How can I help you?
Import to Excel Document
29 Dec 202524 minutes to read
DataTable to Excel
The following code example illustrates on how to import a DataTable into an Excel using ImportDataTable method.
NOTE
XlsIO supports importing of data from data table to worksheet in Windows Forms, WPF, ASP.NET, ASP.NET MVC and ASP.NET Core (2.0 onwards) platforms alone.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
#region Import from Data Table
//Initialize the DataTable
DataTable table = SampleDataTable();
//Import DataTable to the worksheet
worksheet.ImportDataTable(table, true, 1, 1);
#endregion
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ImportDataTable.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Initialize the DataTable
DataTable table = SampleDataTable();
//Import DataTable to the worksheet.
worksheet.ImportDataTable(table, true, 1, 1);
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromDT.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Initialize the DataTable
Dim table As DataTable = sampleDataTable()
'Import DataTable to the worksheet
worksheet.ImportDataTable(table, True, 1, 1)
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromDT.xlsx")
End UsingA complete working example to import data from DataTable to Excel in C# is present on this GitHub page.
NOTE
XlsIO imports the data from data table into Excel worksheet based on the data table column type. So, it is suggested to create the data tables with required column types such as number, text or date time before importing the data table to Excel worksheet.
Preserve Data Types
To preserve data types when importing a DataTable into an Excel worksheet, set the preserveTypes parameter of the ImportDataTable method to true.
worksheet.ImportDataTable(table, false, 1, 1, true); // preserveTypes = trueworksheet.ImportDataTable(table, false, 1, 1, true); // preserveTypes = trueworksheet.ImportDataTable(table, False, 1, 1, True) ' preserveTypes = TrueDataColumn to Excel
The following code example illustrates how to import DataColumn into an Excel using ImportDataColumn method.
NOTE
XlsIO supports importing data column to worksheet in Windows Forms, WPF, ASP.NET, ASP.NET MVC and ASP.NET Core (2.0 onwards) platforms alone.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
#region Import from DataColumn
//Initialize the DataTable
DataTable table = SampleDataTable();
//Import Data Column to the worksheet
DataColumn column = table.Columns[0];
worksheet.ImportDataColumn(column, true, 1, 1);
#endregion
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ImportDataColumn.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Initialize the DataTable
DataTable table = SampleDataTable();
//Import Data Column to the worksheet
DataColumn column = table.Columns[0];
worksheet.ImportDataColumn(column, true, 1, 1);
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromDT.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Initialize the DataTable
Dim table As DataTable = sampleDataTable()
'Import DataColumn to the worksheet
Dim column As DataColumn = table.Columns(0)
worksheet.ImportDataColumn(column, True, 1, 1)
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromDT.xlsx")
End UsingA complete working example to import data from DataColumn to Excel in C# is present on this GitHub page.
DataView to Excel
The following code example illustrates how to import DataView into an Excel using ImportDataView method.
NOTE
XlsIO supports importing data view to worksheet in Windows Forms, WPF, ASP.NET, ASP.NET MVC and ASP.NET Core (2.0 onwards) platforms alone.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
#region Import from DataView
//Initialize the DataTable
DataTable table = SampleDataTable();
//Import DataView to the worksheet
DataView view = table.DefaultView;
worksheet.ImportDataView(view, true, 1, 1);
#endregion
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ImportDataView.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Initialize the DataTable
DataTable table = SampleDataTable();
//Import DataView to the worksheet
DataView view = table.DefaultView;
worksheet.ImportDataView(view, true, 1, 1);
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromDT.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Initialize the DataTable
Dim table As DataTable = sampleDataTable()
'Import DataView to the worksheet
Dim view As DataView = table.DefaultView
worksheet.ImportDataView(view, True, 1, 1)
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromDT.xlsx")
End UsingA complete working example to import data from DataView to Excel in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Collection Objects to Excel
XlsIO allows you to import data directly from Collection Objects as shown below.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import the data to worksheet
IList<Customer> reports = GetSalesReports();
worksheet.ImportData(reports, 2, 1, false);
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ImportCollectionObjects.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import the data to worksheet
IList<Customer> reports = GetSalesReports();
worksheet.ImportData(reports, 2, 1, false);
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromDT.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Import the data to worksheet
Dim reports As IList(Of Customer) = GetSalesReports()
worksheet.ImportData(reports, 2, 1, False)
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromDT.xlsx")
End UsingThe following code snippet provides supporting class for the above code. Here, the attributes DisplayNameAttribute and Bindable are used.
- DisplayNameAttribute - to customize the column header name while importing.
- BindableAttribute - to skip a property while importing.
//Gets a list of sales reports
public static List<Customer> GetSalesReports()
{
List<Customer> reports = new List<Customer>();
reports.Add(new Customer("Andy Bernard", "45000", "58000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Jim Halpert", "34000", "65000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Karen Fillippelli", "75000", "64000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Phyllis Lapin", "56500", "33600" ));
reports.Add(new Customer("Stanley Hudson", "46500", "52000"));
return reports;
}
//Customer details
public class Customer
{
[DisplayNameAttribute("Sales Person Name")]
public string SalesPerson { get; set; }
[Bindable(false)]
public string SalesJanJun { get; set; }
public string SalesJulDec { get; set; }
public Customer(string name, string janToJun, string julToDec)
{
SalesPerson = name;
SalesJanJun = janToJun;
SalesJulDec = julToDec;
}
}//Gets a list of sales reports
public static List<Customer> GetSalesReports()
{
List<Customer> reports = new List<Customer>();
reports.Add(new Customer("Andy Bernard", "45000", "58000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Jim Halpert", "34000", "65000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Karen Fillippelli", "75000", "64000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Phyllis Lapin", "56500", "33600" ));
reports.Add(new Customer("Stanley Hudson", "46500", "52000"));
return reports;
}
//Customer details
public class Customer
{
[DisplayNameAttribute("Sales Person Name")]
public string SalesPerson { get; set;
[Bindable(false)]
public string SalesJanJun { get; set; }
public string SalesJulDec { get; set; }
public Customer(string name, string janToJun, string julToDec)
{
SalesPerson = name;
SalesJanJun = janToJun;
SalesJulDec = julToDec;
}
}'Gets a list of sales reports
Public Function GetSalesReports() As List(Of Customer)
Dim reports As New List(Of Customer)()
reports.Add(New Customer("Andy Bernard", "45000", "58000"))
reports.Add(New Customer("Jim Halpert", "34000", "65000"))
reports.Add(New Customer("Karen Fillippelli", "75000", "64000"))
reports.Add(New Customer("Phyllis Lapin", "56500", "33600"))
reports.Add(New Customer("Stanley Hudson", "46500", "52000"))
Return reports
End Function
'Customer details
Public Class Customer
Private m_SalesPerson As String
Private m_SalesJanJun As String
Private m_SalesJulDec As String
<DisplayNameAttribute("Sales Person Name")>
Public Property SalesPerson() As String
Get
Return m_SalesPerson
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_SalesPerson = Value
End Set
End Property
<Bindable(False)>
Public Property SalesJanJun() As String
Get
Return m_SalesJanJun
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_SalesJanJun = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property SalesJulDec() As String
Get
Return m_SalesJulDec
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_SalesJulDec = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Sub New(name As String, janToJun As String, julToDec As String)
SalesPerson = name
SalesJanJun = janToJun
SalesJulDec = julToDec
End Sub
End ClassA complete working example to import data from Collection Objects to Excel in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Data Options
ExcelImportDataOptions is a support class for ImportData method which contains various properties to import data with formatting.
ExcelImportDataOptions class contains the following properties:
FirstRow - Specifies first row from where the data should be imported.
FirstColumn - Specifies first column from where the data should be imported.
IncludeHeader - Specifies whether class properties names must be imported or not.
PreserveTypes - Indicates whether XlsIO should preserve column types from Data. By default, preserve type is TRUE. Setting it to True will import data based on column type, otherwise will import based on value type.
The following code example illustrates how to import collection objects into an Excel using ImportData method with ExcelImportDataOptions class.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import the data to worksheet with Import Data Options
IList<Customer> reports = GetSalesReports();
ExcelImportDataOptions importDataOptions = new ExcelImportDataOptions();
importDataOptions.FirstRow = 2;
importDataOptions.FirstColumn = 1;
importDataOptions.IncludeHeader = false;
importDataOptions.PreserveTypes = false;
worksheet.ImportData(reports, importDataOptions);
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ImportDataOptions.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import the data to worksheet with Import Data Options
IList<Customer> reports = GetSalesReports();
ExcelImportDataOptions importDataOptions = new ExcelImportDataOptions();
importDataOptions.FirstRow = 2;
importDataOptions.FirstColumn = 1;
importDataOptions.IncludeHeader = false;
importDataOptions.PreserveTypes = false;
worksheet.ImportData(reports, importDataOptions);
workbook.SaveAs("ImportData.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Import the data to worksheet with Import Data Options
Dim reports As IList(Of Customer) = GetSalesReports()
Dim importDataOptions As ExcelImportDataOptions = New ExcelImportDataOptions()
importDataOptions.FirstRow = 2
importDataOptions.FirstColumn = 1
importDataOptions.IncludeHeader = False
importDataOptions.PreserveTypes = False
worksheet.ImportData(output, importDataOptions)
workbook.SaveAs("ImportData.xlsx")
End UsingThe following code snippet provides supporting class for the above code.
//Gets a list of sales reports
public static List<Customer> GetSalesReports()
{
List<Customer> reports = new List<Customer>();
reports.Add(new Customer("Andy Bernard", "45000", "58000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Jim Halpert", "34000", "65000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Karen Fillippelli", "75000", "64000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Phyllis Lapin", "56500", "33600" ));
reports.Add(new Customer("Stanley Hudson", "46500", "52000"));
return reports;
}
//Customer details
public class Customer
{
public string SalesPerson { get; set; }
public string SalesJanJun { get; set; }
public string SalesJulDec { get; set; }
public Customer(string name, string janToJun, string julToDec)
{
SalesPerson = name;
SalesJanJun = janToJun;
SalesJulDec = julToDec;
}
}//Gets a list of sales reports
public static List<Customer> GetSalesReports()
{
List<Customer> reports = new List<Customer>();
reports.Add(new Customer("Andy Bernard", "45000", "58000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Jim Halpert", "34000", "65000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Karen Fillippelli", "75000", "64000"));
reports.Add(new Customer("Phyllis Lapin", "56500", "33600" ));
reports.Add(new Customer("Stanley Hudson", "46500", "52000"));
return reports;
}
//Customer details
public class Customer
{
public string SalesPerson { get; set;
public string SalesJanJun { get; set; }
public string SalesJulDec { get; set; }
public Customer(string name, string janToJun, string julToDec)
{
SalesPerson = name;
SalesJanJun = janToJun;
SalesJulDec = julToDec;
}
}'Gets a list of sales reports
Public Function GetSalesReports() As List(Of Customer)
Dim reports As New List(Of Customer)()
reports.Add(New Customer("Andy Bernard", "45000", "58000"))
reports.Add(New Customer("Jim Halpert", "34000", "65000"))
reports.Add(New Customer("Karen Fillippelli", "75000", "64000"))
reports.Add(New Customer("Phyllis Lapin", "56500", "33600"))
reports.Add(New Customer("Stanley Hudson", "46500", "52000"))
Return reports
End Function
'Customer details
Public Class Customer
Private m_SalesPerson As String
Private m_SalesJanJun As String
Private m_SalesJulDec As String
Public Property SalesPerson() As String
Get
Return m_SalesPerson
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_SalesPerson = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property SalesJanJun() As String
Get
Return m_SalesJanJun
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_SalesJanJun = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property SalesJulDec() As String
Get
Return m_SalesJulDec
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_SalesJulDec = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Sub New(name As String, janToJun As String, julToDec As String)
SalesPerson = name
SalesJanJun = janToJun
SalesJulDec = julToDec
End Sub
End ClassA complete working example to import data to Excel with import data options in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Nested Collection Objects to Excel
Import hierarchical data from nested collections to Excel helps the user to analyze data in its structure. XlsIO provides more flexible options to analyze such data by importing in different layouts and grouping the imported data.
Data import can be done with the layout options:
- Default - Parent records imported in the first row of its collection.
- Merge - Parent records imported in merged rows.
- Repeat - Parent records imported in all the rows.
Imported data can be grouped with the grouping options:
- Expand – Imported data will be grouped and expanded.
- Collapse – Imported data will be grouped and collapsed at first level, by default.
Let’s see these options in detail along with code examples and screenshots.
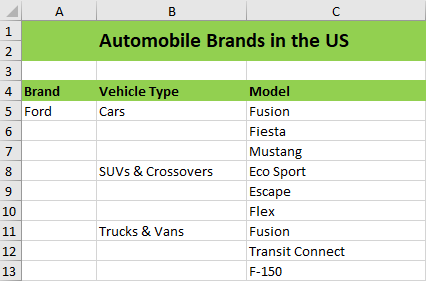
Layout Options
Default layout option
This option adds the property value once per object for the corresponding records in the column while importing.
The following code example illustrates how to import data directly from nested collection objects with default layout option. The input XML file used in the code can be downloaded here.
using System.IO;
using Syncfusion.XlsIO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using System.ComponentModel;
namespace Layout_Options
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ImportData();
}
//Main method to import data from nested collection to Excel worksheet.
private static void ImportData()
{
ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine();
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = excelEngine.Excel.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IList<Brand> vehicles = GetVehicleDetails();
ExcelImportDataOptions importDataOptions = new ExcelImportDataOptions();
//Imports from 4th row.
importDataOptions.FirstRow = 4;
//Imports column headers.
importDataOptions.IncludeHeader = true;
//Set layout options. Available LayoutOptions are Default, Merge and Repeat.
importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.Default;
//Import data from the nested collection.
worksheet.ImportData(vehicles, importDataOptions);
//Apply style to headers
worksheet["A1:C2"].Merge();
worksheet["A1"].Text = "Automobile Brands in the US";
worksheet.UsedRange.AutofitColumns();
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ImportData.xlsx"));
#endregion
}
//Helper method to load data from XML file and add them in collections.
private static IList<Brand> GetVehicleDetails()
{
XmlSerializer deserializer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(BrandObjects));
//Read data from XML file.
TextReader textReader = new StreamReader(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/ExportData.xml"));
BrandObjects brands = (BrandObjects)deserializer.Deserialize(textReader);
//Initialize parent collection to add data from XML file.
List<Brand> list = new List<Brand>();
string brandName = brands.BrandObject[0].BrandName;
string vehicleType = brands.BrandObject[0].VahicleType;
string modelName = brands.BrandObject[0].ModelName;
//Parent class
Brand brand = new Brand(brandName);
brand.VehicleTypes = new List<VehicleType>();
VehicleType vehicle = new VehicleType(vehicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
Model model = new Model(modelName);
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
list.Add(brand);
foreach (BrandObject brandObj in brands.BrandObject)
{
if (brandName == brandObj.BrandName)
{
if (vehicleType == brandObj.VahicleType)
{
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
continue;
}
else
{
vehicle = new VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType;
}
continue;
}
else
{
brand = new Brand(brandObj.BrandName);
vehicle = new VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
brand.VehicleTypes = new List<VehicleType>();
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType;
list.Add(brand);
brandName = brandObj.BrandName;
}
}
textReader.Close();
return list;
}
}
//Parent Class
public class Brand
{
private string m_brandName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Brand")]
public string BrandName
{
get { return m_brandName; }
set { m_brandName = value; }
}
//Vehicle Types Collection
private IList<VehicleType> m_vehicleTypes;
public IList<VehicleType> VehicleTypes
{
get { return m_vehicleTypes; }
set { m_vehicleTypes = value; }
}
public Brand(string brandName)
{
m_brandName = brandName;
}
}
//Child Class
public class VehicleType
{
private string m_vehicleName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Vehicle Type")]
public string VehicleName
{
get { return m_vehicleName; }
set { m_vehicleName = value; }
}
//Models collection
private IList<Model> m_models;
public IList<Model> Models
{
get { return m_models; }
set { m_models = value; }
}
public VehicleType(string vehicle)
{
m_vehicleName = vehicle;
}
}
//Sub-child Class
public class Model
{
private string m_modelName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Model")]
public string ModelName
{
get { return m_modelName; }
set { m_modelName = value; }
}
public Model(string name)
{
m_modelName = name;
}
}
//Helper Classes
[XmlRootAttribute("BrandObjects")]
public class BrandObjects
{
[XmlElement("BrandObject")]
public BrandObject[] BrandObject { get; set; }
}
public class BrandObject
{
public string BrandName { get; set; }
public string VahicleType { get; set; }
public string ModelName { get; set; }
}
}using Syncfusion.XlsIO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.IO;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
namespace ImportFromNestedCollection
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ImportData();
}
//Main method to import data from nested collection to Excel worksheet.
private static void ImportData()
{
ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine();
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2016;
IWorkbook workbook = excelEngine.Excel.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IList<Brand> vehicles = GetVehicleDetails();
ExcelImportDataOptions importDataOptions = new ExcelImportDataOptions();
//Imports from 4th row.
importDataOptions.FirstRow = 4;
//Imports column headers.
importDataOptions.IncludeHeader = true;
//Set layout options.
importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.Default;
//Import data from the nested collection.
worksheet.ImportData(vehicles, importDataOptions);
//Apply style to headers
worksheet["A1:C2"].Merge();
worksheet["A1"].Text = "Automobile Brands in the US";
worksheet.UsedRange.AutofitColumns();
workbook.SaveAs("ImportData.xlsx");
workbook.Close();
excelEngine.Dispose();
}
//Helper method to load data from XML file and add them in collections.
private static IList<Brand> GetVehicleDetails()
{
XmlSerializer deserializer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(BrandObjects));
//Read data from XML file.
TextReader textReader = new StreamReader("../../Data/ExportData.xml");
BrandObjects brands = (BrandObjects)deserializer.Deserialize(textReader);
//Initialize parent collection to add data from XML file.
List<Brand> list = new List<Brand>();
string brandName = brands.BrandObject[0].BrandName;
string vehicleType = brands.BrandObject[0].VahicleType;
string modelName = brands.BrandObject[0].ModelName;
//Parent class
Brand brand = new Brand(brandName);
brand.VehicleTypes = new List<VehicleType>();
VehicleType vehicle = new VehicleType(vehicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
Model model = new Model(modelName);
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
list.Add(brand);
foreach (BrandObject brandObj in brands.BrandObject)
{
if (brandName == brandObj.BrandName)
{
if (vehicleType == brandObj.VahicleType)
{
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
continue;
}
else
{
vehicle = new VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType;
}
continue;
}
else
{
brand = new Brand(brandObj.BrandName);
vehicle = new VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
brand.VehicleTypes = new List<VehicleType>();
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType;
list.Add(brand);
brandName = brandObj.BrandName;
}
}
textReader.Close();
return list;
}
}
//Parent Class
public class Brand
{
private string m_brandName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Brand")]
public string BrandName
{
get { return m_brandName; }
set { m_brandName = value; }
}
//Vehicle Types Collection
private IList<VehicleType> m_vehicleTypes;
public IList<VehicleType> VehicleTypes
{
get { return m_vehicleTypes; }
set { m_vehicleTypes = value; }
}
public Brand(string brandName)
{
m_brandName = brandName;
}
}
//Child Class
public class VehicleType
{
private string m_vehicleName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Vehicle Type")]
public string VehicleName
{
get { return m_vehicleName; }
set { m_vehicleName = value; }
}
//Models collection
private IList<Model> m_models;
public IList<Model> Models
{
get { return m_models; }
set { m_models = value; }
}
public VehicleType(string vehicle)
{
m_vehicleName = vehicle;
}
}
//Sub-child Class
public class Model
{
private string m_modelName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Model")]
public string ModelName
{
get { return m_modelName; }
set { m_modelName = value; }
}
public Model(string name)
{
m_modelName = name;
}
}
//Helper Classes
[XmlRootAttribute("BrandObjects")]
public class BrandObjects
{
[XmlElement("BrandObject")]
public BrandObject[] BrandObject { get; set; }
}
public class BrandObject
{
public string BrandName { get; set; }
public string VahicleType { get; set; }
public string ModelName { get; set; }
}
}Imports Syncfusion.XlsIO
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.ComponentModel
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Xml.Serialization
Namespace ImportFromNestedCollection
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args As String())
ImportData()
End Sub
'Main method to import data from nested collection to Excel worksheet.
Private Shared Sub ImportData()
Dim excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2016
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = excelEngine.Excel.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim vehicles As IList(Of Brand) = GetVehicleDetails()
Dim importDataOptions As ExcelImportDataOptions = New ExcelImportDataOptions()
'Imports from 4th row.
importDataOptions.FirstRow = 4
'Imports column headers.
importDataOptions.IncludeHeader = True
'Set layout options.
importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.Default
'Import data from the nested collection.
worksheet.ImportData(vehicles, importDataOptions)
'Apply style to headers
worksheet("A1:C2").Merge()
worksheet("A1").Text = "Automobile Brands in the US"
worksheet.UsedRange.AutofitColumns()
workbook.SaveAs("ImportData.xlsx")
workbook.Close()
excelEngine.Dispose()
End Sub
'Helper method to load data from XML file and add them in collections.
Private Shared Function GetVehicleDetails() As IList(Of Brand)
Dim deserializer As XmlSerializer = New XmlSerializer(GetType(BrandObjects))
'Read data from XML file.
Dim textReader As TextReader = New StreamReader("../../Data/ExportData.xml")
Dim brands As BrandObjects = CType(deserializer.Deserialize(textReader), BrandObjects)
'Initialize parent collection to add data from XML file.
Dim list As List(Of Brand) = New List(Of Brand)()
Dim brandName As String = brands.BrandObject(0).BrandName
Dim vehicleType As String = brands.BrandObject(0).VahicleType
Dim modelName As String = brands.BrandObject(0).ModelName
'Parent class
Dim brand As Brand = New Brand(brandName)
brand.VehicleTypes = New List(Of VehicleType)()
Dim vehicle As VehicleType = New VehicleType(vehicleType)
vehicle.Models = New List(Of Model)()
Dim model As Model = New Model(modelName)
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle)
list.Add(brand)
For Each brandObj As BrandObject In brands.BrandObject
If brandName = brandObj.BrandName Then
If vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType Then
vehicle.Models.Add(New Model(brandObj.ModelName))
Continue For
Else
vehicle = New VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType)
vehicle.Models = New List(Of Model)()
vehicle.Models.Add(New Model(brandObj.ModelName))
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle)
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType
End If
Continue For
Else
brand = New Brand(brandObj.BrandName)
vehicle = New VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType)
vehicle.Models = New List(Of Model)()
vehicle.Models.Add(New Model(brandObj.ModelName))
brand.VehicleTypes = New List(Of VehicleType)()
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle)
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType
list.Add(brand)
brandName = brandObj.BrandName
End If
Next
textReader.Close()
Return list
End Function
End Class
'Parent Class
Public Class Brand
Private m_brandName As String
<DisplayNameAttribute("Brand")>
Public Property BrandName As String
Get
Return m_brandName
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
m_brandName = value
End Set
End Property
Private m_vehicleTypes As IList(Of VehicleType)
Public Property VehicleTypes As IList(Of VehicleType)
Get
Return m_vehicleTypes
End Get
Set(ByVal value As IList(Of VehicleType))
m_vehicleTypes = value
End Set
End Property
Public Sub New(ByVal brandName As String)
m_brandName = brandName
End Sub
End Class
'Child Class
Public Class VehicleType
Private m_vehicleName As String
<DisplayNameAttribute("Vehicle Type")>
Public Property VehicleName As String
Get
Return m_vehicleName
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
m_vehicleName = value
End Set
End Property
Private m_models As IList(Of Model)
Public Property Models As IList(Of Model)
Get
Return m_models
End Get
Set(ByVal value As IList(Of Model))
m_models = value
End Set
End Property
Public Sub New(ByVal vehicle As String)
m_vehicleName = vehicle
End Sub
End Class
'Sub-child Class
Public Class Model
Private m_modelName As String
<DisplayNameAttribute("Model")>
Public Property ModelName As String
Get
Return m_modelName
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
m_modelName = value
End Set
End Property
Public Sub New(ByVal name As String)
m_modelName = name
End Sub
End Class
<XmlRootAttribute("BrandObjects")>
Public Class BrandObjects
<XmlElement("BrandObject")>
Public Property BrandObject As BrandObject()
End Class
Public Class BrandObject
Public Property BrandName As String
Public Property VahicleType As String
Public Property ModelName As String
End Class
End NamespaceA complete working example to import data to Excel with layout option in C# is present on this GitHub page.
The following screenshot represents the output document with Default layout option.
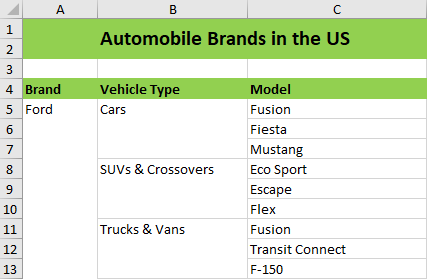
Merge layout option
This option merges the cells in the column for each object while importing.
The following code example helps to import data with merged cells.
importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.Merge;importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.Merge;importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.MergeThe following screenshot represents the output document with Merge layout option.
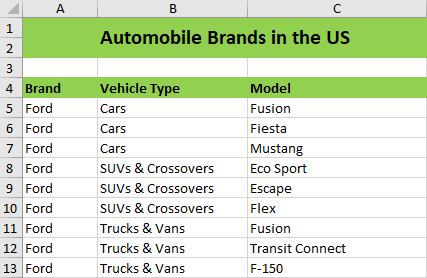
Repeat layout option
This option repeats the parent records imported in all the rows.
The following code example helps to import data with repeated rows.
importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.Repeat;importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.Repeat;importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.RepeatThe following screenshot represents the output document with Repeat layout option.
Grouping Options
Hierarchical data imported into Excel worksheet must be shown its structure to analyze more flexible. In addition, if the data is grouped according to its level, it is easier to analyze. XlsIO supports to import hierarchical data from nested collection and group them while importing.
The following are the options that is supported to group on import.
- Expand – Imported data will be grouped and expanded.
- Collapse – Imported data will be grouped and collapsed at first level, by default.
In addition, CollapseLevel will group and collapse the mentioned level, upto the maximum of 8 levels.
The following code example illustrates how to import data directly from nested collection objects with collapse group option.
using System.IO;
using Syncfusion.XlsIO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using System.ComponentModel;
namespace Grouping_Options
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ImportData();
}
//Main method to import data from nested collection to Excel worksheet.
private static void ImportData()
{
ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine();
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = excelEngine.Excel.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IList<Brand> vehicles = GetVehicleDetails();
ExcelImportDataOptions importDataOptions = new ExcelImportDataOptions();
//Imports from 4th row.
importDataOptions.FirstRow = 4;
//Imports column headers.
importDataOptions.IncludeHeader = true;
//Set layout options.
importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.Default;
//Set grouping option. Available GroupingOptions are Collapse and Expand
importDataOptions.NestedDataGroupOptions = ExcelNestedDataGroupOptions.Collapse;
//Set collapse level.
//GroupingOption must set to ‘Collapse’ before applying ‘CollapseLevel’.
importDataOptions.CollapseLevel = 2;
//Import data from the nested collection.
worksheet.ImportData(vehicles, importDataOptions);
//Apply style to headers
worksheet["A1:C2"].Merge();
worksheet["A1"].Text = "Automobile Brands in the US";
worksheet.UsedRange.AutofitColumns();
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ImportData.xlsx"));
#endregion
}
//Helper method to load data from XML file and add them in collections.
private static IList<Brand> GetVehicleDetails()
{
XmlSerializer deserializer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(BrandObjects));
//Read data from XML file.
TextReader textReader = new StreamReader(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/ExportData.xml"));
BrandObjects brands = (BrandObjects)deserializer.Deserialize(textReader);
//Initialize parent collection to add data from XML file.
List<Brand> list = new List<Brand>();
string brandName = brands.BrandObject[0].BrandName;
string vehicleType = brands.BrandObject[0].VahicleType;
string modelName = brands.BrandObject[0].ModelName;
//Parent class
Brand brand = new Brand(brandName);
brand.VehicleTypes = new List<VehicleType>();
VehicleType vehicle = new VehicleType(vehicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
Model model = new Model(modelName);
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
list.Add(brand);
foreach (BrandObject brandObj in brands.BrandObject)
{
if (brandName == brandObj.BrandName)
{
if (vehicleType == brandObj.VahicleType)
{
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
continue;
}
else
{
vehicle = new VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType;
}
continue;
}
else
{
brand = new Brand(brandObj.BrandName);
vehicle = new VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
brand.VehicleTypes = new List<VehicleType>();
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType;
list.Add(brand);
brandName = brandObj.BrandName;
}
}
textReader.Close();
return list;
}
}
//Parent Class
public class Brand
{
private string m_brandName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Brand")]
public string BrandName
{
get { return m_brandName; }
set { m_brandName = value; }
}
//Vehicle Types Collection
private IList<VehicleType> m_vehicleTypes;
public IList<VehicleType> VehicleTypes
{
get { return m_vehicleTypes; }
set { m_vehicleTypes = value; }
}
public Brand(string brandName)
{
m_brandName = brandName;
}
}
//Child Class
public class VehicleType
{
private string m_vehicleName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Vehicle Type")]
public string VehicleName
{
get { return m_vehicleName; }
set { m_vehicleName = value; }
}
//Models collection
private IList<Model> m_models;
public IList<Model> Models
{
get { return m_models; }
set { m_models = value; }
}
public VehicleType(string vehicle)
{
m_vehicleName = vehicle;
}
}
//Sub-child Class
public class Model
{
private string m_modelName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Model")]
public string ModelName
{
get { return m_modelName; }
set { m_modelName = value; }
}
public Model(string name)
{
m_modelName = name;
}
}
//Helper Classes
[XmlRootAttribute("BrandObjects")]
public class BrandObjects
{
[XmlElement("BrandObject")]
public BrandObject[] BrandObject { get; set; }
}
public class BrandObject
{
public string BrandName { get; set; }
public string VahicleType { get; set; }
public string ModelName { get; set; }
}
}using Syncfusion.XlsIO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.IO;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
namespace ImportFromNestedCollection
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ImportData();
}
//Main method to import data from nested collection to Excel worksheet.
private static void ImportData()
{
ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine();
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2016;
IWorkbook workbook = excelEngine.Excel.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IList<Brand> vehicles = GetVehicleDetails();
ExcelImportDataOptions importDataOptions = new ExcelImportDataOptions();
//Imports from 4th row.
importDataOptions.FirstRow = 4;
//Imports column headers.
importDataOptions.IncludeHeader = true;
//Set layout options.
importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.Default;
//Set grouping option.
importDataOptions.NestedDataGroupOptions = ExcelNestedDataGroupOptions.Collapse;
//Set collapse level.
//GroupingOption must set to ‘Collapse’ before applying ‘CollapseLevel’.
importDataOptions.CollapseLevel = 2;
//Import data from the nested collection.
worksheet.ImportData(vehicles, importDataOptions);
//Apply style to headers
worksheet["A1:C2"].Merge();
worksheet["A1"].Text = "Automobile Brands in the US";
worksheet.UsedRange.AutofitColumns();
workbook.SaveAs("ImportData.xlsx");
workbook.Close();
excelEngine.Dispose();
}
//Helper method to load data from XML file and add them in collections.
private static IList<Brand> GetVehicleDetails()
{
XmlSerializer deserializer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(BrandObjects));
//Read data from XML file.
TextReader textReader = new StreamReader("../../Data/ExportData.xml");
BrandObjects brands = (BrandObjects)deserializer.Deserialize(textReader);
//Initialize parent collection to add data from XML file.
List<Brand> list = new List<Brand>();
string brandName = brands.BrandObject[0].BrandName;
string vehicleType = brands.BrandObject[0].VahicleType;
string modelName = brands.BrandObject[0].ModelName;
//Parent class
Brand brand = new Brand(brandName);
brand.VehicleTypes = new List<VehicleType>();
VehicleType vehicle = new VehicleType(vehicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
Model model = new Model(modelName);
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
list.Add(brand);
foreach (BrandObject brandObj in brands.BrandObject)
{
if (brandName == brandObj.BrandName)
{
if (vehicleType == brandObj.VahicleType)
{
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
continue;
}
else
{
vehicle = new VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType;
}
continue;
}
else
{
brand = new Brand(brandObj.BrandName);
vehicle = new VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType);
vehicle.Models = new List<Model>();
vehicle.Models.Add(new Model(brandObj.ModelName));
brand.VehicleTypes = new List<VehicleType>();
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle);
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType;
list.Add(brand);
brandName = brandObj.BrandName;
}
}
textReader.Close();
return list;
}
}
//Parent Class
public class Brand
{
private string m_brandName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Brand")]
public string BrandName
{
get { return m_brandName; }
set { m_brandName = value; }
}
//Vehicle Types Collection
private IList<VehicleType> m_vehicleTypes;
public IList<VehicleType> VehicleTypes
{
get { return m_vehicleTypes; }
set { m_vehicleTypes = value; }
}
public Brand(string brandName)
{
m_brandName = brandName;
}
}
//Child Class
public class VehicleType
{
private string m_vehicleName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Vehicle Type")]
public string VehicleName
{
get { return m_vehicleName; }
set { m_vehicleName = value; }
}
//Models collection
private IList<Model> m_models;
public IList<Model> Models
{
get { return m_models; }
set { m_models = value; }
}
public VehicleType(string vehicle)
{
m_vehicleName = vehicle;
}
}
//Sub-child Class
public class Model
{
private string m_modelName;
[DisplayNameAttribute("Model")]
public string ModelName
{
get { return m_modelName; }
set { m_modelName = value; }
}
public Model(string name)
{
m_modelName = name;
}
}
//Helper Classes
[XmlRootAttribute("BrandObjects")]
public class BrandObjects
{
[XmlElement("BrandObject")]
public BrandObject[] BrandObject { get; set; }
}
public class BrandObject
{
public string BrandName { get; set; }
public string VahicleType { get; set; }
public string ModelName { get; set; }
}
}Imports Syncfusion.XlsIO
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.ComponentModel
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Xml.Serialization
Namespace ImportFromNestedCollection
Class Program
Private Shared Sub Main(ByVal args As String())
ImportData()
End Sub
'Main method to import data from nested collection to Excel worksheet.
Private Shared Sub ImportData()
Dim excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2016
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = excelEngine.Excel.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim vehicles As IList(Of Brand) = GetVehicleDetails()
Dim importDataOptions As ExcelImportDataOptions = New ExcelImportDataOptions()
'Imports from 4th row.
importDataOptions.FirstRow = 4
'Imports column headers.
importDataOptions.IncludeHeader = True
'Set layout options.
importDataOptions.NestedDataLayoutOptions = ExcelNestedDataLayoutOptions.Default
'Set grouping option.
importDataOptions.NestedDataGroupOptions = ExcelNestedDataGroupOptions.Collapse
'Set collapse level.
'GroupingOption must set to ‘Collapse’ before applying ‘CollapseLevel’.
importDataOptions.CollapseLevel = 2;
'Import data from the nested collection.
worksheet.ImportData(vehicles, importDataOptions)
'Apply style to headers
worksheet("A1:C2").Merge()
worksheet("A1").Text = "Automobile Brands in the US"
worksheet.UsedRange.AutofitColumns()
workbook.SaveAs("ImportData.xlsx")
workbook.Close()
excelEngine.Dispose()
End Sub
'Helper method to load data from XML file and add them in collections.
Private Shared Function GetVehicleDetails() As IList(Of Brand)
Dim deserializer As XmlSerializer = New XmlSerializer(GetType(BrandObjects))
'Read data from XML file.
Dim textReader As TextReader = New StreamReader("../../Data/ExportData.xml")
Dim brands As BrandObjects = CType(deserializer.Deserialize(textReader), BrandObjects)
'Initialize parent collection to add data from XML file.
Dim list As List(Of Brand) = New List(Of Brand)()
Dim brandName As String = brands.BrandObject(0).BrandName
Dim vehicleType As String = brands.BrandObject(0).VahicleType
Dim modelName As String = brands.BrandObject(0).ModelName
'Parent class
Dim brand As Brand = New Brand(brandName)
brand.VehicleTypes = New List(Of VehicleType)()
Dim vehicle As VehicleType = New VehicleType(vehicleType)
vehicle.Models = New List(Of Model)()
Dim model As Model = New Model(modelName)
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle)
list.Add(brand)
For Each brandObj As BrandObject In brands.BrandObject
If brandName = brandObj.BrandName Then
If vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType Then
vehicle.Models.Add(New Model(brandObj.ModelName))
Continue For
Else
vehicle = New VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType)
vehicle.Models = New List(Of Model)()
vehicle.Models.Add(New Model(brandObj.ModelName))
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle)
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType
End If
Continue For
Else
brand = New Brand(brandObj.BrandName)
vehicle = New VehicleType(brandObj.VahicleType)
vehicle.Models = New List(Of Model)()
vehicle.Models.Add(New Model(brandObj.ModelName))
brand.VehicleTypes = New List(Of VehicleType)()
brand.VehicleTypes.Add(vehicle)
vehicleType = brandObj.VahicleType
list.Add(brand)
brandName = brandObj.BrandName
End If
Next
textReader.Close()
Return list
End Function
End Class
'Parent Class
Public Class Brand
Private m_brandName As String
<DisplayNameAttribute("Brand")>
Public Property BrandName As String
Get
Return m_brandName
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
m_brandName = value
End Set
End Property
Private m_vehicleTypes As IList(Of VehicleType)
Public Property VehicleTypes As IList(Of VehicleType)
Get
Return m_vehicleTypes
End Get
Set(ByVal value As IList(Of VehicleType))
m_vehicleTypes = value
End Set
End Property
Public Sub New(ByVal brandName As String)
m_brandName = brandName
End Sub
End Class
'Child Class
Public Class VehicleType
Private m_vehicleName As String
<DisplayNameAttribute("Vehicle Type")>
Public Property VehicleName As String
Get
Return m_vehicleName
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
m_vehicleName = value
End Set
End Property
Private m_models As IList(Of Model)
Public Property Models As IList(Of Model)
Get
Return m_models
End Get
Set(ByVal value As IList(Of Model))
m_models = value
End Set
End Property
Public Sub New(ByVal vehicle As String)
m_vehicleName = vehicle
End Sub
End Class
'Sub-child Class
Public Class Model
Private m_modelName As String
<DisplayNameAttribute("Model")>
Public Property ModelName As String
Get
Return m_modelName
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
m_modelName = value
End Set
End Property
Public Sub New(ByVal name As String)
m_modelName = name
End Sub
End Class
<XmlRootAttribute("BrandObjects")>
Public Class BrandObjects
<XmlElement("BrandObject")>
Public Property BrandObject As BrandObject()
End Class
Public Class BrandObject
Public Property BrandName As String
Public Property VahicleType As String
Public Property ModelName As String
End Class
End NamespaceA complete working example to import data to Excel with grouping option in C# is present on this GitHub page.
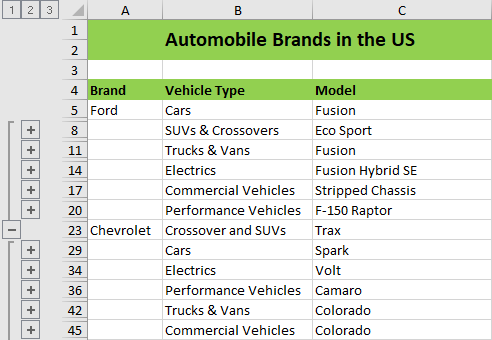
The following screenshot represents the output document of Grouped data imported from nested collection and collapsed at level 2.
Collection Objects with hyperlink
XlsIO allows you to import images, data with URLs, and data with mail IDs as hyperlinks from various data sources binded in Collection Objects as shown below
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import the data to worksheet
IList<Company> reports = GetCompanyDetails();
worksheet.ImportData(reports, 2, 1, false);
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ImportData.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import the data to worksheet
IList<Company> reports = GetCompanyDetails();
worksheet.ImportData(reports, 2, 1, false);
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromBO.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Import the data to worksheet
Dim reports As IList(Of Company) = GetCompanyDetails()
worksheet.ImportData(reports, 2, 1, False)
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromBO.xlsx")
End UsingThe following code snippet provides supporting methods and classes for the previous code.
//Gets a list of company details
private List<Company> GetCompanyDetails()
{
List<Company> companyList = new List<Company>();
Company company = new Company();
company.Name = "Syncfusion";
Hyperlink link = new Hyperlink("https://www.syncfusion.com", "", "", "Syncfusion", ExcelHyperLinkType.Url, null);
company.Link = link;
companyList.Add(company);
company = new Company();
company.Name = "Microsoft";
link = new Hyperlink("https://www.microsoft.com", "", "", "Microsoft", ExcelHyperLinkType.Url, null);
company.Link = link;
companyList.Add(company);
company = new Company();
company.Name = "Google";
link = new Hyperlink("https://www.google.com", "", "", "Google", ExcelHyperLinkType.Url, null);
company.Link = link;
companyList.Add(company);
return companyList;
}
public class Hyperlink : IHyperLink
{
public IApplication Application { get; }
public object Parent { get;}
public string Address { get; set; }
public string Name { get; }
public IRange Range { get; }
public string ScreenTip { get; set; }
public string SubAddress { get; set; }
public string TextToDisplay { get; set; }
public ExcelHyperLinkType Type { get; set; }
public IShape Shape { get; }
public ExcelHyperlinkAttachedType AttachedType { get; }
public byte[] Image { get; set; }
public Hyperlink(string address, string subAddress, string screenTip, string textToDisplay, ExcelHyperLinkType type, byte[] image)
{
Address = address;
ScreenTip = screenTip;
SubAddress = subAddress;
TextToDisplay = textToDisplay;
Type = type;
Image = image;
}
}
public class Company
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public Hyperlink Link { get; set; }
}//Gets a list of company details
private List<Company> GetCompanyDetails()
{
List<Company> companyList = new List<Company>();
Company company = new Company();
company.Name = "Syncfusion";
Hyperlink link = new Hyperlink("https://www.syncfusion.com", "", "", "Syncfusion", ExcelHyperLinkType.Url, null);
company.Link = link;
companyList.Add(company);
company = new Company();
company.Name = "Microsoft";
link = new Hyperlink("https://www.microsoft.com", "", "", "Microsoft", ExcelHyperLinkType.Url, null);
company.Link = link;
companyList.Add(company);
company = new Company();
company.Name = "Google";
link = new Hyperlink("https://www.google.com", "", "", "Google", ExcelHyperLinkType.Url, null);
company.Link = link;
companyList.Add(company);
return companyList;
}
public class Hyperlink : IHyperLink
{
public IApplication Application { get; }
public object Parent { get;}
public string Address { get; set; }
public string Name { get; }
public IRange Range { get; }
public string ScreenTip { get; set; }
public string SubAddress { get; set; }
public string TextToDisplay { get; set; }
public ExcelHyperLinkType Type { get; set; }
public IShape Shape { get; }
public ExcelHyperlinkAttachedType AttachedType { get; }
public byte[] Image { get; set; }
public Hyperlink(string address, string subAddress, string screenTip, string textToDisplay, ExcelHyperLinkType type, byte[] image)
{
Address = address;
ScreenTip = screenTip;
SubAddress = subAddress;
TextToDisplay = textToDisplay;
Type = type;
Image = image;
}
}
public class Company
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public Hyperlink Link { get; set; }
}'Gets a list of company details
Private Function GetCompanyDetails() As List(Of Company)
Dim companyList As List(Of Company) = New List(Of Company)()
Dim company As Company = New Company()
company.Name = "Syncfusion"
Dim link As Hyperlink = New Hyperlink("https://www.syncfusion.com", "", "", "Syncfusion", ExcelHyperLinkType.Url, Nothing)
company.Link = link
companyList.Add(company)
company = New Company()
company.Name = "Microsoft"
link = New Hyperlink("https://www.microsoft.com", "", "", "Microsoft", ExcelHyperLinkType.Url, Nothing)
company.Link = link
companyList.Add(company)
company = New Company()
company.Name = "Google"
link = New Hyperlink("https://www.google.com", "", "", "Google", ExcelHyperLinkType.Url, Nothing)
company.Link = link
companyList.Add(company)
Return companyList
End Function
Public Class Hyperlink
Inherits IHyperLink
Public ReadOnly Property Application As IApplication
Public ReadOnly Property Parent As Object
Public Property Address As String
Public ReadOnly Property Name As String
Public ReadOnly Property Range As IRange
Public Property ScreenTip As String
Public Property SubAddress As String
Public Property TextToDisplay As String
Public Property Type As ExcelHyperLinkType
Public ReadOnly Property Shape As IShape
Public ReadOnly Property AttachedType As ExcelHyperlinkAttachedType
Public Property Image As Byte()
Public Sub New(ByVal address As String, ByVal subAddress As String, ByVal screenTip As String, ByVal textToDisplay As String, ByVal type As ExcelHyperLinkType, ByVal image As Byte())
Address = address
ScreenTip = screenTip
SubAddress = subAddress
TextToDisplay = textToDisplay
Type = type
Image = image
End Sub
End Class
Public Class Company
Public Property Name As String
Public Property Link As Hyperlink
End ClassA complete working example to import data from collection objects with hyperlink to Excel in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Array to Excel
The following code example shows how to import array of data into an Excel using ImportArray method.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Initialize the Object Array
object[] array = new object[4] { "Total Income", "Actual Expense", "Expected Expenses", "Profit" };
//Import the Object Array to Sheet
worksheet.ImportArray(array, 1, 1, false);
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ArrayToWorksheet.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Initialize the Object Array
object[] array = new object[4] { "Total Income", "Actual Expense", "Expected Expenses", "Profit" };
//Import the Object Array to Sheet
worksheet.ImportArray(array, 1, 1, false);
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromDT.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Initialize the Array Object
Dim array() As Object = New Object() {"Total Income", "Actual Expense", "Expected Expenses", "Profit"}
'Import the Array Object to Sheet
worksheet.ImportArray(array, 1, 1, False)
workbook.SaveAs("ImportFromDT.xlsx")
End UsingA complete working example to import data from array to an Excel in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Microsoft Grid Controls to Excel
XlsIO provides support to import data from various Microsoft grid controls with its cell formatting. The supported grid controls are:
- DataGrid
- GridView
- DataGridView
DataGrid
Imports data from Microsoft DataGrid control with its header and cell formatting to Excel worksheet. The following code example illustrates how to import data from Microsoft DataGrid control to Excel.
NOTE
GetDataTable() method returns DataTable of applicable data to import.
//XlsIO supports importing of data from data grid to worksheet in Windows Forms and WPF platforms alone.//Initialize DataGrid control
DataGrid dataGrid = new DataGrid();
dataGrid.DataSource = GetDataTable();
ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine();
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create();
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import data from DataGrid control
worksheet.ImportDataGrid(dataGrid, 1, 1, true, true);
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
workbook.Close();
excelEngine.Dispose();'Initialize DataGrid control
Dim dataGrid As DataGrid = New DataGrid()
dataGrid.DataSource = GetDataTable()
Dim excelEngine As New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create()
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Import data from DataGrid control
worksheet.ImportDataGrid(dataGrid, 1, 1, True, True)
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
workbook.Close()
excelEngine.Dispose()GridView
Imports data from Microsoft GridView control with its header and cell formatting to Excel worksheet. The following code example illustrates how to import data from Microsoft GridView control to Excel.
//XlsIO supports importing of data from data view to worksheet in Windows Forms and WPF platforms alone.//Initialize GridView control
GridView gridView = new GridView();
gridView.DataSource = GetDataTable();
gridView.DataBind();
ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine();
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create();
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import data from GridView control
worksheet.ImportGridView(gridView, 1, 1, true, true);
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
workbook.Close();
excelEngine.Dispose();'Initialize GridView control
Dim gridView As GridView = New GridView ()
gridView.DataSource = GetDataTable()
gridView.DataBind()
Dim excelEngine As New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create()
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Import data from GridView control
worksheet.ImportGridView(gridView, 1, 1, True, True)
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
workbook.Close()
excelEngine.Dispose()DataGridView
Imports data from Microsoft DataGridView control with its header and cell formatting to Excel worksheet. In addition, this API imports sorted data applied in the control. The following code example illustrates how to import data from Microsoft DataGridView control to Excel.
//XlsIO supports importing of data from data grid view to worksheet in Windows Forms and WPF platforms alone.//Initialize DataGridView control
DataGridView dataGridView = new DataGridView();
dataGridView.DataSource = GetDataTable();
//Apply sorting.
dataGridView.Sort(dataGridView.Columns[1], System.ComponentModel.ListSortDirection.Ascending);
ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine();
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create();
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import data from DataGridView control
worksheet.ImportDataGridView(dataGridView, 1, 1, true, true);
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
workbook.Close();
excelEngine.Dispose();'Initialize DataGridView control
Dim dataGridView As DataGridView = New DataGridView()
dataGridView.DataSource = GetDataTable()
'Apply sorting.
dataGridView.Sort(dataGridView.Columns(1), System.ComponentModel.ListSortDirection.Ascending)
Dim excelEngine As New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create()
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Import data from DataGridView control
worksheet.ImportDataGridView(dataGridView, 1, 1, True, True)
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
workbook.Close()
excelEngine.Dispose()HTML Table to Excel
XlsIO supports importing HTML tables into Excel worksheets. The ImportHtmlTable method loads an HTML file and imports all the tables in the file to the worksheet. This import operation includes the table formatting that is defined within the HTML file.
To quickly export an HTML table to Excel with the .NET Excel (XlsIO) Library, please check out this video:
The following code example shows how to import HTML table into an Excel.
using Syncfusion.XlsIO;
using System.IO;
namespace ImportHtml
{
class ImportHtmlTable
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Imports HTML table into the worksheet from first row and first column
worksheet.ImportHtmlTable(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.html"), 1, 1);
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/HTMLTabletoWorksheet.xlsx"));
#endregion
}
}
}
}using Syncfusion.XlsIO;
namespace ImportHtml
{
class ImportHtmlTable
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Imports HTML table into the worksheet from first row and first column
worksheet.ImportHtmlTable("Import-HTML-Table.html", 1, 1);
workbook.SaveAs("Import-HTML-Table.xlsx");
}
}
}
}Imports Syncfusion.XlsIO
Module ImportHtmlTable
Sub Main()
Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Imports HTML table into the worksheet from first row and first column
worksheet.ImportHtmlTable("Import-HTML-Table.html", 1, 1)
workbook.SaveAs("Import-HTML-Table.xlsx")
End Using
End Sub
End ModuleA complete working example to import data from HTML table to Excel in C# is present on this GitHub page.
The following screenshot represents the image of the input HTML file with a table.
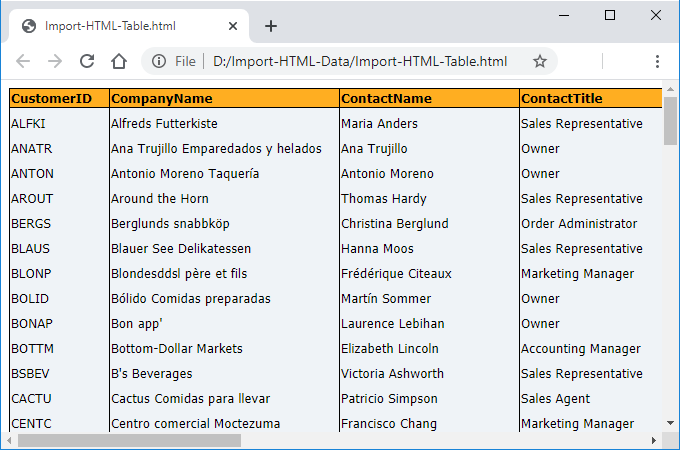
The following screenshot represents the image of the Excel output with data imported from HTML table.
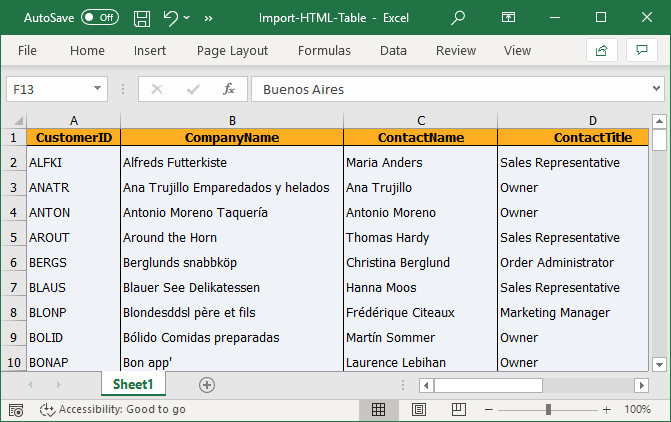
NOTE
Syncfusion® XlsIO supports importing HTML tables with the inline styles alone. HTML documents with embedded styles or style sheets are not supported.
NOTE
Syncfusion® XlsIO depends on the XMLDocument object to load HTML string in which the “<” and “&” symbols are invalid. These symbols needs to be changed as “<” and “&” respectively, to overcome the xml exception.
NOTE
Data formatting can be applied to the Excel cells only after importing the HTML table to Excel.
HTML Table with Formula to Excel
Syncfusion® XlsIO also supports importing HTML table with formula to Excel. The following code snippet explains this.
worksheet.ImportHtmlTable("Sample.html", 1, 1, HtmlImportOptions.DetectFormulas);worksheet.ImportHtmlTable("Sample.html", 1, 1, HtmlImportOptions.DetectFormulas);worksheet.ImportHtmlTable("Sample.html", 1, 1, HtmlImportOptions.DetectFormulas)XML Data to Excel
XlsIO supports importing XML data into Excel worksheets. The ImportXml method is used to load an XML file and import the data into the worksheet.
The following code example shows how to import XML data into an Excel.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import Xml data into the worksheet
FileStream inputStream = new FileStream("../../../Data/XmlFile.xml", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
worksheet.ImportXml(inputStream, 1, 6);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
//Dispose stream
inputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Import Xml data into the worksheet
worksheet.ImportXml("../../Data/XmlFile.xml", 1, 6);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Import XML data into the worksheet
worksheet.ImportXml("../../Data/XmlFile.xml", 1, 6)
'Save the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End UsingAdding XML Maps to Excel
XlsIO also supports adding XML maps to Excel workbooks, enabling you to map XML elements to cells in a worksheet.
The following code example shows how to add XML maps to an Excel workbook.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create();
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Adding Xml maps to the workbook
FileStream inputStream = new FileStream("../../../Data/XmlFile.xml", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
workbook.XmlMaps.Add(inputStream);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
//Dispose stream
inputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create();
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Adding Xml maps to the workbook
workbook.XmlMaps.Add("../../Data/XmlFile.xml");
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create()
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Adding XML maps to the workbook
workbook.XmlMaps.Add("../../Data/XmlFile.xml")
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End Using