Paging support in ASP.NET Core DataManager
27 Jan 202212 minutes to read
Paging is a very important query in DataManager that is used to display only some records from the large data source. Here, you can learn the paging query in detail.
Default
The paging index and the paging size parameters of the paging query determines the number of records to be retrieved from the data source of the DataManager.
Refer to the following code example for the paging options.
/*ej-Tag Helper code to render DataManager*/
<ej-grid query="new ej.Query().page(1,5)" id="FlatGrid" dataamanager-id="myData">
<e-datamanager url="http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders"></e-datamanager>
<e-columns>
<e-column field="OrderID" header-text="Order ID" text-align="Right" width="70"></e-column>
<e-column field="CustomerID" header-text="Customer ID" width="80"></e-column>
<e-column field="EmployeeID" header-text="Employee ID" text-align="Left" width="75"></e-column>
</e-columns>
</ej-grid>/*Razor code to render DataManager*/
@{Html.EJ().DataManager("FlatData").URL("http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders").Render();}
@{Html.EJ().Grid<object>("myGrid")
.DataManagerID("FlatData")
.Query("new ej.Query().page(1,5)")
.Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").IsPrimaryKey(true).TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width(80).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
}).Render();
}Result for the above code example is illustrated as follows.
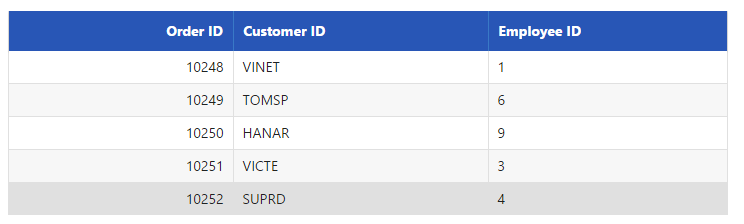
Dynamic Paging
The paging operation can be dynamically performed using the DataManager. With the help of an external button click event, the required page records can be obtained and processed accordingly. The following code example illustrates the dynamic paging.
pageIndex: <input id="pageindx" type="text" placeholder="pageindex" />
pageSize: <input id="pagesize" type="text" placeholder="pagesize" />
@{Html.EJ().Button("submit").Text("Execute").ClientSideEvents(e => { e.Click("onClick"); }).Render(); }/*ej-Tag Helper code to render DataManager*/
<ej-grid query="new ej.Query().page(1,5)" id="myGrid" dataamanager-id="myData">
<e-datamanager url="http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders"></e-datamanager>
<e-columns>
<e-column field="OrderID" header-text="Order ID" text-align="Right" width="70"></e-column>
<e-column field="CustomerID" header-text="Customer ID" width="80"></e-column>
<e-column field="EmployeeID" header-text="Employee ID" text-align="Left" width="75"></e-column>
</e-columns>
</ej-grid>/*Razor code to render DataManager*/
@{Html.EJ().DataManager("FlatData").URL("http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders").Render();}
@{Html.EJ().Grid<object>("myGrid")
.DataManagerID("FlatData")
.Query("new ej.Query().page(1,5)")
.Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").IsPrimaryKey(true).TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width(80).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
}).Render();
}<script type="text/javascript" class="jsScript">
function onClick(e) {
var from = parseInt($("#pageindx").val());
var to = parseInt($("#pagesize").val());
var obj = $("#myGrid").ejGrid("instance")
tempQuery = new ej.Query();
tempQuery.page(from, to);
var dm = window.FlatData.executeQuery(tempQuery).done(function (e1) {
obj.dataSource(e1.result);
})
}
</script>Result of above code example is illustrated as follows.
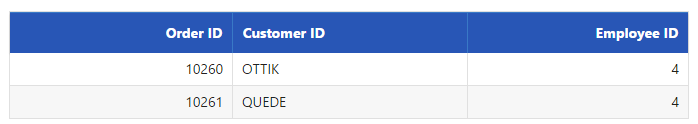
Custom paging
In this section, you can learn how to use customized paging. The following code example illustrates the custom paging.
/*ej-Tag Helper code to render DataManager*/
<ej-grid query="new ej.Query().page(1,5).addParams('PageNumber',7).addParams('PageSize',3).where('CustomerID', 'contains', 'A', false)" id="FlatGrid" dataamanager-id="myData">
<e-datamanager url="http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders"></e-datamanager>
<e-columns>
<e-column field="OrderID" header-text="Order ID" text-align="Right" width="70"></e-column>
<e-column field="CustomerID" header-text="Customer ID" width="80"></e-column>
<e-column field="EmployeeID" header-text="Employee ID" text-align="Left" width="75"></e-column>
</e-columns>
</ej-grid>/*Razor code to render DataManager*/
@{Html.EJ().DataManager("FlatData").URL("http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders").Render();}
@{Html.EJ().Grid<object>("myGrid")
.DataManagerID("FlatData")
.Query("new ej.Query().page(1,5).addParams('PageNumber',7).addParams('PageSize',3).where('CustomerID', 'contains', 'A', false)")
.Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").IsPrimaryKey(true).TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width(80).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
}).Render();
}Result of above code example is illustrated as follows.
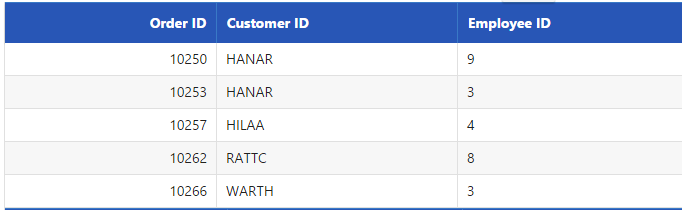
Skip
The skip query is used to skip some number of records.
/*ej-Tag Helper code to render DataManager*/
<ej-grid query="new ej.Query().skip(820)" id="FlatGrid" dataamanager-id="myData">
<e-datamanager url="http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders"></e-datamanager>
<e-columns>
<e-column field="OrderID" header-text="Order ID" text-align="Right" width="70"></e-column>
<e-column field="CustomerID" header-text="Customer ID" width="80"></e-column>
<e-column field="EmployeeID" header-text="Employee ID" text-align="Left" width="75"></e-column>
</e-columns>
</ej-grid>/*Razor code to render DataManager*/
@{Html.EJ().DataManager("FlatData").URL("http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders").Render();}
@{Html.EJ().Grid<object>("myGrid")
.DataManagerID("FlatData")
.Query("new ej.Query().skip(820)")
.Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").IsPrimaryKey(true).TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width(80).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
}).Render();
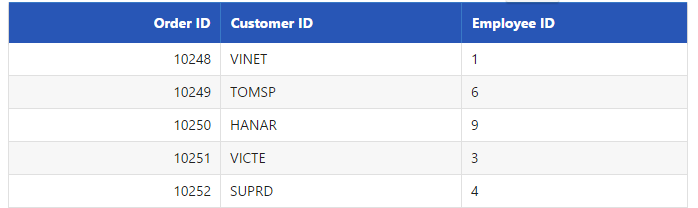
}Result of the above code example is illustrated as follows.

Take
The take query is used to get some certain number of records from the data source of the DataManager.
/*ej-Tag Helper code to render DataManager*/
<ej-grid query="new ej.Query().take(5)" id="FlatGrid" dataamanager-id="myData">
<e-datamanager url="http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders"></e-datamanager>
<e-columns>
<e-column field="OrderID" header-text="Order ID" text-align="Right" width="70"></e-column>
<e-column field="CustomerID" header-text="Customer ID" width="80"></e-column>
<e-column field="EmployeeID" header-text="Employee ID" text-align="Left" width="75"></e-column>
</e-columns>
</ej-grid>/*Razor code to render DataManager*/
@{Html.EJ().DataManager("FlatData").URL("http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders").Render();}
@{Html.EJ().Grid<object>("myGrid")
.DataManagerID("FlatData")
.Query("new ej.Query().take(5)")
.Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").IsPrimaryKey(true).TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width(80).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
}).Render();
}Result of the above code example is illustrated as follows.
RequiresCount
The requiresCount query is used to get the count of the total number of records in the data source of the DataManager.
/*ej-Tag Helper code to render DataManager*/
<ej-grid query="new ej.Query().take(5).requiresCount()" id="FlatGrid" dataamanager-id="myData">
<e-datamanager url="http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders"></e-datamanager>
<e-columns>
<e-column field="OrderID" header-text="Order ID" text-align="Right" width="70"></e-column>
<e-column field="CustomerID" header-text="Customer ID" width="80"></e-column>
<e-column field="EmployeeID" header-text="Employee ID" text-align="Left" width="75"></e-column>
</e-columns>
</ej-grid>/*Razor code to render DataManager*/
@{Html.EJ().DataManager("FlatData").URL("http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders").Render();}
@{Html.EJ().Grid<object>("myGrid")
.DataManagerID("FlatData")
.Query("new ej.Query().take(5).requiresCount()")
.Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").IsPrimaryKey(true).TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width(80).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
}).Render();
}Result of the above code example is illustrated as follows.
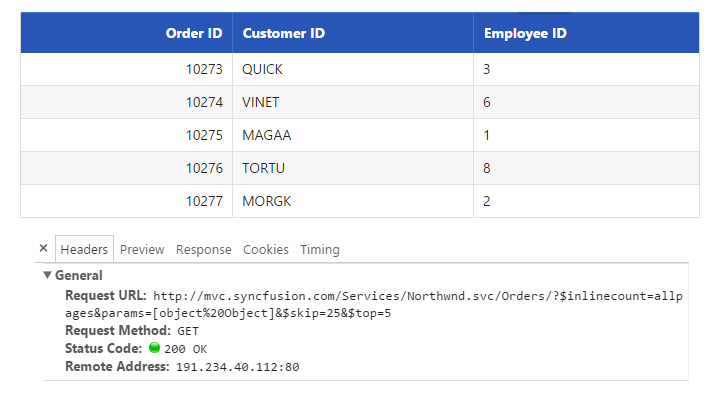
Range
The range query is used to get some particular range of records from the data source of the DataManager.
/*ej-Tag Helper code to render DataManager*/
<ej-grid query="new ej.Query().range(25,30)" id="FlatGrid" dataamanager-id="myData">
<e-datamanager url="http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders"></e-datamanager>
<e-columns>
<e-column field="OrderID" header-text="Order ID" text-align="Right" width="70"></e-column>
<e-column field="CustomerID" header-text="Customer ID" width="80"></e-column>
<e-column field="EmployeeID" header-text="Employee ID" text-align="Left" width="75"></e-column>
</e-columns>
</ej-grid>/*Razor code to render DataManager*/
@{Html.EJ().DataManager("FlatData").URL("http://mvc.syncfusion.com/Services/Northwnd.svc/Orders").Render();}
@{Html.EJ().Grid<object>("myGrid")
.DataManagerID("FlatData")
.Query("new ej.Query().range(25,30)")
.Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").IsPrimaryKey(true).TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width(80).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").TextAlign(TextAlign.Right).Width(75).Add();
}).Render();
}Result of the above code example is illustrated as follows.
