How can I help you?
Getting Started with .NET MAUI Smart DataGrid
19 Feb 202624 minutes to read
This section provides a quick overview for working with the SfSmartDataGrid for .NET MAUI. Follow the steps below to add a basic Smart DataGrid to your project.
NOTE
The Smart DataGrid is distributed as part of the
Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponentspackage and supports AI-assisted interactions such as intelligent sorting, filtering, grouping, and highlighting. Ensure your application has the required AI service configuration to enable these features.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure the following are set up:
- Install .NET 9 SDK or later is installed.
- Set up a .NET MAUI environment with Visual Studio 2026 (v18.0.0 or later).
Step 1: Create a new .NET MAUI Project
- Go to File > New > Project and choose the .NET MAUI App template.
- Name the project and choose a location. Then, click Next.
- Select the .NET framework version and click Create.
Step 2: Install the Syncfusion® MAUI Smart DataGrid NuGet Package
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and choose Manage NuGet Packages.
- Search for Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents and install the latest version.
- Ensure the necessary dependencies are installed correctly, and the project is restored.
Step 3: Register the handler
Syncfusion.Maui.Core NuGet is a dependent package for all Syncfusion® controls of .NET MAUI. In the MauiProgram.cs file, register the handler for Syncfusion® core.
using Microsoft.Maui;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Compatibility;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Syncfusion.Maui.Core.Hosting;
namespace GettingStarted
{
public class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
builder.ConfigureSyncfusionCore();
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 4: Register the AI Service
To configure the AI services, you must call the ConfigureSyncfusionAIServices() method in the MauiProgram.cs file.
using Microsoft.Maui;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Compatibility;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents.Hosting;
namespace GettingStarted
{
public class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
string key = "<MENTION-YOUR-KEY>";
Uri azureEndPoint = new Uri("<MENTION-YOUR-URL>");
string deploymentName = "<MENTION-YOUR-DEPLOYMENT-NAME>";
// Shows how to configure Azure AI service to the Smart Components.
AzureOpenAIClient azureOpenAIClient = new AzureOpenAIClient(azureEndPoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
IChatClient azureChatClient = azureOpenAIClient.GetChatClient(deploymentName).AsIChatClient();
builder.Services.AddChatClient(azureChatClient);
builder.ConfigureSyncfusionAIServices();
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 5: Add a Basic Smart DataGrid
- Import the control namespace
Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponentsin XAML or C# code. - Initialize the SfSmartDataGrid control.
<ContentPage
. . .
xmlns:syncfusion="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents">
<syncfusion:SfSmartDataGrid />
</ContentPage>using Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents;
. . .
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfSmartDataGrid dataGrid = new SfSmartDataGrid();
this.Content = dataGrid;
}
}Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure the following are set up:
- Install .NET 9 SDK or later is installed.
- Set up a .NET MAUI environment with Visual Studio Code.
- Ensure that the .NET MAUI extension is installed and configured as described here.
Step 1: Create a new .NET MAUI Project
- Open the command palette by pressing
Ctrl+Shift+Pand type .NET:New Project and enter. - Choose the .NET MAUI App template.
- Select the project location, type the project name and press Enter.
- Then choose Create project.
Step 2: Install the Syncfusion® MAUI Smart DataGrid NuGet Package
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and choose Manage NuGet Packages.
- Search for Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents and install the latest version.
- Ensure the necessary dependencies are installed correctly, and the project is restored.
Step 3: Register the handler
Syncfusion.Maui.Core NuGet is a dependent package for all Syncfusion® controls of .NET MAUI. In the MauiProgram.cs file, register the handler for Syncfusion® core.
using Microsoft.Maui;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Compatibility;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Syncfusion.Maui.Core.Hosting;
namespace GettingStarted
{
public class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
builder.ConfigureSyncfusionCore();
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 4: Register the AI Service
To configure the AI services, you must call the ConfigureSyncfusionAIServices() method in the MauiProgram.cs file.
using Microsoft.Maui;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Compatibility;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents.Hosting;
namespace GettingStarted
{
public class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
string key = "<MENTION-YOUR-KEY>";
Uri azureEndPoint = new Uri("<MENTION-YOUR-URL>");
string deploymentName = "<MENTION-YOUR-DEPLOYMENT-NAME>";
// Shows how to configure Azure AI service to the Smart Components.
AzureOpenAIClient azureOpenAIClient = new AzureOpenAIClient(azureEndPoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
IChatClient azureChatClient = azureOpenAIClient.GetChatClient(deploymentName).AsIChatClient();
builder.Services.AddChatClient(azureChatClient);
builder.ConfigureSyncfusionAIServices();
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 5: Add a Basic Smart DataGrid
- Import the control namespace
Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponentsin XAML or C# code. - Initialize the SfSmartDataGrid control.
<ContentPage
. . .
xmlns:syncfusion="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents">
<syncfusion:SfSmartDataGrid />
</ContentPage>using Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents;
. . .
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfSmartDataGrid dataGrid = new SfSmartDataGrid();
this.Content = dataGrid;
}
}Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure the following are set up:
- Ensure you have the latest version of JetBrains Rider.
- Install .NET 9 SDK or later is installed.
- Make sure the MAUI workloads are installed and configured as described here.
Step 1: Create a new .NET MAUI Project
- Go to File > New Solution, Select .NET (C#) and choose the .NET MAUI App template.
- Enter the Project Name, Solution Name, and Location.
- Select the .NET framework version and click Create.
Step 2: Install the Syncfusion® MAUI Smart DataGrid NuGet Package
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and choose Manage NuGet Packages.
- Search for Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents and install the latest version.
- Ensure the necessary dependencies are installed correctly, and the project is restored.
Step 3: Register the handler
Syncfusion.Maui.Core NuGet is a dependent package for all Syncfusion® controls of .NET MAUI. In the MauiProgram.cs file, register the handler for Syncfusion® core.
using Microsoft.Maui;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Compatibility;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Syncfusion.Maui.Core.Hosting;
namespace GettingStarted
{
public class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
builder.ConfigureSyncfusionCore();
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 4: Register the AI Service
To configure the AI services, you must call the ConfigureSyncfusionAIServices() method in the MauiProgram.cs file.
using Microsoft.Maui;
using Microsoft.Maui.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Compatibility;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Xaml;
using Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents.Hosting;
namespace GettingStarted
{
public class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
});
string key = "<MENTION-YOUR-KEY>";
Uri azureEndPoint = new Uri("<MENTION-YOUR-URL>");
string deploymentName = "<MENTION-YOUR-DEPLOYMENT-NAME>";
// Shows how to configure Azure AI service to the Smart Components.
AzureOpenAIClient azureOpenAIClient = new AzureOpenAIClient(azureEndPoint, new AzureKeyCredential(key));
IChatClient azureChatClient = azureOpenAIClient.GetChatClient(deploymentName).AsIChatClient();
builder.Services.AddChatClient(azureChatClient);
builder.ConfigureSyncfusionAIServices();
return builder.Build();
}
}
}Step 5: Add a Basic Smart DataGrid
- Import the control namespace
Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponentsin XAML or C# code. - Initialize the SfSmartDataGrid control.
<ContentPage
. . .
xmlns:syncfusion="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents">
<syncfusion:SfSmartDataGrid />
</ContentPage>using Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents;
. . .
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
SfSmartDataGrid dataGrid = new SfSmartDataGrid();
this.Content = dataGrid;
}
}Step 6: Define the View Model
Data Model
Create a simple data model as shown in the following code example, and save it as OrderInfo.cs file:
public class OrderInfo
{
private string orderID;
private string customerID;
private string customer;
private string shipCity;
private string shipCountry;
public string OrderID
{
get { return orderID; }
set { this.orderID = value; }
}
public string CustomerID
{
get { return customerID; }
set { this.customerID = value; }
}
public string ShipCountry
{
get { return shipCountry; }
set { this.shipCountry = value; }
}
public string Customer
{
get { return this.customer; }
set { this.customer = value; }
}
public string ShipCity
{
get { return shipCity; }
set { this.shipCity = value; }
}
public OrderInfo(string orderId, string customerId, string country, string customer, string shipCity)
{
this.OrderID = orderId;
this.CustomerID = customerId;
this.Customer = customer;
this.ShipCountry = country;
this.ShipCity = shipCity;
}
}NOTE
If you want your data model to respond to property changes, implement the
INotifyPropertyChangedinterface in your model class.
View Model
Create a model repository class with OrderInfo collection property initialized with the required number of data objects in a new class file as shown in the following code example, and save it as OrderInfoRepository.cs file:
public class OrderInfoRepository
{
private ObservableCollection<OrderInfo> orderInfo;
public ObservableCollection<OrderInfo> OrderInfoCollection
{
get { return orderInfo; }
set { this.orderInfo = value; }
}
public OrderInfoRepository()
{
orderInfo = new ObservableCollection<OrderInfo>();
this.GenerateOrders();
}
public void GenerateOrders()
{
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1001", "Maria Anders", "Germany", "ALFKI", "Berlin"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1002", "Ana Trujillo", "Mexico", "ANATR", "Mexico D.F."));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1003", "Ant Fuller", "Mexico", "ANTON", "Mexico D.F."));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1004", "Thomas Hardy", "UK", "AROUT", "London"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1005", "Tim Adams", "Sweden", "BERGS", "London"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1006", "Hanna Moos", "Germany", "BLAUS", "Mannheim"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1007", "Andrew Fuller", "France", "BLONP", "Strasbourg"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1008", "Martin King", "Spain", "BOLID", "Madrid"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1009", "Lenny Lin", "France", "BONAP", "Marsiella"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1010", "John Carter", "Canada", "BOTTM", "Lenny Lin"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1011", "Laura King", "UK", "AROUT", "London"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1012", "Anne Wilson", "Germany", "BLAUS", "Mannheim"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1013", "Martin King", "France", "BLONP", "Strasbourg"));
orderInfo.Add(new OrderInfo("1014", "Gina Irene", "UK", "AROUT", "London"));
}
}Binding the ViewModel
Create a ViewModel instance and set it as the DataGrid’s BindingContext. This enables property binding from ViewModel class.
To populate the SfSmartDataGrid, bind the item collection from its BindingContext to SfSmartDataGrid.ItemsSource property.
The following code example binds the collection created in the previous step to the SfSmartDataGrid.ItemsSource property:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:syncfusion="clr-namespace:Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents;assembly=Syncfusion.Maui.SmartComponents"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:GettingStarted"
x:Class="GettingStarted.MainPage">
<ContentPage.BindingContext>
<local:OrderInfoRepository x:Name="viewModel" />
</ContentPage.BindingContext>
<ContentPage.Content>
<syncfusion:SfSmartDataGrid x:Name="dataGrid"
ItemsSource="{Binding OrderInfoCollection}">
<syncfusion:SfSmartDataGrid.Columns>
<syncfusion:TextColumn HeaderText="Order ID" Format="0"
MappingName="OrderID" Width="150"/>
<syncfusion:TextColumn HeaderText="Customer ID"
MappingName="CustomerID"
Width="150" />
<syncfusion:TextColumn HeaderText="Ship Country"
MappingName="ShipCountry"
Width="150" />
</syncfusion:SfSmartDataGrid.Columns>
</syncfusion:SfSmartDataGrid>
</ContentPage.Content>
</ContentPage>OrderInfoRepository viewModel = new OrderInfoRepository();
dataGrid.ItemsSource = viewModel.OrderInfoCollection;Step 7: Enabling AI-Assisted Operations
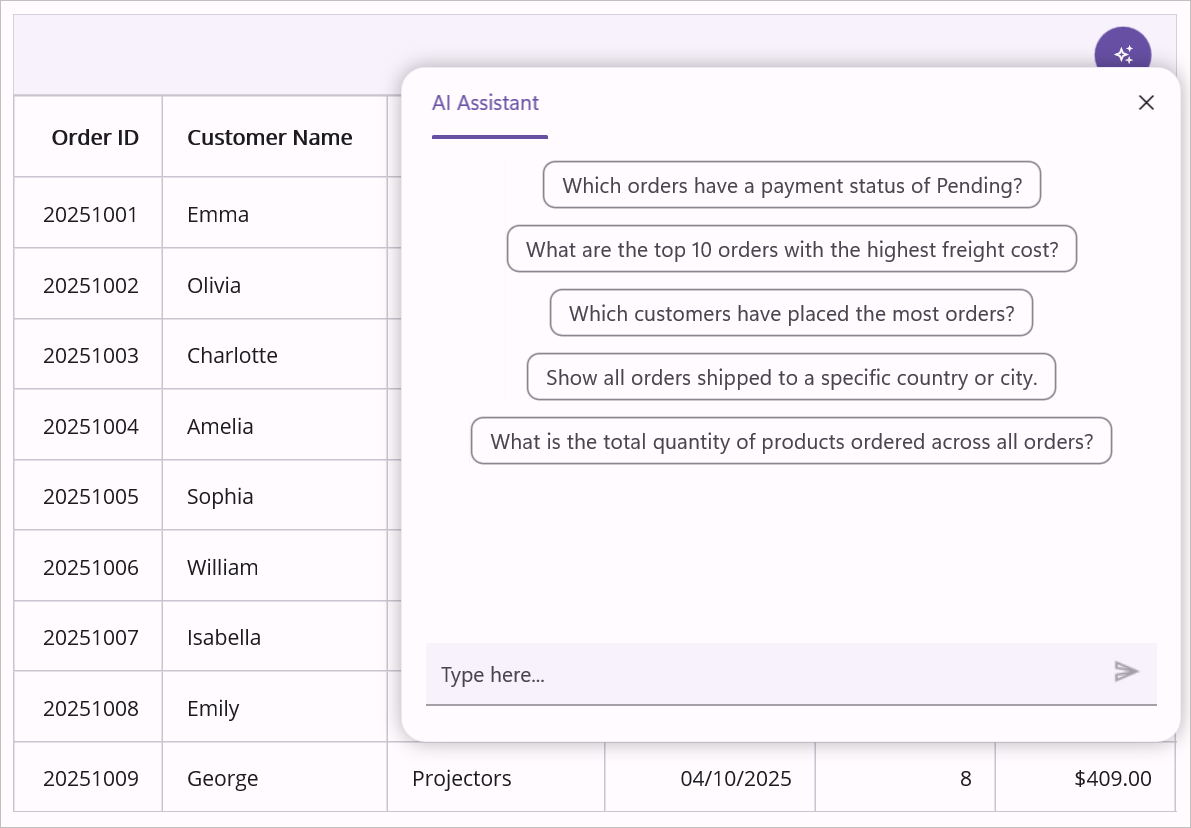
The Smart DataGrid supports natural language operations for enhanced data interaction. These features require configuring an AI provider in your application.
Using AI Features
Once configured, leverage AI-assisted features such as:
- AI Sorting: Sort data intelligently by entering prompts like “Sort by customer name alphabetically”.
- Intelligent Filtering: Apply filters using natural language, e.g., “Show orders from Germany shipped in the last month”.
- Smart Grouping: Group data with prompts like “Group by ship country, then by customer”.
- Row and Cell Highlighting: Highlight critical information, e.g., “Highlight orders where quantity is greater than 10”.
Step 8: Running the Application
Press F5 to build and run the application. Once compiled, the smart datagrid will be displayed with the data provided, and AI features will be available after configuration.
Here is the result of the previous codes,
NOTE
You can refer to our .NET MAUI Smart DataGrid feature tour page for its groundbreaking feature representations. You can also explore our .NET MAUI Smart DataGrid Example that shows you how to render the Smart DataGrid in .NET MAUI.