How can I help you?
What-If Analysis in Excel
29 Oct 202524 minutes to read
What-If Analysis is the process of changing the values in cells to see how those changes will affect the outcome of formulas on the worksheet. XlsIO supports the What-If Analysis of Scenarios type.
Scenario Manager
Scenario Manager in Excel allows you to create and manage scenarios for different sets of input values to see how they impact the results of formulas in a worksheet.
Create Scenario
The following code snippet explains how to create scenarios for different values in an Excel worksheet.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/WhatIfAnalysisTemplate.xlsx"), ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Access the collection of scenarios in the worksheet
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
//Initialize list objects with different values for scenarios
List<object> currentChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.23, 0.8, 1.1, 0.5, 0.35, 0.2 };
List<object> increasedChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.45, 0.56, 0.9, 0.5, 0.58, 0.43 };
List<object> decreasedChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.3, 0.2, 0.5, 0.3, 0.5, 0.23 };
List<object> currentQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1500, 3000, 5000, 4000, 500, 4000 };
List<object> increasedQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1000, 5000, 4500, 3900, 10000, 8900 };
List<object> decreasedQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1000, 2000, 3000, 3000, 300, 4000 };
//Add scenarios in the worksheet with different values for the same cells
scenarios.Add("Current % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], currentChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Increased % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], increasedChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Decreased % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], decreasedChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Current Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], currentQuantity_Values);
scenarios.Add("Increased Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], increasedQuantity_Values);
scenarios.Add("Decreased Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], decreasedQuantity_Values);
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/CreateScenarios.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
//Initialize list objects with different values for scenarios
List<object> currentChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.23, 0.8, 1.1, 0.5, 0.35, 0.2};
List<object> increasedChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.45, 0.56, 0.9, 0.5, 0.58, 0.43};
List<object> decreasedChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.3, 0.2, 0.5, 0.3, 0.5, 0.23};
List<object> currentQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1500, 3000, 5000, 4000, 500, 4000 };
List<object> increasedQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1000, 5000, 4500, 3900, 10000, 8900 };
List<object> decreasedQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1000, 2000, 3000, 3000, 300, 4000 };
//Add scenarios in the worksheet with different values for the same cells
scenarios.Add("Current % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], currentChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Increased % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], increasedChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Decreased % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], decreasedChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Current Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], currentQuantity_Values);
scenarios.Add("Increased Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], increasedQuantity_Values);
scenarios.Add("Decreased Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], decreasedQuantity_Values);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim scenarios As IScenarios = worksheet.Scenarios
Dim currentChangePercentage_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {0.23, 0.8, 1.1, 0.5, 0.35, 0.2}
Dim increasedChangePercentage_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {0.45, 0.56, 0.9, 0.5, 0.58, 0.43}
Dim decreasedChangePercentage_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {0.3, 0.2, 0.5, 0.3, 0.5, 0.23}
Dim currentQuantity_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {1500, 3000, 5000, 4000, 500, 4000}
Dim increasedQuantity_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {1000, 5000, 4500, 3900, 10000, 8900}
Dim decreasedQuantity_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {1000, 2000, 3000, 3000, 300, 4000}
'Add scenarios in the worksheet with different values for the same cells
scenarios.Add("Current % of Change", worksheet.Range("F5:F10"), currentChangePercentage_Values)
scenarios.Add("Increased % of Change", worksheet.Range("F5:F10"), increasedChangePercentage_Values)
scenarios.Add("Decreased % of Change", worksheet.Range("F5:F10"), decreasedChangePercentage_Values)
scenarios.Add("Current Quantity", worksheet.Range("D5:D10"), currentQuantity_Values)
scenarios.Add("Increased Quantity", worksheet.Range("D5:D10"), increasedQuantity_Values)
scenarios.Add("Decreased Quantity", worksheet.Range("D5:D10"), decreasedQuantity_Values)
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End UsingA complete working example to create scenarios in C# is present on this GitHub page.
By executing the program, you will get the Excel file as below.
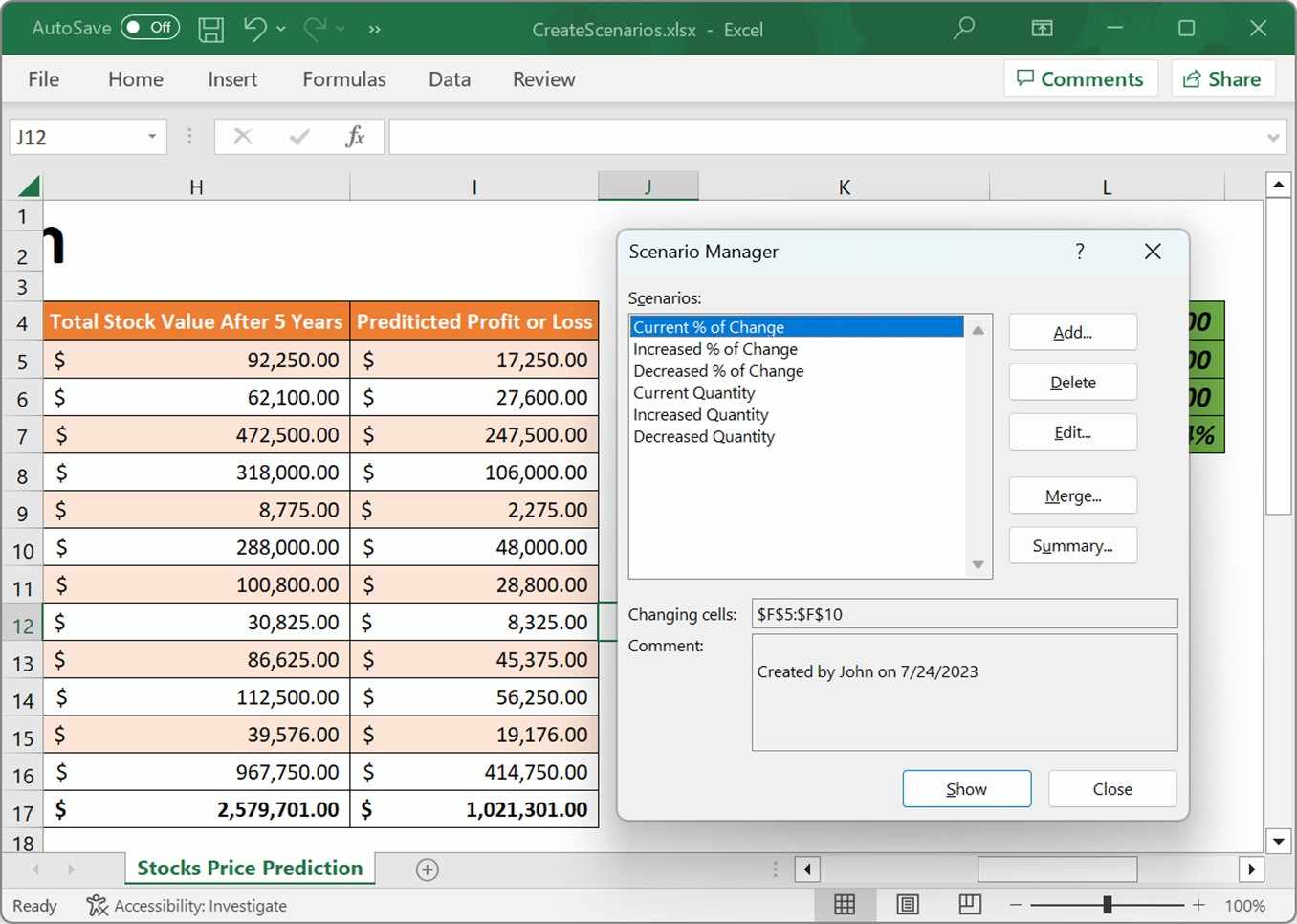
Edit Scenario
An existing scenario can be edited or modified through ModifyScenario method of IScenario.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario1 = scenarios[0];
IScenario scenario2 = scenarios[1];
//Modify the scenario
scenario1.ModifyScenario(scenario2.ChangingCells, scenario2.Values);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario1 = scenarios[0];
IScenario scenario2 = scenarios[1];
//Modify the scenario
scenario1.ModifyScenario(scenario2.ChangingCells, scenario2.Values);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim scenarios As IScenarios = worksheet.Scenarios
Dim scenario1 As IScenario = scenarios(0)
Dim scenario2 As IScenario = scenarios(1)
'Modify the scenario
scenario1.ModifyScenario(scenario2.ChangingCells, scenario2.Values)
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End UsingDelete Scenario
A scenario can be deleted from the Excel worksheet through Delete method of IScenario.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario1 = scenarios[0];
//Delete the scenario
scenario1.Delete();
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario1 = scenarios[0];
IScenario scenario2 = scenarios[1];
//Delete the scenario
scenario1.Delete();
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim scenarios As IScenarios = worksheet.Scenarios
Dim scenario1 As IScenario = scenarios(0)
'Delete the scenario
scenario1.Delete()
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End UsingMerge Scenario
Scenarios in one Excel worksheet can be merged in to another, using Merge method of IScenarios.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IWorksheet worksheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1];
//Merge the second worksheet scenario into first worksheet.
worksheet1.Scenarios.Merge(worksheet2);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IWorksheet worksheet2 = workbook.Worksheets[1];
//Merge the second worksheet scenario into first worksheet.
worksheet1.Scenarios.Merge(worksheet2);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet1 As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim worksheet2 As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(1)
'Merge the second worksheet scenario into first worksheet.
worksheet1.Scenarios.Merge(worksheet2)
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End UsingCreate Summary
CreateSummary method of IScenarios creates a new worksheet that contains a summary report for the scenarios on the specified worksheet.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
//Initialize list objects with different values for scenarios
List<object> currentChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.23, 0.8, 1.1, 0.5, 0.35, 0.2};
List<object> increasedChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.45, 0.56, 0.9, 0.5, 0.58, 0.43};
List<object> decreasedChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.3, 0.2, 0.5, 0.3, 0.5, 0.23};
List<object> currentQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1500, 3000, 5000, 4000, 500, 4000 };
List<object> increasedQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1000, 5000, 4500, 3900, 10000, 8900 };
List<object> decreasedQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1000, 2000, 3000, 3000, 300, 4000 };
//Add scenarios in the worksheet with different values for the same cells
scenarios.Add("Current % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], currentChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Increased % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], increasedChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Decreased % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], decreasedChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Current Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], currentQuantity_Values);
scenarios.Add("Increased Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], increasedQuantity_Values);
scenarios.Add("Decreased Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], decreasedQuantity_Values);
//Create Summary
worksheet.Scenarios.CreateSummary(worksheet.Range["L7"]);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
//Initialize list objects with different values for scenarios
List<object> currentChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.23, 0.8, 1.1, 0.5, 0.35, 0.2};
List<object> increasedChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.45, 0.56, 0.9, 0.5, 0.58, 0.43};
List<object> decreasedChangePercentage_Values = new List<object> { 0.3, 0.2, 0.5, 0.3, 0.5, 0.23};
List<object> currentQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1500, 3000, 5000, 4000, 500, 4000 };
List<object> increasedQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1000, 5000, 4500, 3900, 10000, 8900 };
List<object> decreasedQuantity_Values = new List<object> { 1000, 2000, 3000, 3000, 300, 4000 };
//Add scenarios in the worksheet with different values for the same cells
scenarios.Add("Current % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], currentChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Increased % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], increasedChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Decreased % of Change", worksheet.Range["F5:F10"], decreasedChangePercentage_Values);
scenarios.Add("Current Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], currentQuantity_Values);
scenarios.Add("Increased Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], increasedQuantity_Values);
scenarios.Add("Decreased Quantity", worksheet.Range["D5:D10"], decreasedQuantity_Values);
//Create Summary
worksheet.Scenarios.CreateSummary(worksheet.Range["L7"]);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim scenarios As IScenarios = worksheet.Scenarios
Dim currentChangePercentage_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {0.23, 0.8, 1.1, 0.5, 0.35, 0.2}
Dim increasedChangePercentage_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {0.45, 0.56, 0.9, 0.5, 0.58, 0.43}
Dim decreasedChangePercentage_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {0.3, 0.2, 0.5, 0.3, 0.5, 0.23}
Dim currentQuantity_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {1500, 3000, 5000, 4000, 500, 4000}
Dim increasedQuantity_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {1000, 5000, 4500, 3900, 10000, 8900}
Dim decreasedQuantity_Values As List(Of Object) = New List(Of Object)() {1000, 2000, 3000, 3000, 300, 4000}
'Add scenarios in the worksheet with different values for the same cells
scenarios.Add("Current % of Change", worksheet.Range("F5:F10"), currentChangePercentage_Values)
scenarios.Add("Increased % of Change", worksheet.Range("F5:F10"), increasedChangePercentage_Values)
scenarios.Add("Decreased % of Change", worksheet.Range("F5:F10"), decreasedChangePercentage_Values)
scenarios.Add("Current Quantity", worksheet.Range("D5:D10"), currentQuantity_Values)
scenarios.Add("Increased Quantity", worksheet.Range("D5:D10"), increasedQuantity_Values)
scenarios.Add("Decreased Quantity", worksheet.Range("D5:D10"), decreasedQuantity_Values)
'Create Summary
worksheet.Scenarios.CreateSummary(worksheet.Range("L7"))
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End Using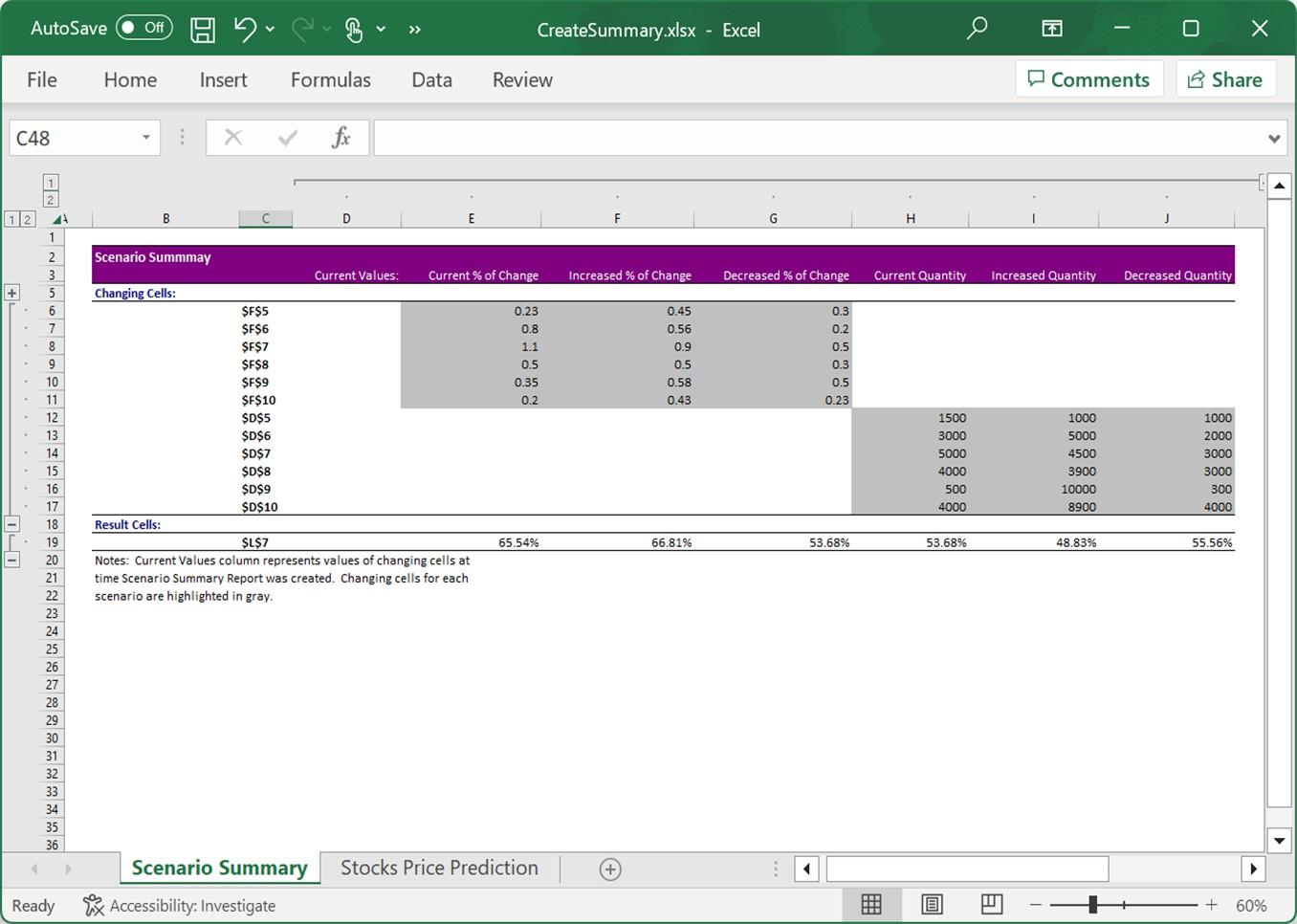
Apply Scenario
Update the scenario values in the worksheet and display it using the Show method.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/WhatIfAnalysisTemplate.xlsx"), ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Access the collection of scenarios in the worksheet
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
for (int pos = 0; pos < scenarios.Count; pos++)
{
//Apply scenarios
scenarios[pos].Show();
IWorkbook newBook = excelEngine.Excel.Workbooks.Create(0);
IWorksheet newSheet = newBook.Worksheets.AddCopy(worksheet);
newSheet.Name = scenarios[pos].Name;
//Saving the new workbook
newBook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath(@"Output/" + scenarios[pos].Name + ".xlsx"));
//To restore the cell values from the previous scenario results
scenarios["Current % of Change"].Show();
scenarios["Current Quantity"].Show();
}
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario1 = scenarios[0];
IScenario scenario2 = scenarios[1];
//Show the scenario
scenario2.Show();
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim scenarios As IScenarios = worksheet.Scenarios
Dim scenario1 As IScenario = scenarios(0)
Dim scenario2 As IScenario = scenarios(1)
'Show the scenario
scenario2.Show()
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End UsingA complete working example to show scenario in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Set Name
The name of the scenario can be defined using the Name property..
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario = scenarios[0];
//Set the name of the scenario
scenario.Name = "Current Quantity";
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario = scenarios[0];
//Set the name of the scenario
scenario.Name = "Current Quantity";
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim scenarios As IScenarios = worksheet.Scenarios
Dim scenario As IScenario = scenarios(0)
'Set the name of the scenario
scenario.Name = "Current Quantity"
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End UsingHide Scenario
The scenario can be hidden by enabling the Hidden property of IScenario.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/WhatIfAnalysisTemplate.xlsx"), ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Access the collection of scenarios in the worksheet
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
//Disable the protection for a specific scenario
scenarios["Increased % of Change"].Hidden = true;
//Enable worksheet protection
worksheet.Protect("Scenario");
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/HideScenario.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario = scenarios[0];
//Hidden the scenario
scenario.Hidden = true;
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim scenarios As IScenarios = worksheet.Scenarios
Dim scenario As IScenario = scenarios(0)
'Hidden the scenario
scenario.Hidden = True
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End UsingA complete working example to hide a scenario in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Protect Scenario
The scenario can be locked or unlocked through Locked property of IScenario. A scenario is locked by default.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/WhatIfAnalysisTemplate.xlsx"), ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Enable worksheet protection
worksheet.Protect("scenario");
// Access the collection of scenarios in the worksheet
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
//To make a scenario editable after protecting the sheet
scenarios[0].Locked = false;
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ProtectScenario.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario = scenarios[0];
//Unlock a scenario
scenario.Locked = false;
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim scenarios As IScenarios = worksheet.Scenarios
Dim scenario As IScenario = scenarios(0)
'Unlock a scenario
scenario.Locked = False
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End UsingA complete working example to unprotect a scenario in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Add Comment
The comment associated with that particular scenario can be generated using the Comment property.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario = scenarios[0];
//Set the comment value
scenario.Comment = "Scenario has been created";
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
IScenarios scenarios = worksheet.Scenarios;
IScenario scenario = scenarios[0];
//Set the comment value
scenario.Comment = "Scenario has been created";
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("InputTemplate.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
Dim scenarios As IScenarios = worksheet.Scenarios
Dim scenario As IScenario = scenarios[0]
'Set the comment value
scenario.Comment = "Scenario has been created"
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End Using