How can I help you?
Master Details View in Windows Forms DataGrid (SfDataGrid)
21 Jan 202524 minutes to read
The SfDataGrid provides support to represent the hierarchical data in the form of nested tables by using Master-Details view. You can expand or collapse the nested table (DetailsViewDataGrid) by using an expander column in a row. You can also expand or collapse the nested table programmatically. The number of tables nested with relations are unlimited.
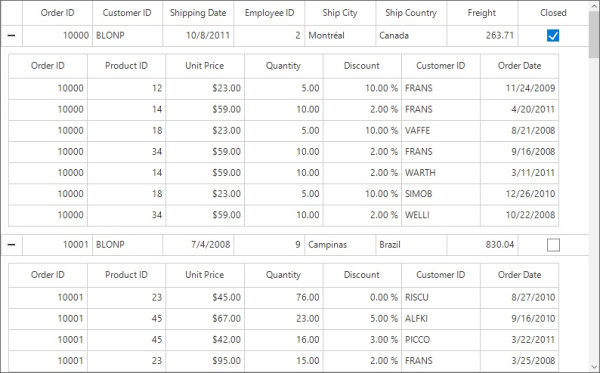
Generating Master-Details view from IEnumerable
The relation of Master-Details view can be generated for the properties of type IEnumerable in the underlying data object.
Follow the steps to generate the Master-Details view for IEnumerable:
- Create the data source with relations (Here, relations are
IEnumerabletype properties). - Defining relations
- Auto generating relations
- Manually defining relations.
Create the data source with relations
Create a OrderInfo class with OrderDetails property of type ObservableCollection to form the relation. The OrderDetails property is defined as ObservableCollection
public class OrderDetails : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private System.Nullable<int> _OrderID;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the order ID.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The order ID.</value>
public System.Nullable<int> OrderID
{
get
{
return this._OrderID;
}
set
{
this._OrderID = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("OrderID");
}
}
private int _ProductID;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the product ID.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The product ID.</value>
public int ProductID
{
get
{
return this._ProductID;
}
set
{
this._ProductID = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("ProductID");
}
}
private decimal _UnitPrice;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the unit price.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The unit price.</value>
public decimal UnitPrice
{
get
{
return this._UnitPrice;
}
set
{
this._UnitPrice = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("UnitPrice");
}
}
private Int16 _Quantity;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the quantity.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The quantity.</value>
public Int16 Quantity
{
get
{
return this._Quantity;
}
set
{
this._Quantity = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("Quantity");
}
}
private double _Discount;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the discount.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The discount.</value>
public double Discount
{
get
{
return this._Discount;
}
set
{
this._Discount = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("Discount");
}
}
private string _customerID;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the customer ID.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The customer ID.</value>
public string CustomerID
{
get
{
return _customerID;
}
set
{
_customerID = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("CustomerID");
}
}
private DateTime _orderDate;
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the order date.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The order date.</value>
public DateTime OrderDate
{
get
{
return _orderDate;
}
set
{
_orderDate = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("OrderDate");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="OrderDetails"/> class.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="orderID">The order ID.</param>
/// <param name="productID">The product ID.</param>
/// <param name="unitPrice">The unit price.</param>
/// <param name="quantity">The quantity.</param>
/// <param name="discount">The discount.</param>
public OrderDetails(int orderID, int productID, decimal unitPrice, Int16 quantity, double discount, string customerID, DateTime orderDate)
{
this._Discount = discount;
this._OrderID = orderID;
this._ProductID = productID;
this._Quantity = quantity;
this._UnitPrice = unitPrice;
this._customerID = customerID;
this._orderDate = orderDate;
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
private void RaisePropertyChanged(string name)
{
if (PropertyChanged != null)
PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(name));
}
}
public class OrderInfo : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private int _OrderID;
private string _CustomerID;
private System.Nullable<int> _EmployeeID;
private string _ShipCity;
private string _ShipCountry;
private double _Freight;
private bool _isClosed;
private DateTime _shippingDate;
private List<OrderDetails> orderDetails;
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="OrderInfo"/> class.
/// </summary>
public OrderInfo()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the order details.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The order details.</value>
public List<OrderDetails> OrderDetails
{
get
{
return this.orderDetails;
}
set
{
this.orderDetails = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("OrderDetails");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the order ID.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The order ID.</value>
[Display(Name = "Order ID")]
public int OrderID
{
get
{
return this._OrderID;
}
set
{
this._OrderID = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("OrderID");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the customer ID.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The customer ID.</value>
[Display(Name = "Customer ID")]
public string CustomerID
{
get
{
return this._CustomerID;
}
set
{
this._CustomerID = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("CustomerID");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the shipping date.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The shipping date.</value>
[Display(Name = "Shipping Date")]
public DateTime ShippingDate
{
get
{
return _shippingDate;
}
set
{
_shippingDate = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("ShippingDate");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the employee ID.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The employee ID.</value>
[Display(Name = "Employee ID")]
public System.Nullable<int> EmployeeID
{
get
{
return this._EmployeeID;
}
set
{
this._EmployeeID = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("EmployeeID");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the ship city.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The ship city.</value>
[Display(Name = "Ship City")]
public string ShipCity
{
get
{
return this._ShipCity;
}
set
{
this._ShipCity = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("ShipCity");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the ship country.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The ship country.</value>
[Display(Name = "Ship Country")]
public string ShipCountry
{
get
{
return this._ShipCountry;
}
set
{
this._ShipCountry = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("ShipCountry");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the freight.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The freight.</value>
public double Freight
{
get
{
return this._Freight;
}
set
{
this._Freight = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("Freight");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets a value indicating whether this instance is closed.
/// </summary>
/// <value><c>true</c> if this instance is closed; otherwise, <c>false</c>.</value>
[Display(Name = "Closed")]
public bool IsClosed
{
get
{
return this._isClosed;
}
set
{
this._isClosed = value;
this.RaisePropertyChanged("IsClosed");
}
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
private void RaisePropertyChanged(string name)
{
if (PropertyChanged != null)
PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(name));
}
}Public Class OrderDetails
Implements INotifyPropertyChanged
Private _OrderID? As Integer
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the order ID.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The order ID.</value>
Public Property OrderID() As Integer?
Get
Return Me._OrderID
End Get
Set(ByVal value? As Integer)
Me._OrderID = value
RaisePropertyChanged("OrderID")
End Set
End Property
Private _ProductID As Integer
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the product ID.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The product ID.</value>
Public Property ProductID() As Integer
Get
Return Me._ProductID
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Integer)
Me._ProductID = value
RaisePropertyChanged("ProductID")
End Set
End Property
Private _UnitPrice As Decimal
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the unit price.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The unit price.</value>
Public Property UnitPrice() As Decimal
Get
Return Me._UnitPrice
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Decimal)
Me._UnitPrice = value
RaisePropertyChanged("UnitPrice")
End Set
End Property
Private _Quantity As Int16
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the quantity.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The quantity.</value>
Public Property Quantity() As Int16
Get
Return Me._Quantity
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Int16)
Me._Quantity = value
RaisePropertyChanged("Quantity")
End Set
End Property
Private _Discount As Double
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the discount.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The discount.</value>
Public Property Discount() As Double
Get
Return Me._Discount
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me._Discount = value
RaisePropertyChanged("Discount")
End Set
End Property
Private _customerID As String
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the customer ID.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The customer ID.</value>
Public Property CustomerID() As String
Get
Return _customerID
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
_customerID = value
RaisePropertyChanged("CustomerID")
End Set
End Property
Private _orderDate As DateTime
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the order date.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The order date.</value>
Public Property OrderDate() As DateTime
Get
Return _orderDate
End Get
Set(ByVal value As DateTime)
_orderDate = value
RaisePropertyChanged("OrderDate")
End Set
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="OrderDetails"/> class.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="orderID">The order ID.</param>
''' <param name="productID">The product ID.</param>
''' <param name="unitPrice">The unit price.</param>
''' <param name="quantity">The quantity.</param>
''' <param name="discount">The discount.</param>
Public Sub New(ByVal orderID As Integer, ByVal productID As Integer, ByVal unitPrice As Decimal, ByVal quantity As Int16, ByVal discount As Double, ByVal customerID As String, ByVal orderDate As DateTime)
Me._Discount = discount
Me._OrderID = orderID
Me._ProductID = productID
Me._Quantity = quantity
Me._UnitPrice = unitPrice
Me._customerID = customerID
Me._orderDate = orderDate
End Sub
Public Event PropertyChanged As PropertyChangedEventHandler
Private Sub RaisePropertyChanged(ByVal name As String)
RaiseEvent PropertyChanged(Me, New PropertyChangedEventArgs(name))
End Sub
End Class
Public Class OrderInfo
Implements INotifyPropertyChanged
Private _OrderID As Integer
Private _CustomerID As String
Private _EmployeeID? As Integer
Private _ShipCity As String
Private _ShipCountry As String
Private _Freight As Double
Private _isClosed As Boolean
Private _shippingDate As DateTime
'INSTANT VB NOTE: The variable orderDetails was renamed since Visual Basic does not allow class members with the same name:
Private orderDetails_Renamed As List(Of OrderDetails)
''' <summary>
''' Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="OrderInfo"/> class.
''' </summary>
Public Sub New()
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the order details.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The order details.</value>
Public Property OrderDetails() As List(Of OrderDetails)
Get
Return Me.orderDetails_Renamed
End Get
Set(ByVal value As List(Of OrderDetails))
Me.orderDetails_Renamed = value
RaisePropertyChanged("OrderDetails")
End Set
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the order ID.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The order ID.</value>
<Display(Name := "Order ID")>
Public Property OrderID() As Integer
Get
Return Me._OrderID
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Integer)
Me._OrderID = value
RaisePropertyChanged("OrderID")
End Set
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the customer ID.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The customer ID.</value>
<Display(Name := "Customer ID")>
Public Property CustomerID() As String
Get
Return Me._CustomerID
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
Me._CustomerID = value
RaisePropertyChanged("CustomerID")
End Set
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the shipping date.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The shipping date.</value>
<Display(Name := "Shipping Date")>
Public Property ShippingDate() As DateTime
Get
Return _shippingDate
End Get
Set(ByVal value As DateTime)
_shippingDate = value
RaisePropertyChanged("ShippingDate")
End Set
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the employee ID.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The employee ID.</value>
<Display(Name := "Employee ID")>
Public Property EmployeeID() As Integer?
Get
Return Me._EmployeeID
End Get
Set(ByVal value? As Integer)
Me._EmployeeID = value
RaisePropertyChanged("EmployeeID")
End Set
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the ship city.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The ship city.</value>
<Display(Name := "Ship City")>
Public Property ShipCity() As String
Get
Return Me._ShipCity
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
Me._ShipCity = value
RaisePropertyChanged("ShipCity")
End Set
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the ship country.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The ship country.</value>
<Display(Name := "Ship Country")>
Public Property ShipCountry() As String
Get
Return Me._ShipCountry
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
Me._ShipCountry = value
RaisePropertyChanged("ShipCountry")
End Set
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets the freight.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The freight.</value>
Public Property Freight() As Double
Get
Return Me._Freight
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me._Freight = value
RaisePropertyChanged("Freight")
End Set
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Gets or sets a value indicating whether this instance is closed.
''' </summary>
''' <value><c>true</c> if this instance is closed; otherwise, <c>false</c>.</value>
<Display(Name := "Closed")>
Public Property IsClosed() As Boolean
Get
Return Me._isClosed
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Boolean)
Me._isClosed = value
Me.RaisePropertyChanged("IsClosed")
End Set
End Property
Public Event PropertyChanged As PropertyChangedEventHandler
Private Sub RaisePropertyChanged(ByVal name As String)
RaiseEvent PropertyChanged(Me, New PropertyChangedEventArgs(name))
End Sub
End ClassCreate a OrderInfoRepository class with GetOrdersDetails method which returns the ObservableCollection<OrderInfo>. The class is initialized with several data objects in the constructor. Similarly, the OrdersDetails property is also initialized.
public class OrderInfoRepository
{
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="OrderInfoRepository"/> class.
/// </summary>
public OrderInfoRepository()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the orders details.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="count">The count.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public List<OrderInfo> GetOrdersDetails(int count)
{
List<OrderInfo> ordersDetails = new List<OrderInfo>();
this.OrderedDates = GetDateBetween(2008, 2012, count);
OrdersAdd(count);
SetShipCity();
for (int i = 10000; i < count + 10000; i++)
{
ordersDetails.Add(GetOrder(i));
}
return ordersDetails;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the customers.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The customers.</value>
public List<string> Customers
{
get
{
return this.CustomerID.ToList();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the ship countries.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The ship countries.</value>
public List<string> ShipCountries
{
get
{
return this.ShipCountry.ToList();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Adds the OrderDetails to the collection.
/// </summary>
private void OrdersAdd(int count)
{
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10000, 12, 23, 5, 10, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10000, 14, 59, 10, 2, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10000, 18, 23, 5, 10, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10000, 34, 59, 10, 2, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10000, 14, 59, 10, 2, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10000, 18, 23, 5, 10, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10000, 34, 59, 10, 2, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10001, 23, 45, 76, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10001, 45, 67, 23, 5, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10001, 45, 42, 16, 3, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10001, 23, 95, 15, 2, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10002, 7, 70, 6, 4, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10002, 2, 30, 5, 2, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10003, 23, 73, 9, 3, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10003, 8, 11, 8, 7, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10003, 1, 150, 1, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10009, 4, 35, 4, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10009, 2, 31, 7, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10010, 7, 23, 3, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10010, 5, 65, 4, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10010, 3, 15, 5, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10010, 2, 31, 1, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10011, 6, 46, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10011, 3, 45, 4, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10011, 2, 41, 7, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10013, 19, 80, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10013, 20, 111, 2, 7, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10021, 54, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10021, 63, 46, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10021, 27, 99, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10022, 59, 80, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10022, 60, 111, 2, 7, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10022, 47, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10032, 4, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10032, 6, 46, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10034, 17, 99, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10034, 19, 80, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10034, 20, 111, 2, 7, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10042, 4, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10042, 4, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10045, 6, 46, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10045, 17, 99, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10045, 19, 80, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10045, 20, 111, 2, 7, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10056, 4, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10056, 4, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10056, 6, 46, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10067, 17, 99, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10067, 19, 80, 2, 0, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
orderDetailsCollection.Add(new OrderDetails(10067, 20, 111, 2, 7, CustomerID[r.Next(15)], this.OrderedDates[r.Next(count - 1)]));
}
private List<DateTime> OrderedDates;
Random r = new Random();
List<OrderDetails> orderDetailsCollection = new List<OrderDetails>();
/// <summary>
/// Gets the order.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="i">The i.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
private OrderInfo GetOrder(int i)
{
var shipCountry = ShipCountry[r.Next(5)];
var shipCity = ShipCity[shipCountry];
return new OrderInfo()
{
OrderID = i,
CustomerID = CustomerID[r.Next(15)],
EmployeeID = r.Next(1, 10),
Freight = Math.Round(r.Next(1000) + r.NextDouble(), 2),
ShipCountry = shipCountry,
ShippingDate = this.OrderedDates[i - 10000],
IsClosed = i % 2 == 0 ? true : false,
ShipCity = shipCity[r.Next(shipCity.Length - 1)],
OrderDetails = GetOrderDetails(i)
};
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the collection of OrderDetails.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="i">The i.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public List<OrderDetails> GetOrderDetails(int i)
{
List<OrderDetails> order = new List<OrderDetails>();
foreach (var orderDetails in orderDetailsCollection)
if (orderDetails.OrderID == i)
order.Add(orderDetails);
return order;
}
string[] ShipCountry = new string[]
{
"Argentina",
"Austria",
"Belgium",
"Brazil",
"Canada",
"Denmark",
"Finland",
"France",
"Germany",
"Ireland",
"Italy",
"Mexico",
"Norway",
"Poland",
"Portugal",
"Spain",
"Sweden",
"Switzerland",
"UK",
"USA",
"Venezuela"
};
Dictionary<string, string[]> ShipCity = new Dictionary<string, string[]>();
/// <summary>
/// Sets the ship city.
/// </summary>
private void SetShipCity()
{
string[] _Argentina = new string[] { "Buenos Aires" };
string[] _Austria = new string[] { "Graz", "Salzburg" };
string[] _Belgium = new string[] { "Bruxelles", "Charleroi" };
string[] _Brazil = new string[] { "Campinas", "Resende", "Rio de Janeiro", "São Paulo" };
string[] _Canada = new string[] { "Montréal", "Tsawassen", "Vancouver" };
string[] _Denmark = new string[] { "Århus", "København" };
string[] _Finland = new string[] { "Helsinki", "Oulu" };
string[] _France = new string[] { "Lille", "Lyon", "Marseille", "Nantes", "Paris", "Reims", "Strasbourg", "Toulouse", "Versailles" };
string[] _Germany = new string[] { "Aachen", "Berlin", "Brandenburg", "Cunewalde", "Frankfurt a.M.", "Köln", "Leipzig", "Mannheim", "München", "Münster", "Stuttgart" };
string[] _Ireland = new string[] { "Cork" };
string[] _Italy = new string[] { "Bergamo", "Reggio Emilia", "Torino" };
string[] _Mexico = new string[] { "México D.F." };
string[] _Norway = new string[] { "Stavern" };
string[] _Poland = new string[] { "Warszawa" };
string[] _Portugal = new string[] { "Lisboa" };
string[] _Spain = new string[] { "Barcelona", "Madrid", "Sevilla" };
string[] _Sweden = new string[] { "Bräcke", "Luleå" };
string[] _Switzerland = new string[] { "Bern", "Genève" };
string[] _UK = new string[] { "Colchester", "Hedge End", "London" };
string[] _USA = new string[] { "Albuquerque", "Anchorage", "Boise", "Butte", "Elgin", "Eugene", "Kirkland", "Lander", "Portland", "San Francisco", "Seattle", "Walla Walla" };
string[] _Venezuela = new string[] { "Barquisimeto", "Caracas", "I. de Margarita", "San Cristóbal" };
ShipCity.Add("Argentina", _Argentina);
ShipCity.Add("Austria", _Austria);
ShipCity.Add("Belgium", _Belgium);
ShipCity.Add("Brazil", _Brazil);
ShipCity.Add("Canada", _Canada);
ShipCity.Add("Denmark", _Denmark);
ShipCity.Add("Finland", _Finland);
ShipCity.Add("France", _France);
ShipCity.Add("Germany", _Germany);
ShipCity.Add("Ireland", _Ireland);
ShipCity.Add("Italy", _Italy);
ShipCity.Add("Mexico", _Mexico);
ShipCity.Add("Norway", _Norway);
ShipCity.Add("Poland", _Poland);
ShipCity.Add("Portugal", _Portugal);
ShipCity.Add("Spain", _Spain);
ShipCity.Add("Sweden", _Sweden);
ShipCity.Add("Switzerland", _Switzerland);
ShipCity.Add("UK", _UK);
ShipCity.Add("USA", _USA);
ShipCity.Add("Venezuela", _Venezuela);
}
string[] CustomerID = new string[]
{
"ALFKI",
"FRANS",
"MEREP",
"FOLKO",
"SIMOB",
"WARTH",
"VAFFE",
"FURIB",
"SEVES",
"LINOD",
"RISCU",
"PICCO",
"BLONP",
"WELLI",
"FOLIG"
};
/// <summary>
/// Gets the date between.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="startYear">The start year.</param>
/// <param name="EndYear">The end year.</param>
/// <param name="Count">The count.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
private List<DateTime> GetDateBetween(int startYear, int EndYear, int Count)
{
List<DateTime> date = new List<DateTime>();
Random d = new Random(1);
Random m = new Random(2);
Random y = new Random(startYear);
for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
{
int year = y.Next(startYear, EndYear);
int month = m.Next(3, 13);
int day = d.Next(1, 31);
date.Add(new DateTime(year, month, day));
}
return date;
}
}Public Class OrderInfoRepository
''' <summary>
''' Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="OrderInfoRepository"/> class.
''' </summary>
Public Sub New()
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Gets the orders details.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="count">The count.</param>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Function GetOrdersDetails(ByVal count As Integer) As List(Of OrderInfo)
Dim ordersDetails As New List(Of OrderInfo)()
Me.OrderedDates = GetDateBetween(2008, 2012, count)
OrdersAdd(count)
SetShipCity()
For i As Integer = 10000 To count + 10000 - 1
ordersDetails.Add(GetOrder(i))
Next i
Return ordersDetails
End Function
''' <summary>
''' Gets the customers.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The customers.</value>
Public ReadOnly Property Customers() As List(Of String)
Get
Return Me.CustomerID.ToList()
End Get
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Gets the ship countries.
''' </summary>
''' <value>The ship countries.</value>
Public ReadOnly Property ShipCountries() As List(Of String)
Get
Return Me.ShipCountry.ToList()
End Get
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Adds the OrderDetails to the collection.
''' </summary>
Private Sub OrdersAdd(ByVal count As Integer)
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10000, 12, 23, 5, 10, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10000, 14, 59, 10, 2, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10000, 18, 23, 5, 10, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10000, 34, 59, 10, 2, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10000, 14, 59, 10, 2, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10000, 18, 23, 5, 10, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10000, 34, 59, 10, 2, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10001, 23, 45, 76, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10001, 45, 67, 23, 5, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10001, 45, 42, 16, 3, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10001, 23, 95, 15, 2, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10002, 7, 70, 6, 4, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10002, 2, 30, 5, 2, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10003, 23, 73, 9, 3, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10003, 8, 11, 8, 7, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10003, 1, 150, 1, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10009, 4, 35, 4, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10009, 2, 31, 7, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10010, 7, 23, 3, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10010, 5, 65, 4, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10010, 3, 15, 5, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10010, 2, 31, 1, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10011, 6, 46, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10011, 3, 45, 4, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10011, 2, 41, 7, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10013, 19, 80, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10013, 20, 111, 2, 7, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10021, 54, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10021, 63, 46, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10021, 27, 99, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10022, 59, 80, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10022, 60, 111, 2, 7, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10022, 47, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10032, 4, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10032, 6, 46, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10034, 17, 99, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10034, 19, 80, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10034, 20, 111, 2, 7, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10042, 4, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10042, 4, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10045, 6, 46, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10045, 17, 99, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10045, 19, 80, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10045, 20, 111, 2, 7, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10056, 4, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10056, 4, 35, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10056, 6, 46, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10067, 17, 99, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10067, 19, 80, 2, 0, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
orderDetailsCollection.Add(New OrderDetails(10067, 20, 111, 2, 7, CustomerID(r.Next(15)), Me.OrderedDates(r.Next(count - 1))))
End Sub
Private OrderedDates As List(Of DateTime)
Private r As New Random()
Private orderDetailsCollection As New List(Of OrderDetails)()
''' <summary>
''' Gets the order.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="i">The i.</param>
''' <returns></returns>
Private Function GetOrder(ByVal i As Integer) As OrderInfo
Dim shipCountry = Me.ShipCountry(r.Next(5))
Dim shipCity = Me.ShipCity(shipCountry)
Return New OrderInfo() With {.OrderID = i, .CustomerID = CustomerID(r.Next(15)), .EmployeeID = r.Next(1, 10), .Freight = Math.Round(r.Next(1000) + r.NextDouble(), 2), .ShipCountry = shipCountry, .ShippingDate = Me.OrderedDates(i - 10000), .IsClosed = If(i Mod 2 = 0, True, False), .ShipCity = shipCity(r.Next(shipCity.Length - 1)), .OrderDetails = GetOrderDetails(i)}
End Function
''' <summary>
''' Gets the collection of OrderDetails.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="i">The i.</param>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Function GetOrderDetails(ByVal i As Integer) As List(Of OrderDetails)
Dim order As New List(Of OrderDetails)()
For Each orderDetails In orderDetailsCollection
If orderDetails.OrderID = i Then
order.Add(orderDetails)
End If
Next orderDetails
Return order
End Function
Private ShipCountry() As String = { "Argentina", "Austria", "Belgium", "Brazil", "Canada", "Denmark", "Finland", "France", "Germany", "Ireland", "Italy", "Mexico", "Norway", "Poland", "Portugal", "Spain", "Sweden", "Switzerland", "UK", "USA", "Venezuela" }
Private ShipCity As New Dictionary(Of String, String())()
''' <summary>
''' Sets the ship city.
''' </summary>
Private Sub SetShipCity()
Dim _Argentina() As String = { "Buenos Aires" }
Dim _Austria() As String = { "Graz", "Salzburg" }
Dim _Belgium() As String = { "Bruxelles", "Charleroi" }
Dim _Brazil() As String = { "Campinas", "Resende", "Rio de Janeiro", "São Paulo" }
Dim _Canada() As String = { "Montréal", "Tsawassen", "Vancouver" }
Dim _Denmark() As String = { "Århus", "København" }
Dim _Finland() As String = { "Helsinki", "Oulu" }
Dim _France() As String = { "Lille", "Lyon", "Marseille", "Nantes", "Paris", "Reims", "Strasbourg", "Toulouse", "Versailles" }
Dim _Germany() As String = { "Aachen", "Berlin", "Brandenburg", "Cunewalde", "Frankfurt a.M.", "Köln", "Leipzig", "Mannheim", "München", "Münster", "Stuttgart" }
Dim _Ireland() As String = { "Cork" }
Dim _Italy() As String = { "Bergamo", "Reggio Emilia", "Torino" }
Dim _Mexico() As String = { "México D.F." }
Dim _Norway() As String = { "Stavern" }
Dim _Poland() As String = { "Warszawa" }
Dim _Portugal() As String = { "Lisboa" }
Dim _Spain() As String = { "Barcelona", "Madrid", "Sevilla" }
Dim _Sweden() As String = { "Bräcke", "Luleå" }
Dim _Switzerland() As String = { "Bern", "Genève" }
Dim _UK() As String = { "Colchester", "Hedge End", "London" }
Dim _USA() As String = { "Albuquerque", "Anchorage", "Boise", "Butte", "Elgin", "Eugene", "Kirkland", "Lander", "Portland", "San Francisco", "Seattle", "Walla Walla" }
Dim _Venezuela() As String = { "Barquisimeto", "Caracas", "I. de Margarita", "San Cristóbal" }
ShipCity.Add("Argentina", _Argentina)
ShipCity.Add("Austria", _Austria)
ShipCity.Add("Belgium", _Belgium)
ShipCity.Add("Brazil", _Brazil)
ShipCity.Add("Canada", _Canada)
ShipCity.Add("Denmark", _Denmark)
ShipCity.Add("Finland", _Finland)
ShipCity.Add("France", _France)
ShipCity.Add("Germany", _Germany)
ShipCity.Add("Ireland", _Ireland)
ShipCity.Add("Italy", _Italy)
ShipCity.Add("Mexico", _Mexico)
ShipCity.Add("Norway", _Norway)
ShipCity.Add("Poland", _Poland)
ShipCity.Add("Portugal", _Portugal)
ShipCity.Add("Spain", _Spain)
ShipCity.Add("Sweden", _Sweden)
ShipCity.Add("Switzerland", _Switzerland)
ShipCity.Add("UK", _UK)
ShipCity.Add("USA", _USA)
ShipCity.Add("Venezuela", _Venezuela)
End Sub
Private CustomerID() As String = { "ALFKI", "FRANS", "MEREP", "FOLKO", "SIMOB", "WARTH", "VAFFE", "FURIB", "SEVES", "LINOD", "RISCU", "PICCO", "BLONP", "WELLI", "FOLIG" }
''' <summary>
''' Gets the date between.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="startYear">The start year.</param>
''' <param name="EndYear">The end year.</param>
''' <param name="Count">The count.</param>
''' <returns></returns>
Private Function GetDateBetween(ByVal startYear As Integer, ByVal EndYear As Integer, ByVal Count As Integer) As List(Of DateTime)
Dim [date] As New List(Of DateTime)()
Dim d As New Random(1)
Dim m As New Random(2)
Dim y As New Random(startYear)
For i As Integer = 0 To Count - 1
Dim year As Integer = y.Next(startYear, EndYear)
Dim month As Integer = m.Next(3, 13)
Dim day As Integer = d.Next(1, 31)
[date].Add(New DateTime(year, month, day))
Next i
Return [date]
End Function
End ClassDefining relations
Auto generating relations
The SfDataGrid will automatically generate relations and inner relations for the IEnumerable property types in the data object. This can be enabled by setting the SfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations to true.
Bind the created collection in the previous step to the SfDataGrid.DataSource and set the SfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations to true.
sfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = true;sfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = TrueWhen relations are auto-generated, you can handle the SfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations event to customize or cancel the GridViewDefinition before adding it to the SfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.
Here, the relation is created from OrderDetails collection property.
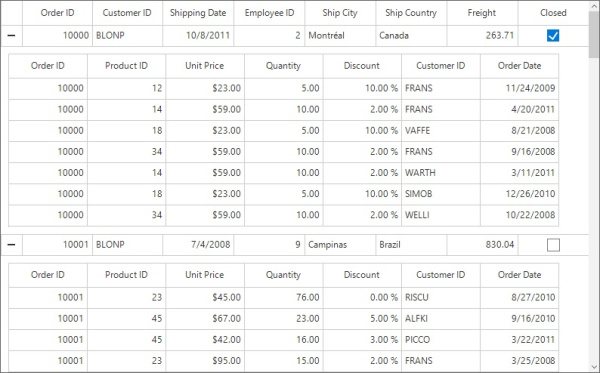
Manual defining relations
You can define the relation of Master-Details view manually by using the SfDataGird.DetailsViewDefinitions when the SfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations is false.
To define the Master-Details view relations, create GridViewDefinition and set the name of IEnumerable type property (from data object) to GridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn. Then, add the GridViewDefinition to the SfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.
sfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = false;
var gridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
gridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails";
gridViewDefinition.DataGrid = new SfDataGrid() { Name = "FirstLevelNestedGrid", AutoGenerateColumns = true };
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(gridViewDefinition);sfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = False
Dim gridViewDefinition = New GridViewDefinition()
gridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails"
gridViewDefinition.DataGrid = New SfDataGrid() With {.Name = "FirstLevelNestedGrid", .AutoGenerateColumns = True}
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(gridViewDefinition)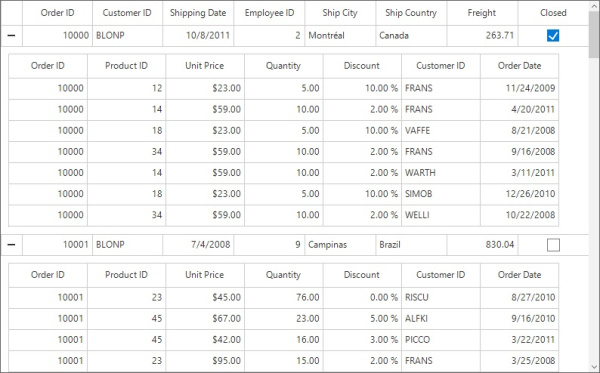
Generating Master-Details view from DataTable
The relation of Master-Details view can be generated for DataTable, when the DataRelation is defined between two tables in the underlying DataSet.
Follow the steps to generate the Master-Details view relation for DataTable,
- Create the DataTable with relations.
- Defining relations
- Auto generating relations
- Manually defining relations
Create the DataTable with relations
Create a method GetDataTable type of DataTable which returns the DataTable with relations between Suppliers and Products tables in the DataSet based on SupplierID column.
/// <summary>
/// Gets the data table.
/// </summary>
public DataTable GetDataTable()
{
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
string connectionString = @"Data Source=" + FindFile("Northwind.sdf");
using (SqlCeConnection con = new SqlCeConnection(connectionString))
{
con.Open();
SqlCeDataAdapter sqlDataAdapter1 = new SqlCeDataAdapter("SELECT * FROM Suppliers", con);
sqlDataAdapter1.Fill(ds, "Suppliers");
}
using (SqlCeConnection con1 = new SqlCeConnection(connectionString))
{
con1.Open();
SqlCeDataAdapter sqlDataAdapter1 = new SqlCeDataAdapter("SELECT * FROM Products", con1);
sqlDataAdapter1.Fill(ds, "Products");
}
ds.Relations.Add(new DataRelation("Supplier_Product", ds.Tables[0].Columns["Supplier ID"], ds.Tables[1].Columns["Supplier ID"]));
if (ds.Tables.Count > 0)
return ds.Tables[0];
else
return null;
}''' <summary>
''' Gets the data table.
''' </summary>
Public Function GetDataTable() As DataTable
Dim ds As New DataSet()
Dim connectionString As String = "Data Source=" & FindFile("Northwind.sdf")
Using con As New SqlCeConnection(connectionString)
con.Open()
Dim sqlDataAdapter1 As New SqlCeDataAdapter("SELECT * FROM Suppliers", con)
sqlDataAdapter1.Fill(ds, "Suppliers")
End Using
Using con1 As New SqlCeConnection(connectionString)
con1.Open()
Dim sqlDataAdapter1 As New SqlCeDataAdapter("SELECT * FROM Products", con1)
sqlDataAdapter1.Fill(ds, "Products")
End Using
ds.Relations.Add(New DataRelation("Supplier_Product", ds.Tables(0).Columns("Supplier ID"), ds.Tables(1).Columns("Supplier ID")))
If ds.Tables.Count > 0 Then
Return ds.Tables(0)
Else
Return Nothing
End If
End FunctionDefining relations
Auto generating relations
The SfDataGrid will automatically generate relations and inner relations based on the relations defined in the DataSet. This can be enabled by setting the SfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations to true.
Bind the created table in the previous step to the SfDataGrid.DataSource and set the SfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations to true.
sfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = true;sfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = TrueWhen the relations are auto-generated, you can handle the SfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations event to customize or cancel the GridViewDefinition before adding it to the SfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.
Here, Master-Details view relation is auto generated based on the Supplier_Product relation.
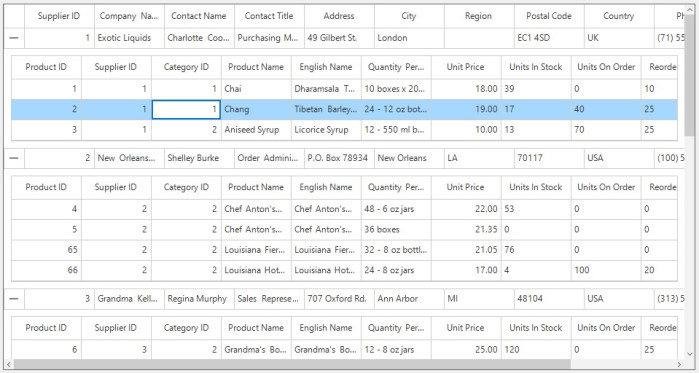
Manual defining relations
You can define the Master-Details view relation manually by using the SfDataGird.DetailsViewDefinitions collection when the SfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations is false.
To define the Master-Details View relations, create GridViewDefinition and set the relation name as Supplier_Product to GridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn. Then, the GridViewDefinition is added to the SfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions collection of the parent DataGrid.
sfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = false;
// GridViewDefinition for DataGrid
var gridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
gridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "Supplier_Product";
gridViewDefinition.DataGrid = new SfDataGrid() { Name = "FirstLevelNestedGrid", AutoGenerateColumns = true };
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinition.Add(gridViewDefinition);sfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = False
' GridViewDefinition for DataGrid
Dim gridViewDefinition = New GridViewDefinition()
gridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "Supplier_Product"
gridViewDefinition.DataGrid = New SfDataGrid() With {.Name = "FirstLevelNestedGrid", .AutoGenerateColumns = True}
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinition.Add(gridViewDefinition)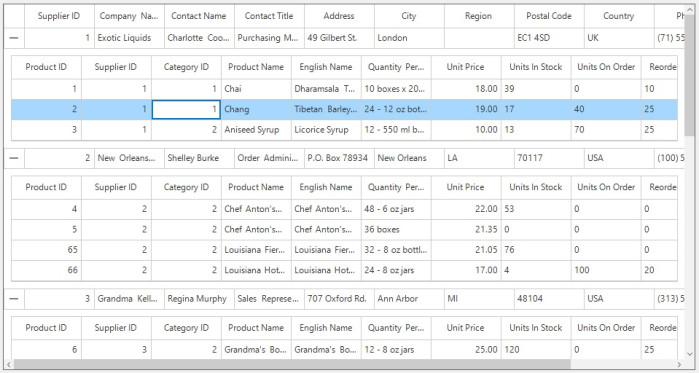
Populating Master-Details view through events
You can load the DataSource for DetailsViewDataGrid asynchronously by handling the SfDataGrid.DetailsViewExpanding event. You can set the DataSource on-demand when expanding the record through DetailsViewExpandingEventArgs.DetailsViewDataSource property in the SfDataGrid.DetailsViewExpanding` event handler.
this.sfDataGrid.DetailsViewExpanding += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding(object sender, DetailsViewExpandingEventArgs e)
{
OrderInfo orderInfo = e.Record as OrderInfo;
if (orderInfo.OrderID == 10000)
e.DetailsViewDataSource.Add("OrderDetails", GetDetailsViewDataSource());
}
private ObservableCollection<OrderDetails> GetDetailsViewDataSource()
{
ObservableCollection<OrderDetails> orderDetails = new ObservableCollection<OrderDetails>();
orderDetails.Add(new OrderDetails(1000, 2, 11, 2, 3, "Alan", DateTime.Today.AddDays(1), "Orlando"));
orderDetails.Add(new OrderDetails(1001, 2, 11, 2, 3, "Michael", DateTime.Today, "Chennai"));
return orderDetails;
}AddHandler sfDataGrid1.DetailsViewExpanding, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewExpandingEventArgs)
Dim orderInfo As OrderInfo = TryCast(e.Record, OrderInfo)
If orderInfo.OrderID = 10000 Then
e.DetailsViewDataSource.Add("OrderDetails", GetDetailsViewDataSource())
End If
End Sub
Private Function GetDetailsViewDataSource() As ObservableCollection(Of OrderDetails)
Dim orderDetails As New ObservableCollection(Of OrderDetails)()
orderDetails.Add(New OrderDetails(1000, 2, 11, 2, 3, "Alan", DateTime.Today.AddDays(1), "Orlando"))
orderDetails.Add(New OrderDetails(1001, 2, 11, 2, 3, "Michael", DateTime.Today, "Chennai"))
Return orderDetails
End FunctionNOTE
This event will be trigged only when the underlying data object contains relations otherwise, you must define a dummy relation to notify the DataGrid to fire this event.
Defining properties for DetailsViewDataGrid
You can set properties like AllowEditing, AllowFiltering, and AllowSorting for DetailsViewDataGrid by using the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid property.
When manually defining relations
For manually defined relations, the properties can be directly set to the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.
GridViewDefinition firstLevelGridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails";
SfDataGrid firstLevelNestedGrid = new SfDataGrid();
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowSorting = true;
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowFiltering = true;
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowResizingColumns = true;
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid;
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition);Dim firstLevelGridViewDefinition As New GridViewDefinition()
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails"
Dim firstLevelNestedGrid As New SfDataGrid()
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowSorting = True
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowFiltering = True
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowResizingColumns = True
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition)For two levels of nesting,
// Creating First level GridViewDefinition.
GridViewDefinition firstLevelGridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails";
// Creating First level DetailsView Grid.
SfDataGrid firstLevelNestedGrid = new SfDataGrid();
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowSorting = true;
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowFiltering = true;
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowResizingColumns = true;
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid;
// Creating Second level GridViewDefinition.
GridViewDefinition secondLevelGridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
secondLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "ProductDetails";
// Creating Second level DetailsView Grid.
SfDataGrid secondLevelDataGrid = new SfDataGrid();
secondLevelDataGrid.AllowSorting = true;
secondLevelDataGrid.AllowFiltering = true;
secondLevelDataGrid.AllowResizingColumns = true;
secondLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = secondLevelDataGrid;
// Adding second level GridViewDefinition to the first level DetailsView Grid.
firstLevelNestedGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(secondLevelGridViewDefinition);
// Adding first level GridViewDefinition to the parent DataGrid.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition);' Creating First level GridViewDefinition.
Dim firstLevelGridViewDefinition As New GridViewDefinition()
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails"
' Creating First level DetailsView Grid.
Dim firstLevelNestedGrid As New SfDataGrid()
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowSorting = True
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowFiltering = True
firstLevelNestedGrid.AllowResizingColumns = True
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid
' Creating Second level GridViewDefinition.
Dim secondLevelGridViewDefinition As New GridViewDefinition()
secondLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "ProductDetails"
' Creating Second level DetailsView Grid.
Dim secondLevelDataGrid As New SfDataGrid()
secondLevelDataGrid.AllowSorting = True
secondLevelDataGrid.AllowFiltering = True
secondLevelDataGrid.AllowResizingColumns = True
secondLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = secondLevelDataGrid
' Adding second level GridViewDefinition to the first level DetailsView Grid.
firstLevelNestedGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(secondLevelGridViewDefinition)
' Adding first level GridViewDefinition to the parent DataGrid.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition)When auto generating relations
When the relation is auto-generated, you can get the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid in the AutoGeneratingRelations event handler to set the property.
sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations += SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations;
private void SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(object sender, AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs e)
{
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowSorting = true;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowFiltering = true;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowResizingColumns = true;
}AddHandler sfDataGrid1. AutoGeneratingRelations, AddressOf SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations
Private Sub SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs)
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowSorting = True
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowFiltering = True
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowResizingColumns = True
End SubFor two levels of nesting,
sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations += SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations;
private void SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(object sender, AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs e)
{
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowSorting = true;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowFiltering = true;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowResizingColumns = true;
// Wiring events to FirstLevel DataGrid.
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = true;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations += FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations;
}
private void FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(object sender, AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs e)
{
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowSorting = true;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowFiltering = true;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowResizingColumns = true;
}AddHandler sfDataGrid1. AutoGeneratingRelations, AddressOf SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations
Private Sub SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs)
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowSorting = True
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowFiltering = True
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowResizingColumns = True
' Wiring events to FirstLevel DataGrid.
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = True
AddHandler e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations, AddressOf FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations
End Sub
Private Sub FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs)
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowSorting = True
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowFiltering = True
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AllowResizingColumns = True
End SubNOTE
When making any change in one DetailsViewDataGrid, that change will be applied to all DetailsViewDataGrid in the same level. For example, when you resize the first column in one DetailsViewDataGrid, the same column width will be applied to all DetailsViewDataGrid at that level. This is applicable for features like filtering, sorting, grouping, and reordering columns.
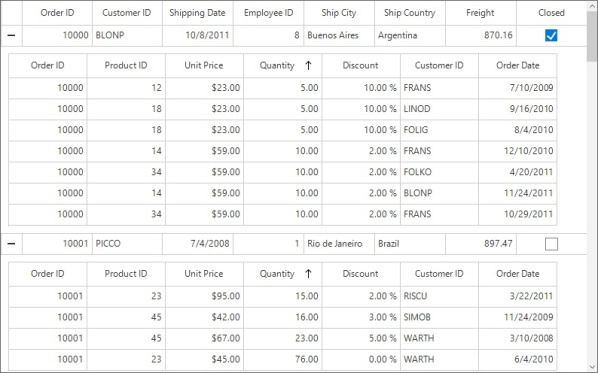
Here, Quantity column is sorted in all DetailsViewDataGrid at the same level.
NOTE
FrozenRowCount, FooterRowCount, FooterColumnCount, and FrozenColumnCount properties are not supported while using Master-Details view.
Defining columns for DetailsViewDataGrid
The GridViewDefinition.DataGrid columns can be generated either automatically or manually like parent DataGrid. You can refer to here to know more about columns.
Auto generating columns
Auto generate the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid columns by setting the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGenerateColumns to true. Cancel or customize the column being created for GridViewDefinition.DataGrid by handling the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGeneratingColumn event.
GridViewDefinition firstLevelGridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails";
SfDataGrid firstLevelNestedGrid = new SfDataGrid();
// Enabling AutoGenerateColumns and Wiring AutoGeneratingColumn event for first level DataGrid.
firstLevelNestedGrid.AutoGenerateColumns = true;
firstLevelNestedGrid.AutoGeneratingColumn += FirstLevelNestedGrid_AutoGeneratingColumn;
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid;
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition);Dim firstLevelGridViewDefinition As New GridViewDefinition()
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails"
Dim firstLevelNestedGrid As New SfDataGrid()
' Enabling AutoGenerateColumns and Wiring AutoGeneratingColumn event for first level DataGrid.
firstLevelNestedGrid.AutoGenerateColumns = True
AddHandler firstLevelNestedGrid.AutoGeneratingColumn, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_AutoGeneratingColumn
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition)When the relation is auto generated, you can set the properties and wire the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGeneratingColumn` event in the SfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations event handler.
sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations += SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations;
private void SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(object sender, AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs e)
{
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGenerateColumns = true;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGeneratingColumn += FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingColumn;
}
private void FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingColumn(object sender, AutoGeneratingColumnArgs e)
{
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations, AddressOf SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations
Private Sub SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs)
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGenerateColumns = True
AddHandler e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGeneratingColumn, AddressOf FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingColumn
End Sub
Private Sub FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingColumn(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As AutoGeneratingColumnArgs)
End SubManually defining columns
You can directly define the columns to GridViewDefinition.DataGrid whenAutoGenerateColumns is false. When the relation is manually defined, you can define the columns directly to the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid by adding desired column to the SfDataGrid.Columns collection.
GridViewDefinition firstLevelGridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails";
SfDataGrid firstLevelNestedGrid = new SfDataGrid();
// Disabling AutoGenerateColumns and manually defining columns for first level DataGrid.
firstLevelNestedGrid.AutoGenerateColumns = false;
firstLevelNestedGrid.Columns.Add(new GridTextColumn() { MappingName = "OrderID", HeaderText = "Order ID" });
firstLevelNestedGrid.Columns.Add(new GridTextColumn() { MappingName = "ProductID", HeaderText = "Product ID" });
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid;
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition);Dim firstLevelGridViewDefinition As New GridViewDefinition()
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails"
Dim firstLevelNestedGrid As New SfDataGrid()
' Disabling AutoGenerateColumns and manually defining columns for first level DataGrid.
firstLevelNestedGrid.AutoGenerateColumns = False
firstLevelNestedGrid.Columns.Add(New GridTextColumn() With {.MappingName = "OrderID", .HeaderText = "Order ID"})
firstLevelNestedGrid.Columns.Add(New GridTextColumn() With {.MappingName = "ProductID", .HeaderText = "Product ID"})
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition)When the relation is auto generated, you can define the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid columns manually through the SfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations event handler.
sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations += SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations;
private void SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(object sender, AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs e)
{
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGenerateColumns = false;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.Columns.Add(new GridTextColumn() { MappingName = "OrderID", HeaderText = "Order ID" });
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.Columns.Add(new GridTextColumn() { MappingName = "ProductID", HeaderText = "Product ID" });
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations, AddressOf SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations
Private Sub SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs)
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGenerateColumns = False
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.Columns.Add(New GridTextColumn() With {.MappingName = "OrderID", .HeaderText = "Order ID"})
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.Columns.Add(New GridTextColumn() With {.MappingName = "ProductID", .HeaderText = "Product ID"})
End SubHandling events for DetailsViewDataGrid
You can handle the DetailsViewDataGrid events by wiring the events to GridViewDefinition.DataGrid where the sender is GridViewDefinition.DataGrid. In another way, you can also handle DetailsViewDataGrid event through parent DataGrid event by setting the NotifyEventsToParentDataGrid property of GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.
When manually defining relations
For manually defined relation, the events can be wired from the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid directly.
GridViewDefinition firstLevelGridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails";
SfDataGrid firstLevelNestedGrid = new SfDataGrid();
// Wiring events for first level DataGrid.
firstLevelNestedGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit += FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit;
firstLevelNestedGrid.SortColumnsChanging += FirstLevelNestedGrid_SortColumnsChanging;
firstLevelNestedGrid.FilterChanging += FirstLevelNestedGrid_FilterChanging;
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid;
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition);Dim firstLevelGridViewDefinition As New GridViewDefinition()
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails"
Dim firstLevelNestedGrid As New SfDataGrid()
' Wiring events for first level DataGrid.
AddHandler firstLevelNestedGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit
AddHandler firstLevelNestedGrid.SortColumnsChanging, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_SortColumnsChanging
AddHandler firstLevelNestedGrid.FilterChanging, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_FilterChanging
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition)For second level nested grid,
GridViewDefinition firstLevelGridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails";
SfDataGrid firstLevelNestedGrid = new SfDataGrid();
// Wiring events for first level DataGrid.
firstLevelNestedGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit += FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit;
firstLevelNestedGrid.SortColumnsChanging += FirstLevelNestedGrid_SortColumnsChanging;
firstLevelNestedGrid.FilterChanging += FirstLevelNestedGrid_FilterChanging;
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid;
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition);
GridViewDefinition secondLevelGridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
secondLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "ProductDetails";
SfDataGrid secondLevelDataGrid = new SfDataGrid();
// Wiring events for second level DataGrid.
secondLevelDataGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit += SecondLevelDataGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit;
secondLevelDataGrid.SortColumnsChanging += SecondLevelDataGrid_SortColumnsChanging;
secondLevelDataGrid.FilterChanging += SecondLevelDataGrid_FilterChanging;
secondLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = secondLevelDataGrid;
firstLevelNestedGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(secondLevelGridViewDefinition);Dim firstLevelGridViewDefinition As New GridViewDefinition()
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails"
Dim firstLevelNestedGrid As New SfDataGrid()
' Wiring events for first level DataGrid.
AddHandler firstLevelNestedGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit
AddHandler firstLevelNestedGrid.SortColumnsChanging, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_SortColumnsChanging
AddHandler firstLevelNestedGrid.FilterChanging, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_FilterChanging
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition)
Dim secondLevelGridViewDefinition As New GridViewDefinition()
secondLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "ProductDetails"
Dim secondLevelDataGrid As New SfDataGrid()
' Wiring events for second level DataGrid.
AddHandler secondLevelDataGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit, AddressOf secondLevelDataGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit
AddHandler secondLevelDataGrid.SortColumnsChanging, AddressOf secondLevelDataGrid_SortColumnsChanging
AddHandler secondLevelDataGrid.FilterChanging, AddressOf secondLevelDataGrid_FilterChanging
secondLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = secondLevelDataGrid
firstLevelNestedGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(secondLevelGridViewDefinition)When auto generating relations
When the relation is auto-generated, you can get the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid in the AutoGeneratingRelations event handler to wire the events.
this.sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations += SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations;
private void SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(object sender, AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs e)
{
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit += FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.SortColumnsChanging += FirstLevelNestedGrid_SortColumnsChanging;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.FilterChanging += FirstLevelNestedGrid_FilterChanging;
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations, AddressOf SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations
Private Sub SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs)
AddHandler e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit
AddHandler e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.SortColumnsChanging, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_SortColumnsChanging
AddHandler e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.FilterChanging, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_FilterChanging
End SubFor second level nested grid,
this.sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations += SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations;
private void SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(object sender, AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs e)
{
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = true;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations += FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations;
}
private void FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(object sender, AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs e)
{
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit += SecondLevelDataGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.SortColumnsChanging += SecondLevelDataGrid_SortColumnsChanging;
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.FilterChanging += SecondLevelDataGrid_FilterChanging;
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations, AddressOf SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations
Private Sub SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs)
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = True
AddHandler e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations, AddressOf FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations
End Sub
Private Sub FirstLevelDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs)
AddHandler e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit, AddressOf SecondLevelDataGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit
AddHandler e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.SortColumnsChanging, AddressOf SecondLevelDataGrid_SortColumnsChanging
AddHandler e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.FilterChanging, AddressOf SecondLevelDataGrid_FilterChanging
End SubListen DetailsViewDataGrid event in ParentDataGrid event handler
You can listen to the DetailsViewDataGrid event in the parent DataGrid event handlers itself by setting the NotifyEventsToParentDataGrid property of GridViewDefinition.DataGrid. Then, no need to listen the events for each level as discussed previously.
GridViewDefinition firstLevelGridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails";
SfDataGrid firstLevelNestedGrid = new SfDataGrid();
// To notify the DetailsView events to parent DataGrid events.
firstLevelNestedGrid.NotifyEventsToParentDataGrid = true;
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid;
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition);Dim firstLevelGridViewDefinition As New GridViewDefinition()
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails"
Dim firstLevelNestedGrid As New SfDataGrid()
' To notify the DetailsView events to parent DataGrid events.
firstLevelNestedGrid.NotifyEventsToParentDataGrid = True
firstLevelGridViewDefinition.DataGrid = firstLevelNestedGrid
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(firstLevelGridViewDefinition)You can wire the events in the parent DataGrid and get the corresponding DetailsViewDataGrid in the parent DataGrid EventArgs.
this.sfDataGrid.RowValidating += SfDataGrid_RowValidating;
private void SfDataGrid_RowValidating(object sender, RowValidatingEventArgs e)
{
var detailsViewDataGrid = e.OriginalSender as DetailsViewDataGrid;
}AddHandler Me.sfDataGrid.RowValidating, AddressOf SfDataGrid_RowValidating
Private Sub SfDataGrid_RowValidating(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As RowValidatingEventArgs)
Dim detailsViewDataGrid = TryCast(e.OriginalSender, DetailsViewDataGrid)
End SubYou can get the source DataGrid in the parent DataGrid events by using the SourceDataGrid property.
this.sfDataGrid.RowValidating += SfDataGrid_RowValidating;
private void SfDataGrid_RowValidating(object sender, RowValidatingEventArgs e)
{
var detailsViewDataGrid = e.OriginalSender as DetailsViewDataGrid;
var sourceDataGrid = detailsViewDataGrid.NotifyListener.SourceDataGrid;
}AddHandler Me.sfDataGrid.RowValidating, AddressOf SfDataGrid_RowValidating
Private Sub SfDataGrid_RowValidating(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As RowValidatingEventArgs)
Dim detailsViewDataGrid = TryCast(e.OriginalSender, DetailsViewDataGrid)
Dim sourceDataGrid = detailsViewDataGrid.NotifyListener.SourceDataGrid
End SubGetting the parent DataGrid while editing DetailsViewDataGrid
You can get the corresponding parent DataGrid while editing the DetailsViewDataGrid through its CurrentCellBeginEdit event handler.
firstLevelNestedGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit += FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit;
private void FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit(object sender, CurrentCellBeginEditEventArgs e)
{
var detailsViewDataGrid = e.OriginalSender as DetailsViewDataGrid;
var parentDataGrid = detailsViewDataGrid.NotifyListener.GetParentDataGrid();
}AddHandler firstLevelNestedGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit
Private Sub FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As CurrentCellBeginEditEventArgs)
Dim detailsViewDataGrid = TryCast(e.OriginalSender, DetailsViewDataGrid)
Dim parentDataGrid = detailsViewDataGrid.NotifyListener.GetParentDataGrid()
End SubHere, the sender is GridViewDefinition.DataGrid. You can get the DetailsViewDataGrid that raises the event by using the OriginalSender.
Column sizing
The SfDataGrid allows you to apply column sizing to the DetailsViewDataGrid by setting the GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.AutoSizeColumnsMode like parent DataGrid. For more information, refer to the Column Sizing section.
Resizing parent DataGrid and DetailsViewDataGrid simultaneously
By default, the DetailsViewDataGrid column width will not be adjusted while resizing the parent DataGrid columns. You can adjust the DetailsViewDataGrid column width simultaneously while resizing the parent DataGrid by handling the DetailsViewLoading and ColumnResizing events.
NOTE
It is applicable only when the parent and
DetailsViewDataGridhaving same number of columns.
Setting the column width of the DetailsViewDataGrid is based on the parent DataGrid column in the DetailsViewLoading event.
this.sfDataGrid.DetailsViewLoading += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading(object sender, DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs e)
{
var parentGrid = e.OriginalSender is DetailsViewDataGrid ? (e.OriginalSender as SfDataGrid) : sender as SfDataGrid;
if (!CanResize(parentGrid))
return;
if (parentGrid.Columns.Count != e.DetailsViewDataGrid.Columns.Count)
return;
double width = 0;
var detailsViewStartColumnIndex = e.DetailsViewDataGrid.TableControl.ResolveToStartColumnIndex();
for (int i = 0; i < parentGrid.Columns.Count; i++)
{
width = i == 0 ? parentGrid.Columns[i].ActualWidth - detailsViewStartColumnIndex * 24 : parentGrid.Columns[i].Width;
if (e.DetailsViewDataGrid.Columns[i].Width != parentGrid.Columns[i].Width)
e.DetailsViewDataGrid.Columns[i].Width = width;
}
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.DetailsViewLoading, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs)
Dim parentGrid = If(TypeOf e.OriginalSender Is DetailsViewDataGrid, (TryCast(e.OriginalSender, SfDataGrid)), TryCast(sender, SfDataGrid))
If Not CanResize(parentGrid) Then
Return
End If
If parentGrid.Columns.Count <> e.DetailsViewDataGrid.Columns.Count Then
Return
End If
Dim width As Double = 0
Dim detailsViewStartColumnIndex = e.DetailsViewDataGrid.TableControl.ResolveToStartColumnIndex()
For i As Integer = 0 To parentGrid.Columns.Count - 1
width = If(i = 0, parentGrid.Columns(i).ActualWidth - detailsViewStartColumnIndex * 24, parentGrid.Columns(i).Width)
If e.DetailsViewDataGrid.Columns(i).Width <> parentGrid.Columns(i).Width Then
e.DetailsViewDataGrid.Columns(i).Width = width
End If
Next i
End SubWhen the column is resized in the parent DataGrid column, the new width will be set to the corresponding column of DetailsViewDataGrid based on the ColumnIndex argument in the ColumnResizing event.
this.sfDataGrid.ColumnResizing += SfDataGrid_ColumnResizing;
private void SfDataGrid_ColumnResizing(object sender, ColumnResizingEventArgs e)
{
var grid = sender as SfDataGrid;
// For DetailsView grid, sender will be RootDataGrid. So need to get OriginalSender
if (e.OriginalSender is DetailsViewDataGrid)
grid = e.OriginalSender as SfDataGrid;
if (grid.View == null)
return;
SetWidth(grid, this.sfDataGrid.TableControl.ResolveToScrollColumnIndex(e.ColumnIndex), e.Width);
}
/// <summary>
/// Decides whether need to resize the child grid columns based on parent grid
/// </summary>
/// <param name="dataGrid">parent DataGrid</param>
/// <returns>bool</returns>
private bool CanResize(SfDataGrid dataGrid)
{
if (dataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions == null && !dataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Any())
return true;
foreach (var definition in dataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions)
{
var detailsViewGrid = (definition as GridViewDefinition).DataGrid;
if (detailsViewGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions == null && !detailsViewGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Any())
return CanResize(detailsViewGrid);
if (detailsViewGrid.Columns.Count != dataGrid.Columns.Count)
return false;
}
return true;
}
/// <summary>
/// Recursively set width in all levels
/// </summary>
/// <param name="grid">SfDataGrid</param>
/// <param name="scrollColumnIndex">scrollColumnIndex</param>
/// <param name="width">width</param>
private void SetWidth(SfDataGrid grid, int scrollColumnIndex, double width)
{
if (grid.DetailsViewDefinitions == null || !grid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Any())
return;
if (!CanResize(grid))
return;
var columnIndex = grid.TableControl.ResolveToGridVisibleColumnIndex(scrollColumnIndex);
if (columnIndex < 0)
return;
var parentStartColumnIndex = grid.TableControl.ResolveToStartColumnIndex();
var indentColumnsWidth = 0;
foreach (var definition in grid.DetailsViewDefinitions)
{
var detailsViewDataGrid = (definition as GridViewDefinition).DataGrid;
var startColumnIndex = detailsViewDataGrid.TableControl.ResolveToStartColumnIndex();
indentColumnsWidth = startColumnIndex * 24;
var tempWidth = width - indentColumnsWidth < 0 ? 0 : width - indentColumnsWidth;
detailsViewDataGrid.Columns[columnIndex].Width = scrollColumnIndex == parentStartColumnIndex ? tempWidth : width;
// If DetailsViewDataGrid has DetailsViewDefinition, recursively set width upto all levels
if (detailsViewDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions != null && detailsViewDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Any())
SetWidth(detailsViewDataGrid, detailsViewDataGrid.TableControl.ResolveToScrollColumnIndex(columnIndex), detailsViewDataGrid.Columns[columnIndex].Width);
}
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.ColumnResizing, AddressOf SfDataGrid_ColumnResizing
Private Sub SfDataGrid_ColumnResizing(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As ColumnResizingEventArgs)
Dim grid = TryCast(sender, SfDataGrid)
' For DetailsView grid, sender will be RootDataGrid. So need to get OriginalSender
If TypeOf e.OriginalSender Is DetailsViewDataGrid Then
grid = TryCast(e.OriginalSender, SfDataGrid)
End If
If grid.View Is Nothing Then
Return
End If
SetWidth(grid, Me.sfDataGrid.TableControl.ResolveToScrollColumnIndex(e.ColumnIndex), e.Width)
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Decides whether need to resize the child grid columns based on parent grid
''' </summary>
''' <param name="dataGrid">parent DataGrid</param>
''' <returns>bool</returns>
Private Function CanResize(ByVal dataGrid As SfDataGrid) As Boolean
If dataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions Is Nothing AndAlso (Not dataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Any()) Then
Return True
End If
For Each definition In dataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions
Dim detailsViewGrid = (TryCast(definition, GridViewDefinition)).DataGrid
If detailsViewGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions Is Nothing AndAlso (Not detailsViewGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Any()) Then
Return CanResize(detailsViewGrid)
End If
If detailsViewGrid.Columns.Count <> dataGrid.Columns.Count Then
Return False
End If
Next definition
Return True
End Function
''' <summary>
''' Recursively set width in all levels
''' </summary>
''' <param name="grid">SfDataGrid</param>
''' <param name="scrollColumnIndex">scrollColumnIndex</param>
''' <param name="width">width</param>
Private Sub SetWidth(ByVal grid As SfDataGrid, ByVal scrollColumnIndex As Integer, ByVal width As Double)
If grid.DetailsViewDefinitions Is Nothing OrElse (Not grid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Any()) Then
Return
End If
If Not CanResize(grid) Then
Return
End If
Dim columnIndex = grid.TableControl.ResolveToGridVisibleColumnIndex(scrollColumnIndex)
If columnIndex < 0 Then
Return
End If
Dim parentStartColumnIndex = grid.TableControl.ResolveToStartColumnIndex()
Dim indentColumnsWidth = 0
For Each definition In grid.DetailsViewDefinitions
Dim detailsViewDataGrid = (TryCast(definition, GridViewDefinition)).DataGrid
Dim startColumnIndex = detailsViewDataGrid.TableControl.ResolveToStartColumnIndex()
indentColumnsWidth = startColumnIndex * 24
Dim tempWidth = If(width - indentColumnsWidth < 0, 0, width - indentColumnsWidth)
detailsViewDataGrid.Columns(columnIndex).Width = If(scrollColumnIndex Is parentStartColumnIndex, tempWidth, width)
' If DetailsViewDataGrid has DetailsViewDefinition, recursively set width upto all levels
If detailsViewDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions IsNot Nothing AndAlso detailsViewDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Any() Then
SetWidth(detailsViewDataGrid, detailsViewDataGrid.TableControl.ResolveToScrollColumnIndex(columnIndex), detailsViewDataGrid.Columns(columnIndex).Width)
End If
Next definition
End SubYou can get the sample here.
NOTE
To display the parent and DetailsViewDataGrid in the same line, set the DetailsViewPadding as Zero for top, bottom, right sides and the expander column width as left, because we have started rendering the grid inside the Expander column itself.
Selection
The DetailsViewDataGrid allows you to select the rows based on the SelectionMode property in its parent DataGrid.
Getting the selected DetailsViewDataGrid
You can get the currently selected DetailsViewDataGrid by using the SelectedDetailsViewGrid property of the parent DataGrid.
var detailsViewDataGrid = this.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid;Dim detailsViewDataGrid = Me.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGridFor accessing nested level SelectedDetailsViewGrid,
var detailsViewDataGrid = this.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid;Dim detailsViewDataGrid = Me.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGridGetting the SelectedItem, SelectedItems, and SelectedIndex of DetailsViewDataGrid
You can access the selected record or records and selected record index of the DetailsViewDataGrid by using the SelectedItem, SelectedItems, and SelectedIndex properties directly.
var detailsViewDataGrid = this.sfDataGrid.GetDetailsViewGrid(2);
int selectedIndex = detailsViewDataGrid.SelectedIndex;
var selectedItem = detailsViewDataGrid.SelectedItem;
var selectedItems = detailsViewDataGrid.SelectedItems;Dim detailsViewDataGrid = Me.sfDataGrid.GetDetailsViewGrid(2)
Dim selectedIndex As Integer = detailsViewDataGrid.SelectedIndex
Dim selectedItem = detailsViewDataGrid.SelectedItem
Dim selectedItems = detailsViewDataGrid.SelectedItemsYou can access the SelectedItem, SelectedItems, and SelectedIndex properties of DetailsViewDataGrid by using the parent SelectedDetailsViewGrid property of dataGrid.
int selectedIndex = this.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.SelectedIndex;
var selectedItem = this.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.SelectedItem;
var selectedItems = this.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.SelectedItems;Dim selectedIndex As Integer = Me.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.SelectedIndex
Dim selectedItem = Me.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.SelectedItem
Dim selectedItems = Me.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.SelectedItemsGetting the CurrentCell of DetailsViewDataGrid
You can get the CurrentCell of DetailsViewDataGrid by using the SelectedDetailsViewGrid property of the parent DataGrid or CurrentCellBeginEdit event of DetailsViewDataGrid.
// Retrieving current cell from SelectedDetailsViewGrid.
var currentCell = this.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.CurrentCell;
firstLevelNestedGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit += FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit;
private void FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit(object sender, CurrentCellBeginEditEventArgs e)
{
// Retrieving current cell when editing the DetailsView.
var detailsViewDataGrid = e.OriginalSender as DetailsViewDataGrid;
var currentCell = detailsViewDataGrid.CurrentCell;
}' Retrieving current cell from SelectedDetailsViewGrid.
Private currentCell = Me.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.CurrentCell
AddHandler firstLevelNestedGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit, AddressOf FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit
Private Sub FirstLevelNestedGrid_CurrentCellBeginEdit(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As CurrentCellBeginEditEventArgs)
' Retrieving current cell when editing the DetailsView.
Dim detailsViewDataGrid = TryCast(e.OriginalSender, DetailsViewDataGrid)
Dim currentCell = detailsViewDataGrid.CurrentCell
End SubYou can refer to [here](#_Handling_events_for “”) to know the handling events of DetailsViewDataGrid.
Getting the parent DataGrid
You can get the immediate parent DataGrid of the corresponding DetailsViewDataGrid through the GetParentDataGrid method of the SfDataGrid.NotifyListener.
var parentDataGrid = this.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.NotifyListener.GetParentDataGrid();Dim parentDataGrid = Me.sfDataGrid.SelectedDetailsViewGrid.NotifyListener.GetParentDataGrid()Getting the DetailsViewDataGrid
You can get the DetailsViewDataGrid based on the row index through GetDetailsViewGrid helper method.
var detailsViewDataGrid = this.sfDataGrid.GetDetailsViewGrid(2);Dim detailsViewDataGrid = Me.sfDataGrid.GetDetailsViewGrid(2)Programmatic selection in DetailsViewDataGrid
In DetailsViewDataGrid, you can add or remove the selection programmatically like parent DataGrid. You can get DetailsViewDataGrid by using the DetailsViewLoading event or GetDetailsViewGrid method to process the selection operations.
Selecting records
You can select a particular record by using the SelectedItem property.
this.sfDataGrid.DetailsViewLoading += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading(object sender, DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs e)
{
var record = e.DetailsViewDataGrid.GetRecordAtRowIndex(1);
e.DetailsViewDataGrid.SelectedItem = record;
}AddHandler Me.sfDataGrid1.DetailsViewLoading, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs)
Dim record = e.DetailsViewDataGrid.GetRecordAtRowIndex(1)
e.DetailsViewDataGrid.SelectedItem = record
End SubYou can also select a particular record by using the SelectedIndex property.
this.sfDataGrid.DetailsViewLoading += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading(object sender, DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs e)
{
e.DetailsViewDataGrid.SelectedIndex = 1;
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.DetailsViewLoading, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs)
e.DetailsViewDataGrid.SelectedIndex = 1
End SubRow selection
You can select multiple rows by using the SelectRows method.
var detailsViewDataGrid = this.sfDataGrid.GetDetailsViewGrid(2);
detailsViewDataGrid.SelectRows(1, 2);Dim detailsViewDataGrid = Me.sfDataGrid.GetDetailsViewGrid(2)
detailsViewDataGrid.SelectRows(1, 2)Appearance Customization
The appearance of the DetailsViewDataGrid can be customized like parent DataGrid through styling support in the SfDataGrid.
Changing header appearance of DetailsViewDataGrid
You can customize the header appearance of the DetailsViewDataGrid through the Style.HeaderStyle property of DetailsViewDataGrid.
sfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = false;
var gridViewDefinition = new GridViewDefinition();
gridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails";
gridViewDefinition.DataGrid = new SfDataGrid() { Name = "FirstLevelNestedGrid", AutoGenerateColumns = true };
gridViewDefinition.DataGrid.Style.HeaderStyle.BackColor = ColorTranslator.FromHtml("#CAECCF");
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(gridViewDefinition);sfDataGrid.AutoGenerateRelations = False
Dim gridViewDefinition = New GridViewDefinition()
gridViewDefinition.RelationalColumn = "OrderDetails"
gridViewDefinition.DataGrid = New SfDataGrid() With {.Name = "FirstLevelNestedGrid", .AutoGenerateColumns = True}
gridViewDefinition.DataGrid.Style.HeaderStyle.BackColor = ColorTranslator.FromHtml("#CAECCF")
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions.Add(gridViewDefinition)When the relation is auto-generated, you can customize the header style to GridViewDefinition.DataGrid in the AutoGeneratingRelations event.
sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations += SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations;
private void SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(object sender, AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs e)
{
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.Style.HeaderStyle.BackColor = ColorTranslator.FromHtml("#CAECCF");
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingRelations, AddressOf SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations
Private Sub SfDataGrid_AutoGeneratingRelations(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As AutoGeneratingRelationsEventArgs)
e.GridViewDefinition.DataGrid.Style.HeaderStyle.BackColor = ColorTranslator.FromHtml("#CAECCF")
End Sub
Hiding header row of Master-Details View
You can hide the header row of the DetailsViewDataGrid by setting the HeaderRowHeight property.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions[0].DataGrid.HeaderRowHeight = 0;sfDataGrid.DetailsViewDefinitions[0].DataGrid.HeaderRowHeight = 0
Customizing padding of the DetailsViewDataGrid
The padding of DetailsViewDataGrid can be customized through the DetailsViewPadding property and it will be set to its corresponding parent DataGrid.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewPadding = new Padding(20);sfDataGrid.DetailsViewPadding = New Padding(20)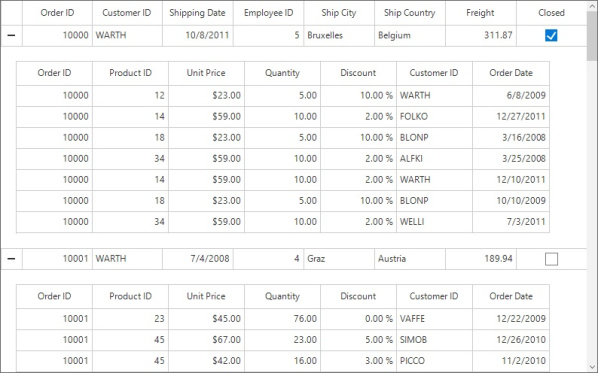
Customize ExpanderColumn width
You can customize the width of the ExpanderColumn in the SfDataGrid by using the ExpanderColumnWidth property .
sfDataGrid.ExpanderColumnWidth = 50;sfDataGrid.ExpanderColumnWidth = 50
Expanding and collapsing the DetailsViewDataGrid programmatically
The SfDataGrid allows you to expand or collapse the DetailsViewDataGrid programmatically in different ways.
Expand or collapse all the DetailsViewDataGrid
You can expand or collapse all the DetailsViewDataGrid programmatically by using the ExpandAllDetailsView and CollapseAllDetailsView methods.
this.sfDataGrid.ExpandAllDetailsView();
this.sfDataGrid.CollapseAllDetailsView();Me.sfDataGrid.ExpandAllDetailsView()
Me.sfDataGrid.CollapseAllDetailsView()Expand or collapse DetailsView based on record index
You can expand or collapse DetailsViewDataGrid based on the record index by using the ExpandDetailsViewAt and CollapseDetailsViewAt methods.
this.sfDataGrid.ExpandDetailsViewAt(0);
this.sfDataGrid.CollapseDetailsViewAt(0);Me.sfDataGrid.ExpandDetailsViewAt(0)
Me.sfDataGrid.CollapseDetailsViewAt(0)Hiding expander when parent record’s relation property has an empty collection or null
By default, the expander will be visible for all the data rows in the parent DataGrid even if its RelationalColumn property has an empty collection or null.
You can hide the expander from the view when corresponding RelationalColumn property has an empty collection or null by setting the HideEmptyGridViewDefinition property to true.
sfDataGrid.HideEmptyGridViewDefinition = true;sfDataGrid.HideEmptyGridViewDefinition = True
Handling events
DetailsViewLoading
The DetailsViewLoading event is raised when the DetailsViewDataGrid is being loaded in to the view (when scrolling, changing window size, and expanding the record using an expander or programmatically).
This event receives two arguments where, the sender as SfDataGrid and DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs which contains the following member:
DetailsViewDataGrid: Gets the DetailsViewDataGrid loaded into view. You can set the customized Renderers, SelectionController, ColumnResizingController, ColumnDragDropController, and AutoSizeController to this. But, it is not preferable to change the value of the public properties like AllowFiltering, AllowSorting, SelectionMode, AllowDeleting, etc. here.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewLoading += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading(object sender, DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs e)
{
if (!(e.DetailsViewDataGrid.SelectionController is CustomSelectionController))
e.DetailsViewDataGrid.SelectionController = new CustomSelectionController(sfDataGrid);
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.DetailsViewLoading, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewLoading(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs)
If Not(TypeOf e.DetailsViewDataGrid.SelectionController Is CustomSelectionController) Then
e.DetailsViewDataGrid.SelectionController = New CustomSelectionController(sfDataGrid)
End If
End SubDetailsViewUnLoading
The DetailsViewUnLoading event is raised when the DetailsViewDataGrid is being unloaded from the view.
This event receives two arguments where, the sender as SfDataGrid and DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs which contains the following member:
DetailsViewDataGrid: Gets the DetailsViewDataGrid unloaded from the view (when scrolling, changing window size, sorting, grouping, filtering, and collapsing the DetailsViewDataGrid using expander or programmatically).
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewUnloading += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewUnloading;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewUnloading(object sender, DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs e)
{
}AddHandler sfDataGrid. DetailsViewUnloading, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewUnLoading
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewUnloading(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewLoadingAndUnloadingEventArgs)
End SubDetailsViewExpanding
The DetailsViewExpanding event is raised when the DetailsViewDataGrid is being expanded by using an expander.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewExpanding += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding(object sender, DetailsViewExpandingEventArgs e)
{
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.DetailsViewExpanding, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewExpandingEventArgs)
End SubDetailsViewExpanded
The DetailsViewExpanded event is raised after the DetailsViewDataGrid is expanded by using an expander.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewExpanded += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanded;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanded(object sender, DetailsViewExpandedEventArgs e)
{
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.DetailsViewExpanded, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanded
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanded(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewExpandedEventArgs)
End SubDetailsViewCollapsing
The DetailsViewCollapsing event is raised when the DetailsViewDataGrid is being collapsed from the view by using an expander.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewCollapsing += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsing;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsing(object sender, DetailsViewCollapsingEventArgs e)
{
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.DetailsViewCollapsing, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsing
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsing(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewCollapsingEventArgs)
End SubDetailsViewCollapsed
The DetailsViewCollapsed event is raised after the DetailsViewDataGrid is collapsed by using an expander.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewCollapsed += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsed;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsed(object sender, DetailsViewCollapsedEventArgs e)
{
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.DetailsViewCollapsed, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsed
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsed(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewCollapsedEventArgs)
End SubCancel expanding or collapsing operations through events
You can cancel the expanding operation while expanding the DetailsViewDataGrid by using the DetailsViewExpandingEventArgs.Cancel property in the DetailsViewExpanding event handler.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewExpanding += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding(object sender, DetailsViewExpandingEventArgs e)
{
if ((e.Record as OrderInfo).OrderID == 1002)
e.Cancel = true;
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.DetailsViewExpanding, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewExpanding(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewExpandingEventArgs)
If (TryCast(e.Record, OrderInfo)).OrderID = 1002 Then
e.Cancel = True
End If
End SubSimilarly, the collapsing operation can be canceled through the DetailsViewCollapsingEventArgs.Cancel property in the DetailsViewCollapsing event handler.
sfDataGrid.DetailsViewCollapsing += SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsing;
private void SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsing(object sender, DetailsViewCollapsingEventArgs e)
{
if ((e.Record as OrderInfo).OrderID == 1002)
e.Cancel = true;
}AddHandler sfDataGrid.DetailsViewCollapsing, AddressOf SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsing
Private Sub SfDataGrid_DetailsViewCollapsing(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As DetailsViewCollapsingEventArgs)
If (TryCast(e.Record, OrderInfo)).OrderID = 1002 Then
e.Cancel = True
End If
End SubMaster-Details view limitations
Limitations are:
-
DetailsViewDataGriddoes not have GroupDropArea. -
DetailsViewDataGriddoes not support AutoGenerateColumnsMode.ResetAll. Instead, it works based on Reset. - Master-Details view does not support data virtualization.
- Master-Details view does not support freeze pane.
- Master-Details view does not support AutoRowHeight.
- For DetailsViewDataGrid, properties like SelectionMode, DetailsViewPadding, AllowSelectionOnMouseDown, and RightToLeft are assigned from its parent grid only. So, both parent DataGrid and DetailsViewDataGrid cannot have different values for these properties.
See also
How to collapse the details view datagrid inside the Groups in DataGrid (SfDataGrid)