How can I help you?
Scrolling in Flutter DataGrid (SfDataGrid)
22 May 202524 minutes to read
SfDataGrid provides support to scroll the content in both horizontal and vertical directions.
Show Scrollbars always
You can show horizontal and vertical scrollbars always by using the SfDataGrid.isScrollbarAlwaysShown property. When the isScrollbarAlwaysShown is set to false, the scrollbar will be shown during scrolling and will fade out otherwise. When it is true, the scrollbar will always be visible and never fade out even after the scrolling.
NOTE
The default value of
isScrollbarAlwaysShownis false.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: SfDataGrid(
source: _employeeDataSource,
isScrollbarAlwaysShown: true,
columns: [
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Name',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'Salary',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
]));
}Change scrollbars visibility
You can control the visibility of horizontal and vertical scrollbars in the DataGrid by setting the SfDataGrid.showVerticalScrollbar and SfDataGrid.showHorizontalScrollbar properties. To disable the default scrollbar of the SingleChildScrollView, wrap the ScrollConfiguration as the parent for the SfDataGrid and set the scrollbars to false.
NOTE
The default value of
showVerticalScrollbarandshowHorizontalScrollbaris true.
The following code snippets demonstrate how to hide the scrollbars in the DataGrid:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Syncfusion Flutter DataGrid'),
),
body: ScrollConfiguration(
behavior: const ScrollBehavior().copyWith(scrollbars: false),
child: SfDataGrid(
source: employeeDataSource,
showVerticalScrollbar: false,
showHorizontalScrollbar: false,
isScrollbarAlwaysShown: true,
columns: <GridColumn>[
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text('Name'))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text('Salary'))),
],
),
),
);
}Setting scroll physics for scroll bars
SfDataGrid allows you to set the ScrollPhysics for horizontal and vertical scrollbars to control how the scroll view should respond to user input by using horizontalScrollPhysics and verticalScrollPhysics properties respectively.
NOTE
The default values of
horizontalScrollPhysicsandverticalScrollPhysicsproperties areAlwaysScrollableScrollPhysics().
The following example shows how to disable the horizontal and vertical scrolling by setting NeverScrollableScrollPhysics().
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: SfDataGrid(
source: _employeeDataSource,
horizontalScrollPhysics: NeverScrollableScrollPhysics(),
verticalScrollPhysics: NeverScrollableScrollPhysics(),
columns: [
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Name',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'Salary',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
]));
}Programmatic scrolling
The Flutter DataTable provides support to scroll to a particular row and column index programmatically.
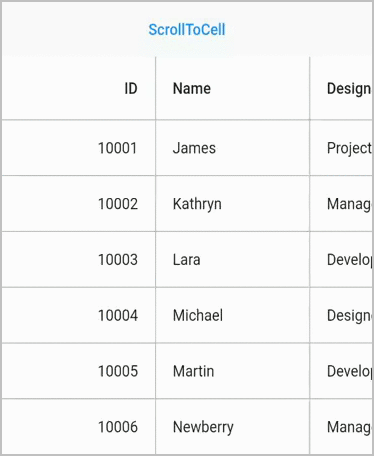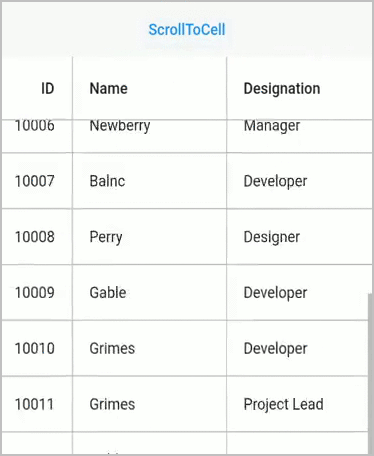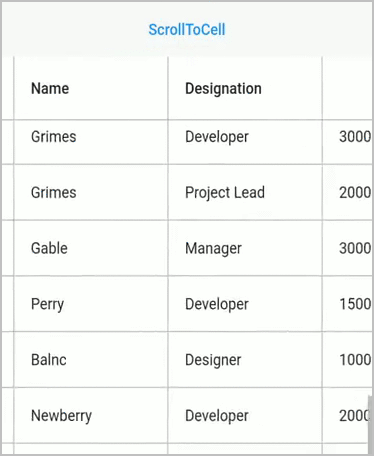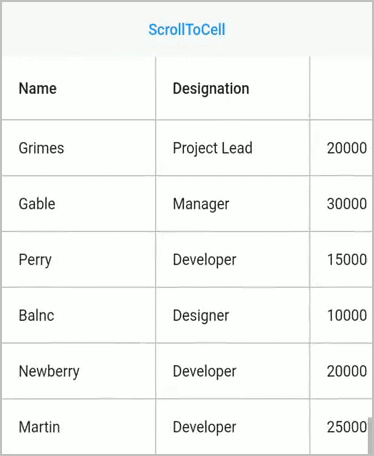
Scroll to cell
Scroll programmatically to a particular cell can be achieved by passing the row and column index in the scrollToCell method. SfDataGrid allows to enable or disable the scrolling animation by passing true to the canAnimate parameter in the scrollToCell method.
NOTE
The default value of
canAnimateisfalse.
final DataGridController _controller = DataGridController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Column(children: [
TextButton(
child: Text('ScrollToCell'),
onPressed: () {
_controller.scrollToCell(10, 1);
}),
Expanded(
child: SfDataGrid(
source: _employeeDataSource,
defaultColumnWidth: 150,
gridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
headerGridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
controller: _controller,
columns: [
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Name',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'Salary',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
]))
]));
}
Scroll to row
Scroll programmatically to a particular row by passing the row index in the scrollToRow method. SfDataGrid allows to enable or disable the scrolling animation by passing true to the canAnimate parameter in the scrollToRow method.
NOTE
The default value of
canAnimateisfalse.
final DataGridController _controller = DataGridController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Column(children: [
TextButton(
child: Text('ScrollToRow'),
onPressed: () {
_controller.scrollToRow(10);
}),
Expanded(
child: SfDataGrid(
source: _employeeDataSource,
defaultColumnWidth: 150,
gridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
headerGridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
controller: _controller,
columns: [
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Name',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'Salary',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
]))
]));
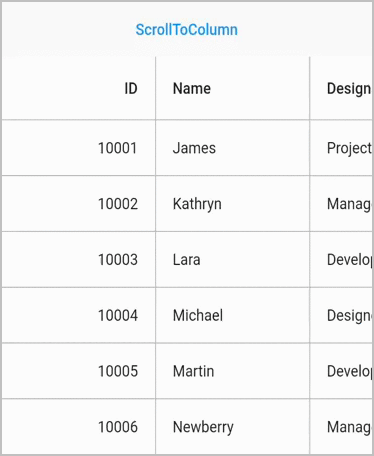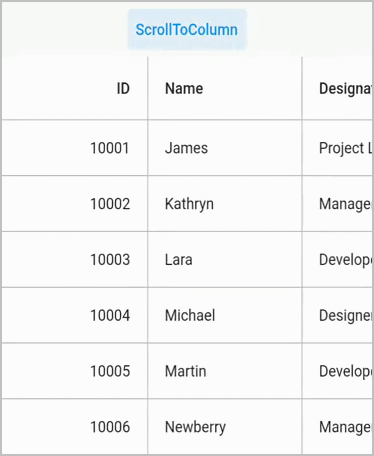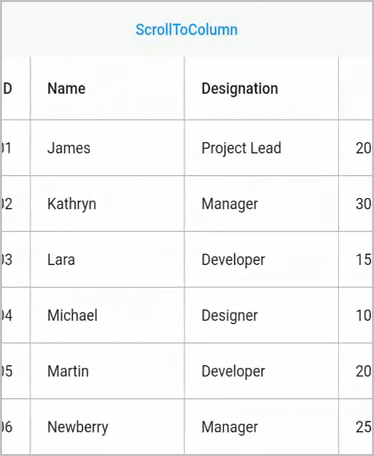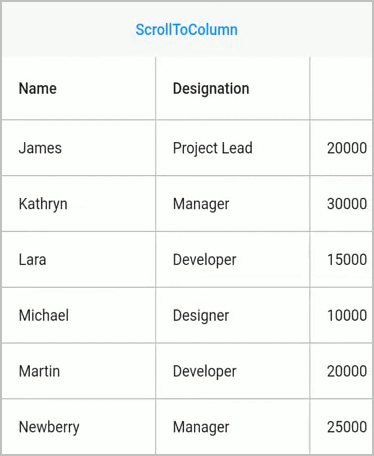
}Scroll to column
Scroll programmatically to a particular column by passing the column index in the scrollToColumn method. SfDataGrid allows to enable or disable the scrolling animation by passing true to the canAnimate parameter in the scrollToColumn method.
NOTE
The default value of
canAnimateisfalse.
final DataGridController _controller = DataGridController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Column(children: [
TextButton(
child: Text('ScrollToColumn'),
onPressed: () {
_controller.scrollToColumn(1);
}),
Expanded(
child: SfDataGrid(
source: _employeeDataSource,
defaultColumnWidth: 150,
gridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
headerGridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
controller: _controller,
columns: [
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Name',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'Salary',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
]))
]));
}
Scroll to the specific position
The SfDataGrid allows positioning of the scrolled row or column in view programmatically by passing the DataGridScrollPosition to rowPosition and columnPosition arguments respectively in scrollToCell and position argument of the scrollToRow and scrollToColumn methods. The following are the four types of positions available.
makeVisible: Scroll to make a specified row/column visible in Datagrid. If the specified row/column is already in view, scrolling will not occur.
start: Scroll to make the row/column positioned at the start of the Datagrid.
center: Scroll to make the row/column positioned at the center of the Datagrid.
end: Scroll to make the row/column positioned at the end of the Datagrid.
NOTE
The default value of
DataGridScrollPositionisStart.
final DataGridController _controller = DataGridController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Column(children: [
TextButton(
child: Text('ScrollToCell'),
onPressed: () {
_controller.scrollToCell(10, 1,
canAnimate: true,
rowPosition: DataGridScrollPosition.start,
columnPosition: DataGridScrollPosition.start);
}),
Expanded(
child: SfDataGrid(
source: _employeeDataSource,
defaultColumnWidth: 150,
gridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
headerGridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
controller: _controller,
columns: [
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Name',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'Salary',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
]))
]));
}Scroll to the vertical offset
The Flutter DataTable supports scrolling programmatically to a particular vertical offset by passing the offset value to the scrollToVerticalOffset method. Also, it allows enabling the scrolling animation by passing true to the canAnimate parameter in the scrollToVerticalOffset method.
NOTE
The default value of
canAnimateisfalse.
final DataGridController _controller = DataGridController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Column(children: [
TextButton(
child: Text('ScrollToVerticalOffset'),
onPressed: () {
_controller.scrollToVerticalOffset(500);
}),
Expanded(
child: SfDataGrid(
source: _employeeDataSource,
defaultColumnWidth: 150,
gridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
headerGridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
controller: _controller,
columns: [
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Name',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'Salary',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
]))
]));
}Scroll to the horizontal offset
The Flutter DataTable supports scrolling programmatically to a particular horizontal offset by passing the offset value to the scrollToHorizontalOffset method. Also, it allows enabling the scrolling animation by passing true to the canAnimate parameter in the scrollToHorizontalOffset method.
NOTE
The default value of
canAnimateisfalse.
final DataGridController _controller = DataGridController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Column(children: [
TextButton(
child: Text('ScrollToHorizontalOffset'),
onPressed: () {
_controller.scrollToHorizontalOffset(400);
}),
Expanded(
child: SfDataGrid(
source: _employeeDataSource,
defaultColumnWidth: 150,
gridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
headerGridLinesVisibility: GridLinesVisibility.both,
controller: _controller,
columns: [
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Name',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'Salary',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
]))
]));
}NOTE
The vertical and horizontal scrolled offset can be retrieved by using
DataGridController.verticalOffsetandDataGridController.horizontalOffsetproperties.
Listen the scroll changes
Listen to the vertical and horizontal scroll changes by using the verticalScrollController and the horizontalScrollController properties respectively. Set the listener in the verticalScrollController and the horizontalScrollController using the addListener method. By subscribing to this listener, the subscribed method in the sample level will be called on vertical or horizontal scrolling.
The following example demonstrates how to load more rows when vertical scrolling reaches 70% of the vertical maxScrollExtent,
import 'package:intl/intl.dart';
late EmployeeDataSource _employeeDataSource;
late ScrollController verticalScrollController;
void verticalListener() {
if (_verticalScrollController.position.pixels >=
_verticalScrollController.position.maxScrollExtent * (70 / 100)) {
_employeeDataSource.loadMoreRows();
}
}
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_employeeDataSource = _EmployeeDataSource();
_verticalScrollController = ScrollController()..addListener(verticalListener);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter DataGrid Sample'),
),
body: SfDataGrid(
source: _employeeDataSource,
verticalScrollController: _verticalScrollController,
columnWidthMode: ColumnWidthMode.fill,
columns: _getColumns()),
);
}
class _EmployeeDataSource extends DataGridSource {
_EmployeeDataSource() {
loadEmployees(25);
}
List<Employee> employees = [];
List<DataGridRow> dataGridRows = [];
@override
List<DataGridRow> get rows => dataGridRows;
@override
DataGridRowAdapter buildRow(DataGridRow row) {
return DataGridRowAdapter(cells: [
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(row.getCells()[0].value.toString(),
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis)),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(row.getCells()[1].value.toString(),
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis)),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(row.getCells()[2].value.toString(),
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis)),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
NumberFormat.currency(locale: 'en_US', symbol: '\$')
.format(row.getCells()[3].value)
.toString(),
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis))
]);
}
void loadEmployees(int count) {
final Random random = Random();
final int startIndex = employees.isNotEmpty ? employees.length : 0,
endIndex = startIndex + count;
for (int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
var employee = Employee(
1000 + i,
1700 + i,
names[i < names.length ? i : random.nextInt(names.length - 1)],
random.nextInt(1000) + random.nextDouble(),
cities[random.nextInt(cities.length - 1)],
1500.0 + random.nextInt(100),
);
employees.add(employee);
dataGridRows.add(employee.getDataGridRow);
}
}
void loadMoreRows() {
loadEmployees(15);
notifyListeners();
}
}NOTE
Download the demo application from GitHub.
Increase row cache limit
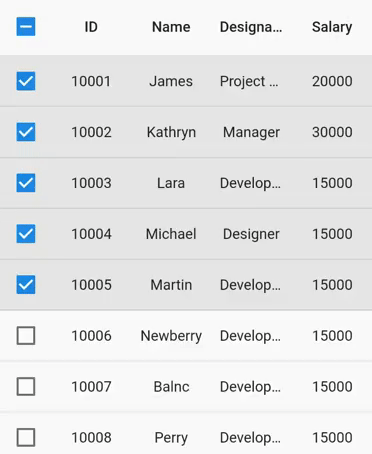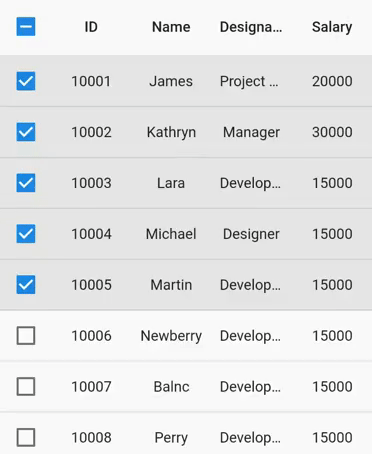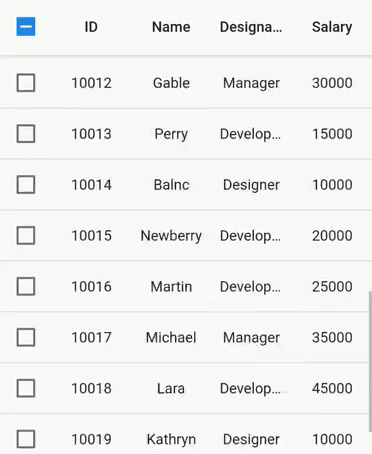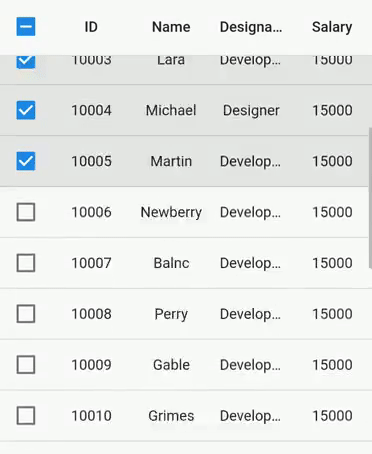
By default, rows are generated based on the viewport size, and these rows are reused while scrolling. Set the SfDataGrid.rowsCacheExtent property to avoid the visible changes caused by re-using. For example, if you show the checkbox in a column without setting the rows using this property, checkbox state changes with animation can be seen when vertical scrolling is performed.
The rowsCacheExtent property will create the additional rows internally with the existing visible rows, which are already allocated based on viewport size. So, the number of rows that will be reused will increase.
List<Employee> employees = <Employee>[];
late EmployeeDataSource employeeDataSource;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
employees = getEmployeeData();
employeeDataSource = EmployeeDataSource(employeeData: employees);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Syncfusion Flutter DataGrid'),
),
body: SfDataGrid(
source: employeeDataSource,
columnWidthMode: ColumnWidthMode.fill,
showCheckboxColumn: true,
selectionMode: SelectionMode.multiple,
rowsCacheExtent: 10,
columns: <GridColumn>[
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16.0),
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text('ID'))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text('Name'))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text('Designation', overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text('Salary'))),
],
),
);
}
Set the height and width of DataGrid based on rows and columns available
If the height or width of the DataGrid is infinity, then DataGrid sets its height or width to 300 by default. Users can set the height or width based on the number of rows or columns available in DataGrid by using the shrinkWrapRows or shrinkWrapColumns property, respectively.
NOTE
Shrink wrapping is significantly more expensive than setting the height and width manually.
import 'package:syncfusion_flutter_datagrid/datagrid.dart';
late EmployeeDataSource _employeeDataSource;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return LayoutBuilder(builder: (context, constraints) {
return SingleChildScrollView(
child: SfDataGrid(
shrinkWrapColumns: true,
shrinkWrapRows: true,
source: _employeeDataSource,
columns: <GridColumn>[
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Name',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'Salary',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
],
),
);
});
}Retrieve the indices of visible rows and columns
In the SfDataGrid, you can obtain the starting and ending indices of the visible rows using the DataGridController.getVisibleRowStartIndex and DataGridController.getVisibleRowEndIndex methods, respectively, by specifying the needed RowRegion. Similarly, for the visible columns, you can retrieve the starting and ending indices using the DataGridController.getVisibleColumnStartIndex and DataGridController.getVisibleColumnEndIndex methods, respectively.
DataGridController dataGridController = DataGridController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Syncfusion Flutter DataGrid')),
body: Column(children: [
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
int? startRowIndex =
dataGridController.getVisibleRowStartIndex(RowRegion.body);
int? endRowIndex =
dataGridController.getVisibleRowEndIndex(RowRegion.body);
int? startColumnIndex =
dataGridController.getVisibleColumnStartIndex(RowRegion.body);
int? endColumnIndex =
dataGridController.getVisibleColumnEndIndex(RowRegion.body);
print('Start Row Index ${startRowIndex}');
print('End Row Index ${endRowIndex}');
print('Start Column Index ${startColumnIndex}');
print('End Column Index ${endColumnIndex}');
},
child: Text('Get Visible Row and Column Index')),
Expanded(
child: SfDataGrid(
source: employeeDataSource,
controller: dataGridController,
columns: <GridColumn>[
GridColumn(
columnName: 'ID',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8),
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text('ID'))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'Name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8),
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text('Name'))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'Designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8),
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text('Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'Salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8),
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text('Salary'))),
]),
),
]),
);
}Set the scroll offset on initial loading
SfDataGrid allows you to set the scroll offset upon initial loading for both horizontal and vertical scroll bars. This can be achieved by assigning the offset value to the initialScrollOffset property of the ScrollController for the needed vertical or horizontal controller.
import 'package:syncfusion_flutter_datagrid/datagrid.dart';
late EmployeeDataSource _employeeDataSource;
late ScrollController _verticalScrollController;
late ScrollController _horizontalScrollController;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
employees = getEmployeeData();
employeeDataSource = EmployeeDataSource(employeeData: employees);
_verticalScrollController = ScrollController(
initialScrollOffset: 500,
);
_horizontalScrollController = ScrollController(
initialScrollOffset: 600,
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return SfDataGrid(
verticalScrollController: _verticalScrollController,
horizontalScrollController: _horizontalScrollController,
source: _employeeDataSource,
columns: <GridColumn>[
GridColumn(
columnName: 'id',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'ID',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'name',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Name',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'designation',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(
'Designation',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
GridColumn(
columnName: 'salary',
label: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text(
'Salary',
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
))),
],
);
}