- Initialize Spreadsheet
- Populate Spreadsheet with Data
- Apply Conditional formatting
- Export Spreadsheet as Excel File
Contact Support
Getting Started
15 Mar 20199 minutes to read
This section explains briefly about how to create Spreadsheet in your ASP.NET MVC application and also how to populate the Spreadsheet with data, formats and how to export Spreadsheet data as excel file.
Initialize Spreadsheet
The following steps explains how to create spreadsheet,
- Create Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC application. You can refer MVC Getting started documentation to create new project and add necessary dll’s and script files.
- Add the following code example in view page to render Spreadsheet control. Spreadsheet is rendered with default height and width. You can also customize Spreadsheet dimension by setting
HeightandWidthproperty inScrollSettings.
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet"))Now, the Spreadsheet is rendered with default row and column count.
Populate Spreadsheet with Data
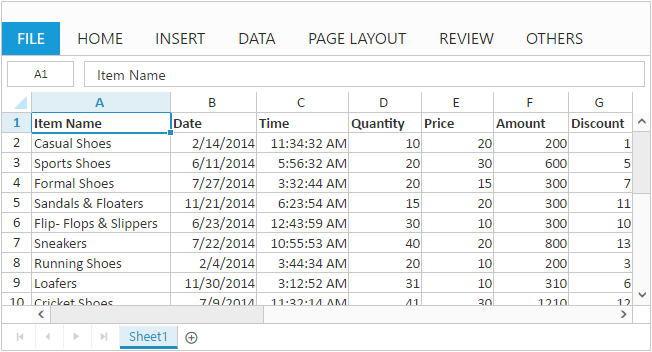
Now, this section explains how to populate JSON data to the Spreadsheet. You can set DataSource property in Sheets settings to populate JSON data in Spreadsheet.
1) Create datasource for Spreadsheet control.
public ActionResult Index()
{
var DataSource = GetAllItemDetails().ToList();
ViewBag.Datasource = DataSource;
return View();
}
public IEnumerable<object> GetAllItemDetails()
{
List<ItemDetail> lItems = new List<ItemDetail>();
lItems.Add(new ItemDetail() { ItemName = "Casual Shoes", Date = new DateTime(2014, 02, 14), Time = new DateTime(2014, 02, 14, 11, 34, 32), Quantity = 10, Price = 20, Amount = 200, Discount = 1, Profit = 10 });
lItems.Add(new ItemDetail() { ItemName = "Sports Shoes", Date = new DateTime(2014, 06, 11), Time = new DateTime(2014, 06, 11, 05, 56, 32), Quantity = 20, Price = 30, Amount = 600, Discount = 5, Profit = 50 });
lItems.Add(new ItemDetail() { ItemName = "Formal Shoes", Date = new DateTime(2014, 07, 27), Time = new DateTime(2014, 07, 27, 03, 32, 44), Quantity = 20, Price = 15, Amount = 300, Discount = 7, Profit = 27 });
lItems.Add(new ItemDetail() { ItemName = "Sandals & Floaters", Date = new DateTime(2014, 11, 21), Time = new DateTime(2014, 11, 21, 06, 23, 54), Quantity = 15, Price = 20, Amount = 300, Discount = 11, Profit = 67 });
lItems.Add(new ItemDetail() { ItemName = "Flip- Flops & Slippers", Date = new DateTime(2014, 06, 23), Time = new DateTime(2014, 06, 23, 12, 43, 59), Quantity = 30, Price = 10, Amount = 300, Discount = 10, Profit = 70 });
lItems.Add(new ItemDetail() { ItemName = "Sneakers", Date = new DateTime(2014, 07, 22), Time = new DateTime(2014, 07, 22, 10, 55, 53), Quantity = 40, Price = 20, Amount = 800, Discount = 13, Profit = 66 });
lItems.Add(new ItemDetail() { ItemName = "Running Shoes", Date = new DateTime(2014, 02, 04), Time = new DateTime(2014, 02, 04, 03, 44, 34), Quantity = 20, Price = 10, Amount = 200, Discount = 3, Profit = 14 });
lItems.Add(new ItemDetail() { ItemName = "Loafers", Date = new DateTime(2014, 11, 30), Time = new DateTime(2014, 11, 30, 03, 12, 52), Quantity = 31, Price = 10, Amount = 310, Discount = 6, Profit = 29 });
lItems.Add(new ItemDetail() { ItemName = "Cricket Shoes", Date = new DateTime(2014, 07, 09), Time = new DateTime(2014, 07, 09, 11, 32, 14), Quantity = 41, Price = 30, Amount = 1210, Discount = 12, Profit = 166 });
lItems.Add(new ItemDetail() { ItemName = "T-Shirts", Date = new DateTime(2014, 10, 31), Time = new DateTime(2014, 10, 31, 12, 01, 44), Quantity = 50, Price = 10, Amount = 500, Discount = 9, Profit = 55 });
return lItems;
}
public class ItemDetail
{
public string ItemName { get; set; }
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
public DateTime Time { get; set; }
public int Quantity { get; set; }
public int Price { get; set; }
public int Amount { get; set; }
public int Discount { get; set; }
public int Profit { get; set; }
}2) Initialize Spreadsheet with datasource.
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet")
.Sheets(sheet =>
{
sheet.RangeSettings(range =>
{
range.Datasource((IEnumerable<object>)ViewBag.Datasource).Add();
}).Add();
})
)
Apply Conditional formatting
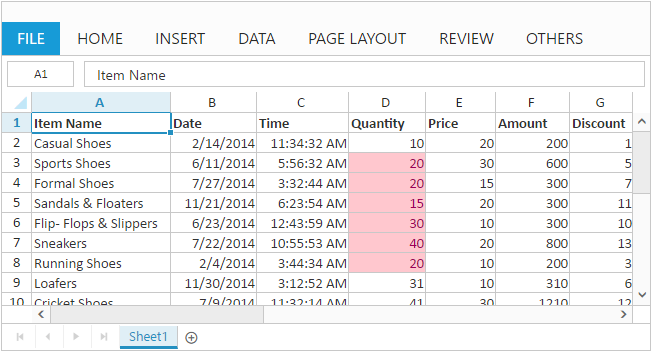
Conditional formatting helps you to apply formats to a cell or range with certain color based on the cells values. You can use AllowConditionalFormats property to enable/disable Conditional formats.
To apply conditional formats for a range use CFormatRule property.The following code example illustrates this behavior,
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet")
.Sheets(sheet =>
{
sheet.RangeSettings(range =>
{
range.Datasource((IEnumerable<object>)ViewBag.Datasource).Add();
}).CFormatRule(formatRule =>
{
formatRule.Action(SpreadsheetCFormatRuleAction.GreaterThan).Inputs(new List<string>() { "10" }).Color(SpreadsheetCFormatHighlightColor.RedFill).Range("D2:D8").Add();
}).Add();
})
)
Export Spreadsheet as Excel File
The Spreadsheet can save its data, style, format into an excel file. To enable save option in Spreadsheet set AllowExporting option in ExportSettings as true. Since Spreadsheet uses server side helper to save documents set ExcelUrl in ExportSettings option. The following code example illustrates this behavior,
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet")
//...
.ExportSettings(export =>
{
export.ExcelUrl("ExportToExcel");
}
)
//...
)[AcceptVerbs(HttpVerbs.Post)]
//...
public void ExportToExcel(string sheetModel, string sheetData, string password)
{
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(password))
Spreadsheet.Save(sheetModel, sheetData, "sample", ExportFormat.XLSX, ExcelVersion.Excel2013);
else
Spreadsheet.Save(sheetModel, sheetData, "sample", ExportFormat.XLSX, ExcelVersion.Excel2013, password);
}
//...Use shortcut Ctrl + S to save Spreadsheet as excel file.
NOTE