How can I help you?
Virtualized Binding (Performance Improvement) in WPF Pivot Grid
27 Feb 202513 minutes to read
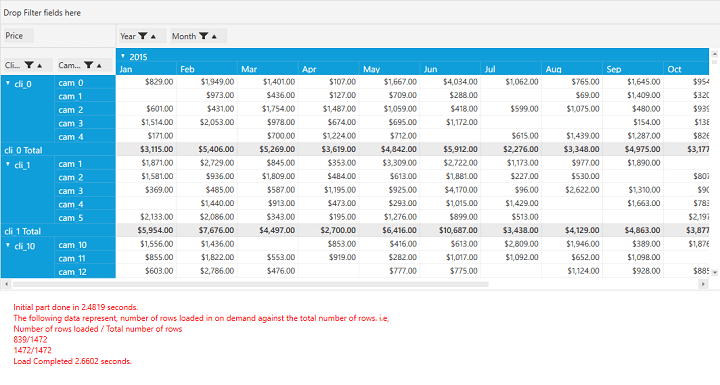
It provides high loading performance for a large set of records. This feature helps to load data in the pivot grid on-demand using the Index Engine.
- UseIndexedEngine: Gets or sets whether an optimized algorithm that relies on indexing the raw data should be used to compute the pivot information.
- EnableOnDemandCalculations: Gets or sets whether the calculations are postponed until the value is requested through the indexer in the PivotEngine.
To achieve this, after defining the pivot grid control, set the EnableOnDemandCalculations and UseIndexedEngine properties of PivotEngine to true. The values for IndexEngine can be obtained by using the ItemObjectLookup() method and the time span should be calculated by using the Dispatcher.BeginInvoke() method. Refer to the following code sample.
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
DateTime _startIndex = DateTime.Now;
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
pivotGrid.PivotEngine.EnableOnDemandCalculations =
pivotGrid.PivotEngine.UseIndexedEngine = true;
pivotGrid.PivotEngine.GetValue = ItemObjectLookup;
ObservableCollection<ItemObject> itemsSourceObject =
(pivotGrid.DataContext as ViewModel.ViewModel).ItemObjectCollection;
pivotGrid.PivotEngine.PivotSchemaChanged +=
PivotEngine_PivotSchemaChanged;
pivotGrid.ItemSource = itemsSourceObject;
}
private void PivotEngine_PivotSchemaChanged(object sender, PivotSchemaChangedArgs e)
{
_startIndex = DateTime.Now;
ScrollViewer _scrollViewer = e.OriginalSource as ScrollViewer;
pivotGrid.Dispatcher.BeginInvoke(DispatcherPriority.SystemIdle, new Action(() =>
{
if (!pivotGrid.IgnoreRefresh)
{
if ((_scrollViewer.Content as TextBlock) != null)
&& (__scrollViewer.Content as TextBlock).Text = string.Empty);
CheckTime(_startIndex, "Initial part done in");
ContinueLoadingAsynchonolously(
pivotGrid.PivotEngine.IndexEngine, _startIndex);
}
}));
}
private void ContinueLoadingAsynchonolously(IndexEngine engine, DateTime startIndex)
{
pivotGrid.Dispatcher.BeginInvoke(new Action(() =>
{
if (engine != null && engine.HighRowLevel < engine.RowCount - 1)
{
int cutOff = Math.Min(engine.HighRowLevel + 800, engine.RowCount - 1);
object o = engine[cutOff, 0]; ////Gets 800 more rows from the pivot engine (on demand calculation).
if ((_scrollViewer.Content as TextBlock) != null)
{
(_scrollViewer.Content as TextBlock).Text +=
string.Format("\n{0}/{1}", engine.HighRowLevel, engine.RowCount - 1);
ContinueLoadingAsynchonolously(engine, startIndex); //Recursive call to update the rows of the PivotEngine until they reach high row level.
}
}
else
{
CheckTime(startIndex, "Load Completed");
}
}), DispatcherPriority.SystemIdle);
}
private void CheckTime(DateTime start, string label)
{
if (_textBlock != null)
_textBlock.Text += string.Format("\n{0} {1:0.0000} seconds.", label,
DateTime.Now.Subtract(start).TotalSeconds);
}
public IComparable ItemObjectLookup(object o, string name)
{
IComparable c = null;
var io = o as ItemObject;
if (io != null)
{
switch (name)
{
case "Date":
c = io.Date;
break;
case "Client":
c = io.Client;
break;
case "Campaign":
c = io.Campaign;
break;
case "Color":
c = io.Color;
break;
case "Shape":
c = io.Shape;
break;
case "Price":
c = io.Price;
break;
case "Spend":
c = io.Spend;
break;
case "ColH":
c = io.ColH;
break;
case "ColI":
c = io.ColI;
break;
case "ColJ":
c = io.ColJ;
break;
}
}
return c;
}
}
NOTE
You can refer to our WPF Pivot Grid feature tour page for its groundbreaking feature representations. You can also explore our WPF Pivot Grid example to knows how to organizes and summarizes business data and displays the result in a cross-table format.