BPMN Shapes
BPMN shapes are used to represent the internal business procedure in a graphical notation and enables you to communicate the procedures in a standard manner. To create a BPMN shape, the type of the node should be set as “bpmn” and its shape should be set as any one of the built-in shape. BPMN Shapes. The following code example illustrates how to create a simple business process.
<div ng-controller="diagramCtrl">
<ej-diagram id="diagram" e-height="500px" e-width="700px" e-nodes="nodes">
</ej-diagram>
</div>var nodes = [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
labels: [{
text: "End Event"
}],
//Sets the type of shape as BPMN
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the type of bpmn shape
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Event,
//Sets type of the Event
event: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNEvents.End
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
NOTE
The default value for the property
shapeis “event”.
The list of BPMN shapes are as follows.
| Shape | Image |
|---|---|
| Event | 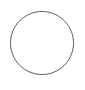 |
| Gateway | 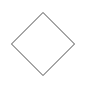 |
| Task | 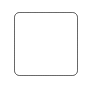 |
| Message |  |
| DataSource | 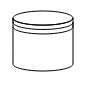 |
| DataObject | 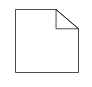 |
| Group |  |
The BPMN shapes and its types are explained as follows.
Event
An event is notated with a circle and it represents an event in a business process. The type of events are as follows.
- Start
- End
- Intermediate
The event property of the node allows you to define the type of the event. The default value of the event is “start”. The following code example illustrates how to create a BPMN Event.
var nodes = [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
//Sets the type as BPMN
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the shape as BPMN Event
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Event,
//Sets type of the Event
event: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNEvents.End,
//Sets sub-type of the Event
trigger: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNTriggers.None
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
Event triggers are notated as icons inside the circle and they represent the specific details of the process. The triggers property of node allows you to set the type of trigger and by default, it is set as “none”. The following table illustrates the type of event triggers.
| Triggers | Start | Non-Interrupting Start | Intermediate | Non-Interrupting Intermediate | Throwing Intermediate | End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 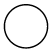 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Message |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Timer |  |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Conditional |  |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Link |  |
 |
||||
| Signal |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Error |  |
 |
 |
|||
| Escalation |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Termination |  |
|||||
| Compensation |  |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Cancel |  |
 |
||||
| Multiple | 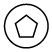 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Parallel |  |
 |
 |
 |
Gateway
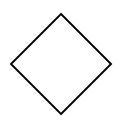
Gateway is used to control the flow of a process. It is represented as a diamond shape. To create a gateway, the shape property of node should be set as “gateway” and the gateway property can be set with any of the appropriate Gateways. The following code example illustrates how to create a BPMN Gateway.
var nodes = [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the shape as Gateway
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Gateway,
//Sets the type of BPMN Gateway
gateway: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNGateways.None,
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
NOTE
By default, the
gatewaywill be set as “none”.
There are several types of gateways as tabulated
| Gateways | Image |
|---|---|
| Exclusive |  |
| Parallel |  |
| Inclusive | 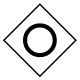 |
| Complex |  |
| EventBased | 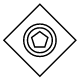 |
| ExclusiveEventBased | 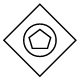 |
| ParallelEventBased |  |
Activity
The activity is the task that is performed in a business process. It is represented by a rounded rectangle.
There are two types of activities .They are listed as follows.
- Task – Occurs within a process and it is not broken down to finer level of detail.
- Subprocess – Occurs within a process and it is broken down to finer level of detail.
To create a BPMN activity, you need to set the shape as “activity”. You also need to set the type of the BPMN Activity by using the activity property of node. By default, the type of the activity is set as “task”. The following code example illustrates how to create an activity.
var nodes = [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the bpmn shape as activity
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
//Sets the type of BPMN Activity
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.Task,
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
The different activities of BPMN process are listed as follows.
Tasks
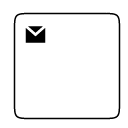
The task property of node allows you to define the type of task such as sending, receiving, user based task etc… By default, the type property of task is set as “none”. The following code illustrates how to create different types of BPMN tasks.
var nodes = [{
name: "task",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the type of bpmn shape
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
//Sets the type of BPMN Activity
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.Task,
//Sets the type of BPMN Task Activity
task: {
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNTasks.Send
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
The various types of BPMN tasks are tabulated as follows.
| Task Type | Image |
|---|---|
| Service | 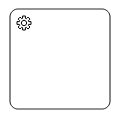 |
| Send |  |
| Receive |  |
| Instantiating Receive |  |
| Manual |  |
| Business Rule |  |
| User |  |
| Script |  |
Subprocess
A sub-process is a group of tasks which is used to hide or reveal details of additional levels which can be done using collapsed property .
var nodes = [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the type of bpmn shape
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
//Sets the type of BPMN Activity
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.SubProcess,
//Sets the state of BPMN Subprocess
subProcess: {
collapsed: true,
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});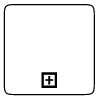
The different types of subprocess are as follows.
- Event Subprocess
- Transaction
Event Subprocess
A Sub-process is defined as an Event Sub-process when it is triggered by an event. An event-subprocess is placed within another subprocess which is not part of the normal flow of its parent process . You can set event to a sub-process with the event and trigger property of subprocess.
var nodes = [{
name: "eventSubProcess",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.SubProcess,
//Creates event subprocess
subProcess: {
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNSubProcessTypes.Event,
event: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNEvents.Start,
trigger: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNTriggers.Message
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
Transaction Subprocess
An transaction is a set of activities that logically belong together, in which all contained activities must complete their parts of the transaction; otherwise the process is undone. The execution result of a transaction is one of Successful Completion, Unsuccessful Completion (Cancel), and Hazard (Exception). The events property of subprocess allows to represent these results as an event attached to the subprocess.
var nodes = [{
name: "transactionSubProcess",
width: 130,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.SubProcess,
//Creates tranaction subprocess
subProcess: {
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNSubProcessTypes.Transaction,
// Defines a collection of events to be attached
events: [
//Defines type of the event and the position relative to the subprocess.
{
event: "intermediate",
trigger: "cancel",
offset: {
x: 0.25,
y: 1
}
},
{
event: "intermediate",
trigger: "error",
offset: {
x: 0.75,
y: 1
}
}
]
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
Processes
Processes is a array collection that defines the children values for BPMN subprocess.
<div id="diagram"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var nodes = [{
name: "group",
offsetX: 500,
offsetY: 300,
width: 300,
height: 200,
type: "bpmn",
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Group,
children: [{
name: "node",
marginLeft: 15,
marginTop: 15,
width: 250,
height: 150,
type: "bpmn",
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.SubProcess,
subProcess: {
collapsed: false,
Processes: [{
name: "subnode01",
marginLeft: 20,
marginTop: 50,
width: 30,
height: 30,
type: "bpmn",
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Event
},
{
name: "subnode02",
marginLeft: 90,
marginTop: 25,
width: 100,
height: 80,
type: "bpmn",
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.Task,
task: {
type: "user"
},
annotation: {
text: "Review Customer Rating",
length: 125,
angle: 24,
width: 100,
height: 30
}
}
]
}
}]
}];
var connectors = [{
name: "connector1",
sourceNode: "subnode01",
targetNode: "subnode02"
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
</script>
Loop
Loop is a task that is internally being looped. The loop property of task allows you to define the type of loop. The default value for loop is “none”.
var diagram = $("#diagram").ejDiagram("instance");
var node = {
name: "task",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the type of BPMN shape
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
//Sets the type of BPMN Activity
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.Task,
//Sets the type of bpmn loops.
task: {
loop: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNLoops.Standard
}
};
diagram.add(node);
node = {
name: "subprocess",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
//Sets the type of BPMN activity
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.SubProcess,
//Sets the type of bpmn loops.
subProcess: {
loop: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNLoops.Standard
}
};
diagram.add(node);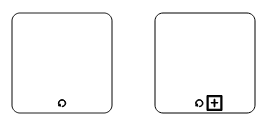
The following table contains various types of BPMN loops.
| Loops | Task | SubProcess |
|---|---|---|
| Standard |  |
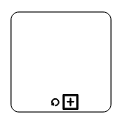 |
| SequenceMultiInstance | 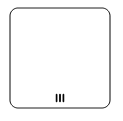 |
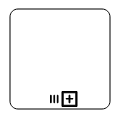 |
| ParallelMultiInstance | 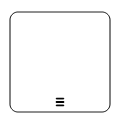 |
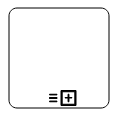 |
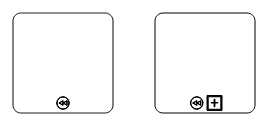
Compensation
Compensation is triggered when operation is partially failed and you can enable it with the compensation property of task.
var nodes = [];
nodes.push({
name: "task",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity
//Sets the type of BPMN Activity
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.Task,
//Creates compensation task
task: {
compensation: true
}
});
nodes.push({
name: "subprocess",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
//Sets the type of BPMN Activity
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.SubProcess,
//Creates compensation subprocess
subProcess: {
compensation: true
}
});
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
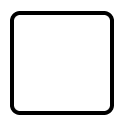
Call
A call activity is a global sub-process that is reused at various points of the business flow and you can set it with the call property of task.
var nodes = [{
name: "task",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
//Sets the type of BPMN Activity
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.Task,
//Creates a call task
task: {
call: true
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
Ad-Hoc
An ad hoc subprocess is a group of tasks that are executed in any order or skipped in order to fulfill the end condition and you can set it with the adhoc property of subprocess.
var nodes = [{
name: "task",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.SubProcess,
//Creates ad hoc subprocess
subProcess: {
adhoc: true
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
Boundary
Boundary represents the type of task that is being processed. The boundary property of sub process allows you to define the type of boundary. By default, it is set as “default”.
var nodes = [{
name: "task",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Activity,
activity: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNActivity.SubProcess,
//Adds boundary to a subprocess
subProcess: {
boundary: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNBoundary.Call
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});The following table contains various types of BPMN boundaries.
| Boundary | Image |
|---|---|
| Call | 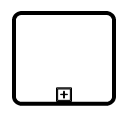 |
| Event |  |
| Default | 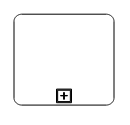 |
Data
A data object represents information flowing through the process, such as data placed into the process, data resulting from the process, data that needs to be collected, or data that must be stored. To define a data object, set the shape as “dataobject” and type property defines whether data is an input or a output. You can create multiple instances of data object with the collection property of data.
var nodes = [{
name: "dataObject",
width: 75,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
//Sets the type of the shape
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the type of BPMN Shape
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.DataObject,
//Sets collection as true when Dataobject is not a Single instance
data: {
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNDataObjects.Input,
collection: true
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});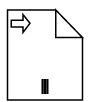
The following table contains various representation of BPMN Data Object.
| Boundary | Image |
|---|---|
| Collection Data Object | 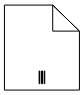 |
| Data Input | 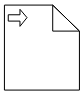 |
| Data Ouptput |  |
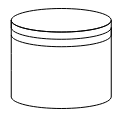
Datasource
DataSource is used to store or access data associated with a business process. To create a data source, set the shape as “datasource”. The following code example illustrate how to create data source.
var nodes = [{
name: "dataSource",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
//Sets type of the shape
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the type of bpmn shape
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.DataSource,
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
Artifact
Artifact is used to show additional information about a Process in order to make it easier to understand. There are 2 types of artifacts in BPMN.
- Text Annotation
- Group
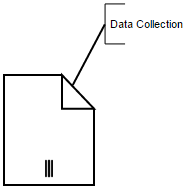
Text Annoatation
A BPMN object can be associated with a text annotation which does not affect the flow but gives details about objects within a flow. The annotation property of the node is used to connect an annotation element to the BPNN node.
var nodes = [{
name: "data",
width: 75,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
//Sets type of the shape
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the type of bpmn shape
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.DataObject,
//Sets collection as true when Dataobject is not a Single instance
data: {
collection: true
},
annotation: {
//Sets the text to annotate the bpmn shape
text: "Data Collection",
//Sets the angle between the bpmn shape and the annotation
angle: 45,
//Sets the dimensions of the text
width: 100,
height: 40,
//Sets the distance between the bpmn shape and the annotation
length: 150
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
Group
A group is used to frame a part of the diagram, shows that elements included in it are logically belong together and don’t have any other semantics other than organizing elements. To create a Group, the shape property of node should be set as “group”. The following code example illustrates how to create a BPMN Group.
var nodes = [{
name: "group",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "black",
//Sets type of the shape
type: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.Shapes.BPMN,
//Sets the type of bpmn shape
shape: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.BPMNShapes.Group,
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.nodes = nodes;
});
BPMN Flows
BPMN Flows are lines that connects BPMN flow objects.
Association
BPMN Association flow is used to link flow objects with its corresponding text or artifact. An association is represented as a dotted graphical line with opened arrow. The type of association are as follows.
- Directional
- BiDirectional
- Default
The association property allows you to define the type of association.The following code example illustrates how to create an association.
var connectors = [{
name: "connect1",
sourcePoint: {
x: 100,
y: 200
},
targetPoint: {
x: 300,
y: 200
},
segments: [{
type: "straight"
}],
shape: {
type: "bpmn",
//Sets the type of the flow as association
flow: "association",
//Sets the type of association
association: "bidirectional"
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.connectors = connectors;
});
The following table demonstrates the visual representation of assosiation flows.
| Association | Image |
|---|---|
| Default |  |
| Directional |  |
| BiDirectional |  |
NOTE
The default value for the property
associationis “default”.
Sequence
A Sequence flow shows the order in which the activities are performed in a BPMN Process and is represented with a solid graphical line.The type of sequence are as follows.
- Normal
- Conditional
- Default
The sequence property allows you to define the type of sequence.The following code example illustrates how to create a sequence flow.
var connectors = [{
name: "connect1",
sourcePoint: {
x: 100,
y: 200
},
targetPoint: {
x: 300,
y: 200
},
segments: [{
type: "straight"
}],
shape: {
type: "bpmn",
flow: "sequence",
//Sets the type of srquence flow
sequence: "conditional"
}
}];
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.connectors = connectors;
});
The following table contains various representation of sequence flows.
| Sequence | Image |
|---|---|
| Default | 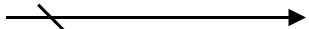 |
| Conditional |  |
| Normal |  |
NOTE
The default value for the property
sequenceis “normal”.
Message
A Message flow shows the flow of messages between two Participents.A message flow is represented by dashed line.The type of message are as follows.
- InitiatingMessage
- NonInitiatingMessage
- Default
The message property allows you to define the type of message.The following code example illustrates how to define a message flow.
var connectors = [{
name: "connect1",
sourcePoint: {
x: 100,
y: 200
},
targetPoint: {
x: 300,
y: 200
},
segments: [{
type: "straight"
}],
shape: {
type: "bpmn",
flow: "message",
//Sets the type of message flow
message: "initiatingmessage"
}
}]
syncApp.controller('diagramCtrl', function($scope) {
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model.
$scope.connectors = connectors;
});
The following table contains various representation of message flows.
| Message | Image |
|---|---|
| Default |  |
| InitiatingMessage |  |
| NonInitiatingMessage |  |
NOTE
The default value for the property
messageis “default”.