How can I help you?
Culture and Formatting in WPF Double TextBox
18 Feb 20254 minutes to read
Value of DoubleTextBox can be formatted in following ways:
- Culture
- NumberFormatInfo
- Dedicated properties (NumberGroupSeparator, NumberGroupSizes, NumberDecimalDigits, NumberDecimalSeparator)
Culture based formatting
The DoubleTextBox provides support for globalization by using the Culture property. The Culture property is used to format the decimal separator and group separator of the DoubleTextBox value based on the respective culture.
<syncfusion:DoubleTextBox x:Name="doubleTextBox" Height="25" Width="150" Culture="bs-Latn" Value="1234567"/>DoubleTextBox doubleTextBox = new DoubleTextBox();
doubleTextBox.Width = 150;
doubleTextBox.Height = 25;
doubleTextBox.Value = 1234567;
//Setting Latin culture for double textbox.
doubleTextBox.Culture = new System.Globalization.CultureInfo("bs-Latn");By default the US culture uses “,” as the NumberGroupSeparator and “.” as the NumberDecimalSeparator where as the Latin culture uses “.” as the NumberGroupSeparator and “,” as the NumberDecimalSeparator.
Default Culture

Latin Culture

NumberFormatInfo based formatting
The number formatting of DoubleTextBox can be customized by setting NumberFormat property.
<syncfusion:DoubleTextBox x:Name="doubleTextBox" Height="25"
Width="200" Value="1234567"
GroupSeperatorEnabled = "True">
<syncfusion:DoubleTextBox.NumberFormat>
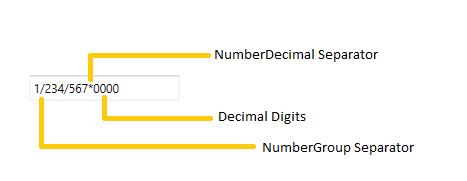
<numberformat:NumberFormatInfo NumberGroupSeparator="/"
NumberDecimalDigits="4"
NumberDecimalSeparator="*"/>
</syncfusion:DoubleTextBox.NumberFormat>
</syncfusion:DoubleTextBox>DoubleTextBox doubleTextBox = new DoubleTextBox();
doubleTextBox.Width = 200;
doubleTextBox.Height = 25;
doubleTextBox.Value = 1234567;
doubleTextBox.GroupSeperatorEnabled = true;
doubleTextBox.NumberFormat = new NumberFormatInfo()
{
NumberGroupSeparator = "/",
NumberDecimalDigits = 4,
NumberDecimalSeparator = "*"
};
The following code illustrate how to set number group size by using the NumberFormat property.
DoubleTextBox doubleTextBox = new DoubleTextBox();
doubleTextBox.Width = 200;
doubleTextBox.Height = 25;
doubleTextBox.Value = 123456789;
doubleTextBox.NumberFormat = new System.Globalization.NumberFormatInfo()
{
NumberDecimalDigits =4,
NumberGroupSeparator = "/",
NumberDecimalSeparator = "*",
// Adding the Number group size via NumberFormat property.
NumberGroupSizes = new int[] { 2, 3, 4 }
};
Formatting with dedicated properties
The number formatting of DoubleTextBox can also be customized by setting NumberGroupSeparator, NumberGroupSizes, NumberDecimalDigits, and NumberDecimalSeparator properties. You can show the group separator by enable the GroupSeperatorEnabled property to true.
The following code illustrate how to format using the NumberDecimalSeparator, NumberDecimalDigits, NumberGroupSeparator, NumberGroupSizes property of the DoubleTextBox.
DoubleTextBox doubleTextBox = new DoubleTextBox();
doubleTextBox.Width = 150;
doubleTextBox.Height = 25;
doubleTextBox.Value = 123456789;
doubleTextBox.NumberGroupSeparator = "/";
doubleTextBox.NumberDecimalSeparator = "*";
doubleTextBox.NumberDecimalDigits = 3;
// Adding the Number group size via NumberGroupSizes property.
doubleTextBox.NumberGroupSizes = new Int32Collection() { 4, 3, 2};
NOTE
When you use both the
NumberFormatand the dedicated properties (NumberGroupSeparator,NumberGroupSizes,NumberDecimalDigits, andNumberDecimalSeparator) to format the value ofDoubleTextbox, theNumberGroupSeparator,NumberGroupSizes,NumberDecimalDigits, andNumberDecimalSeparatorproperties have higher priority.
NOTE
When you use both
NumberFormatandCulture, theNumberFormatwill have a higher priority.