How can I help you?
Annotation in WinUI Radial Gauge
27 Sep 202121 minutes to read
Radial axis allows you to add multiple controls such as text, icon and image etc., as an annotation to a specific point of interest in the radial gauge.
The following properties are available in Annotation to customizes the position and alignment.
-
DirectionValue– Specifies the value that indicates the direction of the annotation based onDirectionUnitproperty. -
DirectionUnit– Specifies the value that indicates the direction of the annotation to be calculated on the basis ofAxis valueorAngle. -
PositionFactor– Specifies the factor value(from 0 to 1) to adjusts the annotation distance from center point. -
HorizontalAlignment– Specifies the horizontal alignment for positioning the annotation. -
VerticalAlignment– Specifies the vertical alignment for positioning the annotation.
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation DirectionUnit="AxisValue"
DirectionValue="50">
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
<TextBlock Text="50.0"
FontWeight="SemiBold"
FontSize="20" />
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation>
</gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
GaugeAnnotation gaugeAnnotation = new GaugeAnnotation();
gaugeAnnotation.DirectionUnit = AnnotationDirection.AxisValue;
gaugeAnnotation.DirectionValue = 50;
gaugeAnnotation.Content = new TextBlock { Text = "50.0", FontWeight = FontWeights.SemiBold, FontSize = 20 };
radialAxis.Annotations.Add(gaugeAnnotation);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;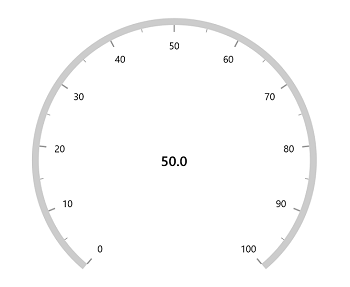
Positioning annotation
The annotation can be positioned using either the Angle or the Axis value. It can be controlled by the DirectionUnit property of Annotation. The default value is Angle.
Positioning annotation using angle
The following example shows how to position the annotation using angle.
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
<gauge:NeedlePointer Value="90" />
</gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation DirectionValue="90"
PositionFactor="0.5">
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
<TextBlock Text="90.0"
FontWeight="SemiBold"
FontSize="20" />
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation>
</gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
NeedlePointer needlePointer = new NeedlePointer();
needlePointer.Value = 90;
radialAxis.Pointers.Add(needlePointer);
GaugeAnnotation gaugeAnnotation = new GaugeAnnotation();
gaugeAnnotation.DirectionValue = 90;
gaugeAnnotation.PositionFactor = 0.5;
gaugeAnnotation.Content = new TextBlock { Text = "90.0", FontWeight = FontWeights.SemiBold, FontSize = 20 };
radialAxis.Annotations.Add(gaugeAnnotation);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;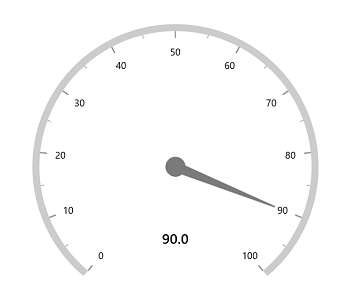
Positioning annotation using axis value
The following example shows how to position the annotation using axis value.
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation DirectionUnit="AxisValue"
DirectionValue="50"
PositionFactor="0.4">
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
<TextBlock Text="50.0"
FontWeight="SemiBold"
FontSize="20" />
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation>
</gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
GaugeAnnotation gaugeAnnotation = new GaugeAnnotation();
gaugeAnnotation.DirectionUnit = AnnotationDirection.AxisValue;
gaugeAnnotation.DirectionValue = 50;
gaugeAnnotation.PositionFactor = 0.4;
gaugeAnnotation.Content = new TextBlock { Text = "50.0", FontWeight = FontWeights.SemiBold, FontSize = 20 };
radialAxis.Annotations.Add(gaugeAnnotation);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;
PositionFactor is used to move the annotation from the center of axis to the edge of the axis. For example, when you specify the PositionFactor as 0.5, the annotation will be moved from the center towards the corresponding direction with the distance of half of the radius value of axis.
By default, the value of PositionFactor is 0.
Setting image for annotation
Annotations provide options to add any image over the gauge control with respect to its offset position. You can add multiple images in a single control.
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis Interval="10"
StartAngle="0"
EndAngle="360"
ShowTicks="False"
ShowLabels="False"
AxisLineWidth="30">
<gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
<gauge:RangePointer Value="73"
PointerWidth="30"
EnableAnimation="True"
Background="#FFFCE38A"
CornerStyle="BothCurve" />
</gauge:RadialAxis.Pointers>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation>
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Image Source="CloudDownload.png"
Height="50"
Width="60" />
<TextBlock Text="73°F"
Grid.Row="1"
FontSize="25"
FontWeight="SemiBold"
VerticalAlignment="Top"
HorizontalAlignment="Left" />
</Grid>
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation>
</gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
radialAxis.Interval = 10;
radialAxis.StartAngle = 0;
radialAxis.EndAngle = 360;
radialAxis.ShowTicks = false;
radialAxis.ShowLabels = false;
radialAxis.AxisLineWidth = 30;
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
RangePointer rangePointer = new RangePointer();
rangePointer.Value = 73;
rangePointer.PointerWidth = 30;
rangePointer.EnableAnimation = true;
rangePointer.Background = new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(255, 252, 227, 138));
rangePointer.CornerStyle = CornerStyle.BothCurve;
radialAxis.Pointers.Add(rangePointer);
Grid grid = new Grid();
grid.RowDefinitions.Add(new RowDefinition { Height = new GridLength { GridUnitType = GridUnitType.Star } });
grid.RowDefinitions.Add(new RowDefinition { Height = new GridLength { GridUnitType = GridUnitType.Auto } });
Image image = new Image();
BitmapImage bm = new BitmapImage();
bm.UriSource = new Uri("ms-appx:/CloudDownload.png", UriKind.Absolute);
image.Source = bm;
image.Height = 50;
image.Width = 60;
Grid.SetRow(image, 0);
grid.Children.Add(image);
TextBlock textBlock = new TextBlock();
textBlock.Text = "73°F";
textBlock.FontSize = 25;
textBlock.FontWeight = FontWeights.SemiBold;
textBlock.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Top;
textBlock.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left;
Grid.SetRow(textBlock, 1);
grid.Children.Add(textBlock);
GaugeAnnotation gaugeAnnotation = new GaugeAnnotation();
gaugeAnnotation.Content = grid;
radialAxis.Annotations.Add(gaugeAnnotation);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;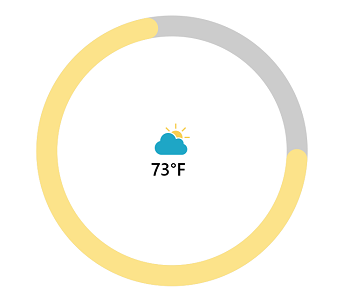
Alignment of annotation
Annotation can be aligned to center, near and far using the HorizontalAlignment and VerticalAlignment properties of annotation.
The following code example demonstrates how to set the HorizontalAlignment for annotation
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation DirectionUnit="AxisValue"
DirectionValue="50"
PositionFactor="0.4"
HorizontalAlignment="Left">
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
<TextBlock Text="50.0"
FontWeight="SemiBold"
FontSize="20" />
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation>
</gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
GaugeAnnotation gaugeAnnotation = new GaugeAnnotation();
gaugeAnnotation.DirectionUnit = AnnotationDirection.AxisValue;
gaugeAnnotation.DirectionValue = 50;
gaugeAnnotation.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left;
gaugeAnnotation.PositionFactor = 0.4;
gaugeAnnotation.Content = new TextBlock { Text = "50.0", FontWeight = FontWeights.SemiBold, FontSize = 20 };
radialAxis.Annotations.Add(gaugeAnnotation);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;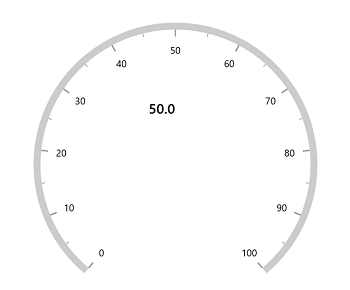
The following code example demonstrates how to set VerticalAlignment for annotation,
<gauge:SfRadialGauge>
<gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
<gauge:RadialAxis>
<gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation DirectionUnit="AxisValue"
DirectionValue="50"
PositionFactor="0.4"
VerticalAlignment="Top">
<gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
<TextBlock Text="50.0"
FontWeight="SemiBold"
FontSize="20" />
</gauge:GaugeAnnotation.Content>
</gauge:RadialAxis.Annotations>
</gauge:RadialAxis>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge.Axes>
</gauge:SfRadialGauge>SfRadialGauge sfRadialGauge = new SfRadialGauge();
RadialAxis radialAxis = new RadialAxis();
sfRadialGauge.Axes.Add(radialAxis);
GaugeAnnotation gaugeAnnotation = new GaugeAnnotation();
gaugeAnnotation.DirectionUnit = AnnotationDirection.AxisValue;
gaugeAnnotation.DirectionValue = 50;
gaugeAnnotation.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Top;
gaugeAnnotation.PositionFactor = 0.4;
gaugeAnnotation.Content = new TextBlock { Text = "50.0", FontWeight = FontWeights.SemiBold, FontSize = 20 };
radialAxis.Annotations.Add(gaugeAnnotation);
this.Content = sfRadialGauge;