How can I help you?
Getting Started with Windows Forms DataGrid (SfDataGrid)
21 Jan 202519 minutes to read
This section provides a quick overview for working with the data grid for WinForms. Walk through the entire process of creating a real world data grid.
To get start quickly with WinForms DataGrid, you can check on this video:
Assembly Deployment
Refer control dependencies section to get the list of assemblies or NuGet package needs to be added as reference to use the SfDataGrid control in any application.
Creating Application with SfDataGrid
In this walk through, users will create WinForms application that contains SfDataGrid control.
Creating the Project
Create new Windows Forms Project in Visual Studio to display SfDataGrid with data objects.
Adding Control via Designer
Windows Forms DataGrid (SfDataGrid) control can be added to the application by dragging it from Toolbox and dropping it in Designer. The required assembly references will be added automatically.
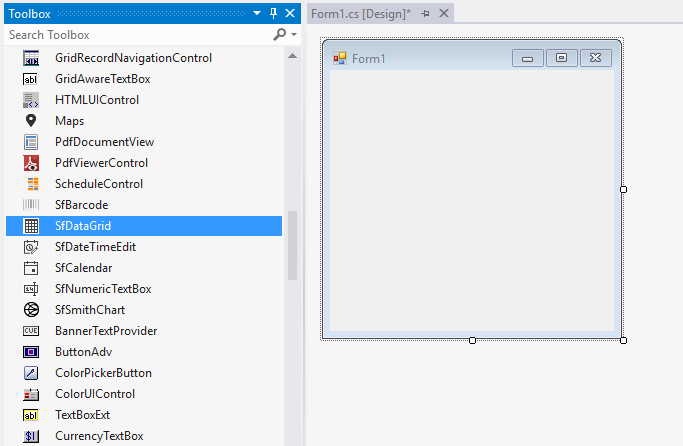
Adding Control in Code
In order to add control manually, do the below steps,
-
Add the required assembly references to the project
-
Create the SfDataGrid control instance and add it to the Form
using Syncfusion.WinForms.DataGrid; namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); SfDataGrid sfDataGrid1 = new SfDataGrid(); sfDataGrid1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(85, 108); sfDataGrid1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(240, 150); this.Controls.Add(sfDataGrid1); } } }Imports Syncfusion.WinForms.DataGrid Namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 Partial Public Class Form1 Inherits Form Public Sub New() InitializeComponent() Dim sfDataGrid1 As New SfDataGrid() sfDataGrid1.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(85, 108) sfDataGrid1.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(240, 150) Me.Controls.Add(sfDataGrid1) End Sub End Class End Namespace
Creating Data for Sample Application
SfDataGrid is a data-bound control. So data must be created for application.
-
Create data object class named “OrderInfo” and declare properties as shown below,
public class OrderInfo { int orderID; string customerId; string country; string customerName; string shippingCity; public int OrderID { get { return orderID; } set { orderID = value; } } public string CustomerID { get { return customerId; } set { customerId = value; } } public string CustomerName { get { return customerName; } set { customerName = value; } } public string Country { get { return country; } set { country = value; } } public string ShipCity { get { return shippingCity; } set { shippingCity = value; } } public OrderInfo(int orderId, string customerName, string country, string customerId, string shipCity) { this.OrderID = orderId; this.CustomerName = customerName; this.Country = country; this.CustomerID = customerId; this.ShipCity = shipCity; } }Public Class OrderInfo Private _orderID As Integer Private _customerId As String Private _country As String Private _customerName As String Private _shippingCity As String Public Property OrderID() As Integer Get Return _orderID End Get Set(ByVal value As Integer) _orderID = value End Set End Property Public Property CustomerID() As String Get Return _customerId End Get Set(ByVal value As String) _customerId = value End Set End Property Public Property CustomerName() As String Get Return _customerName End Get Set(ByVal value As String) _customerName = value End Set End Property Public Property Country() As String Get Return _country End Get Set(ByVal value As String) _country = value End Set End Property Public Property ShipCity() As String Get Return _shippingCity End Get Set(ByVal value As String) _shippingCity = value End Set End Property Public Sub New(ByVal orderId As Integer, ByVal customerName As String, ByVal country As String, ByVal customerId As String, ByVal shipCity As String) Me.OrderID = orderId Me.CustomerName = customerName Me.Country = country Me.CustomerID = customerId Me.ShipCity = shipCity End Sub End Class -
Create an OrderInfoCollection class with Orders property and Orders property is initialized with several data objects in constructor.
public class OrderInfoCollection { private ObservableCollection<OrderInfo> _orders; public ObservableCollection<OrderInfo> Orders { get { return _orders; } set { _orders = value; } } public OrderInfoCollection() { _orders = new ObservableCollection<OrderInfo>(); this.GenerateOrders(); } private void GenerateOrders() { _orders.Add(new OrderInfo(1001, "Maria Anders", "Germany", "ALFKI", "Berlin")); _orders.Add(new OrderInfo(1002, "Ana Trujilo", "Mexico", "ANATR", "Mexico D.F.")); _orders.Add(new OrderInfo(1003, "Antonio Moreno", "Mexico", "ANTON", "Mexico D.F.")); _orders.Add(new OrderInfo(1004, "Thomas Hardy", "UK", "AROUT", "London")); _orders.Add(new OrderInfo(1005, "Christina Berglund", "Sweden", "BERGS", "Lula")); _orders.Add(new OrderInfo(1006, "Hanna Moos", "Germany", "BLAUS", "Mannheim")); _orders.Add(new OrderInfo(1007, "Frederique Citeaux", "France", "BLONP", "Strasbourg")); _orders.Add(new OrderInfo(1008, "Martin Sommer", "Spain", "BOLID", "Madrid")); _orders.Add(new OrderInfo(1009, "Laurence Lebihan", "France", "BONAP", "Marseille")); _orders.Add(new OrderInfo(1010, "Elizabeth Lincoln", "Canada", "BOTTM", "Tsawassen")); } }Public Class OrderInfoCollection Private _orders As ObservableCollection(Of OrderInfo) Public Property Orders() As ObservableCollection(Of OrderInfo) Get Return _orders End Get Set(ByVal value As ObservableCollection(Of OrderInfo)) _orders = value End Set End Property Public Sub New() _orders = New ObservableCollection(Of OrderInfo)() Me.GenerateOrders() End Sub Private Sub GenerateOrders() _orders.Add(New OrderInfo(1001, "Maria Anders", "Germany", "ALFKI", "Berlin")) _orders.Add(New OrderInfo(1002, "Ana Trujilo", "Mexico", "ANATR", "Mexico D.F.")) _orders.Add(New OrderInfo(1003, "Antonio Moreno", "Mexico", "ANTON", "Mexico D.F.")) _orders.Add(New OrderInfo(1004, "Thomas Hardy", "UK", "AROUT", "London")) _orders.Add(New OrderInfo(1005, "Christina Berglund", "Sweden", "BERGS", "Lula")) _orders.Add(New OrderInfo(1006, "Hanna Moos", "Germany", "BLAUS", "Mannheim")) _orders.Add(New OrderInfo(1007, "Frederique Citeaux", "France", "BLONP", "Strasbourg")) _orders.Add(New OrderInfo(1008, "Martin Sommer", "Spain", "BOLID", "Madrid")) _orders.Add(New OrderInfo(1009, "Laurence Lebihan", "France", "BONAP", "Marseille")) _orders.Add(New OrderInfo(1010, "Elizabeth Lincoln", "Canada", "BOTTM", "Tsawassen")) End Sub End Class
Binding to Data
To bind the SfDataGrid to data, set the SfDataGrid.DataSource property to an IEnumerable implementation. Each row in SfDataGrid is bound to an object in data source and each column in SfDataGrid bound to a property in data object.
OrderInfoCollection orderInfoCollection = new OrderInfoCollection();
sfDataGrid1.DataSource = orderInfoCollection.Orders;Dim orderInfoCollection As New OrderInfoCollection()
sfDataGrid1.DataSource = orderInfoCollection.OrdersNow, run the application, the below output will occur.
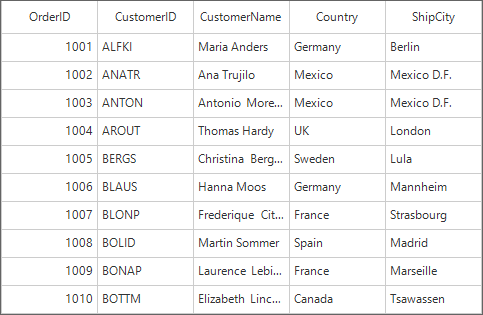
Defining Columns
By default, the SfDataGrid control generates the columns automatically when value assigned to SfDataGrid.DataSource property. The type of the column generated depends on the type of data in the column and the attribute of the property the column bound with.
The following table lists the column types and its constraints for auto column generation.
|
Generated Column Type |
Data Type / Attribute |
| GridTextColumn | Property of type String and any other type apart from below specified cases. |
| GridNumericColumn | Property of type Int, Double, Float, Decimal. |
| GridDateTimeColumn | Property of type DateTime. |
| GridImageColumn | Property of type Byte[] |
| GridHyperLinkColumn | Property of type Uri |
| GridCheckBoxColumn | Property of type Bool. |
When columns are auto-generated, the SfDataGrid.AutoGeneratingColumn event can be handled to customize or cancel the columns before they are added to the SfDataGrid.
The automatic column generation can be prevented by setting SfDataGrid.AutoGenerateColumns property is false, The columns to be displayed should be defined as below,
sfDataGrid1.AutoGenerateColumns = false;
sfDataGrid1.Columns.Add(new GridTextColumn() { MappingName = "OrderID" });
sfDataGrid1.Columns.Add(new GridTextColumn() { MappingName = "CustomerID" });sfDataGrid1.AutoGenerateColumns = False
sfDataGrid1.Columns.Add(New GridTextColumn() With {.MappingName = "OrderID"})
sfDataGrid1.Columns.Add(New GridTextColumn() With {.MappingName = "CustomerID"})Below is the list of column types provided in SfDataGrid.
|
Column Type |
Comments |
| GridTextColumn | Represents SfDataGrid column that hosts textual content in its cells. |
| GridNumericColumn | Represents SfDataGrid column that hosts SfNumericTextBox controls in its cells which is used to format and display Numeric values. |
| GridDataTimeColumn | Represents SfDataGrid column that hosts SfDateTimeEdit controls in its cells which is used to display and format DateTime values. |
| GridImageColumn | Represents SfDataGrid column that hosts Image in its cells. |
| GridHyperLinkColumn | Represents SfDataGrid column that hosts Hyperlink in its cells |
| GridCheckBoxColumn | Represents SfDataGrid column that hosts CheckBox in its cells. |
| GridComboBoxColumn | Represents SfDataGrid column that hosts ComboBox in its cells. |
| GridButtonColumn | Represents SfDataGrid column that hosts Button in its cells. |
| GridUnboundColumn | Represents SfDataGrid column that hosts textual content which are not actually bound with data object of row. |
Selection
By default, the entire row is selected when a user clicks a cell in a SfDataGrid. The SfDataGrid.SelectionMode property can be set to specify whether a user can select single row, or multiple rows. The information about the rows that are selected can be retrieved using SfDataGrid.SelectedItem and SfDataGrid.SelectedItems properties.
sfDataGrid1.SelectionMode = Syncfusion.WinForms.DataGrid.Enums.GridSelectionMode.Extended;sfDataGrid1.SelectionMode = Syncfusion.WinForms.DataGrid.Enums.GridSelectionMode.Extended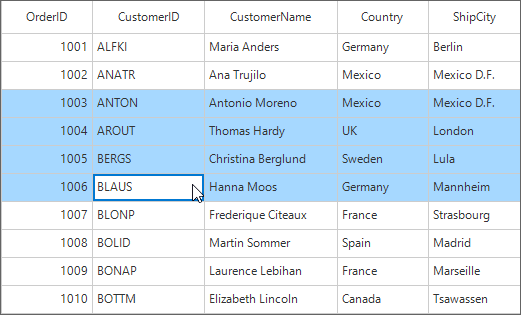
The selection operations can be handled with the help of SfDataGrid.SelectionChanging and SfDataGrid.SelectionChanged events of SfDataGrid.
Sorting, Grouping, and Filtering
Sorting
By default, columns in a SfDataGrid can be sorted by clicking the column header. The sorting can be configured by setting SfDataGrid.SortColumnDescriptions property as below,
OrderInfoCollection orderInfoCollection = new OrderInfoCollection();
sfDataGrid1.DataSource = orderInfoCollection.Orders;
sfDataGrid1.SortColumnDescriptions.Add(new SortColumnDescription() { ColumnName = "Country" });Dim orderInfoCollection As New OrderInfoCollection()
sfDataGrid1.DataSource = orderInfoCollection.Orders
sfDataGrid1.SortColumnDescriptions.Add(New SortColumnDescription() With {.ColumnName = "Country"})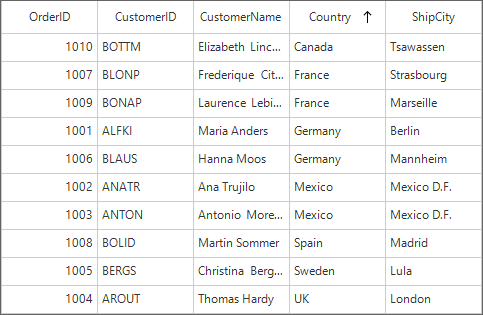
The sorting can be customized by handling the SfDataGrid.SortColumnsChanging and SfDataGrid.SortColumnsChanged events. To cancel the default sort, set the Cancel property to true in SfDataGrid.SortColumnsChanging event.
sfDataGrid1.SortColumnsChanging += sfDataGrid1_SortColumnsChanging;
void sfDataGrid1_SortColumnsChanging(object sender, Syncfusion.WinForms.DataGrid.Events.SortColumnsChangingEventArgs e)
{
if (e.AddedItems[0].ColumnName == "CustomerName")
e.Cancel = true;
}AddHandler sfDataGrid1.SortColumnsChanging, AddressOf sfDataGrid1_SortColumnsChanging
Private Sub sfDataGrid1_SortColumnsChanging(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As Syncfusion.WinForms.DataGrid.Events.SortColumnsChangingEventArgs)
If e.AddedItems(0).ColumnName = "CustomerName" Then
e.Cancel = True
End If
End SubGrouping
Grouping can be enabled by setting SfDataGrid.ShowGroupDropArea property, where group can be dragged by dragging the column header and dropping it in theGroupDropArea over the column headers. The grouping can be configured by setting SfDataGrid.GroupColumnDescriptions property as below,
OrderInfoCollection orderInfoCollection = new OrderInfoCollection();
sfDataGrid1.DataSource = orderInfoCollection.Orders;
sfDataGrid1.GroupColumnDescriptions.Add(new GroupColumnDescription() { ColumnName = "CustomerName" });Dim orderInfoCollection As New OrderInfoCollection()
sfDataGrid1.DataSource = orderInfoCollection.Orders
sfDataGrid1.GroupColumnDescriptions.Add(New GroupColumnDescription() With {.ColumnName = "CustomerName"})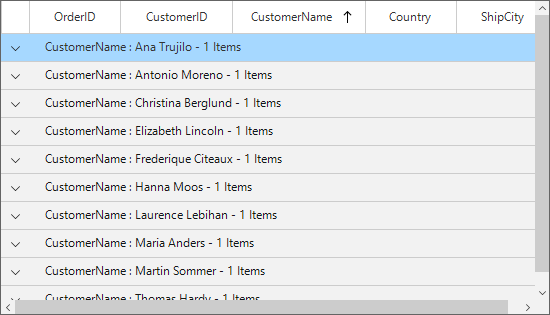
Filtering
Filtering can be enabled by setting SfDataGrid.AllowFiltering property to true, where advanced filter UI can be opened by clicking the Filter icon in column header and filter the SfDataGrid. The filtering operations ca be customized by handling SfDataGrid.FilterChanging and SfDataGrid.FilterChanged events.
OrderInfoCollection orderInfoCollection = new OrderInfoCollection();
sfDataGrid1.DataSource = orderInfoCollection.Orders;
sfDataGrid1.AllowFiltering = true;Dim orderInfoCollection As New OrderInfoCollection()
sfDataGrid1.DataSource = orderInfoCollection.Orders
sfDataGrid1.AllowFiltering = True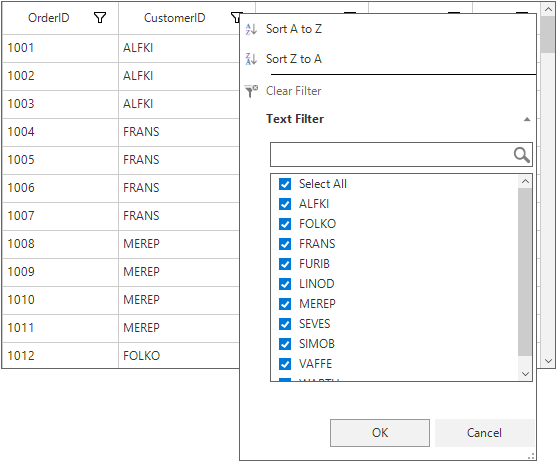
Editing
Editing can be enabled by setting SfDataGrid.AllowEditing property to true. Set SfDataGrid.AllowDeleting property to specify whether user can delete rows by pressing Delete key.
Set SfDataGrid.AddNewRowPosition property to enable additional row either Top or Bottom of SfDataGrid, where user can enter new items into the blank row. Adding new row adds an item to the SfDataGrid.DataSource.
The editing operations can be customized by handling SfDataGrid.CurrentCellBeginEdit and SfDataGrid.CurrentCellEndEdit events.
Handling events
You cannot handle the Key and Mouse events of the SfDataGrid when raising them, because the TableControl is hosted in the SfDataGrid. So, raise the events for SfDataGrid.TableControl.
//KeyDown Event for TableControl
sfDataGrid.TableControl.KeyDown += OnKeyDown;
void OnKeyDown(object sender, KeyEventArgs e)
{
//Do your customization here
}
//MouseDown Event for TableControl
sfDataGrid.TableControl.MouseDown += OnMouseDown;
void OnMouseDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
//Do your customization here
}'KeyDown Event for TableControl
AddHandler sfDataGrid.TableControl.KeyDown, AddressOf OnKeyDown
Private Sub OnKeyDown(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As KeyEventArgs)
'Do your customization here
End Sub
'MouseDown Event for TableControl
AddHandler sfDataGrid.TableControl.MouseDown, AddressOf OnMouseDown
Private Sub OnMouseDown(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As MouseEventArgs)
'Do your customization here
End SubNOTE
You can also explore our WinForms DataGrid example that shows how to render the DataGrid in Windows Forms.