How can I help you?
Create Excel File in C# and VB.NET
10 Nov 202524 minutes to read
To quickly get started on creating an Excel document, please check out this video:
This section explains how to create a simple Excel file in C# and VB.NET using XlsIO. The following assemblies must be referred in your application to create and manipulate the Excel document.
|
Assembly Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Syncfusion.XlsIO.Base |
This assembly contains the core features for creating, reading, and manipulating an Excel file. |
|
Syncfusion.Compression.Base |
This assembly is used to package the Workbook contents. |
|
Syncfusion.Licensing |
Syncfusion® licensing is a .NET library for validating the registered Syncfusion® license in an application at runtime. |
NOTE
Starting with v16.2.0.x, if you reference Syncfusion® assemblies from trial setup or from the NuGet feed, you also have to add “Syncfusion.Licensing” assembly reference and include a license key in your projects. Please refer to this link to know about registering Syncfusion® license key in your applications to use our components.
NOTE
Syncfusion® components are available in nuget.org.
Include the following namespaces in your .cs or .vb file as shown as follows.
using Syncfusion.XlsIO;using Syncfusion.XlsIO;Imports Syncfusion.XlsIOCreate a Hello World Excel File
The following code example explains how to create a hello world sample.
using Syncfusion.XlsIO;
//New instance of ExcelEngine is created equivalent to launching Microsoft Excel with no workbooks open
//Instantiate the spreadsheet creation engine
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
//Instantiate the Excel application object
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
//Assigns default application version
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
//A new workbook is created equivalent to creating a new workbook in Excel
//Create a workbook with 1 worksheet
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
//Access first worksheet from the workbook
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Adding text to a cell
worksheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Hello World";
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx");
}using Syncfusion.XlsIO;
//New instance of ExcelEngine is created equivalent to launching Microsoft Excel with no workbooks open
//Instantiate the spreadsheet creation engine
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
//Instantiate the Excel application object
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
//Assigns default application version
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
//A new workbook is created equivalent to creating a new workbook in Excel
//Create a workbook with 1 worksheet
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
//Access first worksheet from the workbook
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Adding text to a cell
worksheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Hello World";
//Saving the workbook to disk in XLSX format
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx");
}Imports Syncfusion.XlsIO
'New instance of ExcelEngine is created equivalent to launching Microsoft Excel with no workbooks open
'Instantiate the spreadsheet creation engine
Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the Excel application object
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Assigns default application version
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
'A new workbook is created equivalent to creating a new workbook in Excel
'Create a workbook with 1 worksheet
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
'Access first worksheet from workbook
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Adding text to a cell
worksheet.Range("A1").Text = "Hello World"
'Saving the workbook to disk in XLSX format
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx")
End UsingThe output screen-shot of the above code.
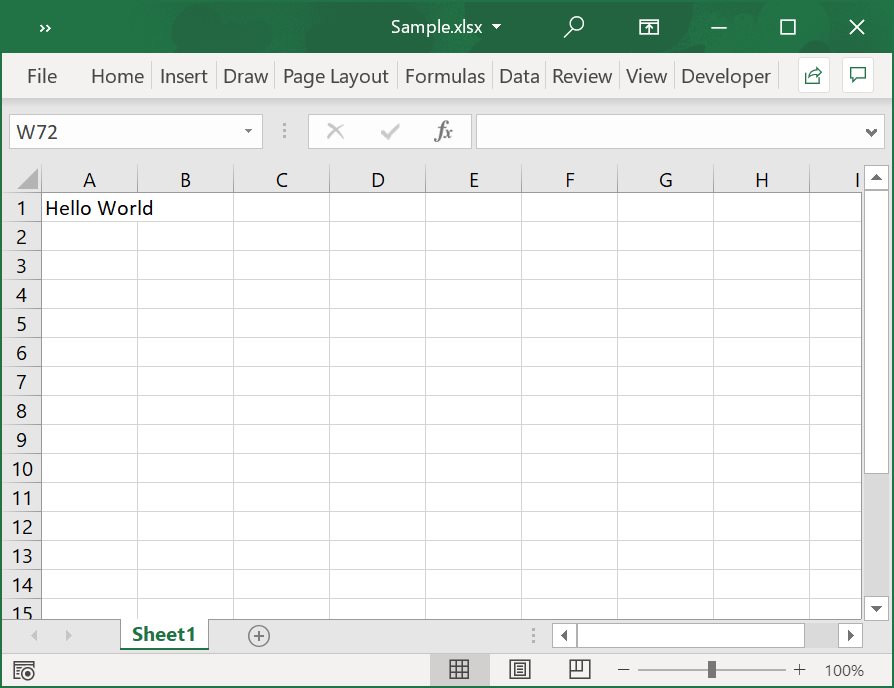
Create a Simple Excel File
An instance of the ExcelEngine gives access to create an application instance that is similar to launching Microsoft Excel application. The following code snippet shows how to initialize the application object for creating or manipulating Excel documents.
//New instance of ExcelEngine is created equivalent to launching Microsoft Excel with no workbooks open
//Instantiate the spreadsheet creation engine
ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine();
//Instantiate the Excel application object
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;//New instance of ExcelEngine is created equivalent to launching Microsoft Excel with no workbooks open
//Instantiate the spreadsheet creation engine
ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine();
//Instantiate the Excel application object
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;'New instance of ExcelEngine is created equivalent to launching Microsoft Excel with no workbooks open
'Instantiate the spreadsheet creation engine
Dim excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine
'Instantiate the Excel application object
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.ExcelBy default, the Excel version 97 to 2003 (*.xls) is associated with application object. XlsIO writes the excel files in the respective format depending on this excel version. You can modify the default Excel version to XLSX as shown as follows.
//Assigns default application version
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;//Assigns default application version
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;'Assigns default application version
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.XlsxThe workbook contains a collection of worksheets and various workbook-level properties. Each worksheet has cells, which can contain text, numbers, dates, formulas and more. The following code snippet illustrates how to create a workbook and access worksheet instance.
//A new workbook is created equivalent to creating a new workbook in Excel
//Create a workbook with 1 worksheet
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
//Access a worksheet from workbook
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];//A new workbook is created equivalent to creating a new workbook in Excel
//Create a workbook with 1 worksheet
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
//Access a worksheet from workbook
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];'A new workbook is created equivalent to creating a new workbook in Excel
'Create a workbook with 1 worksheet
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
'Access a worksheet from workbook
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)//Adding text data
worksheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Month";
worksheet.Range["B1"].Text = "Sales";
worksheet.Range["A6"].Text = "Total";
//Adding DateTime data
worksheet.Range["A2"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 1, 10);
worksheet.Range["A3"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 2, 10);
worksheet.Range["A4"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 3, 10);
//Applying number format for date value cells A2 to A4
worksheet.Range["A2:A4"].NumberFormat = "mmmm, yyyy";
//Auto-size the first column to fit the content
worksheet.AutofitColumn(1);
//Adding numeric data
worksheet.Range["B2"].Number = 68878;
worksheet.Range["B3"].Number = 71550;
worksheet.Range["B4"].Number = 72808;
//Adding formula
worksheet.Range["B6"].Formula = "SUM(B2:B4)";//Adding text data
worksheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Month";
worksheet.Range["B1"].Text = "Sales";
worksheet.Range["A6"].Text = "Total";
//Adding DateTime data
worksheet.Range["A2"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 1, 10);
worksheet.Range["A3"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 2, 10);
worksheet.Range["A4"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 3, 10);
//Applying number format for date value cells A2 to A4
worksheet.Range["A2:A4"].NumberFormat = "mmmm, yyyy";
//Auto-size the first column to fit the content
worksheet.AutofitColumn(1);
//Adding numeric data
worksheet.Range["B2"].Number = 68878;
worksheet.Range["B3"].Number = 71550;
worksheet.Range["B4"].Number = 72808;
//Adding formula
worksheet.Range["B6"].Formula = "SUM(B2:B4)";'Adding text data
worksheet.Range("A1").Text = "Month"
worksheet.Range("B1").Text = "Sales"
worksheet.Range("A6").Text = "Total"
'Adding DateTime data
worksheet.Range("A2").DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 1, 10)
worksheet.Range("A3").DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 2, 10)
worksheet.Range("A4").DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 3, 10)
'Applying number format for date value cells A2 to A4
worksheet.Range("A2:A4").NumberFormat = "mmmm, yyyy"
'Auto-size the first column to fit the content
worksheet.AutofitColumn(1)
'Adding numeric data
worksheet.Range("B2").Number = 68878
worksheet.Range("B3").Number = 71550
worksheet.Range("B4").Number = 72808
'Adding formula
worksheet.Range("B6").Formula = "SUM(B2:B4)"The following code snippet shows how to add an image into the worksheet.
//Inserting image
FileStream imageStream = new FileStream("image.jpg", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
worksheet.Pictures.AddPicture(10, 2, imageStream);//Inserting image
worksheet.Pictures.AddPicture(10, 2, "image.jpg");'Inserting image
worksheet.Pictures.AddPicture(10, 2, "image.jpg")Finally, save the document in file system and close/dispose the instance of IWorkbook and ExcelEngine.
//Save the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx");
//Closing the workbook
workbook.Close();
//Dispose the Excel engine
excelEngine.Dispose();//Saving the workbook to disk in XLSX format
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx");
//Closing the workbook
workbook.Close();
//Dispose the Excel engine
excelEngine.Dispose();'Saving the workbook to disk in XLSX format
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx")
'Closing the workbook
workbook.Close()
'Dispose the Excel engine
excelEngine.Dispose()The complete code to create a simple Excel document is given below.
using Syncfusion.XlsIO;
namespace ExcelCreation
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//New instance of ExcelEngine is created equivalent to launching Excel with no workbooks open
//Instantiate the spreadsheet creation engine
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
//Instantiate the Excel application object
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
//Assigns default application version
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
//A new workbook is created equivalent to creating a new workbook in Excel
//Create a workbook with 1 worksheet
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
//Access a worksheet from workbook
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Adding text data
worksheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Month";
worksheet.Range["B1"].Text = "Sales";
worksheet.Range["A6"].Text = "Total";
//Adding DateTime data
worksheet.Range["A2"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 1, 10);
worksheet.Range["A3"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 2, 10);
worksheet.Range["A4"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 3, 10);
//Applying number format for date value cells A2 to A4
worksheet.Range["A2:A4"].NumberFormat = "mmmm, yyyy";
//Auto-size the first column to fit the content
worksheet.AutofitColumn(1);
//Adding numeric data
worksheet.Range["B2"].Number = 68878;
worksheet.Range["B3"].Number = 71550;
worksheet.Range["B4"].Number = 72808;
//Adding formula
worksheet.Range["B6"].Formula = "SUM(B2:B4)";
//Inserting image
FileStream imageStream = new FileStream("image.jpg", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
worksheet.Pictures.AddPicture(10, 2, imageStream);
//Saving the workbook to disk in XLSX format
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx");
}
}
}
}using Syncfusion.XlsIO;
namespace ExcelCreation
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//New instance of ExcelEngine is created equivalent to launching Excel with no workbooks open
//Instantiate the spreadsheet creation engine
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
//Instantiate the Excel application object
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
//Assigns default application version
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
//A new workbook is created equivalent to creating a new workbook in Excel
//Create a workbook with 1 worksheet
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
//Access a worksheet from workbook
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Adding text data
worksheet.Range["A1"].Text = "Month";
worksheet.Range["B1"].Text = "Sales";
worksheet.Range["A6"].Text = "Total";
//Adding DateTime data
worksheet.Range["A2"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 1, 10);
worksheet.Range["A3"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 2, 10);
worksheet.Range["A4"].DateTime = new DateTime(2015, 3, 10);
//Applying number format for date value cells A2 to A4
worksheet.Range["A2:A4"].NumberFormat = "mmmm, yyyy";
//Auto-size the first column to fit the content
worksheet.AutofitColumn(1);
//Adding numeric data
worksheet.Range["B2"].Number = 68878;
worksheet.Range["B3"].Number = 71550;
worksheet.Range["B4"].Number = 72808;
//Adding formula
worksheet.Range["B6"].Formula = "SUM(B2:B4)";
//Inserting image
worksheet.Pictures.AddPicture(10, 2, "image.jpg");
//Saving the workbook to disk in XLSX format
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx");
}
}
}
}Imports Syncfusion.XlsIO
Namespace ExcelCreation
Module Program
Sub Main(args As String())
'New instance of ExcelEngine is created equivalent to launching Microsoft Excel with no workbooks open
'Instantiate the spreadsheet creation engine
Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the Excel application object
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Assigns default application version
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
'A new workbook is created equivalent to creating a new workbook in Excel
'Create a workbook with 1 worksheet
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
'Access a worksheet from workbook
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Adding text data
worksheet.Range("A1").Text = "Month"
worksheet.Range("B1").Text = "Sales"
worksheet.Range("A6").Text = "Total"
'Adding DateTime data
worksheet.Range("A2").DateTime = New DateTime(2015, 1, 10)
worksheet.Range("A3").DateTime = New DateTime(2015, 2, 10)
worksheet.Range("A4").DateTime = New DateTime(2015, 3, 10)
'Applying number format for date value cells A2 to A4
worksheet.Range("A2:A4").NumberFormat = "mmmm, yyyy"
'Auto-size the first column to fit the content
worksheet.AutofitColumn(1)
'Adding numeric data
worksheet.Range("B2").Number = 68878
worksheet.Range("B3").Number = 71550
worksheet.Range("B4").Number = 72808
'Adding formula
worksheet.Range("B6").Formula = "SUM(B2:B4)"
'Inserting image
worksheet.Pictures.AddPicture(10, 2, "image.jpg")
'Saving the workbook to disk in XLSX format
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx")
End Using
End Sub
End Module
End NamespaceThe screen-shot of the output for above code is given below.
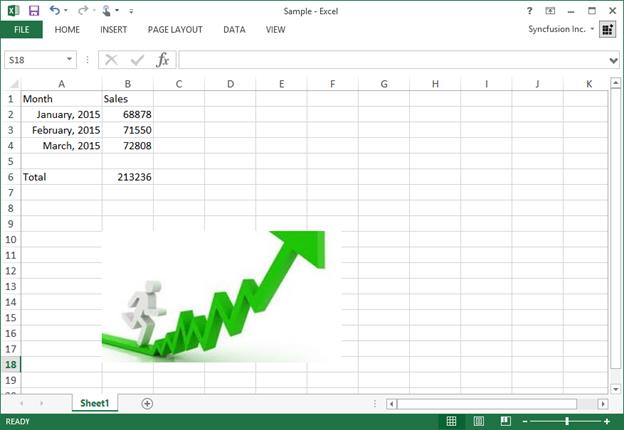
Export Data to Excel Worksheets
XlsIO helps to export data from various data sources into an Excel worksheet. The data from following data sources can be exported to Excel using XlsIO:
- Collection Objects
- Data Table
- Data Column
- Data View
- Array
The following code snippet shows how to export data from objects.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//GetEmployees method returns list of customers
IList<Employee> employees = GetEmployees();
//Import data to worksheet
worksheet.ImportData(employees, 2, 1, false);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//GetEmployees method returns list of customers
IList<Employee> employees = GetEmployees();
//Import data to worksheet
worksheet.ImportData(employees, 2, 1, false);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'GetEmployees method returns list of customers
Dim employees As IList(Of Employee) = GetEmployees()
'Import data to worksheet
worksheet.ImportData(employees, 2, 1, False)
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Sample.xlsx")
End UsingThe following code snippet provides supporting methods and classes for the previous code.
//Gets a list of Employee details
private static List<Employee> GetEmployees()
{
List<Employee> employees = new List<Employee>();
employees.Add(new Employee("Nancy", "Davolio", "Sales Representative", "505 - 20th Ave. E. Apt. 2A,", "Seattle", "WA", "USA", "Nancy.png"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Andrew", "Fuller", "Vice President, Sales", "908 W. Capital Way", "Tacoma", "WA", "USA", "Andrew.png"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Janet", "Leverling", "Sales Representative", "722 Moss Bay Blvd.", "Kirkland", "WA", "USA", "Janet.png"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Margaret", "Peacock", "Sales Representative", "4110 Old Redmond Rd.", "Redmond", "WA", "USA", "Margaret.png"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Steven", "Buchanan", "Sales Manager", "14 Garrett Hill", "London", string.Empty, "UK", "Steven.png"));
return employees;
}
//Employee details
public class Employee
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string Region { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public Employee(string firstName, string lastName, string title, string address, string city, string region, string country, string photoFilePath)
{
FirstName = firstName;
LastName = lastName;
Title = title;
Address = address;
City = city;
Region = region;
Country = country;
}
}//Gets a list of Employee details
private static IList<Employee> GetEmployees()
{
List<Employee> employees = new List<Employee>();
employees.Add(new Employee("Nancy", "Davolio", "Sales Representative", "505 - 20th Ave. E. Apt. 2A,", "Seattle", "WA", "USA", "Nancy.png"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Andrew", "Fuller", "Vice President, Sales", "908 W. Capital Way", "Tacoma", "WA", "USA", "Andrew.png"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Janet", "Leverling", "Sales Representative", "722 Moss Bay Blvd.", "Kirkland", "WA", "USA", "Janet.png"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Margaret", "Peacock", "Sales Representative", "4110 Old Redmond Rd.", "Redmond", "WA", "USA", "Margaret.png"));
employees.Add(new Employee("Steven", "Buchanan", "Sales Manager", "14 Garrett Hill", "London", string.Empty, "UK", "Steven.png"));
return employees;
}
//Employee details
public class Employee
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string Region { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public Employee(string firstName, string lastName, string title, string address, string city, string region, string country, string photoFilePath)
{
FirstName = firstName;
LastName = lastName;
Title = title;
Address = address;
City = city;
Region = region;
Country = country;
}
}'Gets a list Employee details
Private Function GetEmployees() As List(Of Employee)
Dim employees As New List(Of Employee)()
employees.Add(New Employee("Nancy", "Davolio", "Sales Representative", "505 - 20th Ave. E. Apt. 2A,", "Seattle", "WA", "USA", "Nancy.png"))
employees.Add(New Employee("Andrew", "Fuller", "Vice President, Sales", "908 W. Capital Way", "Tacoma", "WA", "USA", "Andrew.png"))
employees.Add(New Employee("Janet", "Leverling", "Sales Representative", "722 Moss Bay Blvd.", "Kirkland", "WA", "USA", "Janet.png"))
employees.Add(New Employee("Margaret", "Peacock", "Sales Representative", "4110 Old Redmond Rd.", "Redmond", "WA", "USA", "Margaret.png"))
employees.Add(New Employee("Steven", "Buchanan", "Sales Manager", "14 Garrett Hill", "London", String.Empty, "UK", "Steven.png"))
Return employees
End Function
'Employee details
Public Class Employee
Public Property FirstName() As String
Get
Return m_FirstName
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_FirstName = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_FirstName As String
Public Property LastName() As String
Get
Return m_LastName
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_LastName = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_LastName As String
Public Property Address() As String
Get
Return m_Address
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_Address = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_Address As String
Public Property City() As String
Get
Return m_City
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_City = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_City As String
Public Property Region() As String
Get
Return m_Region
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_Region = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_Region As String
Public Property Country() As String
Get
Return m_Country
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_Country = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_Country As String
Public Property Title() As String
Get
Return m_Title
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_Title = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_Title As String
Public Sub New(firstName As String, lastName As String, title As String, address As String, city As String, region As String, country As String, photoFilePath As String)
firstName = firstName
lastName = lastName
title = title
address = address
city = city
region = region
country = country
End Sub
End ClassYou can refer various exporting options in the Working with Data section.
Export Data from Excel Worksheets
The worksheet data can be exported to a data table using the ExportDataTable() method. This method provides various options that allows to export data through ExcelExportDataTableOptions.
The following code demonstrates how to export data from a worksheet to a data table with the ColumnNames and DetectColumnTypes options.
//XlsIO supports exporting of data from worksheet to data table from .NET Standard 2.0
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("WorkbookWithData.xlsx");
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Export data from worksheet used range to a DataTable
DataTable customersTable = worksheet.ExportDataTable(worksheet.UsedRange, ExcelExportDataTableOptions.ColumnNames | ExcelExportDataTableOptions.DetectColumnTypes);
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("WorkbookWithData.xlsx");
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
//Export data from worksheet used range to a DataTable
DataTable customersTable = sheet.ExportDataTable(sheet.UsedRange, ExcelExportDataTableOptions.ColumnNames | ExcelExportDataTableOptions.DetectColumnTypes);
//Saving the workbook
string fileName = "Output.xlsx";
workbook.SaveAs(fileName);
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("WorkbookWithData.xlsx")
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
'Export data from worksheet used range to a DataTable
Dim customersTable As DataTable = sheet.ExportDataTable(sheet.UsedRange, ExcelExportDataTableOptions.ColumnNames Or ExcelExportDataTableOptions.DetectColumnTypes)
'Saving the workbook
Dim fileName As String = "Output.xlsx"
workbook.SaveAs(fileName)
End Using//XlsIO supports exporting of data from worksheet to data table from .NET Standard 2.0 along with Windows Forms, WPF, ASP.NET and ASP.NET MVC platforms alone.
//Exporting data from worksheet can be achieved using List as illustrated below.
//To know more about exporting data from worksheet to various collection objects, please refer xlsio/working-with-data section.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
//Instantiates the File Picker
FileOpenPicker openPicker = new FileOpenPicker();
openPicker.SuggestedStartLocation = PickerLocationId.Desktop;
openPicker.FileTypeFilter.Add(".xlsx");
openPicker.FileTypeFilter.Add(".xls");
StorageFile openFile = await openPicker.PickSingleFileAsync();
//Opens the workbook
IWorkbook workbook = await application.Workbooks.OpenAsync(openFile);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Export data
List<Sales> data = worksheet.ExportData<Sales>(1, 1, 41, 4);
//Initializes FileSavePicker
FileSavePicker savePicker = new FileSavePicker();
savePicker.SuggestedStartLocation = PickerLocationId.Desktop;
savePicker.SuggestedFileName = "Output";
savePicker.FileTypeChoices.Add("Excel Files", new List<string>() { ".xlsx" });
//Creates a storage file from FileSavePicker
StorageFile storageFile = await savePicker.PickSaveFileAsync();
//Saves changes to the specified storage file
await workbook.SaveAsAsync(storageFile);
}
//Sales details
public class Sales
{
private string salesPerson;
private int salesJanJune;
private int salesJulyDec;
private int change;
public string SalesPerson
{
get
{
return salesPerson;
}
set
{
salesPerson = value;
}
}
public int SalesJanJune
{
get
{
return salesJanJune;
}
set
{
salesJanJune = value;
}
}
public int SalesJulyDec
{
get
{
return salesJulyDec;
}
set
{
salesJulyDec = value;
}
}
public int Change
{
get
{
return change;
}
set
{
change = value;
}
}
}//XlsIO supports exporting of data from worksheet to data table from .NET Standard 2.0 along with Windows Forms, WPF, ASP.NET and ASP.NET MVC platforms alone.
//Exporting data from worksheet can be achieved using List as illustrated below.
//To know more about exporting data from worksheet to various collection objects, please refer xlsio/working-with-data section.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
Assembly assembly = typeof(App).GetTypeInfo().Assembly;
Stream fileStream = assembly.GetManifestResourceStream("ExportData.WorkbookWithData.xlsx");
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(fileStream);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
List<Sales> data = sheet.ExportData<Sales>(1, 1, 41, 4);
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
workbook.SaveAs(stream);
stream.Position = 0;
//Save the document as file and view the saved document
//The operation in SaveAndView under Xamarin varies between Windows Phone, Android and iOS platforms. Please refer xlsio/xamarin section for respective code samples.
if (Device.OS == TargetPlatform.WinPhone || Device.OS == TargetPlatform.Windows)
{
Xamarin.Forms.DependencyService.Get<ISaveWindowsPhone>().SaveAndView("Output.xlsx", "application/msexcel", stream);
}
else
{
Xamarin.Forms.DependencyService.Get<ISave>().SaveAndView("Output.xlsx", "application/msexcel", stream);
}
}
//Sales details
public class Sales
{
private string salesPerson;
private int salesJanJune;
private int salesJulyDec;
private int change;
public string SalesPerson
{
get
{
return salesPerson;
}
set
{
salesPerson = value;
}
}
public int SalesJanJune
{
get
{
return salesJanJune;
}
set
{
salesJanJune = value;
}
}
public int SalesJulyDec
{
get
{
return salesJulyDec;
}
set
{
salesJulyDec = value;
}
}
public int Change
{
get
{
return change;
}
set
{
change = value;
}
}
}The following screenshot shows the DataTable of previous code.
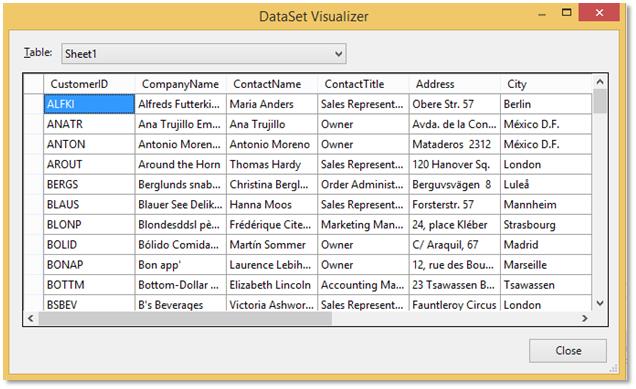
You can refer various exporting options in the Working with Data section.
Template based data filling using Template Markers
A template marker is a special marker symbol that allows to generate a document by filling data in an Excel template from data source. This marker automatically maps the column name in the data source and names of the marker fields in the Excel template document and fills the data (text or image).
This functionality supports the following data sources.
- Collection Objects
- DataTable
- Array
Each marker starts with a prefix “%”, which is followed by a MarkerVariable and its Property. The arguments are delimited by semicolon (;). The following syntax shows the usage of marker in input template document.
|
%<MarkerVariable>.<Property> For example: %Reports.SalesPerson |
Use the following syntax to maintain row formats while filling data.
|
%<MarkerVariable>.<Property>;insert:copystyles For example: %Reports.SalesPerson;insert:copystyles |
Find more details in Template marker section for arguments
For example – let’s consider that you have a template document as shown below.
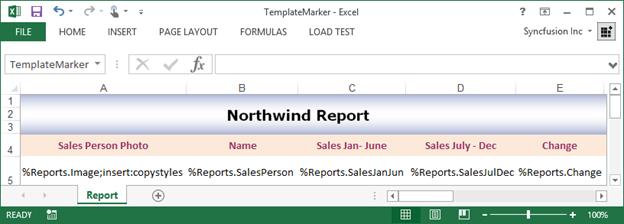
The following code snippet shows how to use template markers with objects.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("TemplateMarker.xlsx");
//Create template marker processor for the workbook
ITemplateMarkersProcessor marker = workbook.CreateTemplateMarkersProcessor();
//GetSalesReports method returns list of sales persons and their reports
IList<Report> reports = GetSalesReports();
//Adding reports collection to marker variables
//Where the name should match with the input template
marker.AddVariable("Reports", reports);
//Applying Markers
marker.ApplyMarkers();
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("TemplateMarkerResult.xlsx");
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("TemplateMarker.xlsx");
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Create template marker processor for the workbook
ITemplateMarkersProcessor marker = workbook.CreateTemplateMarkersProcessor();
//GetSalesReports method returns list of sales persons and their reports
IList<Report> reports = GetSalesReports();
//Adding reports collection to marker variables
//Where the name should match with the input template
marker.AddVariable("Reports", reports);
//Applying Markers
marker.ApplyMarkers();
//Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("TemplateMarkerResult.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("TemplateMarker.xlsx")
Dim worksheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Create template marker processor for the workbook
Dim marker As ITemplateMarkersProcessor = workbook.CreateTemplateMarkersProcessor()
'GetSalesReports method returns list of sales persons and their reports
Dim reports As IList(Of Report) = GetSalesReports()
'Adding reports collection to marker variables
'Where the name should match with the input template
marker.AddVariable("Reports", reports)
'Applying Markers
marker.ApplyMarkers()
'Saving the workbook
workbook.SaveAs("TemplateMarkerResult.xlsx")
End UsingThe following code snippet provides supporting methods and classes for the previous code.
//Gets a list of sales reports
private static List<Report> GetSalesReports()
{
List<Report> reports = new List<Report>();
reports.Add(new Report("Andy Bernard", "45000", "58000", 29 , "Andy.jpg"));
reports.Add(new Report("Jim Halpert", "34000", "65000", 91, "Jim.png"));
reports.Add(new Report("Karen Fillippelli", "75000", "64000", -14, "Karen.jpg"));
reports.Add(new Report("Phyllis Lapin", "56500", "33600", -40, "Phyllis.png"));
reports.Add(new Report("Stanley Hudson", "46500", "52000", 12, "Stanley.jpg"));
return reports;
}
//Sales report
public class Report
{
public string SalesPerson { get; set; }
public string SalesJanJun { get; set; }
public string SalesJulDec { get; set; }
public int Change { get; set; }
public byte[] Image { get; set; }
public Report(string name, string janToJun, string julToDec, int change, string imagePath)
{
SalesPerson = name;
SalesJanJun = janToJun;
SalesJulDec = julToDec;
Change = change;
Image = File.ReadAllBytes(imagePath);
}
}//Gets a list of sales reports
private static List<Report> GetSalesReports()
{
List<Report> reports = new List<Report>();
reports.Add(new Report("Andy Bernard", "45000", "58000", 29 , "Andy.jpg"));
reports.Add(new Report("Jim Halpert", "34000", "65000", 91, "Jim.png"));
reports.Add(new Report("Karen Fillippelli", "75000", "64000", -14, "Karen.jpg"));
reports.Add(new Report("Phyllis Lapin", "56500", "33600", -40, "Phyllis.png"));
reports.Add(new Report("Stanley Hudson", "46500", "52000", 12, "Stanley.jpg"));
return reports;
}
//Sales report
public class Report
{
public string SalesPerson { get; set; }
public string SalesJanJun { get; set; }
public string SalesJulDec { get; set; }
public int Change { get; set; }
public byte[] Image { get; set; }
public Report(string name, string janToJun, string julToDec, int change, string imagePath)
{
SalesPerson = name;
SalesJanJun = janToJun;
SalesJulDec = julToDec;
Change = change;
Image = File.ReadAllBytes(imagePath);
}
}'Gets a list of sales reports
Private Function GetSalesReports() As List(Of Report)
Dim reports As New List(Of Report)()
reports.Add(New Report("Andy Bernard", "45000", "58000", 29, "Andy.jpg"))
reports.Add(New Report("Jim Halpert", "34000", "65000", 91, "Jim.png"))
reports.Add(New Report("Karen Fillippelli", "75000", "64000", -14, "Karen.jpg"))
reports.Add(New Report("Phyllis Lapin", "56500", "33600", -40, "Phyllis.png"))
reports.Add(New Report("Stanley Hudson", "46500", "52000", 12, "Stanley.jpg"))
Return reports
End Function
'Sales report
Public Class Report
Public Property SalesPerson() As String
Get
Return m_SalesPerson
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_SalesPerson = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_SalesPerson As String
Public Property SalesJanJun() As String
Get
Return m_SalesJanJun
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_SalesJanJun = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_SalesJanJun As String
Public Property SalesJulDec() As String
Get
Return m_SalesJulDec
End Get
Set(value As String)
m_SalesJulDec = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_SalesJulDec As String
Public Property Change() As Integer
Get
Return m_Change
End Get
Set(value As Integer)
m_Change = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_Change As Integer
Public Property Image() As Byte()
Get
Return m_Image
End Get
Set(value As Byte())
m_Image = Value
End Set
End Property
Private m_Image As Byte()
Public Sub New(name As String, janToJun As String, julToDec As String, change As Integer, imagePath As String)
SalesPerson = name
SalesJanJun = janToJun
SalesJulDec = julToDec
change = change
Image = File.ReadAllBytes(imagePath)
End Sub
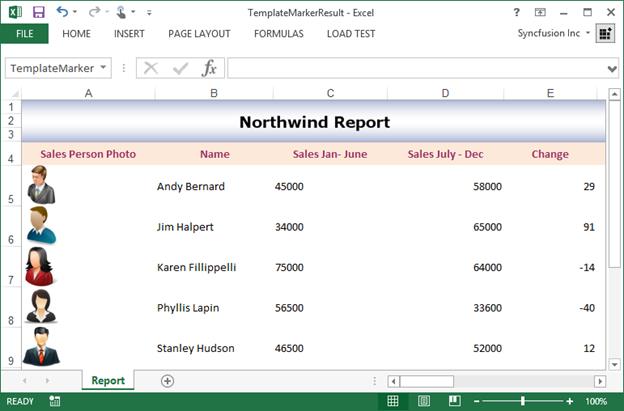
End ClassThe resultant document looks as follows.
NOTE
You can refer to our .Net Excel Framework webpage to see the product’s groundbreaking features. You can also explore our .Net Excel Framework demo that shows how to create and modify Excel files from C# with 5 lines of code on different platforms.