How can I help you?
Scrolling in .NET MAUI PDF Viewer (SfPdfViewer)
12 Dec 20256 minutes to read
The .NET MAUI PDF Viewer provides built-in scrolling capabilities that allow users to navigate through PDF content smoothly. This guide covers how to control scroll positions programmatically, detect scroll changes, and manage scroll-related UI elements.
WARNING
Since the PDF Viewer includes built-in scrolling, avoid placing it inside other scrollable containers like ScrollView, as this may lead to unexpected behavior.
Programmatic Scrolling
Use the ScrollToOffset method to scroll to a specific horizontal and vertical offset. Offset values are measured in device-independent units. If the specified offset is invalid or out of bounds, the scroll action will be ignored and the viewer will retain its current position.
// Scroll to position (100, 1000)
PdfViewer.ScrollToOffset(100, 1000);Detect Scroll Changes
You can monitor scroll changes using the PropertyChanged event. By monitoring the HorizontalOffset and VerticalOffset property changes, you can respond to both the horizontal and vertical scroll movements respectively.
The following is the code example for subscribing to the PropertyChanged event.
<syncfusion:SfPdfViewer
x:Name = "PdfViewer" PropertyChanged = "PdfViewer_PropertyChanged"/>void SubscribeToPropertyChangedEvent()
{
SfPdfViewer PdfViewer = new SfPdfViewer();
// Subscribe to property changed event.
PdfViewer.PropertyChanged += PdfViewer_PropertyChanged;
}The following code example illustrates how implement the event handler and to respond to both horizontal and vertical scroll changes:
private void PdfViewer_PropertyChanged(object sender,
System.ComponentModel.PropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.PropertyName == nameof(SfPdfViewer.HorizontalOffset))
{
// Horizontal scroll change detected
// Your code here
}
else if (e.PropertyName == nameof(SfPdfViewer.VerticalOffset))
{
// Vertical scroll change detected
// Your code here
}
}Detecting End of Document
You can determine if the control has reached the vertical end of the document by evaluating the following properties:
-
VerticalOffset: It provides the current vertically scrolled offset. -
ClientRectangle: It provides the viewport area bounds. -
ExtentHeight: It provides the overall vertical height of the PDF document.
Below is the code example to detect whether the control has reached the vertical end of the document.
private void PdfViewer_PropertyChanged(object sender,
System.ComponentModel.PropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.PropertyName == nameof(SfPdfViewer.VerticalOffset))
{
// Determine if the control has reached the vertical end of the document.
bool isVerticalEndReached = (PdfViewer.VerticalOffset +
PdfViewer.ClientRectangle.Height >= PdfViewer.ExtentHeight);
}
}Similarly, for horizontal end detection, refer to the following code example.
private void PdfViewer_PropertyChanged(object sender,
System.ComponentModel.PropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.PropertyName == nameof(SfPdfViewer.HorizontalOffset))
{
// Determine if the control has reached the horizontal end of the document.
bool isHorizontalEndReached = (PdfViewer.HorizontalOffset +
PdfViewer.ClientRectangle.Width >= PdfViewer.ExtentWidth);
}
}Scroll Head (Mobile Platforms)
On Android and iOS platforms, the scroll head offers a quick way to move through pages. Users can drag the thumb indicator to scroll within the PDF document.
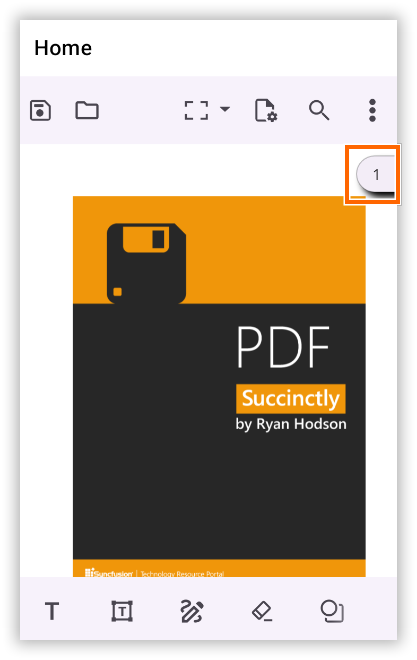
Page Navigation via Scroll Head
Tap the scroll head to open a page navigation dialog. Enter a valid page number and tap OK to jump directly to that page.

Show or Hide the Scroll Head
Use the ShowScrollHead property to control the visibility of the scroll head.
// Hide the scroll head thumb
PdfViewer.ShowScrollHead = false;NOTE
The scroll head is available only on mobile platforms. It is not supported on Windows or macOS.
Render multiple pages while scrolling
When scrolling through large PDF documents, you may notice blank pages appearing temporarily while new pages are being rendered. This happens because the viewer renders pages on demand to optimize memory usage.
To minimize this and provide a smoother scrolling experience, the SfPdfViewer control offers the OverscanCount property. This property defines how many pages should be pre-rendered and kept in memory on each side of the current viewport. Increasing this value reduces the chance of blank pages during fast scrolling but may increase memory usage.
The following example shows how to set OverscanCount property:
<syncfusion:SfPdfViewer x:Name="PdfViewer"
OverscanCount ="15" />SfPdfViewer PdfViewer = new SfPdfViewer();
// Set the cache range (number of pages before and after the current viewport)
PdfViewer.OverscanCount = 15;
// Load a PDF document
PdfViewer.LoadDocument("sample.pdf");NOTE
- Use a reasonable OverscanCount value. Large values can cause memory spikes and app freezes.
- Pages with very high resolution may still render slowly due to native rendering limitations.