How can I help you?
Getting Started with .NET MAUI Kanban Board (SfKanban)
16 Sep 202524 minutes to read
This section provides a quick overview for working with Essential® Kanban for .NET MAUI. It is an efficient way to visualize the workflow at each stage along its path to completion.
To get start quickly with our .NET MAUI Kanban Board, you can check the below video.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure that the following are set up:
- Install .NET 8 SDK or later is installed.
- Set up a .NET MAUI environment with Visual Studio 2022 (v17.8 or later).
Step 1: Create a new .NET MAUI project
- Go to File > New > Project and choose the .NET MAUI App template.
- Name the project and choose a location. Click Next.
- Select the .NET framework version and click Create.
Step 2: Install the Syncfusion® .NET MAUI Kanban Board NuGet Package
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and choose Manage NuGet Packages.
- Search for Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban and install the latest version.
- Ensure the necessary dependencies are installed correctly, and the project is restored.
Step 3: Register the handler
Syncfusion.Maui.Core nuget is a dependent package for all Syncfusion® controls of .NET MAUI. In the MauiProgram.cs file, register the handler for Syncfusion® core.
using Microsoft.Maui;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Compatibility;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Syncfusion.Maui.Core.Hosting;
namespace KanbanGettingStarted
{
public static class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureSyncfusionCore()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 4: Add .NET MAUI Kanban Board Control
- To initialize the control, import the
Syncfusion.Maui.Kanbannamespace into your code. - Initialize SfKanban.
<ContentPage
. . .
xmlns:kanban="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban">
<kanban:SfKanban/>
</ContentPage>You can also create the kanban board programmatically in the MainPage.xaml.cs file:
using Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban;
namespace KanbanGettingStarted
{
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfKanban kanban = new SfKanban();
this.Content = kanban;
}
}
}Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure that the following are set up:
- Install .NET 8 SDK or later is installed.
- Set up a .NET MAUI environment with Visual Studio Code.
- Ensure that the .NET MAUI extension is installed and configured as described here.
Step 1: Create a new .NET MAUI project
- Open the command palette by pressing
Ctrl+Shift+Pand type .NET:New Project and enter. - Choose the .NET MAUI App template.
- Select the project location, type the project name and press Enter.
- Then choose Create project.
Step 2: Install the Syncfusion® .NET MAUI Kanban Board NuGet Package
- Press Ctrl + ` (backtick) to open the integrated terminal in Visual Studio Code.
- Ensure you’re in the project root directory where your .csproj file is located.
- Run the command
dotnet add package Syncfusion.Maui.Kanbanto install the Syncfusion® .NET MAUI Kanban Board NuGet package. - To ensure all dependencies are installed, run
dotnet restore.
Step 3: Register the handler
Syncfusion.Maui.Core nuget is a dependent package for all Syncfusion® controls of .NET MAUI. In the MauiProgram.cs file, register the handler for Syncfusion® core.
using Microsoft.Maui;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Compatibility;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Syncfusion.Maui.Core.Hosting;
namespace KanbanGettingStarted
{
public static class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureSyncfusionCore()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 4: Add .NET MAUI Kanban Board Control
- To initialize the control, import the
Syncfusion.Maui.Kanbannamespace into your code. - Initialize SfKanban.
<ContentPage
. . .
xmlns:kanban="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban">
<kanban:SfKanban/>
</ContentPage>You can also create the kanban board programmatically in the MainPage.xaml.cs file:
using Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban;
namespace KanbanGettingStarted
{
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfKanban kanban = new SfKanban();
this.Content = kanban;
}
}
}Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure the following are set up:
- Ensure you have the latest version of JetBrains Rider.
- Install .NET 8 SDK or later is installed.
- Make sure the MAUI workloads are installed and configured as described here.
Step 1: Create a new .NET MAUI Project
- Go to File > New Solution, Select .NET (C#) and choose the .NET MAUI App template.
- Enter the Project Name, Solution Name, and Location.
- Select the .NET framework version and click Create.
Step 2: Install the Syncfusion® MAUI Kanban NuGet Package
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and choose Manage NuGet Packages.
- Search for Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban and install the latest version.
- Ensure the necessary dependencies are installed correctly, and the project is restored. If not, Open the Terminal in Rider and manually run:
dotnet restore
Step 3: Register the handler
Syncfusion.Maui.Core nuget is a dependent package for all Syncfusion® controls of .NET MAUI. In the MauiProgram.cs file, register the handler for Syncfusion® core.
using Microsoft.Maui;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Compatibility;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Syncfusion.Maui.Core.Hosting;
namespace KanbanGettingStarted
{
public static class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureSyncfusionCore()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 4: Add .NET MAUI Kanban Board Control
- To initialize the control, import the
Syncfusion.Maui.Kanbannamespace into your code. - Initialize SfKanban.
<ContentPage
. . .
xmlns:kanban="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban">
<kanban:SfKanban/>
</ContentPage>You can also create the kanban board programmatically in the MainPage.xaml.cs file:
using Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban;
namespace KanbanGettingStarted
{
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfKanban kanban = new SfKanban();
this.Content = kanban;
}
}
}Populate .NET MAUI Kanban item source
This section explains how to populate the .NET MAUI Kanban control’s ItemsSource by creating and binding both default and custom task data models.
Creating the default model tasks
-
Define the View Model: Create a view model class to set values for the properties listed in the
KanbanModelclass as shown in the following example code. EachKanbanModelinstance represents a card in Kanban control. -
Bind item source for Kanban: To populate the Kanban card items, utilize the
ItemsSourceproperty ofSfKanban. -
Defining columns in the Kanban Board: The columns are generated automatically based on the different values of
Categoryin theKanbanModelclass fromItemsSource. However, you can manually define the columns by setting theAutoGenerateColumnsproperty tofalseand addingKanbanColumninstances to theColumnsproperty ofSfKanban. Define the categories of column using theCategoriesproperty ofKanbanColumn, and cards will be added to the respective columns.
The following sample code demonstrates this process in action:
<kanban:SfKanban x:Name="kanban"
AutoGenerateColumns="False"
ItemsSource="{Binding Cards}">
<kanban:SfKanban.Columns>
<kanban:KanbanColumn Title="To Do"
Categories="Open">
</kanban:KanbanColumn>
<kanban:KanbanColumn Title="In Progress"
Categories="In Progress">
</kanban:KanbanColumn>
<kanban:KanbanColumn Title="Code Review"
Categories="Code Review">
</kanban:KanbanColumn>
<kanban:KanbanColumn Title="Done"
Categories="Done">
</kanban:KanbanColumn>
</kanban:SfKanban.Columns>
<kanban:SfKanban.BindingContext>
<local:KanbanViewModel />
</kanban:SfKanban.BindingContext>
</kanban:SfKanban>using Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban;
SfKanban kanban = new SfKanban();
KanbanViewModel viewModel = new KanbanViewModel();
kanban.AutoGenerateColumns = false;
kanban.Columns.Add(new KanbanColumn
{
Title = "To Do",
Categories = new List<object>() { "Open" },
});
kanban.Columns.Add(new KanbanColumn
{
Title = "In Progress",
Categories = new List<object>() { "In Progress" },
});
kanban.Columns.Add(new KanbanColumn
{
Title = "Code Review",
Categories = new List<object>() { "Code Review" },
});
kanban.Columns.Add(new KanbanColumn
{
Title = "Done",
Categories = new List<object>() { "Done" },
});
kanban.ItemsSource = viewModel.Cards;
this.Content = kanban;
using Syncfusion.Maui.Kanban;
public class KanbanViewModel
{
public ObservableCollection<KanbanModel> Cards { get; set; }
public KanbanViewModel()
{
this.Cards = new ObservableCollection<KanbanModel>();
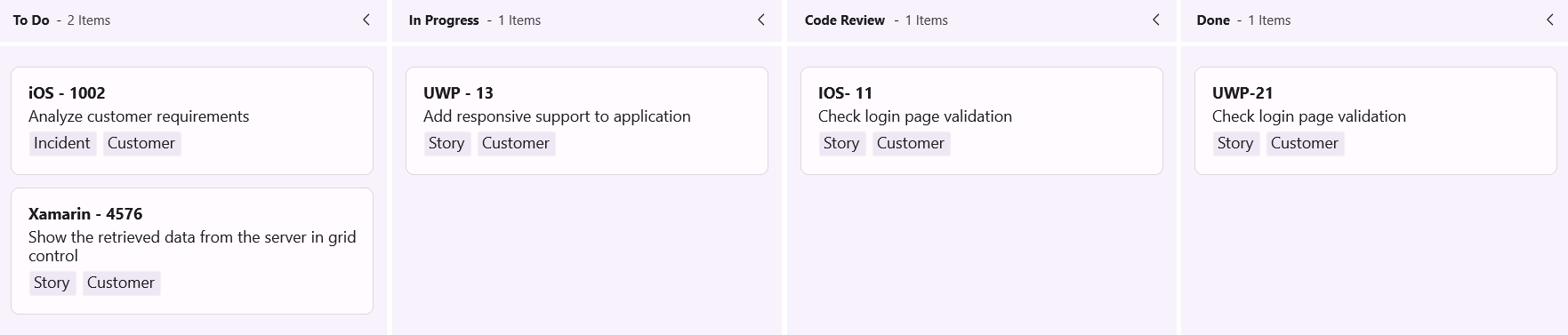
this.Cards.Add(new KanbanModel()
{
ID = 1,
Title = "iOS - 1002",
Category = "Open",
Description = "Analyze customer requirements",
IndicatorFill = Colors.Red,
Tags = new List<string> { "Incident", "Customer" }
});
this.Cards.Add(new KanbanModel()
{
ID = 6,
Title = "Xamarin - 4576",
Category = "Open",
Description = "Show the retrieved data from the server in grid control",
IndicatorFill = Colors.Green,
Tags = new List<string> { "Story", "Customer" }
});
this.Cards.Add(new KanbanModel()
{
ID = 13,
Title = "UWP - 13",
Category = "In Progress",
Description = "Add responsive support to application",
IndicatorFill = Colors.Brown,
Tags = new List<string> { "Story", "Customer" }
});
this.Cards.Add(new KanbanModel()
{
ID = 2543,
Title = "IOS- 11",
Category = "Code Review",
Description = "Check login page validation",
IndicatorFill = Colors.Brown,
Tags = new List<string> { "Story", "Customer" }
});
this.Cards.Add(new KanbanModel()
{
ID = 123,
Title = "UWP-21",
Category = "Done",
Description = "Check login page validation",
IndicatorFill = Colors.Brown,
Tags = new List<string> { "Story", "Customer" }
});
}
}
Creating the custom model tasks with data mapping
You can also map a custom data model to the Kanban control. The following steps demonstrate how to render tasks using the .NET MAUI Kanban control with corresponding custom data properties.
-
Create a data model for Kanban: Create a simple data model in a new class file as shown in the following example code.
-
Create view model: Create a view model class to set values for the properties listed in the model class as shown in the following example code.
-
Bind item source for Kanban: To populate the Kanban card items, utilize the
ItemsSourceproperty of theSfKanbancontrol. Additionally, ensure that the following properties ofSfKanbanare mapped from corresponding properties in theItemsSourcewhile initializing the Kanban control.
The ColumnMappingPath specifies the name of the property within the data object that is used to generate columns in the Kanban control when AutoGenerateColumns is set to true.
-
Defining columns in the Kanban Board: The
Columnsin the Kanban board are mapped based on the values of a specified property (e.g., “Status”) from your custom data model. TheColumnMappingPathspecifies the name of the property within the data object that is used to generate columns in the Kanban control whenAutoGenerateColumnsis set totrue.
Alternatively, you can manually define columns by setting AutoGenerateColumns to false and adding instances of KanbanColumn to the Columns collection of the SfKanban control. Based on the property specified in ColumnMappingPath, the Kanban control will generate the columns and render the corresponding cards accordingly.
Let’s look at the practical code example:
<kanban:SfKanban x:Name="kanban"
ItemsSource="{Binding TaskDetails}"
ColumnMappingPath="Status">
<kanban:SfKanban.CardTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<Border Stroke="Black"
StrokeThickness="1"
Background="#F3CFCE">
<VerticalStackLayout Margin="10">
<Label Text="{Binding Title}"
HorizontalTextAlignment="Center"
FontAttributes="Bold"
FontSize="14" />
<Label Text="{Binding Description}"
HorizontalTextAlignment="Center"
FontSize="12"
LineBreakMode="WordWrap"
Margin="5" />
</VerticalStackLayout>
</Border>
</DataTemplate>
</kanban:SfKanban.CardTemplate>
<kanban:SfKanban.BindingContext>
<local:KanbanViewModel />
</kanban:SfKanban.BindingContext>
</kanban:SfKanban>SfKanban kanban = new SfKanban();
KanbanViewModel viewModel = new KanbanViewModel();
kanban.ColumnMappingPath = "Status";
kanban.CardTemplate = new DataTemplate(() =>
{
var titleLabel = new Label
{
HorizontalTextAlignment = TextAlignment.Center,
FontAttributes = FontAttributes.Bold,
FontSize = 14
};
titleLabel.SetBinding(Label.TextProperty, "Title");
var descriptionLabel = new Label
{
HorizontalTextAlignment = TextAlignment.Center,
FontSize = 12,
LineBreakMode = LineBreakMode.WordWrap,
Margin = new Thickness(5)
};
descriptionLabel.SetBinding(Label.TextProperty, "Description");
var stackLayout = new VerticalStackLayout
{
Margin = new Thickness(10),
Children = { titleLabel, descriptionLabel }
};
var border = new Border
{
Stroke = Colors.Black,
StrokeThickness = 1,
Background = Color.FromArgb("#F3CFCE"),
Content = stackLayout
};
return border;
});
kanban.ItemsSource = viewModel.TaskDetails;
this.Content = kanban;
public class TaskDetails
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public object Status { get; set; }
}public class KanbanViewModel
{
public ObservableCollection<TaskDetails> TaskDetails { get; set; }
public KanbanViewModel()
{
this.TaskDetails = this.GetTaskDetails();
}
private ObservableCollection<TaskDetails> GetTaskDetails()
{
var taskDetails = new ObservableCollection<TaskDetails>();
TaskDetails taskDetail = new TaskDetails();
taskDetail.Title = "UWP Issue";
taskDetail.Description = "Sorting is not working properly in DateTimeAxis";
taskDetail.Status = "Postponed";
taskDetails.Add(taskDetail);
taskDetail = new TaskDetails();
taskDetail.Title = "WPF Issue";
taskDetail.Description = "Crosshair label template not visible in UWP";
taskDetail.Status = "Open";
taskDetails.Add(taskDetail);
taskDetail = new TaskDetails();
taskDetail.Title = "WinUI Issue";
taskDetail.Description = "AxisLabel cropped when rotating the axis label";
taskDetail.Status = "In Progress";
taskDetails.Add(taskDetail);
taskDetail = new TaskDetails();
taskDetail.Title = "UWP Issue";
taskDetail.Description = "Crosshair label template not visible in UWP";
taskDetails.Add(taskDetail);
taskDetail = new TaskDetails();
taskDetail.Title = "Kanban Feature";
taskDetail.Description = "Provide drag and drop support";
taskDetail.Status = "In Progress";
taskDetails.Add(taskDetail);
taskDetail = new TaskDetails();
taskDetail.Title = "WF Issue";
taskDetail.Description = "HorizontalAlignment for tooltip is not working";
taskDetail.Status = "In Progress";
taskDetails.Add(taskDetail);
taskDetail = new TaskDetails();
taskDetail.Title = "WPF Issue";
taskDetail.Description = "In minimized state, first and last segments have incorrect spacing";
taskDetail.Status = "Code Review";
taskDetails.Add(taskDetail);
taskDetail = new TaskDetails();
taskDetail.Title = "WPF Issue";
taskDetail.Description = "In minimized state, first and last segments have incorrect spacing";
taskDetail.Status = "Code Review";
taskDetails.Add(taskDetail);
taskDetail = new TaskDetails();
taskDetail.Title = "New Feature";
taskDetail.Description = "Dragging events support for Kanban";
taskDetail.Status = "Closed";
taskDetails.Add(taskDetail);
return taskDetails;
}
}
NOTE
When using a custom data model, the default card UI is not applicable. You must define a custom
DataTemplateusing theCardTemplateproperty to render the card content appropriately.
NOTE
Running the Application
Press F5 to build and run the application. Once compiled, the Kanban board will display with the data provided.