How can I help you?
Working with Excel Tables
31 Oct 202524 minutes to read
To quickly learn how to create, edit, and format tables in Excel documents, check out this video:
Creating a table
XlsIO supports reading and writing the table which helps to organize and analyze the related data.
- IListObjects represents a collection of tables in the worksheet.
- IListObject represent a table in the worksheet.
You can also create a calculated column in the table. For more details, refer here.
NOTE
In XlsIO, tables are supported only for Excel 2007 and later formats (*.xlsx files).
The following code sample explains the creation of a simple table by the range of data from an existing worksheet.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xlsx"));
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Create for the given data
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet["A1:C5"]);
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/CreateTable.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Create table with the data in given range
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet["A1:C8"]);
string fileName = "Output.xlsx";
workbook.SaveAs(fileName);
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Create table with the data in given range
Dim table As IListObject = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet("A1:C8"))
Dim fileName As String = "Output.xlsx"
workbook.SaveAs(fileName)
End UsingA complete working example to create a table in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Accessing a table
The existing tables in the worksheet can be accessed, as follows.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xlsx"));
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing first table in the sheet
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects[0];
//Modifying table name
table.DisplayName = "SalesTable";
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ReadTable.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing first table in the sheet
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects[0];
//Modifying table name
table.DisplayName = "SalesTable";
string fileName = "Output.xlsx";
workbook.SaveAs(fileName);
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Accessing first table in the sheet
Dim table As IListObject = worksheet.ListObjects(0)
'Modifying table name
table.DisplayName = "SalesTable"
Dim fileName As String = "Output.xlsx"
workbook.SaveAs(fileName)
End UsingA complete working example for accessing a table in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Formatting a table
You can apply built-in styles to the table using XlsIO. You can also customize the table with other table style options such as Header/total row, first/last column, and banded rows to make a table easier to read.
The following code snippet illustrates how to apply built-in table style.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xlsx"));
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating a table
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet["A1:C5"]);
//Formatting table with a built-in style
table.BuiltInTableStyle = TableBuiltInStyles.TableStyleMedium9;
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/FormatTable.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating a table
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet["A1:C8"]);
//Formatting table with a built-in style
table.BuiltInTableStyle = TableBuiltInStyles.TableStyleMedium9;
string fileName = "Output.xlsx";
workbook.SaveAs(fileName);
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating a table
Dim table As IListObject = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet("A1:C8"))
'Formatting table with a built-in style
table.BuiltInTableStyle = TableBuiltInStyles.TableStyleMedium9
Dim fileName As String = "Output.xlsx"
workbook.SaveAs(fileName)
End UsingA complete working example for formatting a table in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Apply Custom Table Style
You can apply custom table style to the table using XlsIO. You can create custom table style in which you can specified border, font, back ground color and format. You can also customized table in with other table style options such as Header/total row, first/last column, banded rows to make a table easier to read.
The below code example shows how to apply custom table style in XlsIO.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Create data for table
worksheet[1, 1].Text = "Products";
worksheet[1, 2].Text = "Qtr1";
worksheet[1, 3].Text = "Qtr2";
worksheet[1, 4].Text = "Qtr3";
worksheet[1, 5].Text = "Qtr4";
worksheet[2, 1].Text = "Alfreds Futterkiste";
worksheet[2, 2].Number = 744.6;
worksheet[2, 3].Number = 162.56;
worksheet[2, 4].Number = 5079.6;
worksheet[2, 5].Number = 1249.2;
worksheet[3, 1].Text = "Antonio Moreno";
worksheet[3, 2].Number = 5079.6;
worksheet[3, 3].Number = 1249.2;
worksheet[3, 4].Number = 943.89;
worksheet[3, 5].Number = 349.6;
worksheet[4, 1].Text = "Around the Horn";
worksheet[4, 2].Number = 1267.5;
worksheet[4, 3].Number = 1062.5;
worksheet[4, 4].Number = 744.6;
worksheet[4, 5].Number = 162.56;
worksheet[5, 1].Text = "Bon app";
worksheet[5, 2].Number = 1418;
worksheet[5, 3].Number = 756;
worksheet[5, 4].Number = 1267.5;
worksheet[5, 5].Number = 1062.5;
worksheet[6, 1].Text = "Eastern Connection";
worksheet[6, 2].Number = 4728;
worksheet[6, 3].Number = 4547.92;
worksheet[6, 4].Number = 1418;
worksheet[6, 5].Number = 756;
worksheet[7, 1].Text = "Ernst Handel";
worksheet[7, 2].Number = 943.89;
worksheet[7, 3].Number = 349.6;
worksheet[7, 4].Number = 4728;
worksheet[7, 5].Number = 4547.92;
//Create style for table number format
IStyle style = workbook.Styles.Add("CurrencyFormat");
style.NumberFormat = "_($* #,##0.00_);_($* (#,##0.00);_($* \" - \"??_);_(@_)";
worksheet["B2:E8"].CellStyleName = "CurrencyFormat";
//Create table
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet["A1:E7"]);
//Apply custom table style
ITableStyles tableStyles = workbook.TableStyles;
ITableStyle tableStyle = tableStyles.Add("Table Style 1");
ITableStyleElements tableStyleElements = tableStyle.TableStyleElements;
ITableStyleElement tableStyleElement = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.SecondColumnStripe);
tableStyleElement.BackColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(217, 225, 242);
ITableStyleElement tableStyleElement1 = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.FirstColumn);
tableStyleElement1.FontColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(128, 128, 128);
ITableStyleElement tableStyleElement2 = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.HeaderRow);
tableStyleElement2.FontColor = ExcelKnownColors.White;
tableStyleElement2.BackColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(0, 112, 192);
ITableStyleElement tableStyleElement3 = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.TotalRow);
tableStyleElement3.BackColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(0, 112, 192);
tableStyleElement3.FontColor = ExcelKnownColors.White;
table.TableStyleName = tableStyle.Name;
//Total row
table.ShowTotals = true;
table.ShowFirstColumn = true;
table.ShowTableStyleColumnStripes = true;
table.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = true;
table.Columns[0].TotalsRowLabel = "Total";
table.Columns[1].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
table.Columns[2].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
table.Columns[3].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
table.Columns[4].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/CustomTableStyle.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2016;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Create data
worksheet[1, 1].Text = "Products";
worksheet[1, 2].Text = "Qtr1";
worksheet[1, 3].Text = "Qtr2";
worksheet[1, 4].Text = "Qtr3";
worksheet[1, 5].Text = "Qtr4";
worksheet[2, 1].Text = "Alfreds Futterkiste";
worksheet[2, 2].Number = 744.6;
worksheet[2, 3].Number = 162.56;
worksheet[2, 4].Number = 5079.6;
worksheet[2, 5].Number = 1249.2;
worksheet[3, 1].Text = "Antonio Moreno";
worksheet[3, 2].Number = 5079.6;
worksheet[3, 3].Number = 1249.2;
worksheet[3, 4].Number = 943.89;
worksheet[3, 5].Number = 349.6;
worksheet[4, 1].Text = "Around the Horn";
worksheet[4, 2].Number = 1267.5;
worksheet[4, 3].Number = 1062.5;
worksheet[4, 4].Number = 744.6;
worksheet[4, 5].Number = 162.56;
worksheet[5, 1].Text = "Bon app";
worksheet[5, 2].Number = 1418;
worksheet[5, 3].Number = 756;
worksheet[5, 4].Number = 1267.5;
worksheet[5, 5].Number = 1062.5;
worksheet[6, 1].Text = "Eastern Connection";
worksheet[6, 2].Number = 4728;
worksheet[6, 3].Number = 4547.92;
worksheet[6, 4].Number = 1418;
worksheet[6, 5].Number = 756;
worksheet[7, 1].Text = "Ernst Handel";
worksheet[7, 2].Number = 943.89;
worksheet[7, 3].Number = 349.6;
worksheet[7, 4].Number = 4728;
worksheet[7, 5].Number = 4547.92;
//Create style for table number format
IStyle style = workbook.Styles.Add("CurrencyFormat");
style.NumberFormat = "_($* #,##0.00_);_($* (#,##0.00);_($* \" - \"??_);_(@_)";
worksheet["B2:E8"].CellStyleName = "CurrencyFormat";
//Create table
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet["A1:E7"]);
//Apply custom table style
ITableStyles tableStyles = workbook.TableStyles;
ITableStyle tableStyle = tableStyles.Add("Table Style 1");
ITableStyleElements tableStyleElements = tableStyle.TableStyleElements;
ITableStyleElement tableStyleElement = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.SecondColumnStripe);
tableStyleElement.BackColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(217, 225, 242);
ITableStyleElement tableStyleElement1 = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.FirstColumn);
tableStyleElement1.FontColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(128, 128, 128);
ITableStyleElement tableStyleElement2 = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.HeaderRow);
tableStyleElement2.FontColor = ExcelKnownColors.White;
tableStyleElement2.BackColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(0, 112, 192);
ITableStyleElement tableStyleElement3 = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.TotalRow);
tableStyleElement3.BackColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(0, 112, 192);
tableStyleElement3.FontColor = ExcelKnownColors.White;
table.TableStyleName = tableStyle.Name;
//Total row
table.ShowTotals = true;
table.ShowFirstColumn = true;
table.ShowTableStyleColumnStripes = true;
table.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = true;
table.Columns[0].TotalsRowLabel = "Total";
table.Columns[1].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
table.Columns[2].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
table.Columns[3].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
table.Columns[4].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
//Save the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("CustomTableStyle.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2016
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Create data
worksheet(1, 1).Text = "Products"
worksheet(1, 2).Text = "Qtr1"
worksheet(1, 3).Text = "Qtr2"
worksheet(1, 4).Text = "Qtr3"
worksheet(1, 5).Text = "Qtr4"
worksheet(2, 1).Text = "Alfreds Futterkiste"
worksheet(2, 2).Number = 744.6
worksheet(2, 3).Number = 162.56
worksheet(2, 4).Number = 5079.6
worksheet(2, 5).Number = 1249.2
worksheet(3, 1).Text = "Antonio Moreno"
worksheet(3, 2).Number = 5079.6
worksheet(3, 3).Number = 1249.2
worksheet(3, 4).Number = 943.89
worksheet(3, 5).Number = 349.6
worksheet(4, 1).Text = "Around the Horn"
worksheet(4, 2).Number = 1267.5
worksheet(4, 3).Number = 1062.5
worksheet(4, 4).Number = 744.6
worksheet(4, 5).Number = 162.56
worksheet(5, 1).Text = "Bon app"
worksheet(5, 2).Number = 1418
worksheet(5, 3).Number = 756
worksheet(5, 4).Number = 1267.5
worksheet(5, 5).Number = 1062.5
worksheet(6, 1).Text = "Eastern Connection"
worksheet(6, 2).Number = 4728
worksheet(6, 3).Number = 4547.92
worksheet(6, 4).Number = 1418
worksheet(6, 5).Number = 756
worksheet(7, 1).Text = "Ernst Handel"
worksheet(7, 2).Number = 943.89
worksheet(7, 3).Number = 349.6
worksheet(7, 4).Number = 4728
worksheet(7, 5).Number = 4547.92
'Ceate style for table number format
Dim style As IStyle = workbook.Styles.Add("CurrencyFormat")
style.NumberFormat = "_($* #,##0.00_);_($* (#,##0.00);_($* "" - ""??_);_(@_)"
worksheet("B2:E8").CellStyleName = "CurrencyFormat"
'Create table
Dim table As IListObject = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet("A1:E7"))
//Apply custom table style
Dim tableStyles As ITableStyles = workbook.TableStyles
Dim tableStyle As ITableStyle = tableStyles.Add("Table Style 1")
Dim tableStyleElements As ITableStyleElements = tableStyle.TableStyleElements
Dim tableStyleElement As ITableStyleElement = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.SecondColumnStripe)
tableStyleElement.BackColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(217, 225, 242)
Dim tableStyleElement1 As ITableStyleElement = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.FirstColumn)
tableStyleElement1.FontColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(128, 128, 128)
Dim tableStyleElement2 As ITableStyleElement = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.HeaderRow)
tableStyleElement2.FontColor = ExcelKnownColors.White
tableStyleElement2.BackColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(0, 112, 192)
Dim tableStyleElement3 As ITableStyleElement = tableStyleElements.Add(ExcelTableStyleElementType.TotalRow)
tableStyleElement3.BackColorRGB = Color.FromArgb(0, 112, 192)
tableStyleElement3.FontColor = ExcelKnownColors.White
table.TableStyleName = tableStyle.Name
'Total row
table.ShowTotals = True
table.ShowFirstColumn = True
table.ShowTableStyleColumnStripes = True
table.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
table.Columns(0).TotalsRowLabel = "Total"
table.Columns(1).TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum
table.Columns(2).TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum
table.Columns(3).TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum
table.Columns(4).TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum
'Save the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("CustomTableStyle.xlsx")
End UsingA complete working example to apply custom table style in C# is present on this GitHub page.
The following screenshot represents generated Excel file with custom table styles in XlsIO.
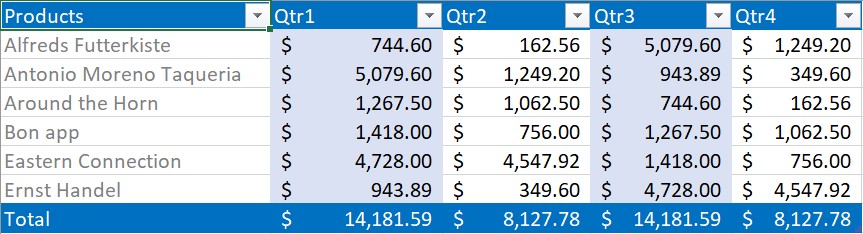
NOTE
The TableStyles API only retrieves custom table styles.
Insert or remove columns in a table
IListObject is a collection of columns, whereas a single column is represented by an instance of IListObjectColumn. XlsIO supports to insert or remove columns from the table using worksheet, as follows.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xlsx"));
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating a table
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet["A1:C5"]);
//Inserting a column in the table
worksheet.InsertColumn(2, 2);
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/InsertTableColumn.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating a table
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet["A1:C8"]);
//Inserting a column in the table
worksheet.InsertColumn(2, 2);
// Removing a column from the table
worksheet.DeleteColumn(2, 1);
string fileName = "Output.xlsx";
workbook.SaveAs(fileName);
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating table
Dim table As IListObject = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet("A1:C8"))
'Inserting a column in the table
worksheet.InsertColumn(2, 2)
'Removing a column from the table
worksheet.DeleteColumn(2, 1)
Dim fileName As String = "Output.xlsx"
workbook.SaveAs(fileName)
End UsingA complete working example to insert column in a table in C# is present on this GitHub page.
A complete working example to delete column in a table in C# is present on this GitHub page.
NOTE
Inserting rows or columns in a worksheet within the table range modifies table structure.
Adding a total row
The “Total Row” is added to a table by accessing the Table Columns. It is possible to set calculation function to be used to the total row cells by using the ExcelTotalsCalculation enumerator. These cells are updated after they are calculated.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xlsx"));
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating a table
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet["A1:C8"]);
//Adding total row
table.ShowTotals = true;
table.Columns[0].TotalsRowLabel = "Total";
table.Columns[1].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
table.Columns[2].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs(Path.GetFullPath("Output/AddTotalRow.xlsx"));
#endregion
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating a table
IListObject table = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet["A1:C8"]);
//Adding total row
table.ShowTotals = true;
table.Columns[0].TotalsRowLabel = "Total";
table.Columns[1].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
table.Columns[2].TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum;
string fileName = "Output.xlsx";
workbook.SaveAs(fileName);
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating a table
Dim table As IListObject = worksheet.ListObjects.Create("Table1", worksheet("A1:C8"))
'Adding total row
table.ShowTotals = True
table.Columns(0).TotalsRowLabel = "Total"
table.Columns(1).TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum
table.Columns(2).TotalsCalculation = ExcelTotalsCalculation.Sum
Dim fileName As String = "Output.xlsx"
workbook.SaveAs(fileName)
End UsingA complete working example to insert total row in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Create a table from external connection
External connection support allows to work with most recent data right in the workbook. After the data is imported, only refresh operations are performed to retrieve the updated data.
The following code snippet explains the method of importing data through an external connection in the workbook.
//XlsIO supports refreshing query table with external connection in windows platform only.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Database path
string dataPath = Path.GetFullPath("../../../Data/access-sakila.mdb");
//Connection string for DataSource, here we are using jet.OLEDB.4.0 which supports only if program targets 32 and for core projects the targe bit is by default OS bit .. so make sure change program's platform target to x86 bit (which is 32 bit) through project -> project config -> build -> platform target -> x86
string ConnectionStringOledb4 = "OLEDB;Provider=Microsoft.JET.OLEDB.4.0;Password=\"\";User ID=Admin;Data Source=" + dataPath;
//Adding a connection to the workbook
IConnection Connection = workbook.Connections.Add("Connection1", "Sample connection with MsAccess", ConnectionStringOledb4, "", ExcelCommandType.Table);
//Adding a QueryTable to sheet object
worksheet.ListObjects.AddEx(ExcelListObjectSourceType.SrcQuery, Connection, worksheet.Range["A1"]);
//Command text for the connection
worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable.CommandText = "select * from actor";
//The query performs asynchronous action
worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable.BackgroundQuery = true;
//The query table is refreshed when the workbook is opened
worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable.RefreshOnFileOpen = true;
//Represents the connection description
Connection.Description = "Sample Connection";
//Bind the GetDataTable method to OnRefreshConnection.
worksheet.ListObjects[0].OnRefreshConnection += GetOleDBDataTable;
//Import data to the sheet from the database
worksheet.ListObjects[0].Refresh();
//Auto-fits the columns
worksheet.UsedRange.AutofitColumns();
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}
//Helper method to get data table using OLEDB connection
void GetOleDBDataTable(object sender, RefreshConnectionEventArgs e)
{
OleDbConnection ole_connection = new OleDbConnection();
ole_connection.ConnectionString = e.ConnectionString;
OleDbCommand command = new OleDbCommand();
command.Connection = ole_connection;
command.CommandText = e.Query;
DataTable table = new DataTable();
OleDbDataAdapter Adapter = new OleDbDataAdapter(command);
Adapter.Fill(table);
ole_connection.Dispose();
Adapter.Dispose();
command.Dispose();
e.Data = table;
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Database path
string dataPath = Path.GetFullPath("c:/company/DB/TestDB.mdb");
//Connection string for DataSource
string ConnectionString = "OLEDB;Provider=Microsoft.JET.OLEDB.4.0;Password=\"\";User ID=Admin;Data Source=" + dataPath;
//Adding a connection to the workbook
IConnection Connection = workbook.Connections.Add("Connection1", "Sample connection with MsAccess", ConnectionString, "", ExcelCommandType.Sql);
//Adding a QueryTable to sheet object
worksheet.ListObjects.AddEx(ExcelListObjectSourceType.SrcQuery, Connection, worksheet.Range["A1"]);
//Command text for the connection
worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable.CommandText = "Select * from tableTest";
//The query performs asynchronous action
worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable.BackgroundQuery = true;
//The query table is refreshed when the workbook is opened
worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable.RefreshOnFileOpen = true;
//Represents the connection description
Connection.Description = "Sample Connection";
//Import data to the sheet from the database
worksheet.ListObjects[0].Refresh();
//Auto-fits the columns
worksheet.UsedRange.AutofitColumns();
string fileName = "Output.xlsx";
workbook.SaveAs(fileName);
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2013
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Database path
Dim dataPath As String = Path.GetFullPath("c:/company/DB/TestDB.mdb")
'Connection string for DataSource
Dim ConnectionString As String = "OLEDB;Provider=Microsoft.JET.OLEDB.4.0;Password="""";User ID=Admin;Data Source=" + dataPath
'Adding a connection to the workbook
Dim Connection As IConnection = workbook.Connections.Add("Connection1", "Sample connection with MsAccess", ConnectionString, "", ExcelCommandType.Sql)
'Adding a QueryTable to sheet object
worksheet.ListObjects.AddEx(ExcelListObjectSourceType.SrcQuery, Connection, worksheet.Range("A1"))
'Command text for the connection
worksheet.ListObjects(0).QueryTable.CommandText = "Select * from tableTest"
'The query performs asynchronous action
worksheet.ListObjects(0).QueryTable.BackgroundQuery = True
'The QueryTable is refreshed when the workbook is opened
worksheet.ListObjects(0).QueryTable.RefreshOnFileOpen = True
'Represents the connection description
Connection.Description = "Sample Connection"
'Import data to the sheet from the database
worksheet.ListObjects(0).Refresh()
'Auto-fits the columns
worksheet.UsedRange.AutofitColumns()
Dim fileName As String = "Output.xlsx"
workbook.SaveAs(fileName)
End UsingThe following table shows different data sources and its connection string formats supported in XlsIO.
| Database |
Connection Type |
Sample connection string |
|---|---|---|
|
Microsoft Access |
OLEDB |
OLEDB;Provider=Microsoft.JET.OLEDB.4.0;Password=\"\"; User ID=Admin;Data Source=C:\\Company\\DB\\TestDB.mdb |
|
ODBC |
ODBC;DSN=MS Access;DBQ=C:\\Company\\DB\\Testing.mdb; DefaultDir=C:\\Company\\DB;FIL=MS Access;MaxBufferSize=2048;PageTimeout=5; |
|
|
SQL |
OLEDB |
OLEDB;Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Integrated Security=SSPI; Persist Security Info=True;Initial Catalog=Temp; Data Source=SYNCFUSION\\SQLEXPRESS;Workstation ID=SYNCINC; |
|
ODBC |
ODBC;DSN=Test1;UID=syncfusion;Trusted_Connection=Yes; APP=Microsoft Office 2010;WSID=SYNCINC;DATABASE=Temp |
|
|
Excel |
OLEDB |
OLEDB;Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;Password=\"\"; User ID=Admin;Data Source="c:\SourceTemplate.xlsx; Jet OLEDB:Engine Type=37; |
|
SharePoint |
OLEDB |
Stars with OLEDB |
|
ODBC |
Stars with ODBC |
Refresh external data connection in Excel table
Excel tables (i.e., ListObjects) that are connected to external data connection can be refreshed programmatically. The Refresh() method in IListObject updates the data, similar to Refresh operation in Microsoft Excel. Here, there is not RefreshAll() option to refresh all the tables in a worksheet. To achieve that, all the tables (ListObjects) has to be accessed and refreshed individually.
The following code example shows how to access existing data connection of Excel tables in a sheet and refresh data of all the tables.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2016;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("ExistingDataSource.xlsx");
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing a connection from the workbook
IConnection connection = workbook.Connections[0];
//Refresh all the data by accessing each ListObject
foreach (IListObject listObject in worksheet.ListObjects)
{
listObject.Refresh();
}
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2016;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("ExistingDataSource.xlsx");
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing a connection from the workbook
IConnection connection = workbook.Connections[0];
//Refresh all the data by accessing each ListObject
foreach(IListObject listObject in worksheet.ListObjects)
{
listObject.Refresh();
}
string fileName = "Output.xlsx";
workbook.SaveAs(fileName);
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Excel2016
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("ExistingDataSource.xlsx")
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Accessing a connection from the workbook
Dim connection As IConnection = workbook.Connections(0)
'Refresh all the data by accessing each ListObject
For Each listObject As IListObject In worksheet.ListObjects
listObject.Refresh()
Next
Dim fileName As String = "Output.xlsx"
workbook.SaveAs(fileName)
End UsingAdding parameters to query in Excel table
Excel tables can be created by importing data from SQL Server through Excel data connections. The queries used to fetch data from SQL Server can be modified at run-time with the help of its parameters. There are three types of parameters which are applied to the WHERE clause of the SQL query. Let’s see the types in detail and how to implement them.
NOTE
Excel table must be refreshed to obtain the filtered result with parameters. Table refresh operation is not supported in UWP, C# [Cross-platform] and Xamarin platforms.
Set parameter as Prompt
The following code example illustrates how to set parameter through prompt event.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("QueryTable.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
///Get query table from list objects.
QueryTableImpl queryTable = worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable;
//Set SQL query to the query table Add parameters to the query table.
queryTable.CommandText = "select * from Employee_Details where Emp_Age > ?;";
//Add parameters to the query table.
IParameter parameter = queryTable.Parameters.Add("parameter1", ExcelParameterDataType.SQLSmallInt);
//Set parameter value through prompt.
parameter.SetParam(ExcelParameterType.Prompt, "Prompt");
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("PromptParameter.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("QueryTable.xlsx");
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Get query table from list objects.
QueryTableImpl queryTable = worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable;
//Set SQL query to the query table Add parameters to the query table.
queryTable.CommandText = "select * from Employee_Details where Emp_Age > ?;";
//Add parameters to the query table.
IParameter parameter = queryTable.Parameters.Add("parameter1", ExcelParameterDataType.SQLSmallInt);
//Set parameter value through prompt.
parameter.SetParam(ExcelParameterType.Prompt, "Prompt");
//Set prompt event handler to update parameter value.
parameter.Prompt += new PromptEventHandler(SetParameter);
//Refresh the listobject
worksheet.ListObjects[0].Refresh();
workbook.SaveAs("PromptParameter.xlsx");
workbook.Close();
}
private void SetParameter(object sender, PromptEventArgs args)
{
args.Value = 20;
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("QueryTable.xlsx")
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Get query table from list objects.
Dim queryTable As QueryTableImpl = worksheet.ListObjects(0).QueryTable
'Set SQL query to the query table Add parameters to the query table.
queryTable.CommandText = "select * from Employee_Details where Emp_Age > ?;"
'Add parameters to the query table.
Dim parameter As IParameter = queryTable.Parameters.Add("parameter1", ExcelParameterDataType.SQLSmallInt)
'Set parameter value through prompt.
parameter.SetParam(ExcelParameterType.Prompt, "Prompt")
'Set prompt event handler to update parameter value
parameter.Prompt += New PromptEventHandler(SetParameter)
'Refresh the listobject
worksheet.ListObjects(0).Refresh()
workbook.SaveAs("PromptParameter.xlsx")
workbook.Close()
End Using
Private Sub SetParameter(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As PromptEventArgs)
args.Value = 20
End SubSet parameter as Constant
The following code example illustrates how to set parameter through constant type.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("QueryTable.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
///Get query table from list objects.
QueryTableImpl queryTable = worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable;
//Set SQL query to the query table Add parameters to the query table.
queryTable.CommandText = "select * from Employee_Details where Emp_Age < ?;";
//Add parameters to the query table.
IParameter parameter = queryTable.Parameters.Add("parameter1", ExcelParameterDataType.SQLSmallInt);
//Set constant to the parameter value.
parameter.SetParam(ExcelParameterType.Constant, 30);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("ConstantParameter.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("QueryTable.xlsx");
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Get query table from list objects.
QueryTableImpl queryTable = worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable;
//Set SQL query to the query table Add parameters to the query table.
queryTable.CommandText = "select * from Employee_Details where Emp_Age < ?;";
//Add parameters to the query table.
IParameter parameter = queryTable.Parameters.Add("parameter1", ExcelParameterDataType.SQLSmallInt);
//Set constant to the parameter value.
parameter.SetParam(ExcelParameterType.Constant, 30);
//Refresh the listobject
worksheet.ListObjects[0].Refresh();
workbook.SaveAs("ConstantParameter.xlsx");
workbook.Close();
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("QueryTable.xlsx")
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Get query table from list objects.
Dim queryTable As QueryTableImpl = worksheet.ListObjects(0).QueryTable
'Set SQL query to the query table Add parameters to the query table.
queryTable.CommandText = "select * from Employee_Details where Emp_Age < ?;"
'Add parameters to the query table.
Dim parameter As IParameter = queryTable.Parameters.Add("parameter1", ExcelParameterDataType.SQLSmallInt)
'Set constant to the parameter value.
parameter.SetParam(ExcelParameterType.Constant, 30)
'Refresh the listobject
worksheet.ListObjects(0).Refresh()
workbook.SaveAs("ConstantParameter.xlsx")
workbook.Close()
End UsingSet parameter as Range
The following code example illustrates how to set parameter type to a specific range.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("QueryTable.xlsx", ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Get query table from list objects.
QueryTableImpl queryTable = worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable;
//Set SQL query to the query table Add parameters to the query table.
queryTable.CommandText = "select * from Employee_Details where Emp_Age > ?;";
//Add parameters to the query table.
IParameter parameter = queryTable.Parameters.Add("parameter1", ExcelParameterDataType.SQLSmallInt);
//Set range to the parameter value.
parameter.SetParam(ExcelParameterType.Range, worksheet.Range["H1"]);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("RangeParameter.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("QueryTable.xlsx");
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Get query table from list objects.
QueryTableImpl queryTable = worksheet.ListObjects[0].QueryTable;
//Set SQL query to the query table Add parameters to the query table.
queryTable.CommandText = "select * from Employee_Details where Emp_Age > ?;";
//Add parameters to the query table.
IParameter parameter = queryTable.Parameters.Add("parameter1", ExcelParameterDataType.SQLSmallInt);
//Set range to the parameter value.
parameter.SetParam(ExcelParameterType.Range, worksheet.Range["H1"]);
//Refresh the listobject
worksheet.ListObjects[0].Refresh();
workbook.SaveAs("RangeParameter.xlsx");
workbook.Close();
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("QueryTable.xlsx")
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Get query table from list objects.
Dim queryTable As QueryTableImpl = worksheet.ListObjects(0).QueryTable
'Set SQL query to the query table Add parameters to the query table.
queryTable.CommandText = "select * from Employee_Details where Emp_Age > ?;"
'Add parameters to the query table.
Dim parameter As IParameter = queryTable.Parameters.Add("parameter1", ExcelParameterDataType.SQLSmallInt)
'Set range to the parameter value.
parameter.SetParam(ExcelParameterType.Range, worksheet.Range["H1"])
'Refresh the listobject
worksheet.ListObjects(0).Refresh()
workbook.SaveAs("RangeParameter.xlsx")
workbook.Close()
End Using