How can I help you?
Syntax Highlighting in Windows Forms Syntax Editor
18 Mar 202524 minutes to read
Provides built-in syntax highlighting support for popular languages like C#, VB.NET, XML, HTML, Java, SQL, PowerShell, C, JavaScript, VBScript, and Delphi.
Configure built-in language
Syntax highlighting built-in languages can be applied by using KnownLanguages enumerator and ApplyConfiguration function.
CSharp
// Considering configuration settings for C# as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.CSharp);' Considering configuration settings for C# as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.CSharp)The LoadFile function in the EditControl helps to load the content of any desired file into the EditControl instead of typing the code in it.
// Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
this.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\FileName.cs");` Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
Me.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\FileName.cs")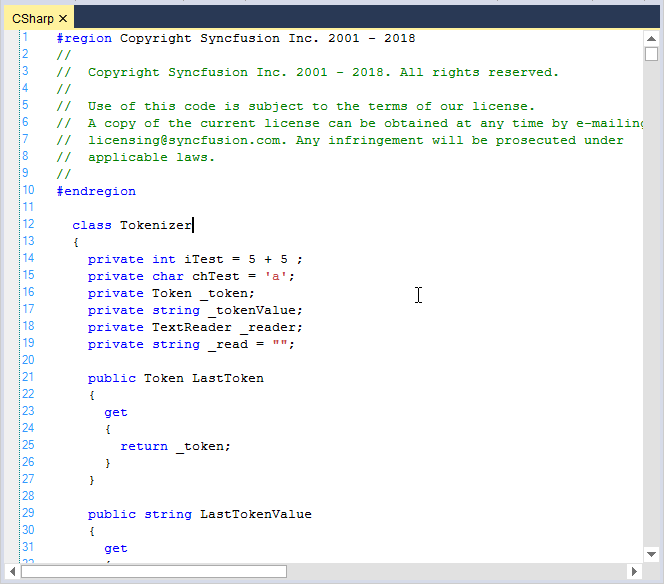
Delphi
// Considering configuration settings for Delphi as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.Delphi);
// Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
this.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\DelphiSource.pas");' Considering configuration settings for Delphi as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.Delphi)
` Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
Me.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\DelphiSource.pas")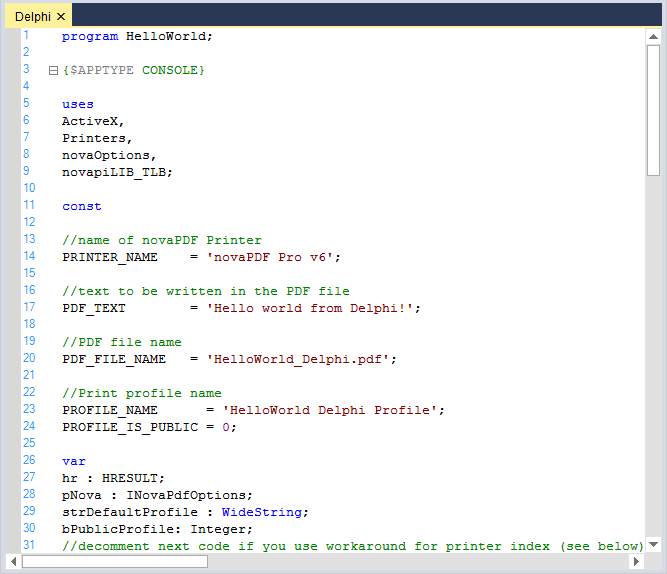
XML
// Considering configuration settings for XML as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.XML);
// Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
this.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\XMLSource.xml");' Considering configuration settings for XML as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.XML)
` Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
Me.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\XMLSource.xml")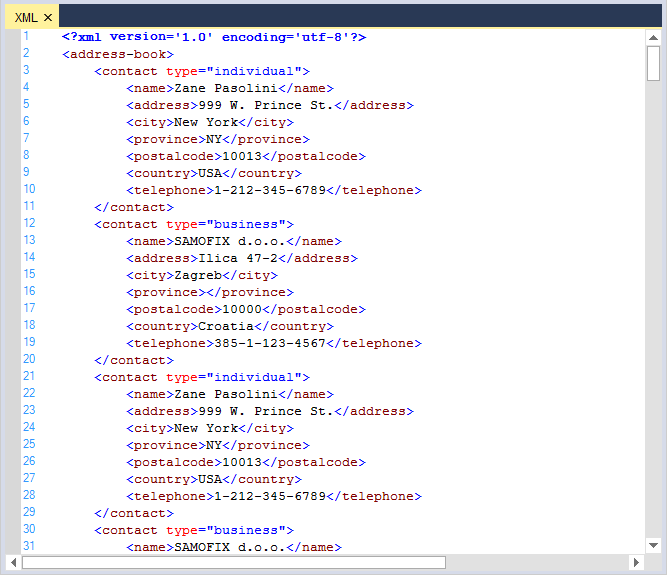
HTML
// Considering configuration settings for HTML as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.HTML);
// Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
this.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\HTMLSource.html");' Considering configuration settings for HTML as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.HTML)
` Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
Me.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\HTMLSource.html")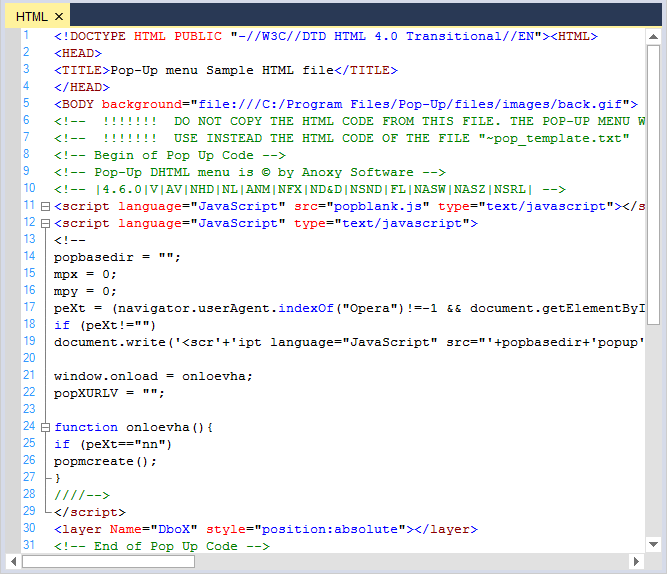
VB.NET
// Considering configuration settings for VB.NET as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.VBNET);
// Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
this.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\VBSource.vb");' Considering configuration settings for VB.NET as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.VBNET)
` Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
Me.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\VBSource.vb")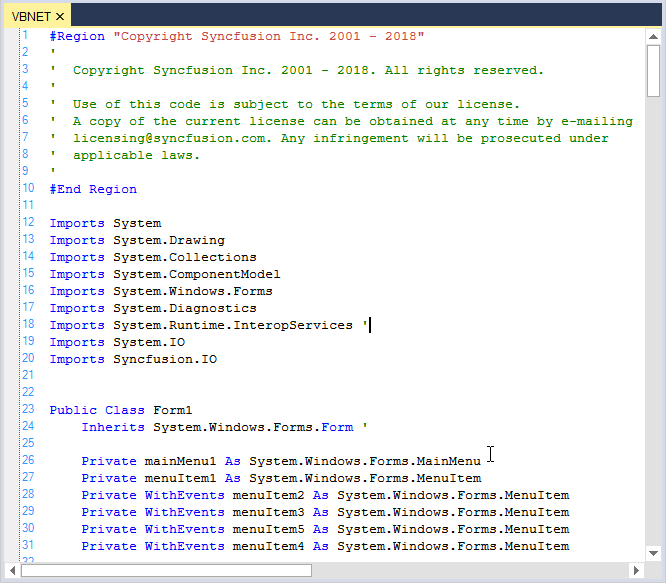
SQL
// Considering configuration settings for SQL as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.SQL);
// Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
this.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\SQLSource.sql");' Considering configuration settings for SQL as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.SQL)
` Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
Me.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\SQLSource.sql")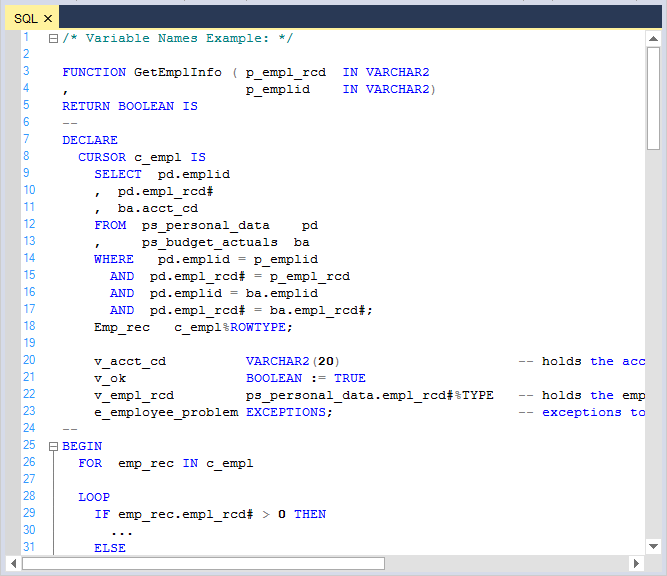
Java
// Considering configuration settings for Java as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.Java);
// Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
this.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\JavaSource.Java");' Considering configuration settings for Java as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.Java)
` Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
Me.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\JavaSource.Java")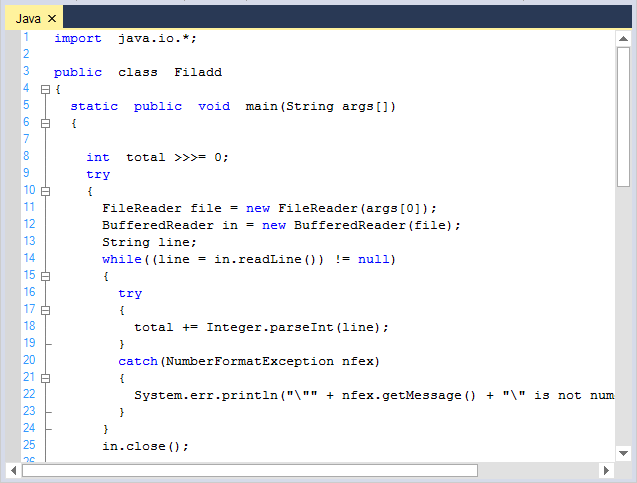
VBScript
// Considering configuration settings for VBScript as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.VBScript);
// Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
this.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\VBScriptSource.vb");' Considering configuration settings for VBScript as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.VBScript)
` Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
Me.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\VBScriptSource.vb")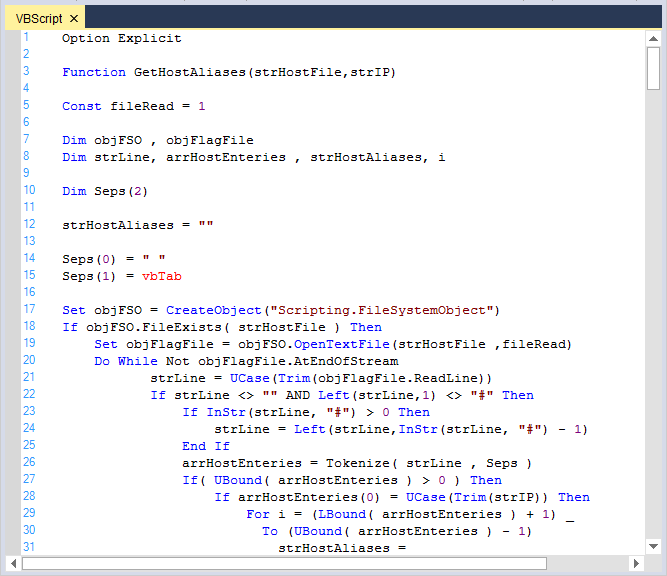
JScript
// Considering configuration settings for JScript as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.JScript);
// Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
this.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\JScriptSource.js");' Considering configuration settings for JScript as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.JScript)
` Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
Me.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\JScriptSource.js")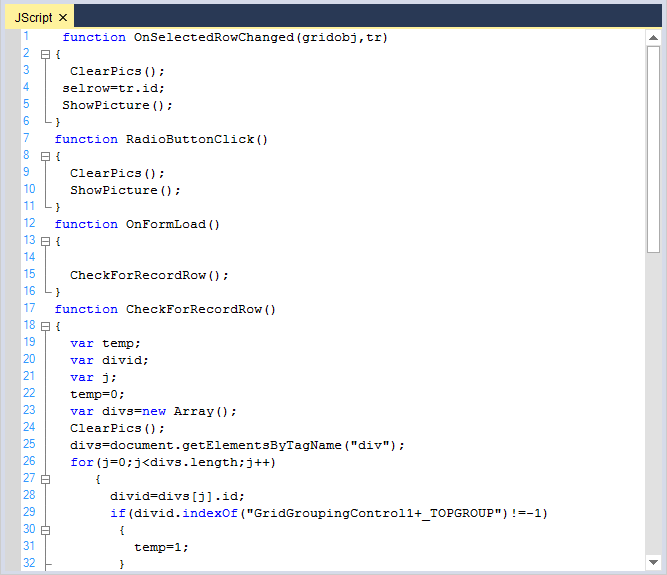
PowerShell
// Considering configuration settings for PowerShell as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.PowerShell);
// Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
this.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\PowerShell.ps1");' Considering configuration settings for PowerShell as an example. Using the KnownLanguages enumerator.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(Syncfusion.Windows.Forms.Edit.Enums.KnownLanguages.PowerShell)
` Loading the files into EditControl by passing the file name as parameter to the LoadFile function.
Me.editControl1.LoadFile(Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\PowerShell.ps1")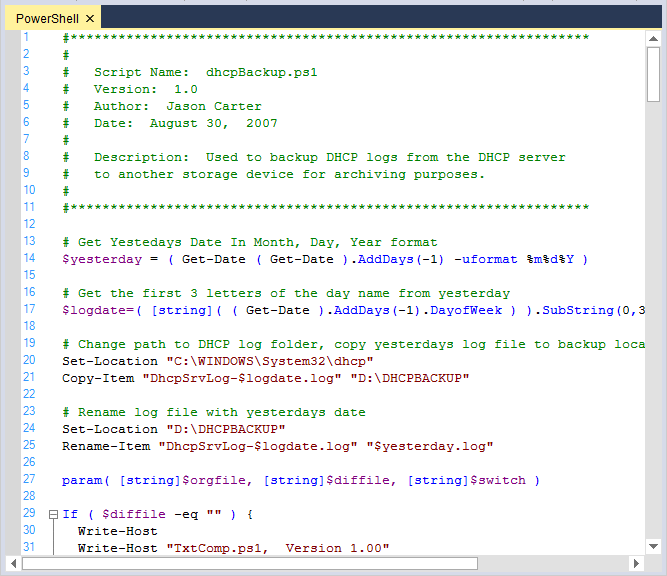
NOTE
Refer to the following sample link that demonstrates the
SyntaxHighlightingfunctionalities of the EditControl:
C:\Users\<User>\AppData\Syncfusion\EssentialStudio\Version Number\Windows\Edit.Windows\Samples\Syntax Highlighting\Syntax Coloring
Customize built-in language settings
The EditControl provides support to customize the built-in language configuration settings.
Initialize the configuration language
In the EditControl, languages should be configured in XML file named Config.xml.
Name of the language must be set by using the name attribute of the ConfigLanguage tag attribute. When the language is case insensitive, you should set the CaseInsensitive attribute to true.
<ConfigLanguage name="C#">
<formats>
</formats>
<extensions>
</extensions>
<lexems>
</lexems>
<splits>
</splits>
</ConfigLanguage>Format
It contains a list of definitions of the formats that can be used later in lexem configuration. Every format contains the attributes such as name, font,foreground color, font color, background color, style, weight, underline, and line color.
<formats>
<format name="Text" Font="Consolas, 12pt"/>
</formats>
Font color
Font color of any format in the specified language can be customized by using the FontColor property of Format tag.
<ConfigLanguage name="C#">
<formats>
<format name="Text" Font="Consolas, 10pt" FontColor="Red" />
</formats>
</ConfigLanguage>
Lexem
Lexem contains rules for parsing the text. Type and FormatName attributes of lexems helps to specify the format of the lexem.
- Type: Used for standard predefined types of the lexems.
- FormatName: Used when the type is Custom.
<lexem BeginBlock="public" Type="KeyWord" />
<lexem BeginBlock="class" Type="KeyWord" />
<lexem BeginBlock="+" Type="Operator" />
<lexem BeginBlock="-" Type="Operator" />For non-complex lexems, you can specify ContinueBlock and EndBlock attributes.
- If you specify ContinueBlock, the parser will read words (tokens) and set the specified formatting for them until it encounters a ContinueBlock.
- If you specify EndBlock, specified formatting will be set only if first token matches ContinueBlock and is followed by EndBlock.
All matched text will be treated later as one word, and won’t be broken into parts in WordWrap mode.
SubLexems
Sublexems must be skipped if they are found after BeginBlock string and before EndBlock string.
<SubLexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="\" EndBlock=""" Type="String" />
</SubLexems>Collapsable region
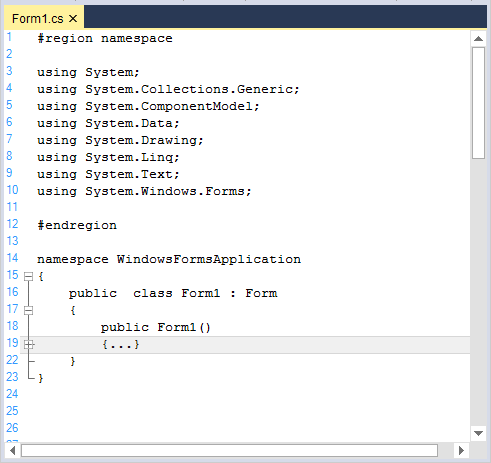
Collapsable region can be customized by adding the desired lexem with attributes such as IsCollapsable and CollapseName.
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="{" EndBlock="}" Type="KeyWord" IsComplex="true" IsCollapsable="true" Indent="true" DropContextPrompt="true" CollapseName="{...}">
<SubLexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="\n" IsBeginRegex="true" />
</SubLexems>
</lexem>
</lexems>This code example works only when the ShowOutliningCollapsers property in EditControl is true.
Keyword
Custom keywords can be added or existing keywords can be customized in built-in languages.
<formats>
<format name="KeyWord" Font="Consolas, 10pt" FontColor="Green" />
</formats>
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="int" Type="KeyWord" />
<lexem BeginBlock="using" Type="KeyWord" />
</lexems>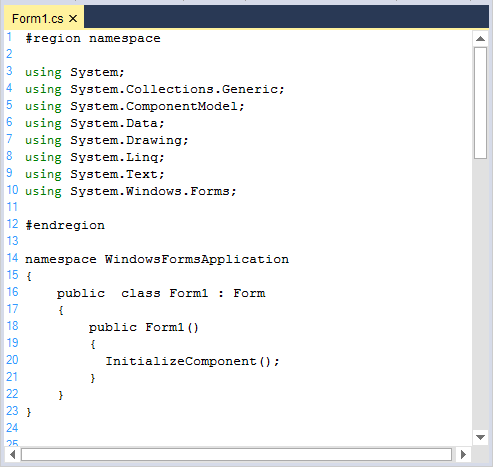
Operator
Custom operators can be added or existing operators can be customized in built-in languages by using Lexem configuration.
<formats>
<format name="Operator" Font="Consolas, 10pt" FontColor="Brown" />
</formats>
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="++" Type="Operator" />
<lexem BeginBlock="+" Type="Operator" />
</lexems>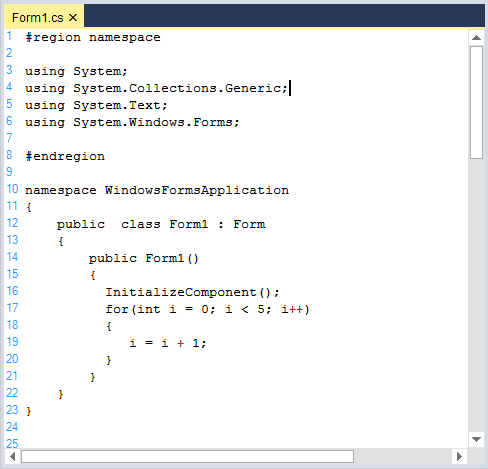
Regex
A regular expression is a pattern that could be matched against any input text.
For example, to customize the strings ends with !, set the regex property of IsBeginRegex and IsEndRegex to true based on the expression given in the lexem.
<formats>
<format name="String" Font="Courier New, 13pt, style=Bold" FontColor="Brown" />
</formats>
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="[A-z\s]+\!" IsBeginRegex="true" Type="String"/>
</lexems>
// we have to mention the same Regex expression in the Split tag.
<splits>
<split IsRegex="true">[A-z\s]+\!</split>
</splits>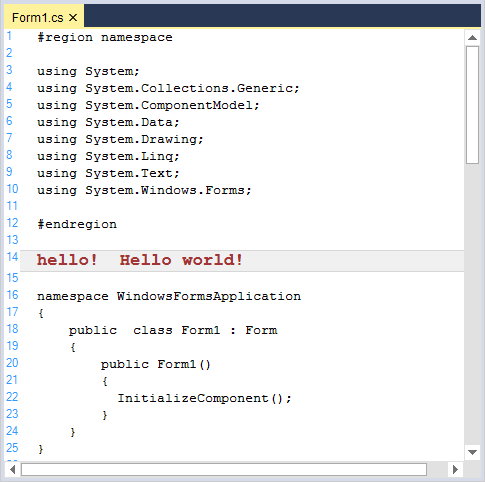
Error words highlighting
Error lexems can be added to the language by declaring a format names Error. It can be highlighted using underlines. Following code is an example of declaring “#endregion” as error. If #region is not BeginBlock, priority values will be assigned to order the interrupt.
<formats>
<format name="Error" Font="Courier New, 10pt" FontColor="Black" underline="Wave" LineColor="Red" />
</formats>
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="pubblic" Type="Error" Priority="-10" />
<lexem BeginBlock="#else" Type="Error" Priority="-10" />
</lexems>
<splits>
<split>#else</split>
</splits>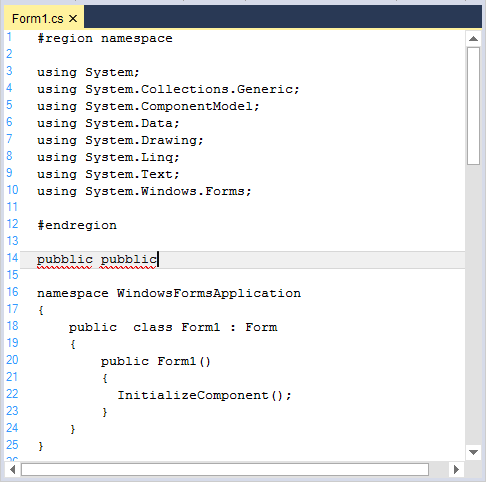
Splits
Splits helps to configure two different words as single. For example, consider # and region that can be treated as single word by using Split configuration.
<formats>
<format name="KeyWord" Font="Courier New, 14pt" FontColor="Orange" />
</formats>
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="#region" Type="KeyWord" />
<lexem BeginBlock="#endregion" Type="KeyWord" />
</lexems>
<splits>
<split>#region</split>
<split>#endregion</split>
</splits>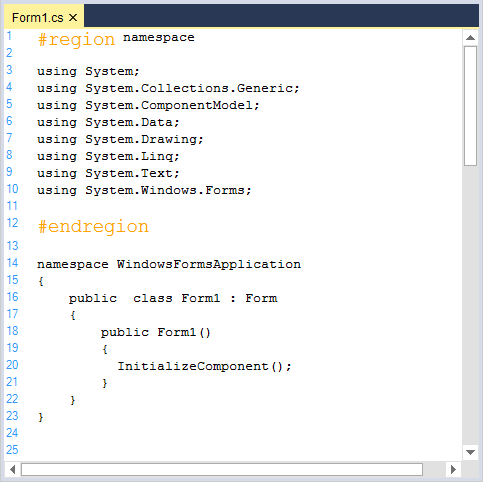
Auto replace triggers
AutoReplaceTriggers attribute helps to auto corrects the incorrect spelling of lexems.
<ConfigLanguage name="C#" TriggersActivators=".">
<AutoReplaceTriggers>
<AutoReplaceTrigger From="teh" To="the" />
<AutoReplaceTrigger From="itn" To="int" />
</AutoReplaceTriggers>
</ConfigLanguage>this.editControl1.UseAutoreplaceTriggers = true;Me.editControl1.UseAutoreplaceTriggers = True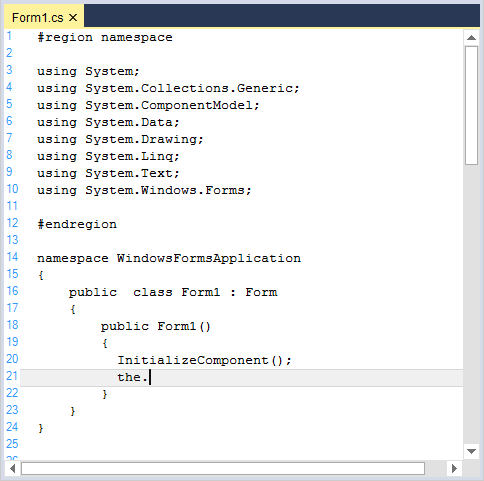
NOTE
To enable this feature, set the
TriggersActivatorsproperty of ConfigLanguage tag attribute and theUseAutoreplaceTriggersproperty of EditControl should be set totrue.
File extension
Extensions contain a list of extensions associated with that particular language.
<extensions>
<extension>csi</extension>
</extensions>Apply custom configuration in EditControl
The following code examples helps you to configure the configuration file in the EditControl.
private string configFile = Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\config.xml";
// Plug-in an external configuration file.
this.editControl1.Configurator.Open(configFile);
// Apply the configuration defined in the configuration file.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration("C#");private string configFile = Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\config.xml";
' Plug-in an external configuration file.
Me.editControl1.Configurator.Open(configFile)
' Apply the configuration defined in the configuration file.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration("C#")Custom language using XML
The EditControl provides supports for custom language configuration. You can plug-in an external configuration file that defines a custom language to the EditControl by using the Configurator.Open and ApplyConfiguration functions.
Initialize the configuration language.
In the EditControl, languages should be configured in XML file named Config.xml.
Name of the language must be set by using the name attribute of the ConfigLanguage tag attribute. When the language is case insensitive, you should set the CaseInsensitive attribute to true.
<ConfigLanguage name="C++">
<formats>
</formats>
<extensions>
</extensions>
<lexems>
</lexems>
<splits>
</splits>
</ConfigLanguage>Format
It contains a list of definitions of the formats that can be used later in lexem configuration. Every format is specified by a tag
<formats>
<format name="Text" Font="Consolas, 12pt"/>
</formats>
Font color
Font color of any format in the specified language can be customized by using the FontColor property of Format tag.
<formats>
<format name="Text" Font="Courier New, 10pt style=Bold" FontColor="Red" />
</formats>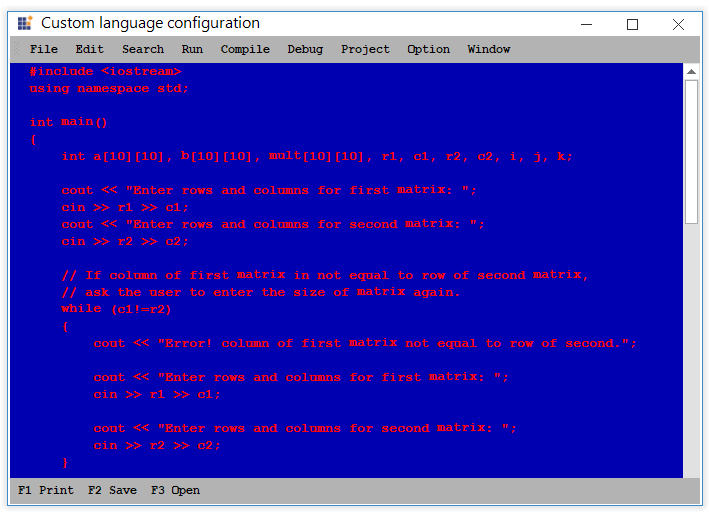
Lexem
Lexem contains rules for parsing the text. Type and FormatName attributes of lexems helps to specify the format of the lexem.
- Type: Used for standard predefined types of the lexems.
- FormatName: Used when the type is Custom.
<lexems>
<!--Adds the Keywords in the lexem-->.
<lexem BeginBlock="int" Type="KeyWord" />
<lexem BeginBlock="while" Type="KeyWord" />
<!--Adds the operator in the Lexem-->.
<lexem BeginBlock="<" Type="Operator" />
<lexem BeginBlock=">" Type="Operator" />
</lexems>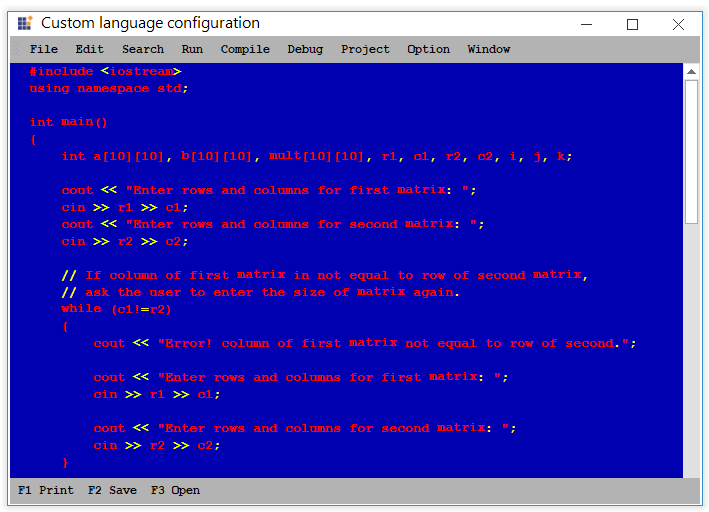
For non-complex lexems, you can specify ContinueBlock and EndBlock attributes.
- If you specify ContinueBlock, the parser will read words (tokens) and set the specified formatting for them until it encounters a ContinueBlock.
- If you specify EndBlock, specified formatting will be set only if first token matches ContinueBlock and is followed by EndBlock.
All matched text will be treated later as one word, and won’t be broken into parts in WordWrap mode.
SubLexems
Sublexems must be skipped if they are found after BeginBlock string and before EndBlock string.
<SubLexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="\" EndBlock=""" Type="String" />
</SubLexems>Collapsable region
Collapsable region can be customized by adding the desired lexem with attributes such as IsCollapsable and CollapseName.
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="{" EndBlock="}" Type="KeyWord" IsComplex="true" IsCollapsable="true" Indent="true" DropContextPrompt="true" CollapseName="{...}">
<SubLexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="\n" IsBeginRegex="true" />
</SubLexems>
</lexem>
</lexems>This code example works only when the ShowOutliningCollapsers property in the EditControl is true.
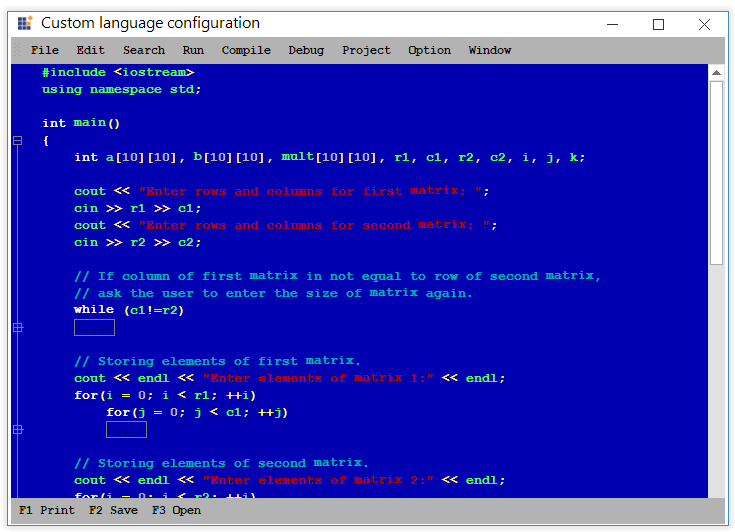
Keyword
Custom keywords can be added or existing keywords can be customized in built-in languages by using Lexem configuration.
<formats>
<format name="KeyWord" Font="Consolas, 10pt" FontColor="White" />
</formats>
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="int" Type="KeyWord" />
<lexem BeginBlock="using" Type="KeyWord" />
</lexems>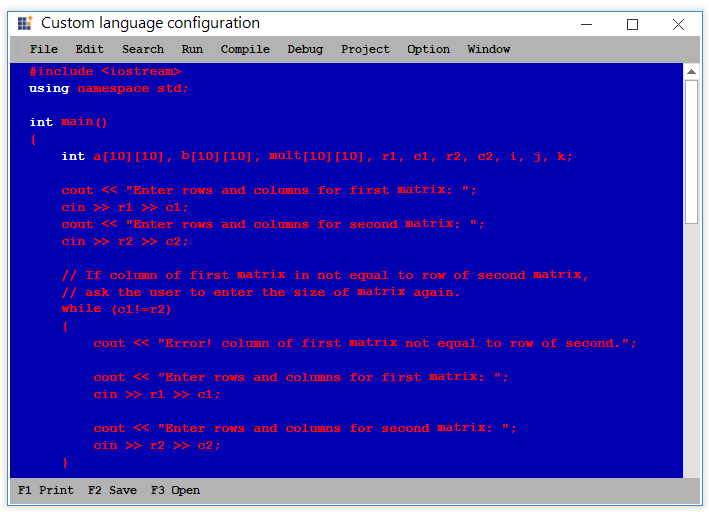
Operator
Custom operators can be added or existing operators can be customized in built-in languages.
<formats>
<format name="Operator" Font="Consolas, 10pt" FontColor="Brown" />
</formats>
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="<" Type="Operator" />
<lexem BeginBlock=">" Type="Operator" />
</lexem>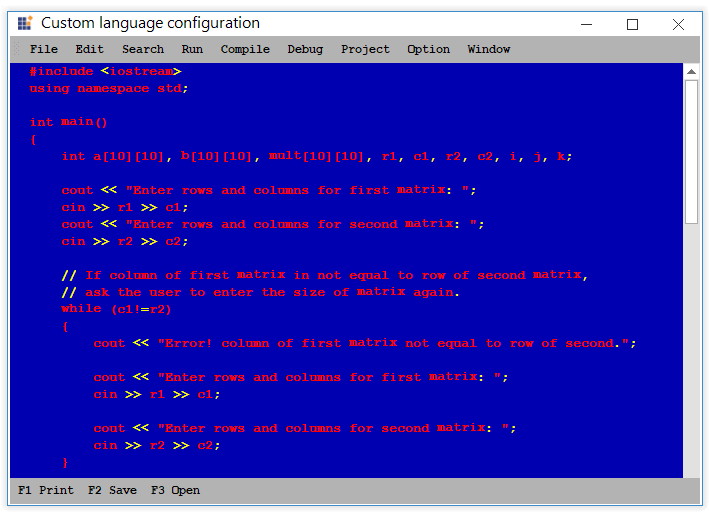
Regex
A regular expression is a pattern that could be matched against any input text.
For example, to customize the strings that ends with !, set the regex property of IsBeginRegex and IsEndRegex to true based on the expression given in the lexem.
<formats>
<format name="String" Font="Courier New, 13pt, style=Bold" FontColor="Brown" />
</formats>
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="[A-z\s]+\!" IsBeginRegex="true" Type="String"/>
</lexems>
// we have to mention the same Regex expression in the Split tag.
<splits>
<split IsRegex="true">[A-z\s]+\!</split>
</splits>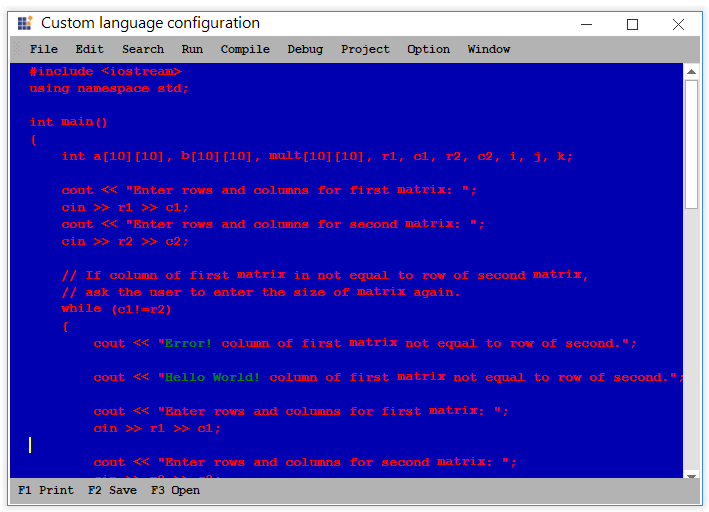
Error words highlighting
Error lexems can be added to the language by declaring a format names Error and it can be highlighted using underlines.
<formats>
<format name="Error" Font="Courier New, 10pt" FontColor="Black" underline="Wave" LineColor="Red" />
</formats>
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="#endregion" Type="Error" Priority="-10" />
<lexem BeginBlock="#endif" Type="Error" Priority="-10" />
<lexem BeginBlock="#else" Type="Error" Priority="-10" />
</lexems>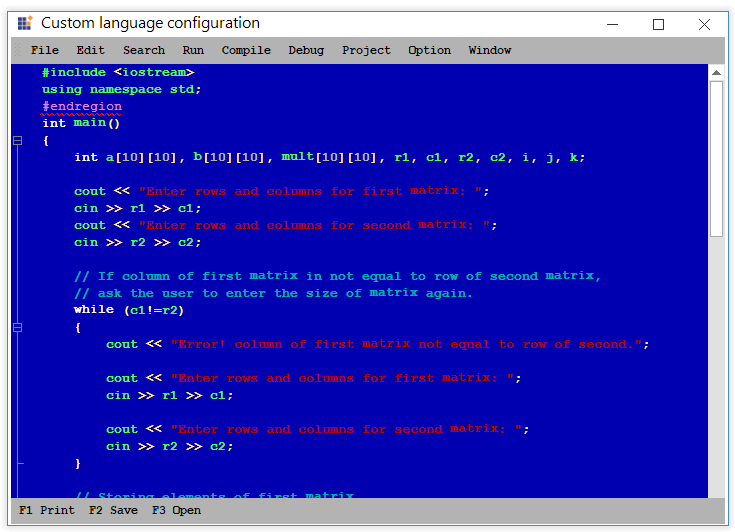
Splits
Splits helps to configure two different words as a single. For example, consider # and include that can be treated as single word by using Split configuration.
<formats>
<format name="KeyWord" Font="Courier New, 14pt" FontColor="Orange" />
</formats>
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="#include" Type="KeyWord" />
</lexems>
<splits>
<split>#include</split>
</splits>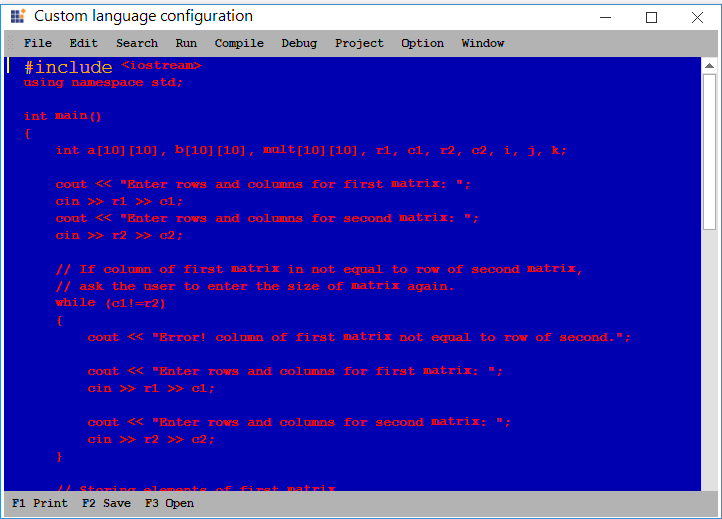
Auto replace triggers
AutoReplaceTriggers attribute helps to auto corrects the incorrect spelling of lexems.
<ConfigLanguage name="C#" TriggersActivators=".">
<AutoReplaceTriggers>
<AutoReplaceTrigger From="teh" To="the" />
<AutoReplaceTrigger From="itn" To="int" />
</AutoReplaceTriggers>
</ConfigLanguage>this.editControl1.UseAutoreplaceTriggers = true;Me.editControl1.UseAutoreplaceTriggers = True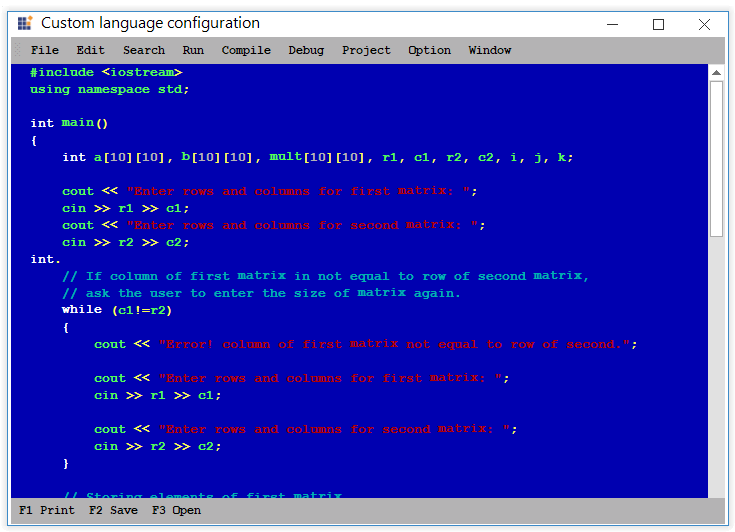
NOTE
To enable this feature, set the
TriggersActivatorsproperty of ConfigLanguage tag attribute and theUseAutoreplaceTriggersproperty of the EditControl should be set totrue.
File extension
Extensions contain a list of extensions associated with that particular language.
<extensions>
<extension>cpp</extension>
</extensions>Multiple language configuration
The EditControl supports multiple language configuration helps to configure one or more languages in single language configuration.
<ConfigLanguage name="HTML (Light)" CaseInsensitive="true" Known="HTML" StartComment="<!--" EndComment="-->">
<formats>
<format name="Text" Font="Courier New, 10pt" FontColor="Black" />
<format name="TagName" Font="Courier New, 10pt" FontColor="Green" />
<format name="AttributeName" Font="Courier New, 10pt" FontColor="Red" />
<format name="KeyWord" Font="Courier New, 10pt" FontColor="Blue" />
<format name="Operator" Font="Courier New, 10pt" FontColor="Blue" />
</formats>
<extensions>
<extension>html</extension>
<extension>htm</extension>
</extensions>
<!--JavaScript and HTML-->
<lexems>
<lexem BeginBlock="<" Type="Operator" />
<lexem BeginBlock=">" Type="Operator" />
<lexem BeginBlock="if" Type="KeyWord" />
<lexem BeginBlock="var" Type="KeyWord" />
<lexem BeginBlock="escape" Type="KeyWord" />
<lexem BeginBlock="head" Type="AttributeName" />
<lexem BeginBlock="body" Type="AttributeName" />
<lexem BeginBlock="meta" Type="AttributeName" />
<lexem BeginBlock="title" Type="AttributeName" />
<lexem BeginBlock="HTML" Type="AttributeName" />
<lexem BeginBlock="PUBLIC" Type="AttributeName" />
<lexem BeginBlock="script" EndBlock="(>)|(/>)" IsEndRegex="true" IsPseudoEnd="true" IsComplex="true" Type="Custom" FormatName="TagName"/>
</lexems>
</ConfigLanguage>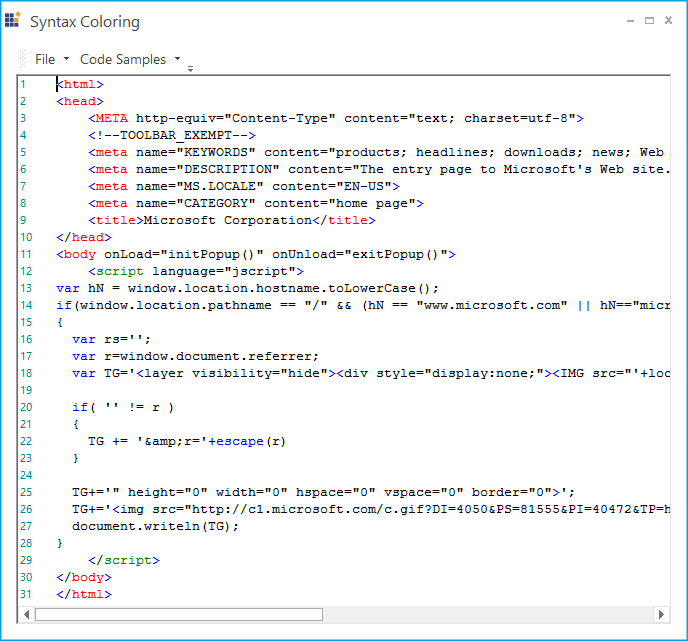
NOTE
Refer to the following sample link that demonstrates the Custom language configuration in the EditControl:
C:\Users\<User>\AppData\Syncfusion\EssentialStudio\Version Number\Windows\Edit.Windows\Samples\Syntax Highlighting\Syntax Coloring
Apply custom configuration in EditControl
private string configFile = Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\config.xml";
// Plug-in an external configuration file.
this.editControl1.Configurator.Open(configFile);
// Apply the configuration defined in the configuration file.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration("C++");private string configFile = Path.GetDirectoryName(Application.ExecutablePath) + @"\..\..\config.xml";
' Plug-in an external configuration file.
Me.editControl1.Configurator.Open(configFile)
' Apply the configuration defined in the configuration file.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration("C++")NOTE
Refer to the following sample link that demonstrates the Custom language configuration in the EditControl:
C:\Users\<User>\AppData\Syncfusion\EssentialStudio\Version Number\Windows\Edit.Windows\Samples\Syntax Highlighting\Custom Config
Configure custom language using code
The EditControl also offers extensive support to create configuration settings programmatically. This provides greater flexibility so that users can dynamically modify configuration settings of the currently loaded configuration. The following procedure will walks through the entire process of creating configuration settings programmatically.
Add new configuration language to EditControl
A new configuration language can be added to the EditControl by using the CreateLanguageConfiguration function of Config class. Once the new configuration language is created, apply it to the contents of EditControl by using the ApplyConfiguration function.
// Create a new configuration language and apply the same to the contents of the EditControl.
IConfigLanguage currentConfigLanguage = this.editControl1.Configurator.CreateLanguageConfiguration("New");
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(currentConfigLanguage);' Create a new configuration language and apply the same to the contents of the EditControl.
Dim currentConfigLanguage As IConfigLanguage = Me.editControl1.Configurator.CreateLanguageConfiguration("New")
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(currentConfigLanguage)Format configuration
Create a custom format object by using the Language.Add function in the EditControl and defines its attributes.
// Creating a custom format object.
ISnippetFormat formatMethod = this.editControl1.Language.Add("CodeBehind");
// Defining its attributes.
formatMethod.Font = new Font("Garamond", 12);
formatMethod.BackColor = Color.Yellow;' Creating a custom format object.
Dim formatMethod As ISnippetFormat = Me.EditControl1.Language.Add("CodeBehind")
' Defining its attributes.
formatMethod.Font = New Font("Garamond", 12)
formatMethod.BackColor = Color.YellowFont configuration
Font color of newly created format in the specified language can be customized by using its FontColor property of ISnippetFormat interface.
formatMethod.Font = new Font("Garamond", 17);
formatMethod.FontColor = Color.Red;formatMethod.Font = new Font("Garamond", 17)
formatMethod.FontColor = Color.Red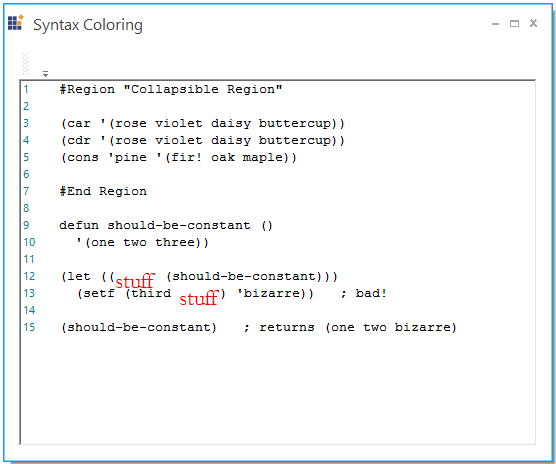
Lexem configuration
Create a ConfigLexem object belongs to the above defined format and define its attributes. Add the ConfigLexem object to the Lexems collection of the current language.
ConfigLexem stuff = new ConfigLexem("stuff", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
stuff.FormatName = "CodeBehind";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(stuff);Dim stuff As ConfigLexem = new ConfigLexem("stuff", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
stuff.FormatName = "CodeBehind"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(stuff)Keywords configuration
Create a custom format object named keyword by using the Language.Add function in the EditControl.
ISnippetFormat keyword = this.editControl1.Language.Add("keyword");
keyword.FontColor = Color.Blue;
keyword.Font = new Font("Garamond", 12);
ConfigLexem car = new ConfigLexem("car", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
car.FormatName = "keyword";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(car);
ConfigLexem cdr = new ConfigLexem("cdr", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
cdr.FormatName = "keyword";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(cdr);
ConfigLexem cons = new ConfigLexem("cons", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
cons.FormatName = "keyword";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(cons);Dim keyword As ISnippetFormat = Me.editControl1.Language.Add("keyword")
keyword.FontColor = Color.Blue
keyword.Font = new Font("Garamond", 12)
Dim car As ConfigLexem = new ConfigLexem("car", "",FormatType.Custom, False)
car.FormatName = "keyword"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(car)
Dim cdr As ConfigLexem = new ConfigLexem("cdr", "",FormatType.Custom, False)
cdr.FormatName = "keyword"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(cdr)
Dim cons As ConfigLexem = new ConfigLexem("cons", "",FormatType.Custom, False)
cons.FormatName = "keyword"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(cons)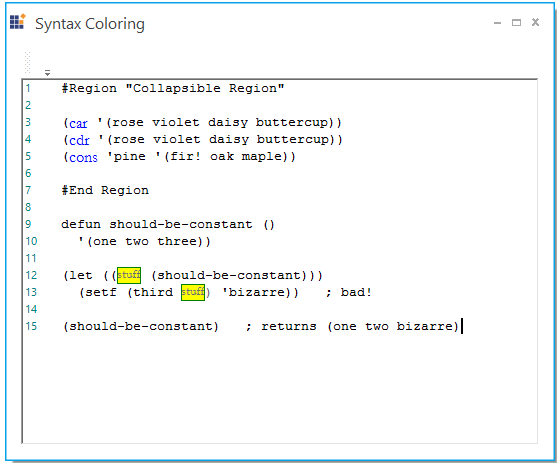
Operators configuration
Create a custom format object named Operators by using the Language.Add function in the EditControl.
ISnippetFormat Operators = this.editControl1.Language.Add("Operators");
Operators.FontColor = Color.Red;
ConfigLexem open = new ConfigLexem("(","",FormatType.Custom,false);
open.FormatName = "Operators";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(open);
ConfigLexem close = new ConfigLexem(")", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
close.FormatName = "Operators";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(close);
ConfigLexem Symbol = new ConfigLexem("#", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
Symbol.FormatName = "Operators";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(Symbol);Dim Operators As ISnippetFormat = this.editControl1.Language.Add("Operators")
Operators.FontColor = Color.Red
Dim open As ConfigLexem = new ConfigLexem("(","",FormatType.Custom, False)
open.FormatName = "Operators"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(open)
Dim close As ConfigLexem = new ConfigLexem(")", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
close.FormatName = "Operators"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(close)
Dim Symbol As ConfigLexem = new ConfigLexem("$", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
Symbol.FormatName = "Operators"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(Symbol)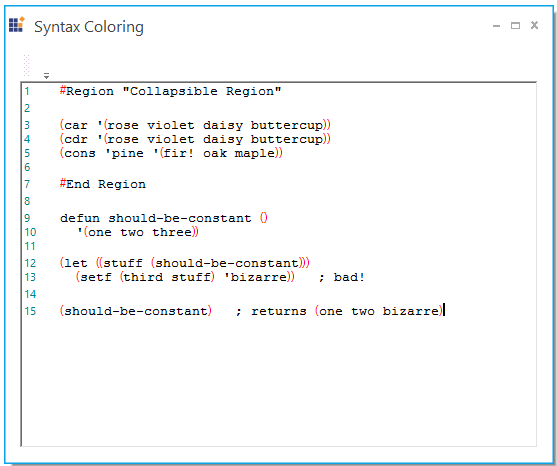
Regex configuration
A regular expression is a pattern that could be matched against any input text.
Color configuration
Color configuration for custom formats can be defined by using its built-in color properties such as FontColor, BackColor, ForeColor, LineColor, and BorderColor properties.
formatMethod.Font = new Font("Garamond", 10);
formatMethod.FontColor = Color.Red;
formatMethod.BorderStyle = FrameBorderStyle.Solid;
formatMethod.BackColor = Color.Yellow;
formatMethod.BorderColor = Color.Green;formatMethod.Font = new Font("Garamond", 10)
formatMethod.FontColor = Color.Red
formatMethod.BorderStyle = FrameBorderStyle.Solid
formatMethod.BackColor = Color.Yellow
formatMethod.BorderColor = Color.Green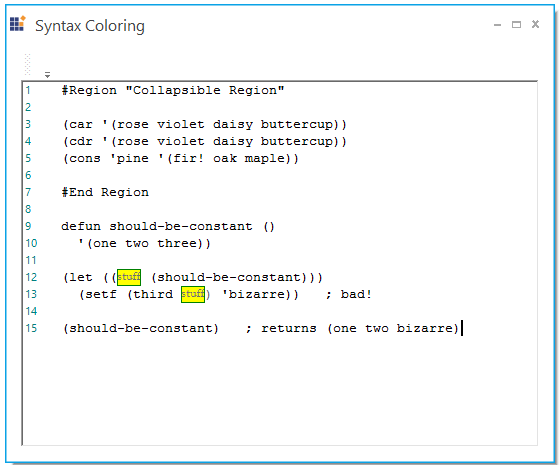
Error words highlighting
Error lexems can be added to the language by declaring a format names Error. It can be highlighted by using underlines.
ISnippetFormat Error = this.editControl1.Language.Add("Error");
Error.FontColor = Color.Black;
Error.UnderlineStyle = UnderlineStyle.Wave;
Error.UnderlineWeight = UnderlineWeight.Thin;
Error.LineColor = Color.Red;
ConfigLexem err = new ConfigLexem("pubblic", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
err.FormatName = "Error";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(err);Dim Error As ISnippetFormat = Me.editControl1.Language.Add("Error")
Error.FontColor = Color.Black
Error.UnderlineStyle = UnderlineStyle.Wave
Error.UnderlineWeight = UnderlineWeight.Thin
Error.LineColor = Color.Red
Dim err As ConfigLexem = new ConfigLexem("pubblic", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
err.FormatName = "Error"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(err)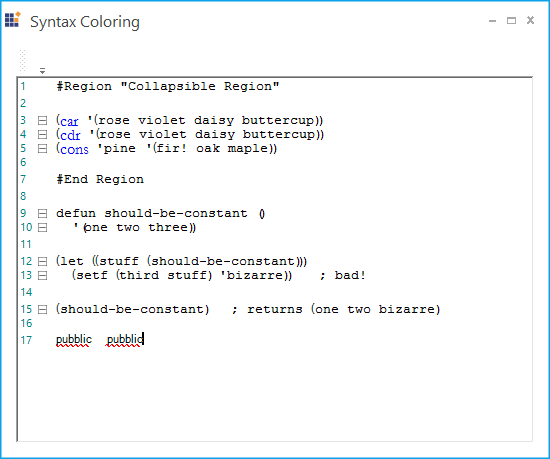
Splits configuration
Splits helps to configure two different words as single. For example, consider # and region that can be treated as single word by using Split configuration. This can be done by adding the appropriate splits to the Language.Splits collections.
// Adding the necessary split definitions to the current language's Splits collection. Split configuration should be initialized before applying new language configuration to EditControl.
Split split = new Split();
split.Text = "#region";
currentConfigLanguage.Splits.Add(split);
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(currentConfigLanguage);
ISnippetFormat keyword = this.editControl1.Language.Add("keyword");
keyword.FontColor = Color.Orange;
keyword.Font = new Font("Garamond", 14);
ConfigLexem region = new ConfigLexem("#region", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
region.FormatName = "keyword";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(region);' Adding the necessary split definitions to the current language's Splits collection. Split configuration should be initialized before applying new language configuration to EditControl.
Dim split As Split = new Split()
split.Text = "#region"
currentConfigLanguage.Splits.Add(split)
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(currentConfigLanguage)
Dim keyword As ISnippetFormat = Me.editControl1.Language.Add("keyword")
keyword.FontColor = Color.Orange
keyword.Font = new Font("Garamond", 14)
Dim region As ConfigLexem = new ConfigLexem("#region", "",FormatType.Custom, False)
region.FormatName = "keyword"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(region)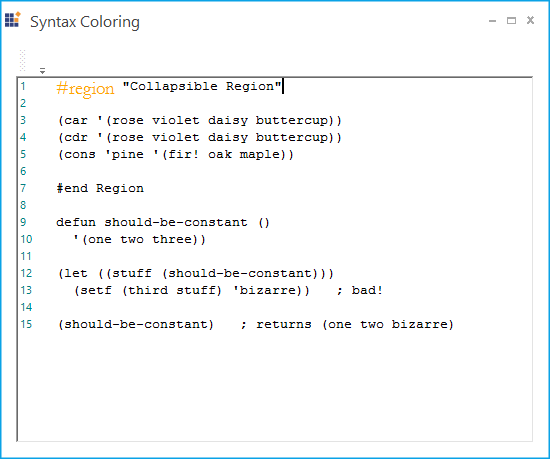
Auto replace triggers
Create a AutoReplaceTrigger object using AutoReplaceTrigger class where those “from” and “to” can be passed while initializing. Add it to the Language.AutoReplaceTriggers collections.
this.editControl1.UseAutoreplaceTriggers = true;
ConfigLanguage language = currentConfigLanguage as ConfigLanguage;
language.TriggersActivators = new char[] { '.' };
AutoReplaceTrigger trigger1 = new AutoReplaceTrigger("teh","the");
this.editControl1.Language.AutoReplaceTriggers.Add(trigger1);Me.editControl1.UseAutoreplaceTriggers = True
Dim language As ConfigLanguage = TryCast(currentConfigLanguage, ConfigLanguage)
language.TriggersActivators = New Char() { "."c }
Dim trigger1 As AutoReplaceTrigger = new AutoReplaceTrigger("teh","the")
Me.editControl1.Language.AutoReplaceTriggers.Add(trigger1)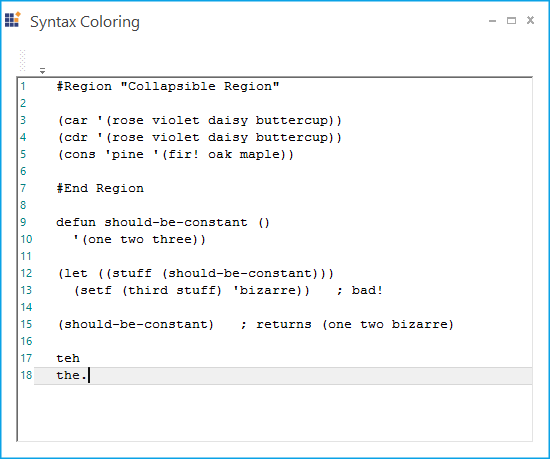
NOTE
To enable this feature, we must set the
TriggersActivatorsproperty of ConfigLanguage tag attribute andUseAutoreplaceTriggersproperty of EditControl should be set totrue.
File extension
Add appropriate extensions to the Language.Extensions collections.
// Adding the necessary extension definitions to the current language's Extensions collection.
this.editControl1.Language.Extensions.Add("lisp");' Adding the necessary extension definitions to the current language's Extensions collection.
Me.editControl1.Language.Extensions.Add("lisp")Multiple language configuration
The EditControl supports multiple language configuration helps to configure one or more languages in single language configuration.
IConfigLanguage currentConfigLanguage = this.editControl1.Configurator.CreateLanguageConfiguration("HTML_JScript");
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(currentConfigLanguage);
ISnippetFormat keyword = this.editControl1.Language.Add("keyword");
keyword.FontColor = Color.Blue;
keyword.Font = new Font("Courier New", 10);
ISnippetFormat attributeName = this.editControl1.Language.Add("AttributeName");
attributeName.FontColor = Color.Red;
attributeName.Font = new Font("Courier New", 10);
ISnippetFormat operators = this.editControl1.Language.Add("Operators");
operators.FontColor = Color.Blue;
operators.Font = new Font("Courier New", 10);
ISnippetFormat tagName = this.editControl1.Language.Add("TagName");
tagName.FontColor = Color.Green;
tagName.Font = new Font("Courier New", 10);
ConfigLexem operator1 = new ConfigLexem("<", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
operator1.FormatName = "Operators";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(operator1);
ConfigLexem operator2 = new ConfigLexem("", ">", FormatType.Custom, false);
operator2.FormatName = "Operators";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(operator2);
ConfigLexem keyword1 = new ConfigLexem("if", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
keyword1.FormatName = "keyword";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(keyword1);
ConfigLexem keyword2 = new ConfigLexem("var", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
keyword2.FormatName = "keyword";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(keyword2);
ConfigLexem keyword3 = new ConfigLexem("escape", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
keyword3.FormatName = "keyword";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(keyword3);
ConfigLexem html = new ConfigLexem("html", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
html.FormatName = "AttributeName";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(html);
ConfigLexem head = new ConfigLexem("head", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
head.FormatName = "AttributeName";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(head);
ConfigLexem body = new ConfigLexem("body", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
body.FormatName = "AttributeName";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(body);
ConfigLexem meta = new ConfigLexem("meta", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
meta.FormatName = "AttributeName";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(meta);
ConfigLexem title = new ConfigLexem("title", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
title.FormatName = "AttributeName";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(title);
ConfigLexem pub = new ConfigLexem("public", "", FormatType.Custom, false);
pub.FormatName = "AttributeName";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(pub);
ConfigLexem script = new ConfigLexem("script", "(>)|(/>)", FormatType.Custom, false);
script.IsBeginRegex = true;
script.IsPseudoEnd = true;
script.IsComplex = true;
script.FormatName = "TagName";
this.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(script);
this.editControl1.Language.Extensions.Add("htm");Dim currentConfigLanguage As IConfigLanguage = Me.editControl1.Configurator.CreateLanguageConfiguration("HTML_JScript")
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(currentConfigLanguage)
Dim keyword As ISnippetFormat = Me.editControl1.Language.Add("keyword")
keyword.FontColor = Color.Blue
keyword.Font = New Font("Courier New", 10)
Dim attributeName As ISnippetFormat = Me.editControl1.Language.Add("AttributeName")
attributeName.FontColor = Color.Red
attributeName.Font = New Font("Courier New", 10)
Dim operators As ISnippetFormat = Me.editControl1.Language.Add("Operators")
operators.FontColor = Color.Blue
operators.Font = New Font("Courier New", 10)
Dim tagName As ISnippetFormat = Me.editControl1.Language.Add("TagName")
tagName.FontColor = Color.Green
tagName.Font = New Font("Courier New", 10)
Dim operator1 As New ConfigLexem("<", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
operator1.FormatName = "Operators"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(operator1)
Dim operator2 As New ConfigLexem("", ">", FormatType.Custom, False)
operator2.FormatName = "Operators"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(operator2)
Dim keyword1 As New ConfigLexem("if", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
keyword1.FormatName = "keyword"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(keyword1)
Dim keyword2 As New ConfigLexem("var", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
keyword2.FormatName = "keyword"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(keyword2)
Dim keyword3 As New ConfigLexem("escape", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
keyword3.FormatName = "keyword"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(keyword3)
Dim html As New ConfigLexem("html", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
html.FormatName = "AttributeName"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(html)
Dim head As New ConfigLexem("head", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
head.FormatName = "AttributeName"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(head)
Dim body As New ConfigLexem("body", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
body.FormatName = "AttributeName"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(body)
Dim meta As New ConfigLexem("meta", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
meta.FormatName = "AttributeName"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(meta)
Dim title As New ConfigLexem("title", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
title.FormatName = "AttributeName"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(title)
Dim pub As New ConfigLexem("public", "", FormatType.Custom, False)
pub.FormatName = "AttributeName"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(pub)
Dim script As New ConfigLexem("script", "(>)|(/>)", FormatType.Custom, False)
script.IsBeginRegex = True
script.IsPseudoEnd = True
script.IsComplex = True
script.FormatName = "TagName"
Me.editControl1.Language.Lexems.Add(script)
Me.editControl1.Language.Extensions.Add("htm")
Invoking newly added configuration language
Invoke the ResetCaches function to apply the newly added configuration settings.
// Reset the current configuration language cache to reflect these changes.
this.editControl1.Language.ResetCaches();' Reset the current configuration language cache to reflect these changes.
Me.editControl1.Language.ResetCaches()Configure syntax highlighting through dialog box
Syntax highlighting and code coloring can be implemented at runtime by using the Language Coloring Configuration Editor. It can be customized by using ConfigurationDialog class and IConfig interface.
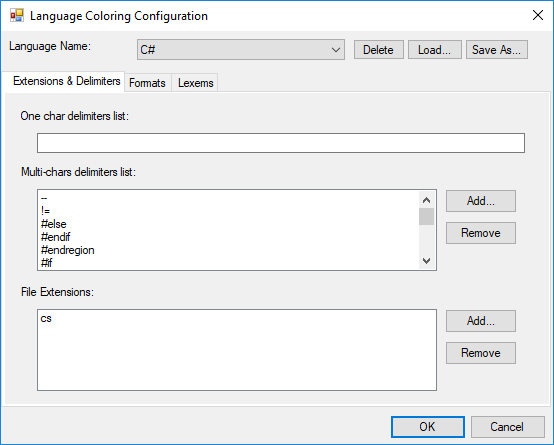
IConfigLanguage activeLang = this.editControl1.Parser.Formats as IConfigLanguage;
// Create an instance of ConfigurationDialog.
ConfigurationDialog editConfig = new ConfigurationDialog(this.editControl1.Configurator, activeLang);
if(editConfig.ShowDialog(this) == DialogResult.OK && activeLang != null)
{
IConfigLanguage newLang = editConfig.Configurator.KnownLanguageNames.Contains(activeLang.Language) ? editConfig.Configurator[activeLang.Language] : editConfig.Configurator.DefaultLanguage;
if(newLang != null)
{
// Set language configuration instance object.
this.editControl1.Configurator = editConfig.Configurator;
// Applies coloring of the specified language to the text.
this.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(newLang);
}
}Dim activeLang As IConfigLanguage = Me.EditControl1.Parser.Formats
' Create an instance of ConfigurationDialog.
Dim editConfig As New frmConfigDialog(Me.editControl1.Configurator, activeLang)
If editConfig.ShowDialog(Me) = DialogResult.OK AndAlso Not (activeLang Is Nothing) Then
Dim newLang As IConfigLanguage = If(editConfig.Configurator.KnownLanguageNames.Contains(activeLang.Language), editConfig.Configurator(activeLang.Language), editConfig.Configurator.DefaultLanguage)
If Not (newLang Is Nothing) Then
' Set language configuration instance object.
Me.editControl1.Configurator = editConfig.Configurator
' Applies coloring of the specified language to the text.
Me.editControl1.ApplyConfiguration(newLang)
End If
End IfSee Also
How to programmatically configure syntax highlighting in WinForms SyntaxEditor?