Activity in WPF Diagram (SfDiagram)
29 Nov 202417 minutes to read
The Activity is a task that is performed in a business process. It is represented by a rounded rectangle.
There are two types of activities. They are listed as follows:
-
Task: Occurs within a process and it is not broken down to a finer level of detail. -
CollapsedSubProcess: Occurs within a process and it is broken down to a finer level of detail.
You can specify the any one of the above activity type using the ActivityType property of BpmnNodeViewModel.
<!--Initialize the SfDiagram-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram x:Name="diagram">
<!--Initialize the Node-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
<!--Initialize the Node Collection-->
<syncfusion:NodeCollection>
<!--Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel-->
<syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel UnitHeight="70" UnitWidth="100" OffsetX="100" OffsetY="100" Type="Activity" ActivityType="Task">
</syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel>
</syncfusion:NodeCollection>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram>//Initialize the diagram.
SfDiagram diagram = new SfDiagram();
//Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel.
BpmnNodeViewModel node = new BpmnNodeViewModel()
{
OffsetX = 100,
OffsetY = 100,
UnitHeight = 70,
UnitWidth = 100,
Type = BpmnShapeType.Activity,
ActivityType=ActivityType.Task,
};
// Add the node into the Node's collection.
(diagram.Nodes as NodeCollection).Add(node);
BPMN activity task
The TaskType property of the BpmnNodeViewModel allows you to define the type of task such as sending, receiving, user-based task, and more. By default, the TaskType property of the task is set to None. This is shown by a small event symbol in the top of the corner. The following code explains how to create different types of BPMN tasks.
<!--Initialize the SfDiagram-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram x:Name="diagram">
<!--Initialize the Node-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
<!--Initialize the Node Collection-->
<syncfusion:NodeCollection>
<!--Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel-->
<syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel UnitHeight="70" UnitWidth="100" OffsetX="100" OffsetY="100" Type="Activity" ActivityType="Task" TaskType="Send">
</syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel>
</syncfusion:NodeCollection>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram>//Initialize the diagram.
SfDiagram diagram = new SfDiagram();
//Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel.
BpmnNodeViewModel node = new BpmnNodeViewModel()
{
OffsetX = 100,
OffsetY = 100,
UnitHeight = 70,
UnitWidth = 100,
Type = BpmnShapeType.Activity,
ActivityType=ActivityType.Task,
TaskType = TaskType.Send
};
// Add the node into the Node's collection.
(diagram.Nodes as NodeCollection).Add(node);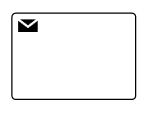
The various types of BPMN tasks are tabulated as follows.
| Task type | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Service | 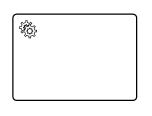 |
A Service task is a task that uses a web service, an automated application, or other kinds of service in completing the task |
| Send |  |
A Send task is represents a task that sends a message from one to another. The task is completed once the message has been sent |
| Receive | 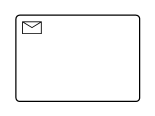 |
A Receive task indicates the wait for the arrival of a certain message. The task is completed once the message has been received |
| Instantiating Receive | 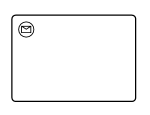 |
A receive task is used to instantiate a process that is the receive task replace the message start event |
| Manual | 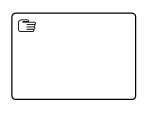 |
A Manual task is a task that is performed without the aid of any business process execution engine or any application |
| Business Rule | 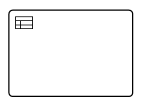 |
A Business Rule task is used to synchronously execute one or more rules |
| User | 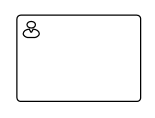 |
A User task represents that a human performer performs the task with the use of a software application |
| Script | 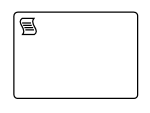 |
A Script task is an automated activity when a process execution arrives at the Script task, the corresponding script is executed |
BPMN activity sub process
A CollapsedSubProcess is a group of tasks that is used to hide or reveal details of additional levels. The following code explains how to create CollapsedSubProcess.
<!--Initialize the SfDiagram-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram x:Name="diagram">
<!--Initialize the Node-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
<!--Initialize the Node Collection-->
<syncfusion:NodeCollection>
<!--Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel-->
<syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel UnitHeight="70" UnitWidth="100" OffsetX="100" OffsetY="100" Type="Activity" ActivityType="CollapsedSubProcess" >
</syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel>
</syncfusion:NodeCollection>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram>//Initialize the diagram.
SfDiagram diagram = new SfDiagram();
//Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel.
BpmnNodeViewModel node = new BpmnNodeViewModel()
{
OffsetX = 100,
OffsetY = 100,
UnitHeight = 70,
UnitWidth = 100,
Type = BpmnShapeType.Activity,
ActivityType=ActivityType.CollapsedSubProcess,
};
// Add the node into the Node's collection.
(diagram.Nodes as NodeCollection).Add(node);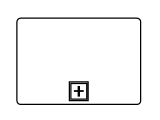
Loop
LoopActivity is a task that is internally being looped. The LoopActivity property of BpmnNodeViewModel allows you to define the type of loop. The default value for the LoopActivity is None.
You can define the LoopActivity in both tasks and collapsed subprocess of the Activity.
<!--Initialize the SfDiagram-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram x:Name="diagram">
<!--Initialize the Node-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
<!--Initialize the Node Collection-->
<syncfusion:NodeCollection>
<!--Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel-->
<syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel UnitHeight="70" UnitWidth="100" OffsetX="100" OffsetY="100" Type="Activity" ActivityType="Task" LoopActivity="Standard" >
</syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel>
</syncfusion:NodeCollection>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram>//Initialize the diagram.
SfDiagram diagram = new SfDiagram();
//Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel.
BpmnNodeViewModel node = new BpmnNodeViewModel()
{
OffsetX = 100,
OffsetY = 100,
UnitHeight = 70,
UnitWidth = 100,
Type = BpmnShapeType.Activity,
ActivityType = ActivityType.Task,
LoopActivity = LoopCharacteristic.Standard
};
// Add the node into the Node's collection.
(diagram.Nodes as NodeCollection).Add(node);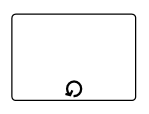
The following table contains various types of BPMN loops.
| LoopActivity | Task | CollapsedSubProcess | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| None |  |
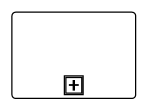 |
None of the shape shows in the sub-process |
| Standard |  |
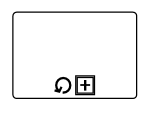 |
Loop marker indicates that the sub-process repeats itself in the sequence |
| SequenceMultiInstance | 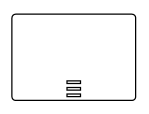 |
 |
Multi-Instance marker indicates that the sub-process can run with other identical sub-processes simultaneously. The three horizontal lines indicate the sequential execution |
| ParallelMultiInstance | 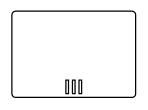 |
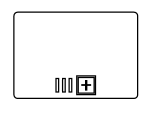 |
Multi-Instance marker indicates that the sub-process can run with other identical sub-processes simultaneously. The three vertical lines indicate that the instances will be executed in parallel |
Compensation
Compensation is triggered when the operation is partially failed and enabled it with the compensation property in both task and the collapsed subprocess. To create a compensation, you have to enable the IsCompensationActivity property of the BpmnNodeViewModel. By default, the IsCompensationActivity property is false.
<!--Initialize the SfDiagram-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram x:Name="diagram">
<!--Initialize the Node-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
<!--Initialize the Node Collection-->
<syncfusion:NodeCollection>
<!--Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel-->
<syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel UnitHeight="70" UnitWidth="100" OffsetX="100" OffsetY="100" Type="Activity" ActivityType="Task" IsCompensationActivity="True" >
</syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel>
</syncfusion:NodeCollection>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram>//Initialize the diagram.
SfDiagram diagram = new SfDiagram();
//Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel.
BpmnNodeViewModel node = new BpmnNodeViewModel()
{
OffsetX = 100,
OffsetY = 100,
UnitHeight = 70,
UnitWidth = 100,
Type = BpmnShapeType.Activity,
ActivityType = ActivityType.Task,
IsCompensationActivity = true
};
// Add the node into the Node's collection.
(diagram.Nodes as NodeCollection).Add(node);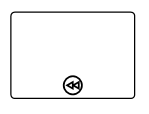
Call
A Call activity is a global sub-process that is reused at various points of the business flow. To create a Call activity, you have to enable the IsCallActivity property of the BpmnNodeViewModel. By default, the IsCallActivity property is false.
<!--Initialize the SfDiagram-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram x:Name="diagram">
<!--Initialize the Node-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
<!--Initialize the Node Collection-->
<syncfusion:NodeCollection>
<!--Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel-->
<syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel UnitHeight="70" UnitWidth="100" OffsetX="100" OffsetY="100" Type="Activity" ActivityType="Task" IsCallActivity="True" >
</syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel>
</syncfusion:NodeCollection>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram>//Initialize the diagram.
SfDiagram diagram = new SfDiagram();
//Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel.
BpmnNodeViewModel node = new BpmnNodeViewModel()
{
OffsetX = 100,
OffsetY = 100,
UnitHeight = 70,
UnitWidth = 100,
Type = BpmnShapeType.Activity,
ActivityType = ActivityType.Task,
IsCallActivity = true
};
// Add the node into the Node's collection.
(diagram.Nodes as NodeCollection).Add(node);
Ad-Hoc
An ad-hoc subprocess is a group of tasks that are executed in any order or skipped in order to fulfill the end condition. To create a ad-hoc activity, you have to enable the IsAdhocActivity property of the BpmnNodeViewModel. By default, the IsAdhocActivity property is false.
<!--Initialize the SfDiagram-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram x:Name="diagram">
<!--Initialize the Node-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
<!--Initialize the Node Collection-->
<syncfusion:NodeCollection>
<!--Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel-->
<syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel UnitHeight="100" UnitWidth="100" OffsetX="100" OffsetY="100" Type="Activity" ActivityType="CollapsedSubProcess" IsAdhocActivity="True" >
</syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel>
</syncfusion:NodeCollection>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram>//Initialize the diagram.
SfDiagram diagram = new SfDiagram();
//Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel.
BpmnNodeViewModel node = new BpmnNodeViewModel()
{
OffsetX = 100,
OffsetY = 100,
UnitHeight = 100,
UnitWidth = 100,
Type = BpmnShapeType.Activity,
ActivityType = ActivityType.CollapsedSubProcess,
IsAdhocActivity = true
};
// Add the node into the Node's collection.
(diagram.Nodes as NodeCollection).Add(node);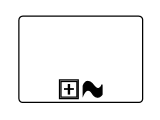
SubProcessType
SubProcessType represents the type of task that is being processed. The SubProcessType property of BpmnNodeViewModel allows you to define the type of SubProcess. By default, it is set to Default.
<!--Initialize the SfDiagram-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram x:Name="diagram">
<!--Initialize the Node-->
<syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
<!--Initialize the Node Collection-->
<syncfusion:NodeCollection>
<!--Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel-->
<syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel UnitHeight="100" UnitWidth="100" OffsetX="100" OffsetY="100" Type="Activity" ActivityType="CollapsedSubProcess" SubProcessType="Event" >
</syncfusion:BpmnNodeViewModel>
</syncfusion:NodeCollection>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram.Nodes>
</syncfusion:SfDiagram>//Initialize the diagram.
SfDiagram diagram = new SfDiagram();
//Initialize the BpmnNodeViewModel.
BpmnNodeViewModel node = new BpmnNodeViewModel()
{
OffsetX = 100,
OffsetY = 100,
UnitHeight = 100,
UnitWidth = 100,
Type = BpmnShapeType.Activity,
ActivityType = ActivityType.CollapsedSubProcess,
SubProcessType = SubProcessType.Event
};
// Add the node into the Node's collection.
(diagram.Nodes as NodeCollection).Add(node);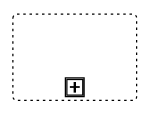
The following table contains the various types of BPMN SubProcess.
| SubProcessType | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Call | 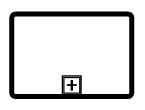 |
It is a global sub-process that is reused at various points in the business flow |
| Event |  |
The event sub-process is a sub-process that is triggered by an event. An event sub-process can be added at the process level or at any sub-process level |
| Default |  |
The task that is performed in a business process. It is represented by a rounded rectangle |
| Transaction |  |
It is a specialized sub-process that involves payment |