- Initial Load
- Method
- User Interface
Contact Support
Formulas
15 Mar 201912 minutes to read
Formulas are used for calculation of data in sheet. You can refer the formula cell reference in following ways,
- Cell reference from same sheet
- Cell reference from different sheets
You can set formula for a cell in following ways,
- Initial Load
- Method
- User Interface
Initial Load
You can set formula for a cell by specifying Value property in cell data binding. The following code example describes the above behavior,
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet")
.Sheets(sheet =>
{
sheet.Rows(rows =>
{
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("1").Add();
}).Add();
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("2").Add();
}).Add();
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("=SUM(A1,A2)").Add();
}).Add();
}).Add();
sheet.Rows(rows =>
{
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("=Sheet1!A1:A2").Add();
}).Add();
}).Add();
})
)The following output is displayed as a result of the above code example.
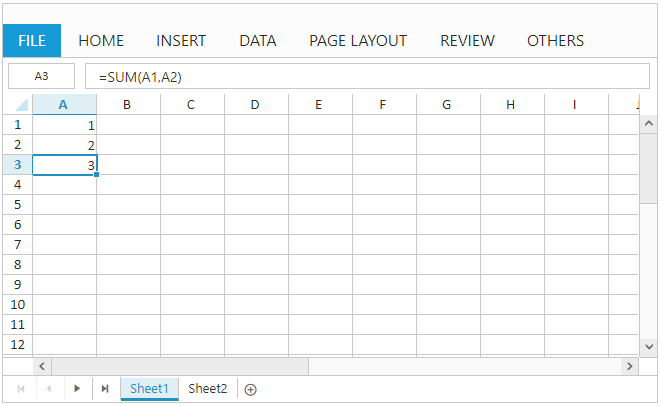
Cell Reference from Same sheet
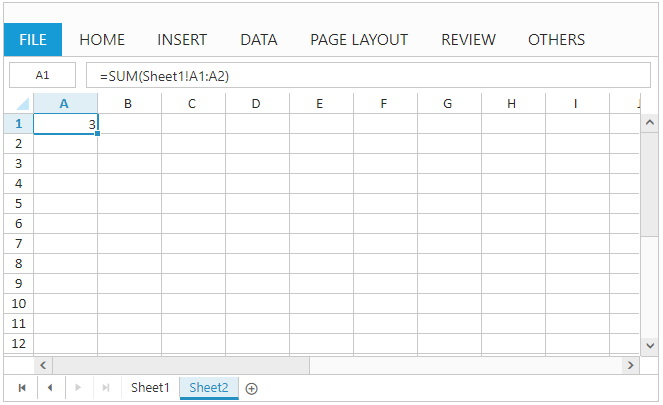
Cell Reference from different sheets
Method
You can set formula for a cell using updateCellValue method. The following code example describes the above behavior,
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet")
.Sheets(sheet =>
{
sheet.Rows(rows =>
{
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("1").Add();
}).Add();
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("2").Add();
}).Add();
}).Add();
})
.ClientSideEvents(events => events.LoadComplete("loadComplete"))
)
<script>
function loadComplete() {
this.XLEdit.updateCellValue({ rowIndex: 2, colIndex: 0 }, "=SUM(A1,A2)");
}
</script>The following output is displayed as a result of the above code example.
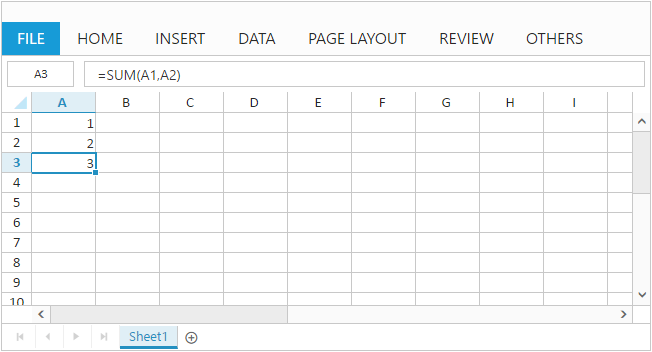
User Interface
You can set formula for a cell by edit and save a cell through user interface using Editing feature.
The following code example and screenshot describes the above behavior,
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet")
.Sheets(sheet =>
{
sheet.Rows(rows =>
{
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("1").Add();
}).Add();
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("2").Add();
}).Add();
}).Add();
})
)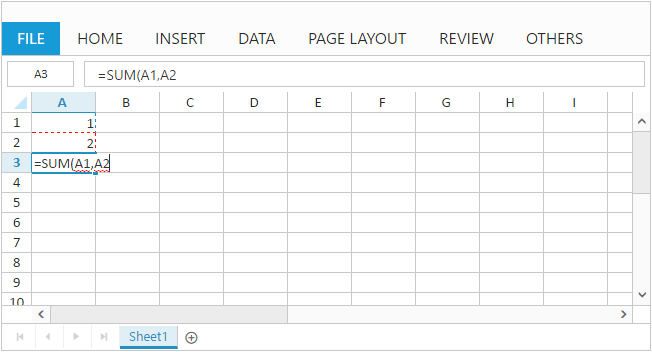
The following output is displayed while saving edited cell with above code example.

NOTE
- The list of supported formulas can be find in following
link- Constant values, cell references, formulas and named ranges can be passed as argument to formulas
- Selection can be used to mention cell references within formula
User Defined Functions
The list of formulas supported in Spreadsheet is sufficient for most of your calculations. If not, you can create and use your own function using user defined function option. You can add user defined function to Spreadsheet in following ways,
-
Initial Load
-
Method
Initial Load
You can add your own function to Spreadsheet at initial load with CustomFormulas property. The following code example describes the above behavior,
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet")
.Sheets(sheet =>
{
sheet.Rows(rows =>
{
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("1").Add();
}).Add();
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("2").Add();
}).Add();
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("=CUSTOMTOTAL(A1,A2,3)").Add();
}).Add();
}).Add();
})
.CustomFormulas(formula => { formula.FormulaName("CUSTOMTOTAL").FunctionName("customTotal").Add(); })
)
<script>
function customTotal(args) {
var param1, param2, param3, value, excelObj = $('#Spreadsheet').data("ejSpreadsheet"),
argument = excelObj.getValueFromFormulaArg(args);
param1 = argument["arg1"];
param2 = argument["arg2"];
param3 = argument["arg3"];
value = param1 * param2 + param3;
return value;
}
</script>The following output is displayed as a result of the above code example.
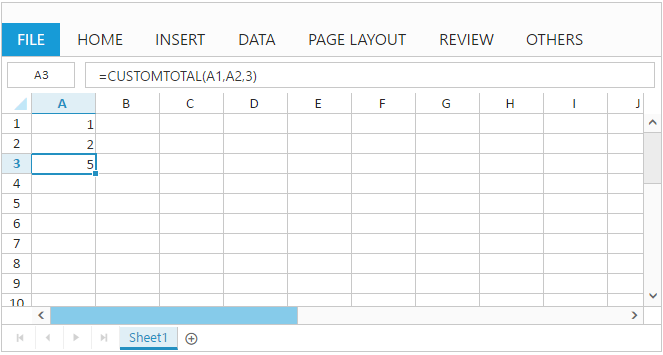
Method
You can add your own function to Spreadsheet using addCustomFormula method. The following code example describes the above behavior,
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet")
.Sheets(sheet =>
{
sheet.Rows(rows =>
{
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("1").Add();
}).Add();
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("2").Add();
}).Add();
}).Add();
})
.ClientSideEvents(events => events.LoadComplete("loadComplete"))
)
<script>
function loadComplete() {
this.addCustomFormula("CUSTOMTOTAL", "customTotal");
this.XLEdit.updateCellValue({ rowIndex: 2, colIndex: 0 }, "=CUSTOMTOTAL(A1,A2,3)");
}
function customTotal(args) {
var param1, param2, param3, value, excelObj = $('#Spreadsheet').data("ejSpreadsheet"),
argument = excelObj.getValueFromFormulaArg(args);
param1 = argument["arg1"];
param2 = argument["arg2"];
param3 = argument["arg3"];
value = param1 * param2 + param3;
return value;
}
</script>The following output is displayed as a result of the above code example.

To remove user defined function from Spreadsheet use removeCustomFormula method.
Named Ranges
To understand the purpose of cell reference or table, you can define a meaningful name using named ranges support. By using names, you can make your formula much easier to understand and maintain. You can add named ranges to Spreadsheet in following ways,
-
Initial Load
-
Method
-
User Interface
Initial Load
To add named ranges at initial load by using nameManager API, and also you can specify the name and address of the range by using name and refersto API. You can find the added named range list collection in Spreadsheet by accessing nameManager API.
The following code example describes the above behavior,
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet")
.Sheets(sheet =>
{
sheet.Rows(rows =>
{
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("1").Add();
}).Add();
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("2").Add();
}).Add();
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("=SUM(inputRange)").Add();
}).Add();
}).Add();
})
.NameManager(manager => { manager.Name("inputRange").RefersTo("=Sheet1!$A$1:$A$2").Add(); })
)The following output is displayed as a result of the above code example.
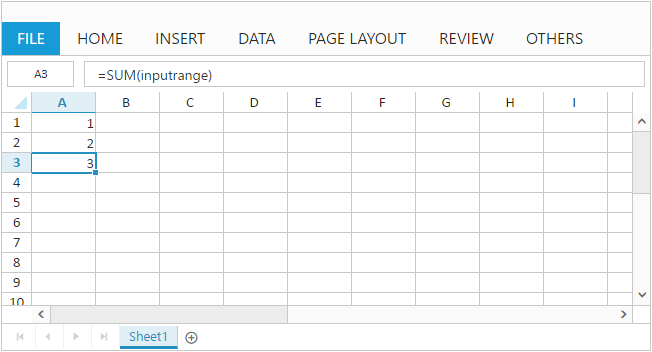
Method
You can add named range to Spreadsheet with addNamedRange method and it can be removed with removeNamedRange method.
The following code example describes the above behavior,
@(Html.EJ().Spreadsheet<object>("Spreadsheet")
.Sheets(sheet =>
{
sheet.Rows(rows =>
{
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("1").Add();
}).Add();
rows.Cells(cells =>
{
cells.Value("2").Add();
}).Add();
}).Add();
})
.ClientSideEvents(events => events.LoadComplete("loadComplete"))
)
<script>
function loadComplete() {
this.XLRibbon.addNamedRange("inputRange", "=Sheet1!$A$1:$A$2", "named range demo", this.getActiveSheetIndex());
this.XLEdit.updateCellValue({rowIndex: 2, colIndex: 0}, "=SUM(inputRange)");
}
</script>The following output is displayed as a result of the above code example.

User Interface
You can define name for range of cells through user interface using Define Name option in OTHERS tab. The following screenshot describes the above behavior,
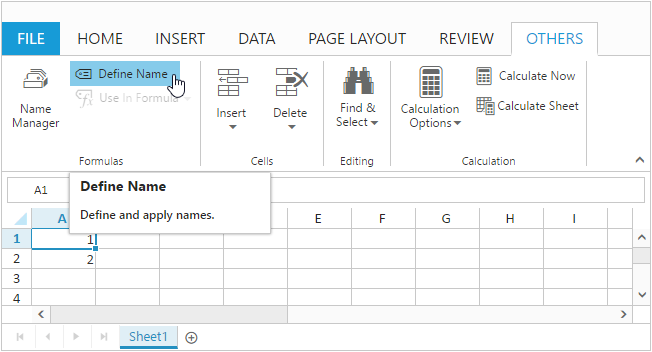
NOTE
- Defining name for cell reference or table will be accessible across all sheets.
- Named Ranges will be displayed in Name Manger dialog box.
Formula Bar
Formula bar is used to edit or enter cell data in much easier way. To enable formula bar set AllowFormulaBar as true.
Auto Sum
To sum a row or column of data, select a cell next to the data you want to sum, click AutoSum on the HOME tab and press enter. To enable auto sum set AllowAutoSum API as true.
The auto sum options in ribbon is used to perform basic operations like sum, average, count, minimum, maximum etc.