Getting Started of Xamarin.Android Maps(SfMaps)
8 Jan 20259 minutes to read
This section explains the steps required to configure the SfMaps control and provides information to its basic customization.
Configuring SfMaps
This section describes on configuring the SfMaps control along with its basic customization.
Adding namespace
The following namespace needs to be added.
using Com.Syncfusion.Maps;Initializing Maps
Create an instance for maps control, and add it as content.
SfMaps maps = new SfMaps(this);
SetContentView(maps);Initialize Maps in AXML Layout
To initialize the SfMaps control, add the following code to the activity_main.axml file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:minWidth="25px"
android:minHeight="25px">
<Com.Syncfusion.Maps.SfMaps
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/sfMaps"
/>
</LinearLayout>The following code in MainActivity allows you to access the maps instance defined in the axml page.
public class MainActivity : Activity
{
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
base.OnCreate(savedInstanceState);
Xamarin.Essentials.Platform.Init(this, savedInstanceState);
// Set our view from the "main" layout resource
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.activity_main);
SfMaps sfMaps = FindViewById<SfMaps>(Resource.Id.sfMaps);
ImageryLayer layer = new ImageryLayer();
sfMaps.Layers.Add(layer);
}
}After initializing the Maps control in AXML Layout, the following output will be reproduced.
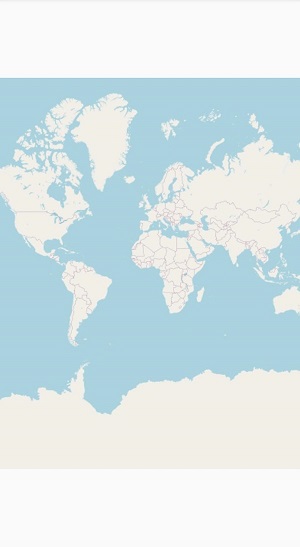
Adding layers
Map is maintained through Layers. It can accommodate one or more shape file layers.
SfMaps maps = new SfMaps(this);
ShapeFileLayer layer = new ShapeFileLayer();
maps.Layers.Add(layer);
SetContentView(maps);Adding shape files
Shape file is a set of files that are stored in a non-topological geometry with the attribute information for the spatial features and records in a data set.
Maps control supports reading and loading the shape files.
Shape file can be a set of files or a single file. Generally, a shape file contains the following files:
-
Main file (.shp)
-
dBase file (.dbf)
Android
- Add the necessary shape files in the Assets folder.
- Right-click the added shape file, and navigate to properties.
- Choose the
AndroidAssetoption under BuildAction of respective shape file.
Uri property in shape file layer is used to retrieve the location of the shape file that is added.
SfMaps maps = new SfMaps(this);
maps.SetBackgroundColor(Android.Graphics.Color.White);
ShapeFileLayer layer = new ShapeFileLayer();
layer.Uri = "usa_state.shp";
maps.Layers.Add(layer);
SetContentView(maps);After loading the shapes file, the following output will be reproduced.
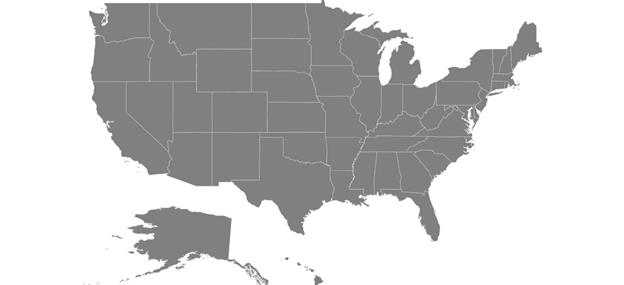
GeoJSON support
Maps control supports reading and loading the GeoJSON files. GeoJSON file contains attribute information for the spatial features and coordinates in a dataset.
ShapeFileLayer layer = new ShapeFileLayer();
layer.Uri = "usa_state.json";Data binding
Data can be binded to the shape file layer using the DataSource, ShapeIdPath, ShapeIdTableField properties.
Populate data topic gives the detailed explanation of data binding.
SfMaps maps = new SfMaps(this);
maps.SetBackgroundColor(Android.Graphics.Color.White);
ShapeFileLayer layer = new ShapeFileLayer();
layer.Uri = "usa_state.shp";
layer.DataSource = viewModel.Data;
layer.ShapeIdTableField = "STATE_NAME";
layer.ShapeIdPath = "State";
maps.Layers.Add(layer);
SetContentView(maps);Adding marker
Markers are used to identify the shapes. This can be added to the shape file layers as shown in the following code sample.
Markers can be customized using the MarkerSetting property in shape file layer.
Detailed explanation of marker and its customization is provided under Markers topic.
MapMarker marker = new MapMarker();
marker.Label = "California";
marker.Latitude = 37;
marker.Longitude = -120;
layer.Markers.Add(marker);Color mapping
The color mapping support enables the customization of shape colors based on the underlying value of shape received from the bounded data.
Both range and equal color mapping is supported in maps.
Detailed explanation of color mapping is provided in colorMapping topic.
EqualColorMapping colorMapping = new EqualColorMapping();
colorMapping.Color = Color.ParseColor("#D84444");
colorMapping.LegendLabel = "Romney";
colorMapping.Value = "Romney";
EqualColorMapping colorMapping1 = new EqualColorMapping();
colorMapping1.Color = Color.ParseColor("#316DB5");
colorMapping1.LegendLabel = "Obama";
colorMapping1.Value = "Obama";
ShapeSetting shapeSetting = new ShapeSetting();
shapeSetting.ShapeValuePath = "Candidate";
shapeSetting.ShapeColorValuePath = "Candidate";
shapeSetting.ColorMapping.Add(colorMapping);
shapeSetting.ColorMapping.Add(colorMapping1);
layer.ShapeSettings = shapeSetting;Adding legend
The legends interpret what the map displays. It can be added to the shape file layer as in below code snippet. Legends will be displayed based on the data bound to the layer and color mapping plays a major role in that.
Detailed explanation of legend is provided under Legend topic.
LegendSetting setting = new LegendSetting();
setting.ShowLegend = true;
setting.LegendPosition = new Point(75, 90);
layer.LegendSetting = setting;The following code example gives you the complete code for map with marker and legend.
ViewModel viewModel = new ViewModel();
SfMaps maps = new SfMaps(this);
maps.SetBackgroundColor(Color.White);
ShapeFileLayer layer = new ShapeFileLayer();
layer.Uri = "usa_state.shp";
layer.DataSource = viewModel.Data;
layer.ShapeIdTableField = "STATE_NAME";
layer.ShapeIdPath = "State";
maps.Layers.Add(layer);
MapMarker marker = new MapMarker();
marker.Label = "California";
marker.Latitude = 37;
marker.Longitude = -120;
layer.Markers.Add(marker);
EqualColorMapping colorMapping = new EqualColorMapping();
colorMapping.Color = Color.ParseColor("#D84444");
colorMapping.LegendLabel = "Romney";
colorMapping.Value = "Romney";
EqualColorMapping colorMapping1 = new EqualColorMapping();
colorMapping1.Color = Color.ParseColor("#316DB5");
colorMapping1.LegendLabel = "Obama";
colorMapping1.Value = "Obama";
ShapeSetting shapeSetting = new ShapeSetting();
shapeSetting.ShapeValuePath = "Candidate";
shapeSetting.ShapeColorValuePath = "Candidate";
shapeSetting.ColorMapping.Add(colorMapping);
shapeSetting.ColorMapping.Add(colorMapping1);
layer.ShapeSettings = shapeSetting;
LegendSetting setting = new LegendSetting();
setting.ShowLegend = true;
setting.LegendPosition = new Point(75, 90);
layer.LegendSetting = setting;
SetContentView(maps);The following output is reproduced as a result of above codes.
You can download the complete getting started sample from this link.