How can I help you?
Getting Started with .NET MAUI AI AssistView
26 Jun 202524 minutes to read
This section guides you through setting up and configuring AI AssistView (SfAIAssistView) in your .NET MAUI application. Follow the steps below to add a basic AI AssistView to your project.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure the following are in place:
- Install .NET 8 SDK or later.
- Set up a .NET MAUI environment with Visual Studio 2022 (v17.8 or later).
Step 1: Create a .NET MAUI project
- Go to File > New > Project and choose the .NET MAUI App template.
- Name the project and choose a location. Then, click Next.
- Select the .NET framework version and click Create.
Step 2: Install the Syncfusion® MAUI AI AssistView NuGet package
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and choose Manage NuGet Packages.
- Search for Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView and install the latest version.
- Ensure the necessary dependencies are installed correctly, and the project is restored.
Step 3: Register the handler
The Syncfusion.Maui.Core is a dependent package for all Syncfusion controls of .NET MAUI. In the MauiProgram.cs file, register the handler for Syncfusion core.
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Syncfusion.Maui.Core.Hosting;
namespace GettingStarted
{
public class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
builder.ConfigureSyncfusionCore();
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 4: Add a basic AI AssistView
- To initialize the control, import the
Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistViewnamespace into your code. - Initialize SfAIAssistView.
<ContentPage>
. . .
xmlns:syncfusion="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView">
<syncfusion:SfAIAssistView />
</ContentPage>using Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView;
. . .
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfAIAssistView sfAIAssistView = new SfAIAssistView();
this.Content = sfAIAssistView;
}
}Step 5: Define the view model
Next, create a view model class and initialize the collection of AssistItem instance as follows
using Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView;
public class GettingStartedViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
/// <summary>
/// Collection of assistItem in a conversation.
/// </summary>
private ObservableCollection<IAssistItem> assistItems;
public GettingStartedViewModel()
{
this.assistItems = new ObservableCollection<IAssistItem>();
this.GenerateAssistItems();
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the collection of AssistItem of a conversation.
/// </summary>
public ObservableCollection<IAssistItem> AssistItems
{
get
{
return this.assistItems;
}
set
{
this.assistItems = value;
}
}
private async void GenerateAssistItems()
{
// Adding a request item
AssistItem requestItem = new AssistItem()
{
Text = "listening",
IsRequested = true
};
// Add the request item to the collection
this.AssistItems.Add(requestItem);
// Generating response item
await GetResult(requestItem);
}
private async Task GetResult(AssistItem requestItem)
{
await Task.Delay(1000).ConfigureAwait(true);
AssistItem responseItem = new AssistItem()
{
Text ="Types of Listening : For a good communication, it is not only enough to convey the information efficiently, but it also needs to include good listening skill. Common types of Listening are Active listening and Passive listening.",
IsRequested = false,
};
// Add the response item to the collection
this.AssistItems.Add(responseItem);
}
/// <summary>
/// Property changed handler.
/// </summary>
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
/// <summary>
/// Occurs when property is changed.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="propName">changed property name</param>
public void RaisePropertyChanged(string propName)
{
if (this.PropertyChanged != null)
{
this.PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propName));
}
}
}NOTE
The
SfAIAssistView.AssistItemsproperty is of typeIList<IAssistItem>. To ensure the AssistItems property functions correctly, it is recommended to use a collection property in the ViewModel with the same type, such asObservableCollection<IAssistItem>.
Bind AssistItems
Set the ViewModel as the BindingContext for the AI AssistView or the parent ContentPage. This allows data binding between the UI and the ViewModel properties.
To populate AI AssistView, bind the assist items in ViewModel to AssistItems property of AI AssistView.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:syncfusion="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:GettingStarted.ViewModel"
x:Class="GettingStarted.MainPage">
<ContentPage.BindingContext>
<local:GettingStartedViewModel/>
</ContentPage.BindingContext>
<ContentPage.Content>
<syncfusion:SfAIAssistView x:Name="sfAIAssistView"
AssistItems="{Binding AssistItems}"/>
</ContentPage.Content>
</ContentPage>public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfAIAssistView aiAssistView = new SfAIAssistView();
GettingStartedViewModel viewModel = new GettingStartedViewModel();
this.aiAssistView.AssistItems = viewModel.AssistItems;
this.Content = aiAssistView;
}
}Step 6: Running the application
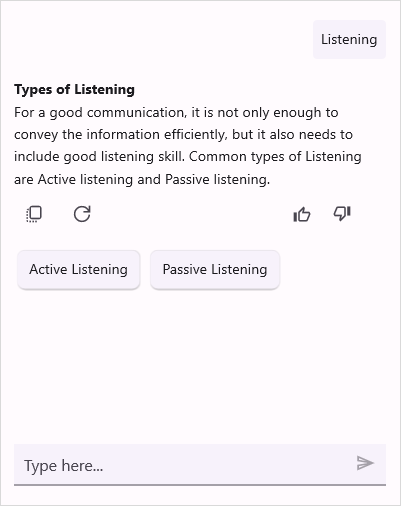
Press F5 to build and run the application. Once compiled, the AI AssistView will be displayed with the data provided.
Here is the result of the previous codes,
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure the following are in place:
- Install .NET 8 SDK or later is installed.
- Set up a .NET MAUI environment with Visual Studio Code.
- Ensure that the .NET MAUI extension is installed and configured as described here.
Step 1: Create a new .NET MAUI project
- Open the command palette by pressing
Ctrl+Shift+Pand type .NET:New Project and enter. - Choose the .NET MAUI App template.
- Select the project location, type the project name and press Enter.
- Then choose Create project.
Step 2: Install the Syncfusion® MAUI AI AssistView NuGet package
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and choose Manage NuGet Packages.
- Search for Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView and install the latest version.
- Ensure the necessary dependencies are installed correctly, and the project is restored.
Step 3: Register the handler
The Syncfusion.Maui.Core is a dependent package for all Syncfusion controls of .NET MAUI. In the MauiProgram.cs file, register the handler for Syncfusion core.
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Syncfusion.Maui.Core.Hosting;
namespace GettingStarted
{
public class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
builder.ConfigureSyncfusionCore();
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 4: Add a basic AI AssistView
- To initialize the control, import the
Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistViewnamespace into your code. - Initialize SfAIAssistView.
<ContentPage>
. . .
xmlns:syncfusion="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView">
<syncfusion:SfAIAssistView />
</ContentPage>using Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView;
. . .
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfAIAssistView sfAIAssistView = new SfAIAssistView();
this.Content = sfAIAssistView;
}
}Step 5: Define the view model
Next, create a view model class and initialize the collection of AssistItem instance as follows
using Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView;
public class GettingStartedViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
/// <summary>
/// Collection of assistItem in a conversation.
/// </summary>
private ObservableCollection<IAssistItem> assistItems;
public GettingStartedViewModel()
{
this.assistItems = new ObservableCollection<IAssistItem>();
this.GenerateAssistItems();
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the collection of AssistItem of a conversation.
/// </summary>
public ObservableCollection<IAssistItem> AssistItems
{
get
{
return this.assistItems;
}
set
{
this.assistItems = value;
}
}
private async void GenerateAssistItems()
{
// Adding a request item
AssistItem requestItem = new AssistItem()
{
Text = "listening",
IsRequested = true
};
// Add the request item to the collection
this.AssistItems.Add(requestItem);
// Generating response item
await GetResult(requestItem);
}
private async Task GetResult(AssistItem requestItem)
{
await Task.Delay(1000).ConfigureAwait(true);
AssistItem responseItem = new AssistItem()
{
Text ="Types of Listening : For a good communication, it is not only enough to convey the information efficiently, but it also needs to include good listening skill. Common types of Listening are Active listening and Passive listening.",
IsRequested = false,
};
// Add the response item to the collection
this.AssistItems.Add(responseItem);
}
/// <summary>
/// Property changed handler.
/// </summary>
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
/// <summary>
/// Occurs when property is changed.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="propName">changed property name</param>
public void RaisePropertyChanged(string propName)
{
if (this.PropertyChanged != null)
{
this.PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propName));
}
}
}NOTE
The
SfAIAssistView.AssistItemsproperty is of typeIList<IAssistItem>. To ensure the AssistItems property functions correctly, it is recommended to use a collection property in the ViewModel with the same type, such asObservableCollection<IAssistItem>.
Bind AssistItems
Set the ViewModel as the BindingContext for the AI AssistView or the parent ContentPage. This allows data binding between the UI and the ViewModel properties.
To populate AI AssistView, bind the assist items in ViewModel to AssistItems property of AI AssistView.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:syncfusion="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:GettingStarted.ViewModel"
x:Class="GettingStarted.MainPage">
<ContentPage.BindingContext>
<local:GettingStartedViewModel/>
</ContentPage.BindingContext>
<ContentPage.Content>
<syncfusion:SfAIAssistView x:Name="sfAIAssistView"
AssistItems="{Binding AssistItems}"/>
</ContentPage.Content>
</ContentPage>public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfAIAssistView aiAssistView = new SfAIAssistView();
GettingStartedViewModel viewModel = new GettingStartedViewModel();
this.aiAssistView.AssistItems = viewModel.AssistItems;
this.Content = aiAssistView;
}
}Step 6: Running the application
Press F5 to build and run the application. Once compiled, the AI AssistView will be displayed with the data provided.
Here is the result of the previous codes,

Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure the following are set up:
- Ensure you have the latest version of JetBrains Rider.
- Install .NET 8 SDK or later is installed.
- Make sure the MAUI workloads are installed and configured as described here.
Step 1: Create a new .NET MAUI project
- Go to File > New Solution, Select .NET (C#) and choose the .NET MAUI App template.
- Enter the Project Name, Solution Name, and Location.
- Select the .NET framework version and click Create.
Step 2: Install the Syncfusion® MAUI AI AssistView NuGet package
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and choose Manage NuGet Packages.
- Search for Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView and install the latest version.
- Ensure the necessary dependencies are installed correctly, and the project is restored. If not, Open the Terminal in Rider and manually run:
dotnet restore
Step 3: Register the handler
The Syncfusion.Maui.Core is a dependent package for all Syncfusion controls of .NET MAUI. In the MauiProgram.cs file, register the handler for Syncfusion core.
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Syncfusion.Maui.Core.Hosting;
namespace GettingStarted
{
public class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
builder.ConfigureSyncfusionCore();
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 4: Add a basic AI AssistView
- To initialize the control, import the
Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistViewnamespace into your code. - Initialize SfAIAssistView.
<ContentPage>
. . .
xmlns:syncfusion="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView">
<syncfusion:SfAIAssistView />
</ContentPage>using Syncfusion.Maui.AIAssistView;
. . .
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfAIAssistView sfAIAssistView = new SfAIAssistView();
this.Content = sfAIAssistView;
}
}Request and response item
The IsRequested property is used to determine whether a item is a Request or a Response. If IsRequested property is set to true, the item is a Request item.
Request item
These are the items sent by the user. They typically appear aligned to the right side of the window to visually differentiate them as user inputs.
AssistItem requestItem = new AssistItem()
{
Text = "listening",
IsRequested = true
};Response item
These are messages generated by the AI in reply to a request. They are usually aligned to the left side of the window to indicate that they are responses.
AssistItem responseItem = new AssistItem()
{
Text ="Types of Listening : For a good communication, it is not only enough to convey the information efficiently, but it also needs to include good listening skill. Common types of Listening are Active listening and Passive listening.",
IsRequested = false,
};NOTE