How can I help you?
Label in JavaScript Diagram Control
Label is a block of text that can be displayed over a node or connector. Label is used to textually represent an object with a string that can be edited at run time. You can add Multiple Labels to a node/connector.
Create Label
You can add a label to a node/connector by defining the label object and adding that to the labels collection of node/connector. The text property of label defines the text to be displayed. The following code illustrates how to create a Label.
//Initializes Diagram
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
//Initializes nodes collection
nodes: [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
//Initializes labels collection
labels: [
// Defines JSON to create a label
{
//Defines the text to be displayed
text: "Label"
}
]
}],
//Initializes connectors collection
connectors: [{
name: "connector1",
sourcePoint: {
x: 200,
y: 50
},
targetPoint: {
x: 300,
y: 150
},
segments: [{
type: "orthogonal",
length: 50,
direction: "bottom"
}],
//Initializes labels collection
labels: [
//Defines JSON to create a label
{
//Defines the text to be displayed
text: "Label",
//Defines the background color of the text block
fillColor: "white"
}
]
}]
});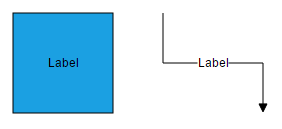
To explore more label properties, refer to Label Properties.
Add Labels at runtime
-
Labels can be added at runtime by using the client side method addLabel. Also, we can insert a label into a node’s label collection at runtime using client side method insertLabel. The following code illustrates how to add a label to a node.
-
The label’s name property is used to define the name of the label and its further used to find the label at runtime and do any customization.
var diagram = $("#sourceDiagram").ejDiagram("instance");
// Defines JSON to create a label
var label = { name: "label", text: "Node" };
diagram.addLabel("node1", label);
//Insert label at a specific index of labels collection
var label = { name: "label", text: "New Label", offset: { x: 0.1, y: 0.1 } };
diagram.insertLabel("node1", label, 1);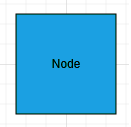
Remove Labels at runtime
You can remove a collection of labels from the node by using client side method removeLabels. Please refer to below link which shows how to use removeLabels method.
Update Label at runtime
The client side API updateLabel is used to update the labels at run time.
The following code example illustrates how to change the label properties.
var diagram = $("#diagram").ejDiagram("instance");
var selectedObject = diagram.model.selectedItems.children[0];
diagram.updateLabel(selectedObject.name, selectedObject.labels[0], { text: "label", fillColor: "red" });Alignment
Label can be aligned relative to the node boundaries. It has margin, offset, horizontal and vertical alignment settings. It is quite tricky when all four alignments are used together but gives you more control over alignment.
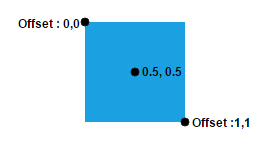
Offset
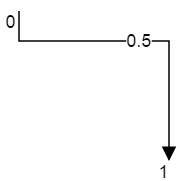
The offset property of label is used to align the labels based on fractions. 0 represents top/left corner, 1 represents bottom/right corner, and 0.5 represents half of width/height.
To set size for a nodes label, use width and height properties.
The following image shows the relationship between the label position (black colored circle) and offset (fraction values).
Horizontal and vertical alignments
The horizontalAlignment property of label is used to set how the label is horizontally aligned at the label position determined from the fraction values. The verticalAlignment property is used to set how label is vertically aligned at the label position.
The following tables illustrates all the possible alignments visually with offset (0, 0).
| Horizontal Alignment | Vertical Alignment | Output with Offset(0,0) |
|---|---|---|
| Left | Top |  |
| Center |  |
|
| Right | 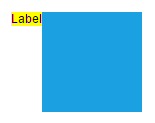 |
|
| Left | Center | 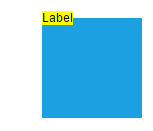 |
| Center | 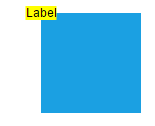 |
|
| Right | 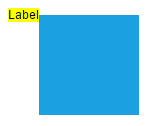 |
|
| Left | Bottom | 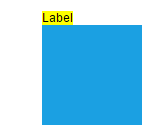 |
| Center | 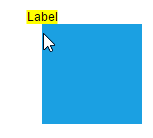 |
|
| Right | 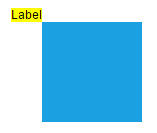 |
The following codes illustrates how to align labels.
//Initializes Diagram
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
nodes: [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
labels: [{
text: "Label",
// Sets offset to label
offset: {
x: 0,
y: 0.5
},
// Sets to align label horizontally relative to given offset
horizontalAlignment: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.HorizontalAlignment.Left,
// Sets to align label vertically relative to given offset
verticalAlignment: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.VerticalAlignment.Center,
// Sets text alignment to label
textAlign: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.TextAlign.Center
}]
}],
});
Label alignment with respect to Segments
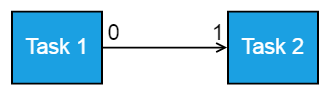
segmentOffset and alignment properties of label allows you to align the connector labels with respect to the segments. In the following image, the labels are placed exactly over the segments regardless of its rectangular bounds.
Following code example illustrates how to align connector labels.
var nodes = [
{ name: "node1", width: 50, height: 40, offsetX: 200, offsetY: 200, labels: [{ "text": "Task 1" }] },
{ name: "node2", width: 50, height: 40, offsetX: 400, offsetY: 200, labels: [{ "text": "Task 2" }] }
];
var connectors = [
{ name: "connector1", sourceNode: "node1", targetNode: "node2"}
];
//Initializes Diagram
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
nodes: nodes,
connectors: connectors,
snapSettings: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.SnapConstraints.None,
defaultSettings: {
connector: {
segments: [{ type: "orthogonal" }],
// Sets labels for segments
labels: [{
text: "0",
fontColor: "black",
// Aligns the label either top or left(before) of the connector segment
alignment: "before",
// Sets the position of the label with respect to the segment
segmentOffset: 0
},{
text: "1",
fontColor: "black",
// Aligns the label either bottom or right(after) of the connector segment
alignment: "after",
// Sets segmentOffset as 1
segmentOffset: 1,
// Enables boundaryConstraints for the label should be docked within the label bounds
boundaryConstraints: true,
}], lineWidth: 2
},
node: { borderColor: "#000000", fillColor: "#1BA0E2", labels: [{ "fontColor": "black", }]},
},
});
By default, connector labels will be aligned with respect to the segments. The relativeMode property of label allows you to disable this segment specific label alignment. Following code example illustrates how to disable the segment specific label alignment.
var nodes = [
{ name: "node1", width: 50, height: 40, offsetX: 200, offsetY: 200, labels: [{ "text": "Task 1" }] },
{ name: "node2", width: 50, height: 40, offsetX: 400, offsetY: 200, labels: [{ "text": "Task 2" }] }
];
var connectors = [
{ name: "connector1", sourceNode: "node1", targetNode: "node2",
lineWidth: 2,
segments: [{ type: "orthogonal" }],
// Sets labels for segments
labels: [{
text: "0",
fontColor: "black",
//Sets the relativeMode as segmentpath
relativeMode: "segmentpath",
}]
}];
//Initializes Diagram
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
connectors: connectors,
snapSettings: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.SnapConstraints.None
});Margin
Margin is an absolute value used to add some blank space in any one of its four sides. You can displace the labels with the margin property.
The following code example illustrates how to align a label based on its offset, horizontalAlignment, verticalAlignment and margin values.
//Initializes Diagram
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model
nodes: [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
labels: [{
text: "Label",
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 1
},
horizontalAlignment: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.HorizontalAlignment.Center,
verticalAlignment: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.VerticalAlignment.Top,
//Sets margin to add label outside a node
margin: {
top: 10
}
}]
}],
});
Text Alignment
The textAlign property of label allows you to set how the text should be aligned (left, right, center, or justify) inside the text block. The following codes illustrate how to set textAlign for a label.
//Initializes Diagram
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
nodes: [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
// Sets text alignment for a label
labels: [{
text: "Text Align is set as Left",
textAlign: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.TextAlign.Left
}]
}],
});
| TextAlign | Image |
|---|---|
| Left |  |
| Right |  |
| Center |  |
| Justify |  |
Hyperlink
Diagram provides a support to add a hyperlink for the nodes/connectors label. It can also be customized.
// Defines JSON to create a node
var nodes = [{
name: "hyperLinkNode",
fillColor: "white",
width: 150, height: 60,
offsetX: 100, offsetY: 100,
// Sets the hyperlink for the node label
labels: [{ "hyperText": "https://www.syncfusion.com" }]
}];
//Initializes Diagram
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%", height: "100%",
//Initializes nodes collection
nodes: nodes
});
Template support for Label
Diagram provides a template support for label. You need to define a id of template(SVG/Html) using label’s templateId property.
Wrapping
When text overflows node boundaries, you can control it by using text wrapping. So, it is wrapped into multiple lines. The wrapping property of label defines how the text should be wrapped. The following code illustrates how to wrap a text in a node.
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
nodes: [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
//Enables Text-wrapping
labels: [{
text: "Label Text Wrapping",
wrapping: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.TextWrapping.Wrap
}]
}],
});
| Values | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| NoWrap | Text will not be wrapped |  |
| Wrap | Text-wrapping occurs when the text overflows beyond the available node width. |  |
| WrapWithOverflow (Default) | Text-wrapping occurs when the text overflows beyond the available node width. However, the text may overflow beyond the node width in the case of a very long word. |  |
TextOverflow
- The label’s textOverflow property is used control whether to display the overflowed content in node or not.
- Also you can use label’s overflowType property to define whether the overflowed content can be clipped (i.e. cut off, hidden) or display an ellipsis (‘…’).
Appearance
-
You can change the font style of the labels with the font specific properties(fontSize, fontFamily, fontColor. The following code illustrates how to customize the appearance of a label.
-
The label’s bold, italic and textDecoration properties are used to style the label’s text.
-
The label’s fillColor, borderColor, [borderWidth] (/api/js/ejdiagram#members:nodes-labels-borderwidth “borderWidth”) properties are used to define the background color and border color of the label and opacity property is used to define the transparency of the labels.
-
The cssClass property used to customize the style of label using user defined CSS class.
-
The visible property of the label enables or disables the visibility of label.
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model
nodes: [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
labels: [{
text: "Label Text",
//Sets styles to a label
fontSize: 12,
fontFamily: "TimesNewRoman",
fontColor: "black",
bold: true,
italic: true,
textDecoration: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.TextDecorations.Underline
}]
}],
});
The fill, border and opacity appearances of the text can also be customized with appearance specific properties of label.The following code illustrates how to customize background, opacity and border of a label.
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
//Sets nodes collection to Diagram model
nodes: [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
labels: [{
text: "Label Text",
//Customizes background and borders of a label
fillColor: "white",
borderColor: "black",
borderWidth: 1,
//Customize transparency of a label
opacity: 0.7
}]
}],
});
Drag
A Label can be displaced from its original position to any preferred location interactively. Dragging is disabled by default. You can enable label dragging with the constraints property of node/connector. The following code illustrates how to enable label dragging.
var nodeConstraints = ej.datavisualization.Diagram.NodeConstraints;
var nodes = [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
//Enables Label Dragging for node.
constraints: nodeConstraints.Default | nodeConstraints.DragLabel,
labels: [{
text: "Label Text"
}]
}];
var connectorConstraints = ej.datavisualization.Diagram.ConnectorConstraints;
var connectors = [{
name: "connector1",
sourcePoint: {
x: 200,
y: 50
},
targetPoint: {
x: 300,
y: 150
},
segments: [{
type: "orthogonal",
length: 50,
direction: "bottom"
}],
//Enables Label Dragging for connector.
constraints: connectorConstraints.Default | connectorConstraints.DragLabel,
labels: [{
text: "Label "
}]
}];
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
nodes: nodes,
connectors: connectors
});
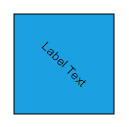
Rotate
You can rotate the labels to any desired angle. Labels are rotated to the angle that is defined by the rotateAngle property of label. The following code illustrates how to rotate a label.
//Initializes Diagram
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
nodes: [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
labels: [{
text: "Label",
//Sets label's rotation Angle
rotateAngle: 45
}]
}]
});
NOTE
There is no built-in support to rotate labels interactively.
Edit
Diagram provides support to edit a Label at runtime, either programmatically or interactively. By default, label is in View mode. But it can be brought to edit mode in two ways;
- By double-clicking the label.
- By selecting the item and pressing the F2 key.
Double-clicking any label will enables editing of that. Double-clicking the node enables first label editing. When the focus of editor is lost, the label for the node is updated.
When you double click on the node/connector/diagram model, the doubleClick event gets triggered.
You can programmatically edit the label by changing the mode of the label. Also, you can use client side method startLabelEdit to edit the label at runtime. The following code illustrates how to edit the label programmatically.
var diagram = $("#diagram").ejDiagram("instance");
var node = diagram.model.selectedItems.children[0];
//Sets label mode as Edit
var options = {
mode: ej.datavisualization.Diagram.LabelEditMode.Edit
};
diagram.updateLabel(node.name, node.labels[0], options);
//edit the label at runtime
diagram.startLabelEdit(node,node.labels[0]);
- Once the text editing is ended and text editor is focused, you can use the below events to do your customization.
- The diagram client side event editorFocusChange gets triggered when editor got focus at the time of node’s label or text node editing.
- The diagram client side event textChange gets triggered when label editing is ended.
Read Only labels
Diagram allows to create read only labels. You have to set the readOnly property of label to enable/disable the read only mode. The following code illustrates how to enable readOnly mode.
//Initializes Diagram
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
nodes: [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
//Sets label as read-only
labels: [{
text: "Label",
readOnly: true
}]
}],
});Drag Limit
-
The diagram control now supports defining the dragLimit to the label while dragging from the connector and also update the postion to the nearest segment offset.
-
You can set the value to dragLimit left, right, top and bottom properties which allows the dragging of connector labels to a certain limit based on user defined values.
-
By default, drag limit will be disabled for connector. It can be enabled with the constraints property of connector.
var connectorConstraints = ej.datavisualization.Diagram.ConnectorConstraints;
//Enables drag limit for a connector.
var constraints = connectorConstraints.Default | connectorConstraints.DragLimit | connectorConstraints.DragLabel;
//Initializes Diagram
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
connectors:[
{
name:"connector1",
constraints: constraints,
labels:[
{ text:"connector", { dragLimit:{ left: 10, right: 10, top: 10, bottom: 10 }}}
]
}
]
});Multiple labels
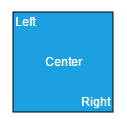
You can add any number of labels to a node or connector. The following code illustrates how to add multiple labels to a node.
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
pageSettings: {
scrollLimit: "diagram"
},
nodes: [{
name: "node",
width: 100,
height: 100,
offsetX: 100,
offsetY: 100,
borderColor: "black",
fillColor: "#1BA0E2",
//Adds multiple labels to a node
labels: [{
text: "Left",
offset: {
x: 0.12,
y: 0.1
}
}, {
text: "Center",
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0.5
}
}, {
text: "Right",
offset: {
x: 0.82,
y: 0.9
}
}]
}],
});
LabelRendering Mode
Diagram provides a support to render the label in the diagram in two mode by using labelRenderingMode property.
-
Text wrapping is not available for SVG elements by default. So while rendering the label in SVG mode, we have to achieve the wrapping by some calculation. So it will take more time when compared to rendering the label in HTML mode. Since text wrapping is available for HTML elements by default.
-
However while rendering the label in HTML mode, we have to face the below limitation.
$("#diagram").ejDiagram({
//renders label in same layer
labelRenderingMode: "svg"
});Constraints
The constraints property of label allows you to enable/disable certain label behaviours. For instance, you can disable label interaction such as dragging, resizing, rotation and so on.
Limitation
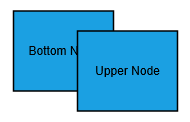
- To enable faster rendering, labels are rendered in a separate layer because of this, all the labels always stay on top. When two nodes are overlapped, text of underlying node is not hidden by the overlapped node.
| Expected behavior | Current behavior |
|---|---|
 |
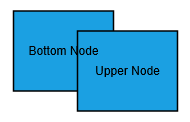 |