How can I help you?
Range Pointer in WinUI Radial Gauge
26 May 202110 minutes to read
A range pointer is an accenting line or shaded background range that can be placed on a gauge to mark the current value.
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
<gauge:RangePointer Value="30" />
</gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
RangePointer rangePointer = new RangePointer();
rangePointer.Value = 30;
radialAxis.Pointers.Add(rangePointer);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;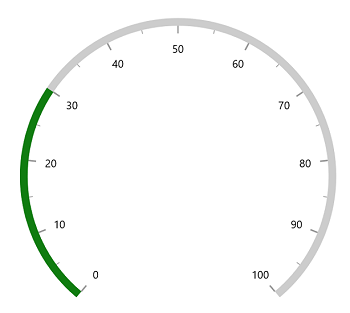
The following properties are used to customize the range pointer:
-
Background– Customizes the color of range pointer. -
PointerWidth- Specifies the width of pointer either in pixels or factor. -
WidthUnit– Specifies whether thePointerWidthis defined in pixels or factor.
The PointerWidth of the pointer can be specified either in pixel or factor. If the WidthUnit is specified as Pixel, then the range will be rendered based on the provided pixel value. If the WidthUnit is set as factor, the provided factor value will be multiplied with axis radius. For example, if the pointer width is set as 0.1, then 10% of axis radius is considered as range pointer width.
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
<gauge:RangePointer Value="30"
PointerWidth="0.1"
WidthUnit="Factor"
Background="Indigo" />
</gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
RangePointer rangePointer = new RangePointer();
rangePointer.Value = 30;
rangePointer.PointerWidth = 0.1;
rangePointer.WidthUnit = SizeUnit.Factor;
rangePointer.Background = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.Indigo);
radialAxis.Pointers.Add(rangePointer);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;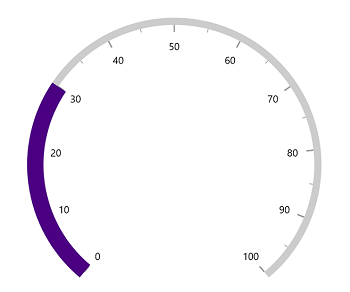
The default value of WidthUnit and OffsetUnit is SizeUnit.Pixel.
Setting gradient brush to the pointer
The GradientStops property of range pointer allows to specify the smooth color transition to pointer by specifying the different colors based on provided axis value.
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis AxisLineWidth="0.1"
AxisLineWidthUnit="Factor">
<gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
<gauge:RangePointer Value="40"
PointerWidth="0.1"
WidthUnit="Factor">
<gauge:RangePointer.GradientStops>
<gauge:GaugeGradientStop Value="10"
Color="#FFCC2B5E" />
<gauge:GaugeGradientStop Value="30"
Color="#FF753A88" />
</gauge:RangePointer.GradientStops>
</gauge:RangePointer>
</gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
radialAxis.AxisLineWidth = 0.1;
radialAxis.AxisLineWidthUnit = SizeUnit.Factor;
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
RangePointer rangePointer = new RangePointer();
rangePointer.Value = 40;
rangePointer.PointerWidth = 0.1;
rangePointer.WidthUnit = SizeUnit.Factor;
rangePointer.GradientStops.Add(new GaugeGradientStop { Value = 10, Color = Color.FromArgb(255, 204, 43, 94) });
rangePointer.GradientStops.Add(new GaugeGradientStop { Value = 30, Color = Color.FromArgb(255, 117, 58, 136) });
radialAxis.Pointers.Add(rangePointer);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;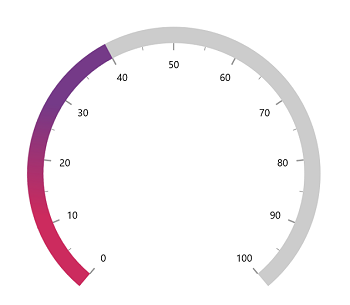
Corner style customization
The CornerStyle property of range pointer specifies the corner type for pointer. The corners can be customized using the BothFlat, BothCurve, StartCurve and EndCurve options. The default value of this property is BothFlat.
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
<gauge:RangePointer Value="30"
CornerStyle="BothCurve" />
</gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
RangePointer rangePointer = new RangePointer();
rangePointer.Value = 30;
rangePointer.CornerStyle = CornerStyle.BothCurve;
radialAxis.Pointers.Add(rangePointer);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;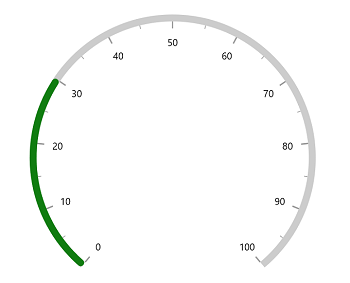
Position customization
The following properties are used to customize the position of range pointer:
-
PointerOffset- Specifies the position value for pointer either in pixels or factor. -
OffsetUnit– Specifies whether thePointerOffsetis defined in pixels or factor.
The range pointer can be moved far or near to the axis line using the PointerOffset property. The PointerOffset can be set either in pixel or factor value using its OffsetUnit.
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
<gauge:RangePointer Value="30"
PointerOffset="70" />
</gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
RangePointer rangePointer = new RangePointer();
rangePointer.Value = 30;
rangePointer.PointerOffset = 70;
radialAxis.Pointers.Add(rangePointer);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;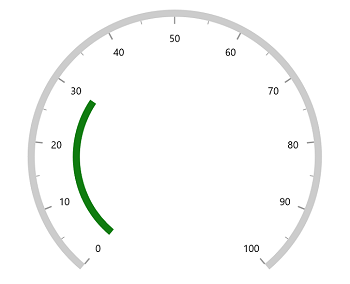
When you set the OffsetUnit as pixel, the pointer will be moved to the provided pixel value.
If the OffsetUnit is specified as factor, the factor value will be multiplied with the axis radius. For example, if you set PointerOffset as 0.1, then the pointer offset is considered as 10% of axis radius.