- Adding an Expression Column
- Deleting an Expression Column
- Updating an Expression Column
- Configuring Expression Column in Widgets
Contact Support
Configuring Expression Columns
An expression column is used to create an expression which is a combination of data columns, operators and built-in functions. This expression column will act as a calculated measure that can be configured to widget like other normal numeric columns as a quantitative measure.
Adding an Expression Column
An expression field can be added either through the Settings menu with certain built-in functions based on the respective column or through the expression designer.
NOTE
Adding expression column through the Settings menu in table design view is not supported for SSAS data source currently.
Using Date Expressions
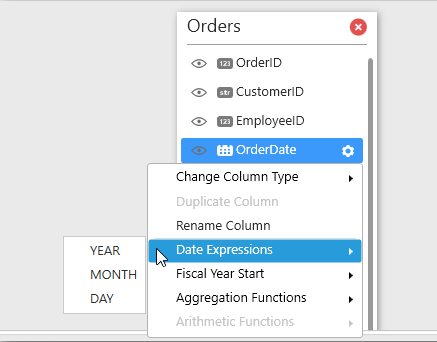
Using Aggregation Functions
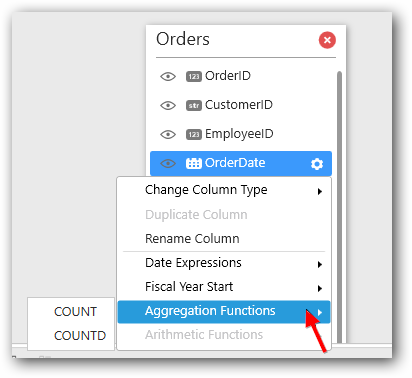
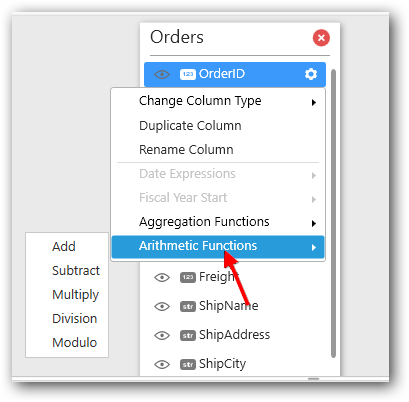
Using Arithmetic Function
Expression Designer can be launched either through the tools pane in the data design view highlighted below:
![]()
Or through the Expression Columns container in Widget View highlighted below:
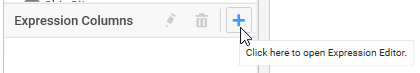
Click Add in the Expression Designer window to add a new expression column.
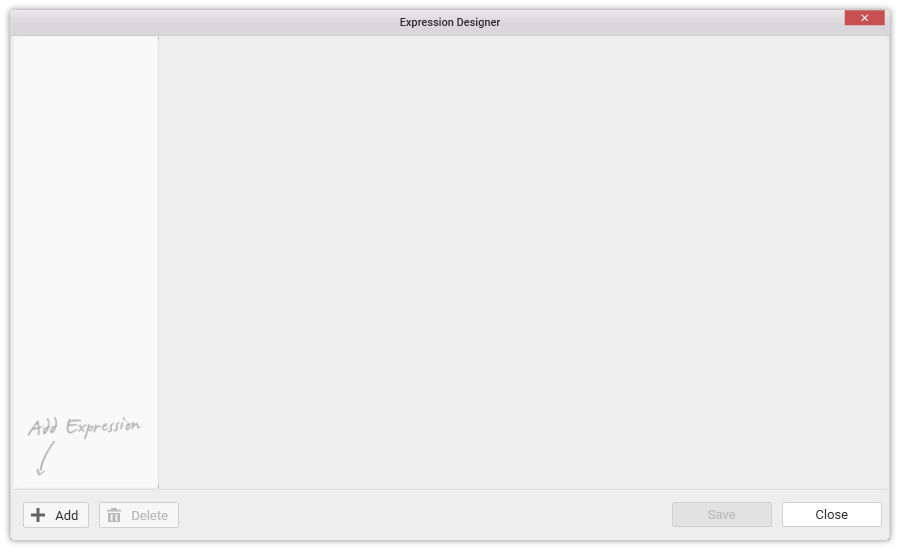
Enter a suitable name for the expression in the Name text area. By default, it will be Expression1.
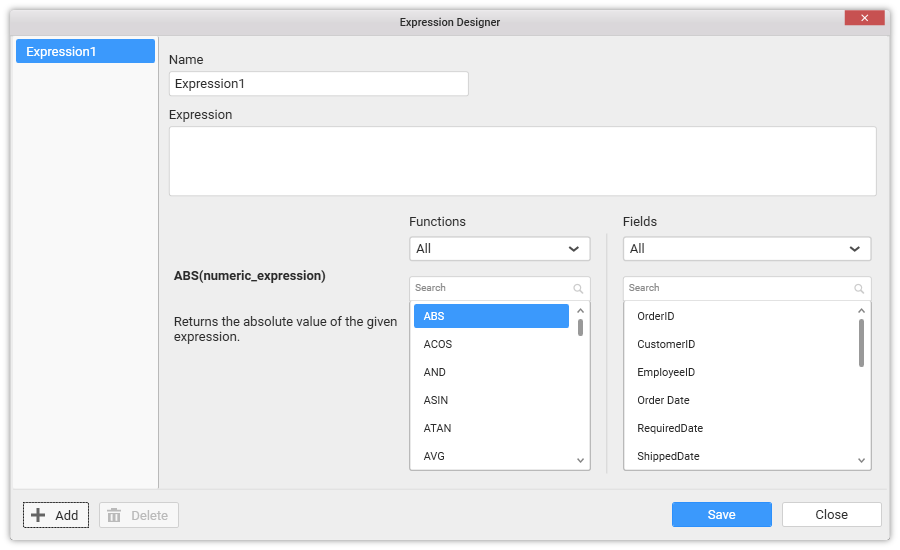
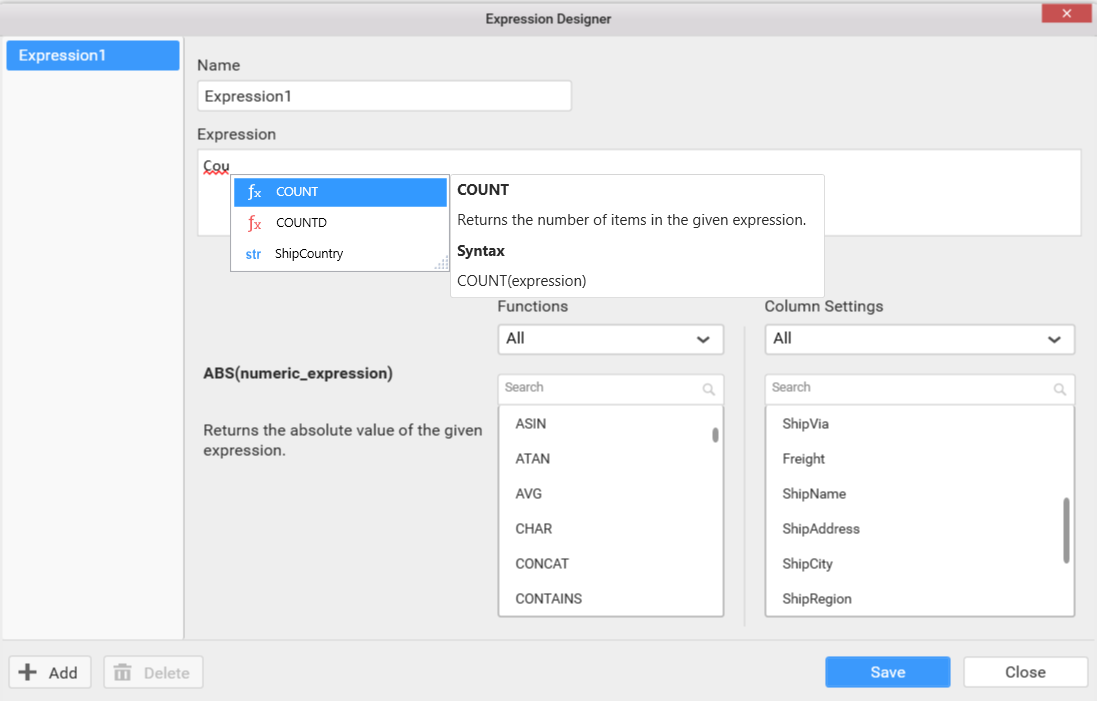
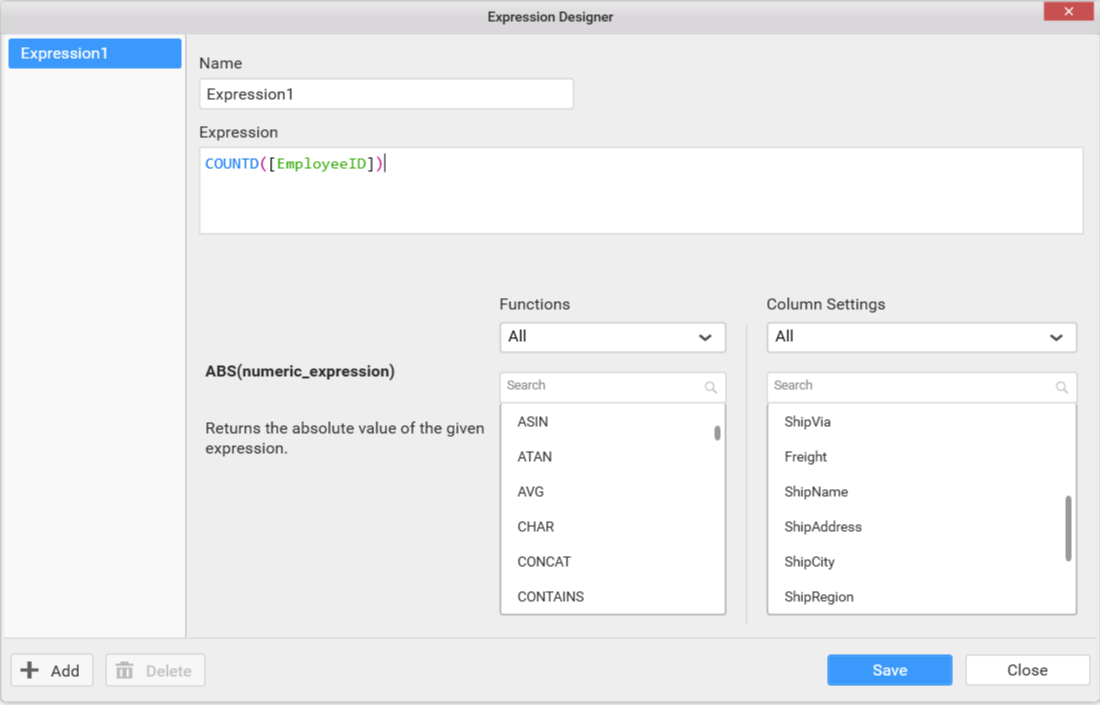
Enter the expression that you like to define in the Expression text area. The syntax for defining a simple expression is,
{function name(}[columnname]{operator[columnname]…}
Where, content within curly braces is optional.
Some expressions for reference:
1) YEAR([Order Date]) – To compute year of order date.
2) COUNTD([EmployeeID]) – To compute distinct count of employees.
3) [Freight]+100 – To compute the total with 100 added to Freight.
NOTE
Currently, SSAS data source supports only functions existing under Numbers category.
Following built-in functions are supported in Expression Designer.
</tr> </tr>| Category | Functions | Syntax & Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
| Numbers | ABS |
ABS(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the absolute value of the given expression. Example: ABS([Freight]) |
| ACOS |
ACOS(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the inverse cosine (also known as arccosine) of the given numeric expression. Example: ACOS(0.25) |
|
| ASIN |
ASIN(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the inverse sine (also known as arcsine) of the given numeric expression. Example: ASIN(0.25) |
|
| ATAN |
ATAN(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the inverse tangent (also known as arctangent) of the given numeric expression. Example: ATAN(0.25) |
|
| COS |
COS(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the cosine of the angle specified in radians, in the given expression. Example: COS(0.25) |
|
| DEGREES |
DEGREES(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the angle in degrees for the one specified in radians, in the given numeric expression. Example: DEGREES(1.5708) |
|
| EXP |
EXP(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the exponential value of the given expression. Example: EXP([UnitsInStock]) |
|
| LOG |
LOG(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the logarithm of the given expression to the specified base. Example: LOG(DEGREES(PI())) |
|
| PI |
PI() Description: Returns the constant value of PI. Example: EXP(PI()) |
|
| POWER |
POWER(expression1, expression2) Description: Returns the value of the given expression (expression1) to the specified power (expression2). Example: POWER(EXP(1),SIN(90)) |
|
| ROUND |
ROUND(numeric_expression) Description: Returns a rounded value. Example: ROUND(PI()) |
|
| RADIAN |
RADIAN(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the angle in radians for the one specified in degrees, in the given numeric expression. Example: RADIANS(90) | |
| SIGN |
SIGN(numeric_expression) Description: Returns a value representing the positive (+1), zero (0), or negative (-1) sign of the given numeric expression. Example: SIGN([UnitsOnOrder]) |
|
| SIN |
SIN(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the sine of the angle specified in radians, in the given expression. Example: SIN(0.25) |
|
| SQRT |
SQRT(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the square root of the given numeric expression. Example: SQRT([UnitsInStock]) |
|
| TAN |
TAN(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the tangent of the given numeric expression. Example: TAN(0.25) |
|
| Aggregation | AVG |
AVG(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the average of the values in the given expression. Example: AVG([UnitPrice]) |
| COUNT |
COUNT(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the number of items in the given expression. Example: COUNT([OrderID]) |
|
| COUNTD |
COUNTD(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the distinct number of items in the given expression. Example: COUNTD([OrderID]) |
|
| MAX |
MAX(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the maximum value in the given expression. Example: MAX([UnitPrice]) |
|
| MIN |
MIN(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the minimum value in the given expression. Example: MIN([UnitPrice]) |
|
| STDEV |
STDEV(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the standard deviation of values in the given expression. Example: STDEV[OrderID] |
|
| SUM |
SUM(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the sum of values in the given expression. Example: SUM([UnitPrice]) |
|
| VAR |
VAR(numeric_expression) Description: Returns the variance of values in the given expression. Example: VAR([OrderID]) |
|
| TOTAL |
TOTAL(aggregated_expression) Description: Returns the summarized total of values across each table row resulted from the aggregated expression. Example: TOTAL(SUM([UnitPrice])) |
|
| Conditional | IF |
IF(expression, true_part, false_part) Description: Returns either true part or false part, depending on the evaluation of the expression. Example: IF([CustomerID]='VINET' AND [OrderID]=10248, [Discount], [Discount]+0.1) |
| IFNULL |
IFNULL(expression1, expression2) Description: Returns expression1 if the expression1 evaluates to be not null. Example: IFNULL([ShipRegion],'Region not specified') |
|
| ISNULL |
ISNULL(expression) Description: Returns true if the given expression evaluates to null. Example: ISNULL([ShipRegion]) |
|
| ISNOTNULL |
ISNOTNULL(expression) Description: Returns true if the given expression evaluates to be not null. Example: ISNOTNULL([ShipRegion]) |
|
| Logical | AND |
(expression1) AND (expression2) Description: Returns true if both the expressions evaluates to true. Example: IF([CustomerID]='VINET' AND [OrderID]=10248, [Discount], [Discount]+0.1) |
| NOT |
NOT(expression) Description: Returns the reversed logical value of the expression being evaluated. Example: IF(NOT [CustomerID]='VINET', [Freight], [Freight] - 100 ) |
|
| OR |
(expression1) OR (expression2) Description: Returns true if any of the expressions evaluates to true. Example: IF([CustomerID]='VINET' OR [OrderID]=10248, [Discount], [Discount]+0.1) |
|
| Date | DATEADD |
DATEADD(numeric_expression, date_expression) Description: Adds the number of days to the specified date. Example: DATEADD(7,[OrderDate]) |
| DATESUB |
DATESUB(numeric_expression, date_expression) Description: Returns the date subtracted from the specified date. Example: DATESUB(7,[OrderDate]) |
|
| DAY |
DAY(date_expression) Description: Returns a numeric value representing the day part of the specified date. Example: DAY([OrderDate]) |
|
| DAYDIFF |
DAYDIFF(start_date_expression, end_date_expression) Description: Returns a numeric value representing the difference between two specified dates. Example: DAYDIFF(MAX([OrderDate]),'1998-08-08') |
|
| HOUR |
HOUR(date_expression) Description: Returns the hour of the given date as an integer. Example: HOUR([OrderDate]) |
|
| MINUTE |
MINUTE(date_expression) Description: Returns a numeric value representing the minute part of the date resulted from specified date expression. Example: MINUTE([OrderDate]) |
|
| MONTH |
MONTH(date_expression) Description: Returns a numeric value representing the month part of the date resulted from specified date expression. Example: MONTH([OrderDate]) |
|
| NOW |
NOW() Description: Returns the current date and time. Example: DATEPART("year",NOW()) |
|
| TODAY |
TODAY() Description: Returns the current date. Example: DATEPART("month",TODAY()) |
|
| YEAR |
YEAR(date_expression) Description: Returns a numeric value representing the year part of the date resulting from the specified date expression. Example: YEAR([OrderDate]) |
|
| DATENAME |
DATENAME(date_part, date_expression) Description: Returns a string representing the specified date_part of the given date expression. Example: DATENAME("day",[OrderDate]) |
|
| DATEPART |
DATEPART(date_part, date_expression) Description: Returns an integer value representing the specified date_part of the given date expression. Example: DATEPART("year",MAX([OrderDate])) |
|
| MAX |
MAX(expression) Description: Returns the maximum value in the given expression. Example: MAX([OrderDate]) |
|
| MIN |
MIN(expression) Description: Returns the minimum value in the given expression. Example: MIN([OrderDate]) |
|
| String | LEN |
LEN(string_expression) Description: Returns the number of characters in the given string expression. Example: LEN([ShipPostalCode]) |
| CHAR |
CHAR(integer_expression) Description: Converts the given integer ASCII code into a character. Example: CHAR(70) |
|
| CONCAT |
CONCAT(string_expression1, string_expression2,…, string_expressionN) Description: Returns a string value resulting from the concatenation of two or more string values. Example: CONCAT('http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/',[ShipCity]) |
|
| CONTAINS |
CONTAINS(string_expression, substring_expression) Description: Returns true if the given string expression contains the specified substring expression. Example: CONTAINS([Shipping Address], [ShipCountry]) |
|
| ENDSWITH |
ENDSWITH(string_expression substring_expression) Description: Returns true if the given string expression ends with the specified substring expression. Example: ENDSWITH([CustomerID],'A') |
|
| LEFT |
LEFT(string_expression, numeric_expression) Description: Returns the specified number of characters from start of the given string expression. Example: LEFT([ShipAddress],6) |
|
| LOWER |
LOWER(string_expression) Description: Returns a lower case converted string value from a given string expression. Example: LOWER([ShipCountry]) |
|
| LTRIM |
LTRIM(string_expression) Description: Returns the string value with any leading blanks removed from string expression. Example: LTRIM(' Removes trailing spaces.') |
|
| MAX |
MAX(expression) Description: Returns the maximum value in the given expression. Example: MAX([ProductName]) |
|
| MIN |
MIN(expression) Description: Returns the minimum value in the given expression. Example: MIN([ProductName]) |
|
| RIGHT |
RIGHT(string_expression, numeric_expression) Description: Returns the specified number of characters from end of the given string expression. Example: RIGHT([ProductName],6) |
|
| RTRIM |
RTRIM(string_expression) Description: Returns the string value with any trailing blanks removed from string expression. Example: RTRIM('Removes trailing spaces. ') |
|
| STARTSWITH |
STARTSWITH(string_expression, substring_expression) Description: Returns true if the given string expression starts with the specified substring expression. Example: STARTSWITH([CustomerID],'A') |
|
| SUBSTR |
SUBSTR(string_expression, starting_index, length_of_the_string) Description: Returns a specific length of string starting from specific index from the given string expression. Example: SUBSTR([CustomerID],1,3) |
|
| UPPER |
UPPER(string_expression) Description: Returns an upper case converted string value from a given string expression. Example: UPPER([ShipCountry]) |
|
| Filter | CURRENTUSER |
CURRENTUSER()=[column_name] Description: Returns the current user name. This function uses Dashboard Server user name when the user is signed in, else it returns null. Example: CURRENTUSER()=[CustomerID] |
| FULLNAME |
FULLNAME()=[column_name] Description: Returns the current user's Full name. This function uses Dashboard Server user's full name when the user is signed in, else it returns null. Example: FULLNAME()=[CustomerID] |
|
EMAIL()=[column_name] Description: Returns the current user's email. This function uses Dashboard Server user's Email id when the user is signed in, else it returns null. Example: EMAIL()=[CustomerID] |
||
| Row | INDEX |
INDEX() Description: Returns index value of each row. Example: INDEX() |
| RUNNINGAVG |
RUNNINGAVG(aggregated_expression) Description: Returns Running Average of each row. Example: RUNNINGAVG(MAX([UnitsInStock])) |
|
| RUNNINGCOUNT |
RUNNINGCOUNT(aggregated_expression) Description: Returns Running Count of each row. Example: RUNNINGCOUNT(MAX([OrderID])) |
|
| RUNNINGMAX |
RUNNINGMAX(aggregated_expression) Description: Returns Running Maximum value of each row. Example: RUNNINGMAX(SUM([UnitsInStock])) |
|
| RUNNINGMIN |
RUNNINGMIN(aggregated_expression) Description: Returns Running Minimum value of each row. Example: RUNNINGMIN(SUM([UnitsInStock])) |
|
| RUNNINGSTDEV |
RUNNINGSTDEV(aggregated_expression) Description: Returns Running Stdev value of each row. Example: RUNNINGSTDEV(MAX([UnitsInStock])) |
|
| RUNNINGSUM |
RUNNINGSUM(aggregated_expression) Description: Returns Running Sum of each row. Example: RUNNINGSUM(MAX([UnitsInStock])) |
|
| RUNNINGVAR |
RUNNINGVAR(aggregated_expression) Description: Returns Running Variance value of each row. Example: RUNNINGVAR(MAX([UnitsInStock])) |
You may also include the function names and the column names just by placing the cursor in respective position in the Expression text area and double-clicking the specific name in respective lists.
Once framing an expression, click Save in Expression Designer window.
Deleting an Expression Column
Select an expression column in left pane.
Click Delete to remove the selected expression column.
![]()
Updating an Expression Column
Select an expression column in left pane that you need to update.
Edit the Name and Expression text areas, if required.
Click Save in Expression Designer window to save the modifications handled.
Configuring Expression Column in Widgets
Saved expression will be shown in Expression Columns section of Data Configuration pane like below.
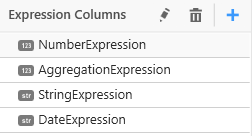
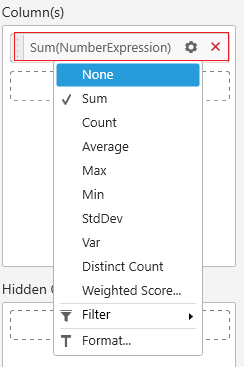
You can also drag and drop expression column into widgets just like measure and dimension fields. For numeric expressions, you can apply any aggregation function like below.
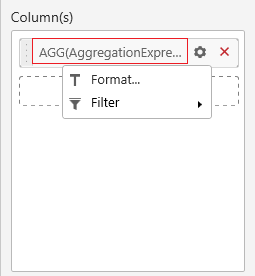
For aggregation expressions alone, AGG keyword will be automatically added in front of the expression name to represent that the created expression is of aggregation type. You can’t change the aggregation type in this case.
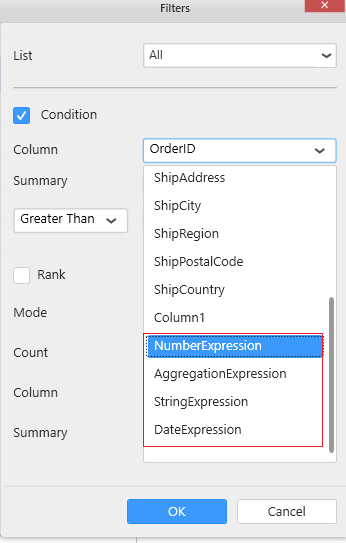
You can also apply filters for expression column which is used in widget. For aggregation and numeric expressions, you can apply filter just like a measure filter. For string and date expressions, you can apply filter just like a dimension filter.
Expression column will also be shown in Columns section of condition and rank filter.
NOTE
Expression Designerallows you to create an expression using the functions which are supported by the corresponding database server. Since few functions will have compatibility with specific database server, it is not listed inExpression Designer. For example, CONVERT function is supported in SQL server and MySQL server but not in SQLite. Hence you can create an expression using CONVERT function with appropriate syntax supported by SQL and MySQL server.
