRow() dataRow(0) = i dataRow(1) = String.Format("parentName{0}", i) dataRow(1) = String.Format("parentName{0}", i) dataTable.Rows.Add(dataRow) Next i Return dataTable End Function 'Creates Child Table. Private Function GetChildTable() As DataTable Dim dataTable As New DataTable("ChildTable") dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("childID")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("Name")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("ParentID")) For i As Integer = 0 To numberChildRows - 1 Dim dataRow As DataRow = dataTable.NewRow() dataRow(0) = i.ToString() dataRow(1) = String.Format("ChildName{0}", i) dataRow(2) = (i Mod numberParentRows).ToString() dataTable.Rows.Add(dataRow) Next i Return dataTable End Function 'Creates Grand Child Table. Private Function GetGrandChildTable() As DataTable Dim dataTable As New DataTable("GrandChildTable") dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("GrandChildID")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("Name")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("ChildID")) For i As Integer = 0 To numberGrandChildRows - 1 Dim dataRow As DataRow = dataTable.NewRow() dataRow(0) = i.ToString() dataRow(1) = String.Format("GrandChildName{0}", i) dataRow(2) = (i Mod numberChildRows).ToString() dataTable.Rows.Add(dataRow) Next i Return dataTable End Function -
Manually set up relationships between tables and add relation to the parent and child tables.
DataTable parentTable = GetParentTable(); DataTable childTable = GetChildTable(); DataTable grandChildTable = GetGrandChildTable(); GridRelationDescriptor parentToChildRelationDescriptor = new GridRelationDescriptor(); //Same as SourceListSetEntry.Name for Child Table. parentToChildRelationDescriptor.ChildTableName = "MyChildTable"; parentToChildRelationDescriptor.RelationKind = RelationKind.RelatedMasterDetails; parentToChildRelationDescriptor.RelationKeys.Add("parentID", "ParentID"); //Adds relation to Parent Table. gridGroupingControl1.TableDescriptor.Relations.Add(parentToChildRelationDescriptor); GridRelationDescriptor childToGrandChildRelationDescriptor = new GridRelationDescriptor(); //Same as SourceListSetEntry.Name for Grand Child Table. childToGrandChildRelationDescriptor.ChildTableName = "MyGrandChildTable"; childToGrandChildRelationDescriptor.RelationKind = RelationKind.RelatedMasterDetails; childToGrandChildRelationDescriptor.RelationKeys.Add("childID", "ChildID"); //Adds relation to Child Table. parentToChildRelationDescriptor.ChildTableDescriptor.Relations.Add(childToGrandChildRelationDescriptor);Dim parentTable As DataTable = GetParentTable() Dim childTable As DataTable = GetChildTable() Dim grandChildTable As DataTable = GetGrandChildTable() Dim parentToChildRelationDescriptor As New GridRelationDescriptor() 'Same as SourceListSetEntry.Name for Child Table. parentToChildRelationDescriptor.ChildTableName = "MyChildTable" parentToChildRelationDescriptor.RelationKind = RelationKind.RelatedMasterDetails parentToChildRelationDescriptor.RelationKeys.Add("parentID", "ParentID") 'Adds relation to Parent Table. gridGroupingControl1.TableDescriptor.Relations.Add(parentToChildRelationDescriptor) Dim childToGrandChildRelationDescriptor As New GridRelationDescriptor() 'Same as SourceListSetEntry.Name for Grand Child Table. childToGrandChildRelationDescriptor.ChildTableName = "MyGrandChildTable" childToGrandChildRelationDescriptor.RelationKind = RelationKind.RelatedMasterDetails childToGrandChildRelationDescriptor.RelationKeys.Add("childID", "ChildID") 'Adds relation to Child Table. parentToChildRelationDescriptor.ChildTableDescriptor.Relations.Add(childToGrandChildRelationDescriptor) -
Register the data tables withEngine.SourceListSet so that RelationDescriptor can resolve the name.
// Register any DataTable/IList with SourceListSet, so that RelationDescriptor can resolve the name this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("MyParentTable", parentTable); this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("MyChildTable", childTable); this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("MyGrandChildTable", grandChildTable);' Register any DataTable/IList with SourceListSet, so that RelationDescriptor can resolve the name Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("MyParentTable", parentTable) Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("MyChildTable", childTable) Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("MyGrandChildTable", grandChildTable) -
Finally, bind hierarchical data source, which has been created through the above steps to a grid by assigning parent table to the data source.
this.gridGroupingControl1.DataSource = parentTable;Me.gridGroupingControl1.DataSource = parentTable
While running the sample the tables are connected with Master-Details relation as of follows,
Sample Location:
<Installed_Location>\Syncfusion\EssentialStudio[Version_Number]\Windows\Windows\Grid.Grouping.Windows\Samples\
Relation And Hierarchy\Related Master Details Demo
Foreign Key Reference Relation
It is a foreign-key relation for looking up values where an id column in the main table can be used to look up a record in a related table. This is an n:1 relation where multiple records in the parent table can reference the same record in the related table. Fields in the related table can be referenced using a . dot in the FieldDescriptor.MappingName of the main table.
Creating Foreign Key Reference
This section sets up a foreign key reference relation between data table and the collection USStates. Data table represents parent table of the relation and USStates collection serves as the related child list wherein the values can be looked up using a key. The collection derives from ArrayList in which every item is an USState object having two properties named Key and Name. It also defines a method named CreateDefaultCollection that returns an instance of itself populated with a set of values.
A foreign key reference relation can be set up between the lists by defining a relation descriptor with its attributes carrying the relation details and adding this descriptor to the Relations collection of the main table.
The following steps demonstrate this process.
-
Create a collection named
USStatesin which each entry storesUSStateobject.//US States Collection. [Serializable] public class USStatesCollection : ArrayList { public new USState this[int index] { get { return (USState)base[index]; } set { base[index] = value; } } public static USStatesCollection CreateDefaultCollection() { USStatesCollection states = new USStatesCollection(); states.Add(new USState("AL", "Alabama")); states.Add(new USState("AK", "Alaska")); states.Add(new USState("CA", "California")); states.Add(new USState("FL", "Florida")); states.Add(new USState("GA", "Georgia")); states.Add(new USState("IN", "Indiana")); states.Add(new USState("MS", "Mississippi")); states.Add(new USState("NJ", "New Jersey")); states.Add(new USState("NM", "New Mexico")); states.Add(new USState("NY", "New York")); states.Add(new USState("TX", "Texas")); states.Add(new USState("WA", "Washington")); states.Add(new USState("PE", "Prince Edward Island")); states.Add(new USState("YT", "Yukon Territories")); return states; } public override bool IsReadOnly { get { return true; } } public override bool IsFixedSize { get { return true; } } } //US State Class. [Serializable] public class USState { private string _code; private string _name; public USState() { } public USState(string key, string name) { this._code = key; this._name = name; } [Browsable(true)] public string Key { get { return _code; } set { _code = value; } } [Browsable(true)] public string Name { get { return _name; } set { _name = value; } } public override string ToString() { return this._name + "(" + this._code + ")"; } }'US States Collection. <Serializable> Public Class USStatesCollection Inherits ArrayList Default Public Shadows Property Item(ByVal index As Integer) As USState Get Return CType(MyBase.Item(index), USState) End Get Set(ByVal value As USState) MyBase.Item(index) = value End Set End Property Public Shared Function CreateDefaultCollection() As USStatesCollection Dim states As New USStatesCollection() states.Add(New USState("AL", "Alabama")) states.Add(New USState("AK", "Alaska")) states.Add(New USState("CA", "California")) states.Add(New USState("FL", "Florida")) states.Add(New USState("GA", "Georgia")) states.Add(New USState("IN", "Indiana")) states.Add(New USState("MS", "Mississippi")) states.Add(New USState("NJ", "New Jersey")) states.Add(New USState("NM", "New Mexico")) states.Add(New USState("NY", "New York")) states.Add(New USState("TX", "Texas")) states.Add(New USState("WA", "Washington")) states.Add(New USState("PE", "Prince Edward Island")) states.Add(New USState("YT", "Yukon Territories")) Return states End Function Public Overrides ReadOnly Property IsReadOnly() As Boolean Get Return True End Get End Property Public Overrides ReadOnly Property IsFixedSize() As Boolean Get Return True End Get End Property End Class 'US State Class. <Serializable> Public Class USState Private _code As String Private _name As String Public Sub New() End Sub Public Sub New(ByVal key As String, ByVal name As String) Me._code = key Me._name = name End Sub <Browsable(True)> Public Property Key() As String Get Return _code End Get Set(ByVal value As String) _code = value End Set End Property <Browsable(True)> Public Property Name() As String Get Return _name End Get Set(ByVal value As String) _name = value End Set End Property Public Overrides Function ToString() As String Return Me._name & "(" & Me._code & ")" End Function End Class -
Create an object of
USStatesand add this object into theSourceListSet with a lookup name.USStatesCollection usStates = USStatesCollection.CreateDefaultCollection(); this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("USStates", usStates);Dim usStates As USStatesCollection = USStatesCollection.CreateDefaultCollection() Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("USStates", usStates) -
Creates a DataTable with the Key from USState as one of the columns.
DataTable table = new DataTable(); table.Columns.Add("Id", typeof(string)); table.Columns.Add("State", typeof(string)); //Adds rows. for (int i = 0; i < 25; i++) { table.Rows.Add(table.NewRow()); table.Rows[i][0] = i; table.Rows[i][1] = usStates[i % 8].Key; }Dim table As New DataTable() table.Columns.Add("Id", GetType(String)) table.Columns.Add("State", GetType(String)) 'Adds rows. For i As Integer = 0 To 24 table.Rows.Add(table.NewRow()) table.Rows(i)(0) = i table.Rows(i)(1) = usStates(i Mod 8).Key Next i -
Establish Foreign key Reference relationship.
GridTableDescriptor mainTd = this.gridGroupingControl1.TableDescriptor; GridRelationDescriptor usStatesRd = new GridRelationDescriptor(); usStatesRd.Name = "State"; usStatesRd.RelationKind = RelationKind.ForeignKeyReference; //SourceListSet name for look up. usStatesRd.ChildTableName = "USStates"; usStatesRd.RelationKeys.Add("State", "Key"); //Formats ChildList. usStatesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.Appearance.AlternateRecordFieldCell.BackColor = Color.FromArgb(255, 245, 227); //Hides the Key column. usStatesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.VisibleColumns.Add("Name"); usStatesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.SortedColumns.Add("Name"); usStatesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowEdit = false; //Disallows users to modify states. usStatesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowNew = false; mainTd.Relations.Add(usStatesRd); //Assigns data source. this.gridGroupingControl1.DataSource = table; mainTd.Name = "ForeignKeyReference";Dim mainTd As GridTableDescriptor = Me.gridGroupingControl1.TableDescriptor Dim usStatesRd As New GridRelationDescriptor() usStatesRd.Name = "State" usStatesRd.RelationKind = RelationKind.ForeignKeyReference 'SourceListSet name for look up. usStatesRd.ChildTableName = "USStates" usStatesRd.RelationKeys.Add("State", "Key") 'Formats ChildList. usStatesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.Appearance.AlternateRecordFieldCell.BackColor = Color.FromArgb(255, 245, 227) 'Hides the Key column. usStatesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.VisibleColumns.Add("Name") usStatesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.SortedColumns.Add("Name") usStatesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowEdit = False 'Disallows users to modify states. usStatesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowNew = False mainTd.Relations.Add(usStatesRd) 'Assigns data source. Me.gridGroupingControl1.DataSource = table mainTd.Name = "ForeignKeyReference"
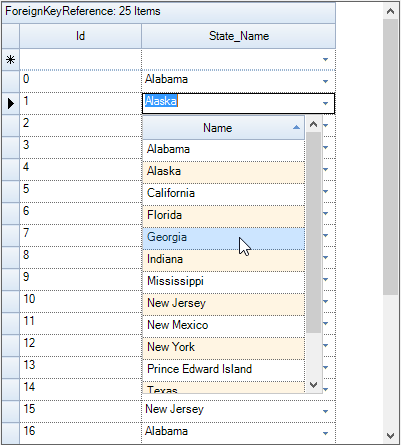
Sample Location:
<Install_Location>\Syncfusion\EssentialStudio[Version_Number]\Windows\Grid.Grouping.Windows\Samples\Relation And Hierarchy\Foreign-Key Reference Demo
ForeignKey Helper
The foreign key relations can be easily added to the grid by using the GridForeignKeyHelper. It is used to create the foreign key look up with a single method call instead of going through all the steps described above.
The GridForeignKeyHelper class exposes a static method called SetupForeignTableLookUp that accepts GridGroupingControl, main table, foreign table, main table column, foreign table value column and foreign table display column and sets up the Foreign Key relation using these parameter values.
string valueColInMainTable = "Country", valueColInForeignTable = "CountryCode", displayColInForeignTable = "CountryName";
GridForeignKeyHelper.SetupForeignTableLookUp(gridGroupingControl1, valueColInMainTable, countries, valueColInForeignTable, displayColInForeignTable);Dim valueColInMainTable As String = "Country", valueColInForeignTable As String = "CountryCode", displayColInForeignTable As String = "CountryName"
GridForeignKeyHelper.SetupForeignTableLookUp(gridGroupingControl1, valueColInMainTable, countries, valueColInForeignTable, displayColInForeignTable)ForeignKey KeyWords Relation
It is a unique relation kind offered by the grouping engine. It is a foreign key relation where matching keys in the columns of the parent and child table define a relationship between two tables. This is an m:n relation. Field summaries of the related child table can be referenced using a . dot in the FieldDescriptor.MappingName of the main table. This relation kind allows the user to have multi-valued columns in the grid.
The following steps illustrates the creation of ForeignKeyKeyWords relation.
-
Create two data tables, Customers and Items, and add a list of records into them.
private int numberParentRow = 6; private int numberChildRow = 20; private DataTable GetParentTable() { DataTable dataTable = new DataTable("Customers"); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("customerID")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("CustomerName")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Address")); for (int i = 0; i < numberParentRow; ++i) { DataRow dataRow = dataTable.NewRow(); dataRow[0] = i; dataRow[1] = string.Format("CustomerName{0}", i); dataRow[2] = string.Format("Address{0}", i); dataTable.Rows.Add(dataRow); } return dataTable; } private DataTable GetChildTable() { DataTable dataTable = new DataTable("Items"); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("ItemID")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("ItemName")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("CustomerID")); dataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn("Price")); Random rand = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < numberChildRow; ++i) { DataRow dataRow = dataTable.NewRow(); dataRow[0] = i.ToString(); dataRow[1] = string.Format("ItemName{0}", i); dataRow[2] = (i % numberParentRows).ToString(); dataRow[3] = rand.Next(500).ToString(); dataTable.Rows.Add(dataRow); } return dataTable; }Private numberParentRow As Integer = 6 Private numberChildRow As Integer = 20 Private Function GetParentTable() As DataTable Dim dataTable As New DataTable("Customers") dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("customerID")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("CustomerName")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("Address")) For i As Integer = 0 To numberParentRow - 1 Dim dataRow As DataRow = dataTable.NewRow() dataRow(0) = i dataRow(1) = String.Format("CustomerName{0}", i) dataRow(2) = String.Format("Address{0}", i) dataTable.Rows.Add(dataRow) Next i Return dataTable End Function Private Function GetChildTable() As DataTable Dim dataTable As New DataTable("Items") dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("ItemID")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("ItemName")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("CustomerID")) dataTable.Columns.Add(New DataColumn("Price")) Dim rand As New Random() For i As Integer = 0 To numberChildRow - 1 Dim dataRow As DataRow = dataTable.NewRow() dataRow(0) = i.ToString() dataRow(1) = String.Format("ItemName{0}", i) dataRow(2) = (i Mod numberParentRows).ToString() dataRow(3) = rand.Next(500).ToString() dataTable.Rows.Add(dataRow) Next i Return dataTable End Function -
Register the child table (Items) into the
SourceListSetof the grouping engine.DataTable parentTable = GetParentTable(); DataTable childTable = GetChildTable(); this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("Items", childTable);Dim parentTable As DataTable = GetParentTable() Dim childTable As DataTable = GetChildTable() Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("Items", childTable) -
Assign the data source for the GridGroupingControl.
this.gridGroupingControl1.DataSource = parentTable;Me.gridGroupingControl1.DataSource = parentTable -
Establish
ForeignKeyKeyWordsrelationship between the tables.GridRelationDescriptor childRelation = new GridRelationDescriptor(); childRelation.RelationKind = RelationKind.ForeignKeyKeyWords; //SourceListSet name for look up. childRelation.ChildTableName = "Items"; childRelation.RelationKeys.Add("customerID", "CustomerID"); childRelation.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowEdit = true; childRelation.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowNew = true; this.gridGroupingControl1.TableDescriptor.Relations.Add(childRelation);Dim childRelation As New GridRelationDescriptor() childRelation.RelationKind = RelationKind.ForeignKeyKeyWords 'SourceListSet name for look up. childRelation.ChildTableName = "Items" childRelation.RelationKeys.Add("customerID", "CustomerID") childRelation.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowEdit = True childRelation.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowNew = True Me.gridGroupingControl1.TableDescriptor.Relations.Add(childRelation)
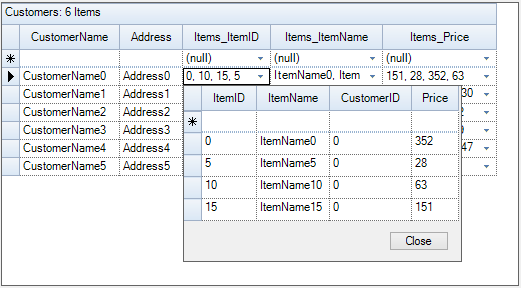
Sample Location:
<Install_Location>\Syncfusion\EssentialStudio[Version_Number]\Windows\Grid.Grouping.Windows\Samples\Relation And Hierarchy\Employee Territory Order Demo
List Item Reference Relation
It is an object reference relation for looking up values from a strong typed collection. Like ForeignKeyReference, it is also an n:1 relation where multiple records in the parent table can reference the same record in the related table. One difference between the ForeignKeyReference and ListItemReference is that the former uses a key to look up the values whereas the latter uses an object to look up the values in a nested collection.
The following steps demonstrate creating process of List item reference relation.
-
Create a collection named Countries in which each entry stores a Country object.
//Countries Collection. public class CountriesCollection : ArrayList { public new Country this[int index] { get { return (Country)base[index]; } set { base[index] = value; } } public static CountriesCollection CreateDefaultCollection() { CountriesCollection countries = new CountriesCollection(); countries.Add(new Country("US", "United States")); countries.Add(new Country("CA", "Canada")); countries.Add(new Country("AU", "Australia")); countries.Add(new Country("BR", "Brazil")); countries.Add(new Country("IO", "British Indian Ocean Territory")); countries.Add(new Country("CN", "China")); countries.Add(new Country("FI", "Finland")); countries.Add(new Country("FR", "France")); countries.Add(new Country("DE", "Germany")); countries.Add(new Country("HK", "Hong Kong")); countries.Add(new Country("HU", "Hungary")); countries.Add(new Country("IS", "Iceland")); countries.Add(new Country("IN", "India")); countries.Add(new Country("JP", "Japan")); countries.Add(new Country("MY", "Malaysia")); countries.Add(new Country("SG", "Singapore")); countries.Add(new Country("CH", "Switzerland")); return countries; } public override bool IsReadOnly { get { return true; } } public override bool IsFixedSize { get { return true; } } } //Country Class. public class Country { private string _code; private string _name; public Country() { } public Country(string strCode, string strName) { this._code = strCode; this._name = strName; } public string CountryCode { get { return _code; } set { _code = value; } } public string Name { get { return _name; } set { _name = value; } } public override string ToString() { return this._name + "(" + this._code + ")"; } }'Countries Collection. Public Class CountriesCollection Inherits ArrayList Default Public Shadows Property Item(ByVal index As Integer) As Country Get Return CType(MyBase.Item(index), Country) End Get Set(ByVal value As Country) MyBase.Item(index) = value End Set End Property Public Shared Function CreateDefaultCollection() As CountriesCollection Dim countries As New CountriesCollection() countries.Add(New Country("US", "United States")) countries.Add(New Country("CA", "Canada")) countries.Add(New Country("AU", "Australia")) countries.Add(New Country("BR", "Brazil")) countries.Add(New Country("IO", "British Indian Ocean Territory")) countries.Add(New Country("CN", "China")) countries.Add(New Country("FI", "Finland")) countries.Add(New Country("FR", "France")) countries.Add(New Country("DE", "Germany")) countries.Add(New Country("HK", "Hong Kong")) countries.Add(New Country("HU", "Hungary")) countries.Add(New Country("IS", "Iceland")) countries.Add(New Country("IN", "India")) countries.Add(New Country("JP", "Japan")) countries.Add(New Country("MY", "Malaysia")) countries.Add(New Country("SG", "Singapore")) countries.Add(New Country("CH", "Switzerland")) Return countries End Function Public Overrides ReadOnly Property IsReadOnly() As Boolean Get Return True End Get End Property Public Overrides ReadOnly Property IsFixedSize() As Boolean Get Return True End Get End Property End Class 'Country Class. Public Class Country Private _code As String Private _name As String Public Sub New() End Sub Public Sub New(ByVal strCode As String, ByVal strName As String) Me._code = strCode Me._name = strName End Sub Public Property CountryCode() As String Get Return _code End Get Set(ByVal value As String) _code = value End Set End Property Public Property Name() As String Get Return _name End Get Set(ByVal value As String) _name = value End Set End Property Public Overrides Function ToString() As String Return Me._name & "(" & Me._code & ")" End Function End Class -
Create an object of
USStatesand add this object into theSourceListSetwith a lookup name.CountriesCollection countries = CountriesCollection.CreateDefaultCollection(); this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("Countries", countries);Dim countries As CountriesCollection = CountriesCollection.CreateDefaultCollection() Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.SourceListSet.Add("Countries", countries) -
Create a data table with one of the columns type as Country.
DataTable table = new DataTable(); table.Columns.Add("Id", typeof(string)); table.Columns.Add("Country", typeof(Country)); //Adds Rows. for (int i = 0; i < 25; i++) { table.Rows.Add(table.NewRow()); table.Rows[i][0] = i; table.Rows[i][1] = countries[i % 8]; }Dim table As New DataTable() table.Columns.Add("Id", GetType(String)) table.Columns.Add("Country", GetType(Country)) 'Adds Rows. For i As Integer = 0 To 24 table.Rows.Add(table.NewRow()) table.Rows(i)(0) = i table.Rows(i)(1) = countries(i Mod 8) Next i -
Establish the
ForeignKeyReferencerelationship.GridTableDescriptor mainTd = this.gridGroupingControl1.TableDescriptor; GridRelationDescriptor countriesRd = new GridRelationDescriptor(); countriesRd.Name = "Country"; countriesRd.MappingName = "Country"; countriesRd.RelationKind = RelationKind.ListItemReference; //SourceListSet name for look up. countriesRd.ChildTableName = "Countries"; //Formats ChildList. countriesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.Appearance.AlternateRecordFieldCell.BackColor = Color.FromArgb(255, 245, 227); //Hides Key column. countriesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.VisibleColumns.Add("Name"); countriesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.SortedColumns.Add("Name"); countriesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowEdit = true; //Disallows users to modify states. countriesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowNew = true; mainTd.Relations.Add(countriesRd); //Assigns data source. this.gridGroupingControl1.DataSource = table; mainTd.Name = "ListItemReference";Dim mainTd As GridTableDescriptor = Me.gridGroupingControl1.TableDescriptor Dim countriesRd As New GridRelationDescriptor() countriesRd.Name = "Country" countriesRd.MappingName = "Country" countriesRd.RelationKind = RelationKind.ListItemReference 'SourceListSet name for look up. countriesRd.ChildTableName = "Countries" 'Formats ChildList. countriesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.Appearance.AlternateRecordFieldCell.BackColor = Color.FromArgb(255, 245, 227) 'Hides Key column. countriesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.VisibleColumns.Add("Name") countriesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.SortedColumns.Add("Name") countriesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowEdit = True 'Disallows users to modify states. countriesRd.ChildTableDescriptor.AllowNew = True mainTd.Relations.Add(countriesRd) 'Assigns data source. Me.gridGroupingControl1.DataSource = table mainTd.Name = "ListItemReference"
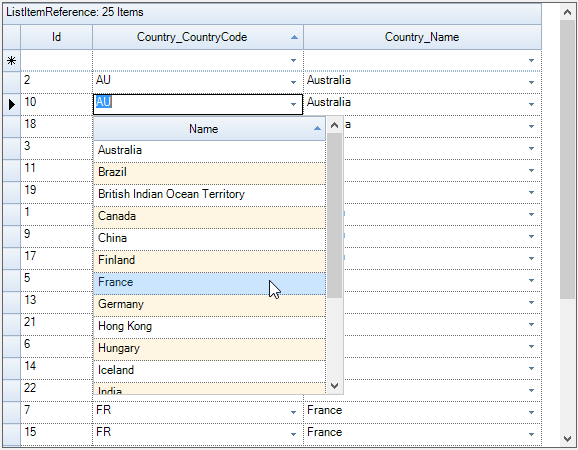
Sample Location:
<Install_Location>\Syncfusion\EssentialStudio[Version_Number]\Windows\Grid.Grouping.Windows\Samples\Relation And Hierarchy\List Item Reference Demo
Uniform Child List Relation
This relation can be used to map nested strong typed collection inside a parent collection. If a public property is an object, then it will be displayed in a Nested Table. The collection in the below example consists of two kinds of objects, ParentObj and ChildObj, where every ParentObj is associated with a collection of ChildObj and is represented by the public property named ‘Child’. Hence, a nested table is always created to display associated children for a given parent.
The following steps are used to create the UniformChildList Relation,
-
Create a class (ChildObj) whose instances form the child table records.
public class ChildObj : INotifyPropertyChanged { private string f1, f2; private int f3; public ChildObj(string f1, string f2, int f3) { this.f1 = f1; this.f2 = f2; this.f3 = f3; } public string Field1 { get { return f1; } set { if (f1 != value) { f1 = value; RaisePropertyChanged("Field1"); } } } public string Field2 { get { return f2; } set { if (f2 != value) { f2 = value; RaisePropertyChanged("Field2"); } } } public int Field3 { get { return f3; } set { if (f3 != value) { f3 = value; RaisePropertyChanged("Field3"); } } } void RaisePropertyChanged(string name) { if (PropertyChanged != null) PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(name)); } public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; }Public Class ChildObj Implements INotifyPropertyChanged Private f1, f2 As String Private f3 As Integer Public Sub New(ByVal f1 As String, ByVal f2 As String, ByVal f3 As Integer) Me.f1 = f1 Me.f2 = f2 Me.f3 = f3 End Sub Public Property Field1() As String Get Return f1 End Get Set(ByVal value As String) If f1 <> value Then f1 = value RaisePropertyChanged("Field1") End If End Set End Property Public Property Field2() As String Get Return f2 End Get Set(ByVal value As String) If f2 <> value Then f2 = value RaisePropertyChanged("Field2") End If End Set End Property Public Property Field3() As Integer Get Return f3 End Get Set(ByVal value As Integer) If f3 <> value Then f3 = value RaisePropertyChanged("Field3") End If End Set End Property Private Sub RaisePropertyChanged(ByVal name As String) RaiseEvent PropertyChanged(Me, New PropertyChangedEventArgs(name)) End Sub Public Event PropertyChanged As PropertyChangedEventHandler End Class -
Create another class (ParentObj) that contains a reference to the above class (ChildObj). The instances of this class make the parent records. Both the classes implement
INotifyPropertyChangedinterface in order to get notified of any property changes.public class ParentObj : INotifyPropertyChanged { private string f1, f2; private int f3; private BindingList<ChildObj> childObj = new BindingList<ChildObj>(); public ParentObj(string f1, string f2, int f3, params ChildObj[] c) { this.f1 = f1; this.f2 = f2; this.f3 = f3; foreach (ChildObj i in c) childObj.Add(i); } public string Field1 { get { return f1; } set { if (f1 != value) { f1 = value; RaisePropertyChanged("Field1"); } } } public string Field2 { get { return f2; } set { if (f2 != value) { f2 = value; RaisePropertyChanged("Field2"); } } } public int Field3 { get { return f3; } set { if (f3 != value) { f3 = value; RaisePropertyChanged("Field3"); } } } public BindingList<ChildObj> Child { get { return childObj; } } void RaisePropertyChanged(string name) { if (PropertyChanged != null) PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(name)); } public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; }Public Class ParentObj Implements INotifyPropertyChanged Private f1, f2 As String Private f3 As Integer Private childObj As New BindingList(Of ChildObj)() Public Sub New(ByVal f1 As String, ByVal f2 As String, ByVal f3 As Integer, ParamArray ByVal c() As ChildObj) Me.f1 = f1 Me.f2 = f2 Me.f3 = f3 For Each i As ChildObj In c childObj.Add(i) Next i End Sub Public Property Field1() As String Get Return f1 End Get Set(ByVal value As String) If f1 <> value Then f1 = value RaisePropertyChanged("Field1") End If End Set End Property Public Property Field2() As String Get Return f2 End Get Set(ByVal value As String) If f2 <> value Then f2 = value RaisePropertyChanged("Field2") End If End Set End Property Public Property Field3() As Integer Get Return f3 End Get Set(ByVal value As Integer) If f3 <> value Then f3 = value RaisePropertyChanged("Field3") End If End Set End Property Public ReadOnly Property Child() As BindingList(Of ChildObj) Get Return childObj End Get End Property Private Sub RaisePropertyChanged(ByVal name As String) RaiseEvent PropertyChanged(Me, New PropertyChangedEventArgs(name)) End Sub Public Event PropertyChanged As PropertyChangedEventHandler End Class -
Generate the collection using
BindingListclass, which implements ListChanged events in itself so that the grid can listen to those events when the list is changed. Add few items into the collection.BindingList<ParentObj> topList = new BindingList<ParentObj>(); BindingList<ChildObj> childList = new BindingList<ChildObj>(); Random r = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) childList.Add(new ChildObj(string.Format("Name{0}", r.Next(10)), string.Format("Desc{0}", r.Next(20)), r.Next(30))); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { topList.Add(new ParentObj(string.Format("Name{0}", r.Next(5)), string.Format("Desc{0}", r.Next(15)), r.Next(20))); for (int j = i * 5; j < (i * 5) + 5; j++) topList[i].Child.Add(childList[j]); }Dim topList As New BindingList(Of ParentObj)() Dim childList As New BindingList(Of ChildObj)() Dim r As New Random() For i As Integer = 0 To 29 childList.Add(New ChildObj(String.Format("Name{0}", r.Next(10)), String.Format("Desc{0}", r.Next(20)), r.Next(30))) Next i For i As Integer = 0 To 4 topList.Add(New ParentObj(String.Format("Name{0}", r.Next(5)), String.Format("Desc{0}", r.Next(15)), r.Next(20))) For j As Integer = i * 5 To (i * 5) + 5 - 1 topList(i).Child.Add(childList(j)) Next j Next i -
Assign the above collection to the data source of GridGroupingControl.
this.gridGroupingControl1.DataSource = topList;Me.gridGroupingControl1.DataSource = topList -
Establish UniformChildList relation kind.
GridRelationDescriptor relation = new GridRelationDescriptor(); relation.RelationKind = RelationKind.UniformChildList; relation.MappingName = "Child"; relation.Name = "Child"; relation.ChildTableName = "ChildTable"; gridGroupingControl1.TableDescriptor.Relations.Add(relation); this.gridGroupingControl1.ShowGroupDropArea = true; GridTable childTable = gridGroupingControl1.GetTable("ChildTable"); this.gridGroupingControl1.AddGroupDropArea(childTable); childTable.TableDescriptor.GroupedColumns.Add("Field1");Dim relation As New GridRelationDescriptor() relation.RelationKind = RelationKind.UniformChildList relation.MappingName = "Child" relation.Name = "Child" relation.ChildTableName = "ChildTable" gridGroupingControl1.TableDescriptor.Relations.Add(relation) Me.gridGroupingControl1.ShowGroupDropArea = True Dim childTable As GridTable = gridGroupingControl1.GetTable("ChildTable") Me.gridGroupingControl1.AddGroupDropArea(childTable) childTable.TableDescriptor.GroupedColumns.Add("Field1")
The following screenshot will be the outcome of the above steps,
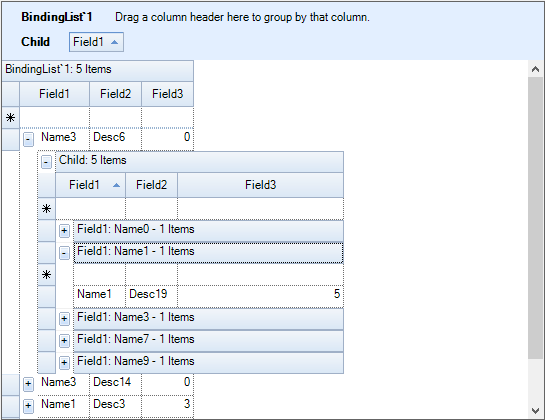
Generate Auto Relations
The AutoPopulateRelations property is used to specify, whether the relations should be automatically generated when the DataSource assigned to a DataTable with constraints or a DataSet with relations defined. This will be enabled by default.
this.gridGroupingControl1.AutoPopulateRelations = false;Me.gridGroupingControl1.AutoPopulateRelations = FalseDisplay Dependent Fields
When a foreign key relation (or related collection) is used, ShowRelationFields property controls the display of dependent fields from a related table in the main table.
Hide - Hides all the fields.
ShowAllRelatedFields - Shows all related fields including Primary and Foreign Keys.ShowDisplayFieldsOnly- Shows only dependent fields; Hides Primary and Foreign Keys.
The default value of this property is set to ShowDisplayFieldsOnly.
this.gridGroupingControl1.ShowRelationFields = ShowRelationFields.ShowAllRelatedFields;Me.gridGroupingControl1.ShowRelationFields = ShowRelationFields.ShowAllRelatedFieldsSelf-Relation Recurrence
When nested collection is used, MaxNestedCollectionRecursionLevel property specifies the number of levels of recursion allowed when self-relations are detected. The settings below lets the grid to loop through up to four recursion levels.
this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.MaxNestedCollectionRecurseLevel = 4;Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.MaxNestedCollectionRecurseLevel = 4Display Relation Fields
The QueryShowRelationDisplayFields is raised for every foreign-key relation. At runtime, it allows the user to control related fields of the child table to be added to the FieldDescriptorCollection. Inside this event, can get the specific fields and set e.Cancel to true to avoid adding those fields.
this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.QueryShowRelationDisplayFields += new QueryShowRelationFieldsEventHandler(Engine_QueryShowRelationDisplayFields);
void Engine_QueryShowRelationDisplayFields(object sender, QueryShowRelationFieldsEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Relation.ChildTableName == "Countries")
{
e.ShowRelationFields = ShowRelationFields.Hide;
}
}Private Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.QueryShowRelationDisplayFields += New QueryShowRelationFieldsEventHandler(AddressOf Engine_QueryShowRelationDisplayFields)
Private Sub Engine_QueryShowRelationDisplayFields(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As QueryShowRelationFieldsEventArgs)
If e.Relation.ChildTableName = "Countries" Then
e.ShowRelationFields = ShowRelationFields.Hide
End If
End SubRemoving unwanted fields through Event
The QueryShowField gets fired for every field in the FieldDescriptorCollection of individual tables in the dataset. It lets you control the population of field descriptors. Using this event, user can check for specific fields and cancel the population of desired fields at runtime.
this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.QueryShowField += new QueryShowFieldEventHandler(Engine_QueryShowField);
void Engine_QueryShowField(object sender, QueryShowFieldEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Field.Name == "GrandChildID")
e.Cancel = true;
}Private Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.QueryShowField += New QueryShowFieldEventHandler(AddressOf Engine_QueryShowField)
Private Sub Engine_QueryShowField(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As QueryShowFieldEventArgs)
If e.Field.Name = "GrandChildID" Then
e.Cancel = True
End If
End SubNotify Adding Relation
The QueryAddRelation event is invoked for every relation that is being added to the RelationDescriptorCollection. By setting e.Cancel to true, user can avoid specific relations being added.
this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.QueryAddRelation += new QueryAddRelationEventHandler(Engine_QueryAddRelation);
void Engine_QueryAddRelation(object sender, QueryAddRelationEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Relation.Name);
}Private Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.QueryAddRelation += New QueryAddRelationEventHandler(AddressOf Engine_QueryAddRelation)
Private Sub Engine_QueryAddRelation(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As QueryAddRelationEventArgs)
Console.WriteLine(e.Relation.Name)
End SubDisplay Individual Fields
The QueryShowNestedPropertiesFields event is called when there exists nested properties in the bound data source. With the help of this event, user can determine if the individual fields in the nested property should be displayed.
this.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.QueryShowNestedPropertiesFields += new QueryShowNestedPropertiesFieldsEventHandler(Engine_QueryShowNestedPropertiesFields);
void Engine_QueryShowNestedPropertiesFields(object sender, QueryShowNestedPropertiesFieldsEventArgs e)
{
if (e.PropertyDescriptor.PropertyType == typeof(BaseClass))
e.Cancel = true;
}Private Me.gridGroupingControl1.Engine.QueryShowNestedPropertiesFields += New QueryShowNestedPropertiesFieldsEventHandler(AddressOf Engine_QueryShowNestedPropertiesFields)
Private Sub Engine_QueryShowNestedPropertiesFields(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As QueryShowNestedPropertiesFieldsEventArgs)
If e.PropertyDescriptor.PropertyType Is GetType(BaseClass) Then
e.Cancel = True
End If
End Sub