Interactive Features
28 Feb 202524 minutes to read
Context menu
SfTreeGrid provides an entirely customizable menu to expose the functionalities on user interface. You can create context menus for different rows in an efficient manner.
The following code example shows the context menu with command bindings.
<ContextMenu Style="{x:Null}">
<MenuItem Command="{Binding Copy, Source={StaticResource viewModel}}"
CommandParameter="{Binding}" Header="Copy">
</MenuItem>
</ContextMenu>public class BaseCommand : ICommand
{
#region Fields
readonly Action<object> _execute;
readonly Predicate<object> _canExecute;
#endregion
#region Constructors
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new command that can always execute.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="execute">The execution logic.</param>
public BaseCommand(Action<object> execute)
: this(execute, null)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new command.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="execute">The execution logic.</param>
/// <param name="canExecute">The execution status logic.</param>
public BaseCommand(Action<object> execute, Predicate<object> canExecute)
{
if (execute == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("execute");
_execute = execute;
_canExecute = canExecute;
}
#endregion
#region ICommand Members
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
{
return _canExecute == null ? true : _canExecute(parameter);
}
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged
{
add { CommandManager.RequerySuggested += value; }
remove { CommandManager.RequerySuggested -= value; } }
}
public void Execute(object parameter)
{
_execute(parameter);
}
#endregion
}
public class EmployeeInfoViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
public EmployeeInfoViewModel()
{
CopyCommand = new ContextMenuDemo.BaseCommand(ShowMessage);
}
private ICommand copyCommand
public ICommand CopyCommand
{
get
{
return copyCommand;
}
set
{
copyCommand = value;
}
}
public void ShowMessage(object obj)
{
if (obj is GridRecordContextMenuInfo)
{
var grid = (obj as GridRecordContextMenuInfo).DataGrid;
grid.GridCopyPaste.Copy();
}
}
}ContextMenu based on rows
You can set different context menus for SfTreeGrid based on rows.
ContextMenu for nodes
You can set the context menu for data rows using the SfTreeGrid.RecordContextMenu property.
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.RecordContextMenu>
<ContextMenu>
<MenuItem x:Name="Cut" Header="Cut" />
<MenuItem x:Name="Copy" Header="Copy" />
<MenuItem x:Name="Paste" Header="Paste" />
<MenuItem x:Name="Delete" Header="Delete" />
</ContextMenu>
</syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.RecordContextMenu>this.treeGrid.RecordContextMenu = new ContextMenu();
this.treeGrid.RecordContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header = "Cut" });
this.treeGrid.RecordContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header = "Copy" });
this.treeGrid.RecordContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header = "Paste" });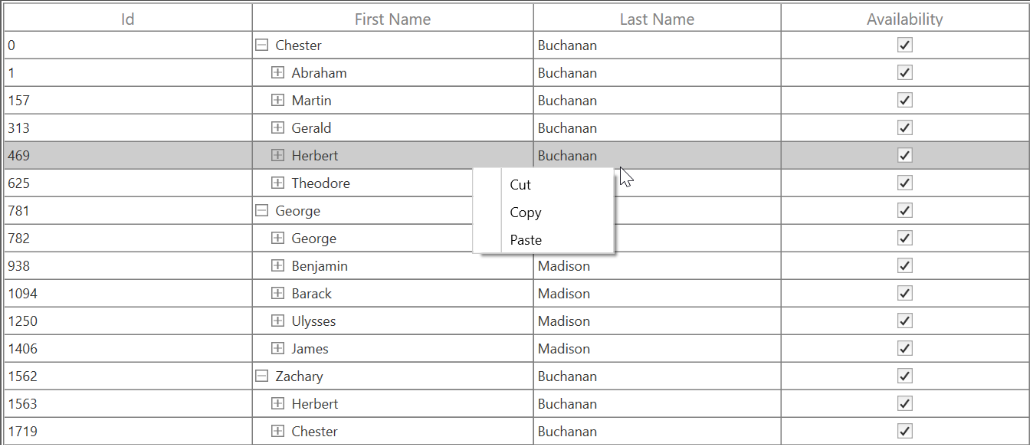
When binding the menu item using CommandBinding, you can get the command parameter as TreeGridNodeContextMenuInfo, which contains the node of the corresponding row.
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.RecordContextMenu>
<MenuItem Command="{Binding Copy, Source={StaticResource viewModel}}" CommandParameter="{Binding}"
Header="Copy">
</MenuItem>
</syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.RecordContextMenu>private static void OnCopyClicked(object obj)
{
var contextMenuInfo = obj as TreeGridNodeContextMenuInfo;
if (contextMenuInfo == null)
return;
var grid = contextMenuInfo.TreeGrid;
grid.GridCopyOption = GridCopyOption.CopyData;
grid.TreeGridCopyPaste.Copy();
}ContextMenu for header
You can set the context menu to header using the SfTreeGrid.HeaderContextMenu property.
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.HeaderContextMenu>
<ContextMenu>
<MenuItem x:Name=" SortAscending " Header="SortAscending" />
<MenuItem x:Name=" SortDescending " Header="SortDescending" />
<MenuItem x:Name=" ClearSorting " Header="ClearSorting" />
<MenuItem x:Name=" ClearFiltering " Header="ClearFiltering" />
</ContextMenu>
</syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.HeaderContextMenu>this.treeGrid.HeaderContextMenu = new ContextMenu();
this.treeGrid.HeaderContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header = "SortAscending" });
this.treeGrid.HeaderContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header = "SortDescending" });
this.treeGrid.HeaderContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header = "ClearSorting" });
this.treeGrid.HeaderContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header = "ClearFiltering " });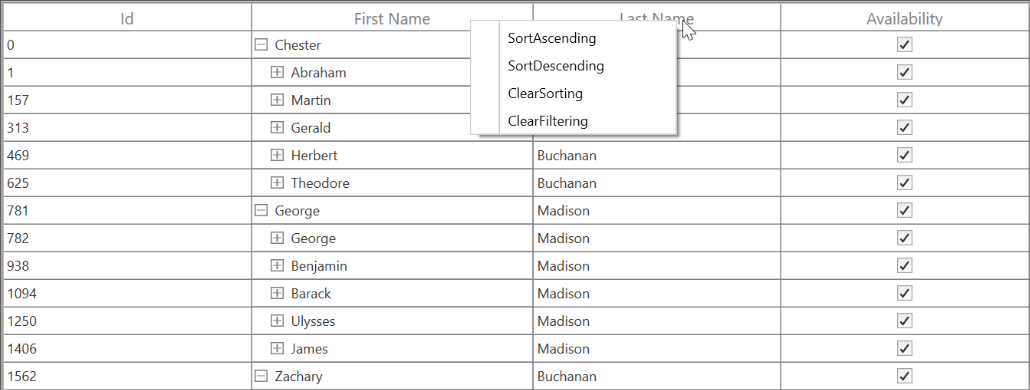
When binding the menu item using CommandBinding, you can get the parameter as TreeGridColumnContextMenuInfo, which contains a particular GridColumn.
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.HeaderContextMenu>
<MenuItem Command="{Binding Source={x:Static <MenuItem Command="{Binding SortAscending, Source={StaticResource viewModel}}"
Header="Sort Ascending">
</MenuItem>
</syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.HeaderContextMenu>private static void OnSortAscendingClicked(object obj)
{
var contextMenuInfo = obj as TreeGridColumnContextMenuInfo;
if (contextMenuInfo == null)
return;
var grid = contextMenuInfo.TreeGrid;
var column = contextMenuInfo.Column;
grid.SortColumnDescriptions.Clear();
grid.SortColumnDescriptions.Add(new SortColumnDescription() { ColumnName = column.MappingName, SortDirection = ListSortDirection.Ascending });
}ContextMenu for expander
You can set the context menu to header using the SfTreeGrid.ExpanderContextMenu property.
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.ExpanderContextMenu>
<ContextMenu>
<MenuItem x:Name=" Expand " Header="SortAscending" />
<MenuItem x:Name=" Collapse" Header="Collapse" />
</ContextMenu>
</syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.ExpanderContextMenu>this.treeGrid.ExpanderContextMenu = new ContextMenu();
this.treeGrid.ExpanderContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header = " Expand" });
this.treeGrid.ExpanderContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header = "Collapse" });When binding the menu item using CommandBinding, you can get the parameter as TreeGridNodeContextMenuInfo, which contains the expander node.
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.HeaderContextMenu>
<MenuItem Command="{Binding Expand, Source={StaticResource viewModel}}"
CommandParameter="{Binding}"
Header="Expand" />
</syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.HeaderContextMenu>private static void OnExpandClicked(object obj)
{
var contextMenuInfo = obj as TreeGridNodeContextMenuInfo;
if (contextMenuInfo == null)
return;
var grid = contextMenuInfo.TreeGrid;
grid.ExpandNode(contextMenuInfo.TreeNode);
}Events
The TreeGridContextMenuOpening: Occurs when opening the context menu in SfTreeGrid. TreeGridContextMenuEventArgs has the following members, which provides information about the TreeGridContextMenuOpening event:
ContextMenu – Gets the corresponding context menu.
ContextMenuInfo – Returns the context menu info based on the row that opens the context menu.
ContextMenuType – Returns the type of context menu.
RowColumnIndex – RowColumnIndex of the context menu that is currently going to be opened. RowColumnIndex is updated only for the RecordContextMenu and remains empty.
Handled - Indicates whether the TreeGridContextMenuOpening event is handled or not.
Customizing ContextMenus
Changing the menu item when ContextMenu opening
You can use the TreeGridContextMenuOpening event to change the menu item when the context menu opens.
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.RecordContextMenu>
<ContextMenu>
<MenuItem Command="{Binding Cut, Source={StaticResource viewModel}}"
CommandParameter="{Binding}"
Header="Cut">
</MenuItem>
<MenuItem Command="{Binding Copy, Source={StaticResource viewModel}}"
CommandParameter="{Binding}"
Header="Copy">
</MenuItem>
<MenuItem Command="{Binding Paste, Source={StaticResource viewModel}}"
CommandParameter="{Binding}"
Header="Paste">
</MenuItem>
</ContextMenu>
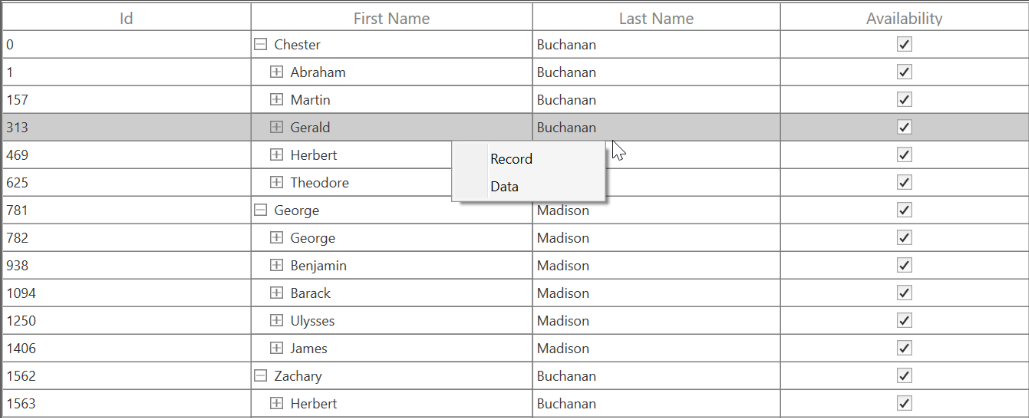
</syncfusion:SfTreeGrid.RecordContextMenu>this.treeGrid.TreeGridContextMenuOpening += treeGrid_ TreeGridContextMenuOpening;
void dataGrid_ TreeGridContextMenuOpening (object sender, TreeGridContextMenuEventArgs e)
{
e.ContextMenu.Items.Clear();
if(e.ContextMenuType == ContextMenuType.RecordCell)
{
e.ContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header="Record"});
e.ContextMenu.Items.Add(new MenuItem() { Header = "Data" });
}
}
Changing background to ContextMenu
You can change the appearance of the context menu by customizing the style with TargetType as ContextMenu.
<Style x:Name="ToolTipStyle" TargetType="ContextMenu">
<Setter Property="BorderThickness" Value="1,1,1,1" />
<Setter Property="BorderBrush" Value="Red" />
<Setter Property="Background" Value="LightGreen" />
</Style>
<ContextMenu>
<MenuItem x:Name="Cut" Header="Expand />
<MenuItem x:Name="Copy" Header="Collapse" />
</ContextMenu>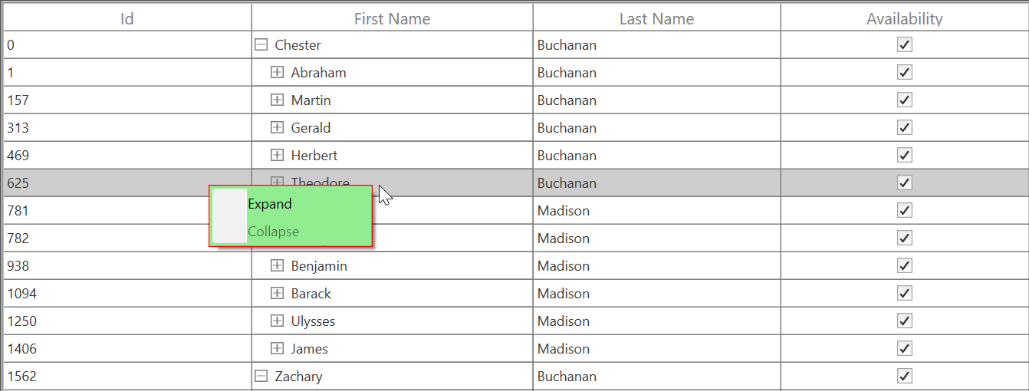
Drag and drop rows
It allows users to drag and drop the rows in SfTreeGrid and between two SfTreeGrid by setting the SfTreeGrid.AllowDraggingRows property to true. It is also possible to drag and drop from any other control.
<syncfusion:SfTreeGrid Name="treeGrid"
AllowDraggingRows="True"
ChildPropertyName="Children"
ItemsSource="{Binding PersonDetails}" />treeGrid.AllowDraggingRows = true;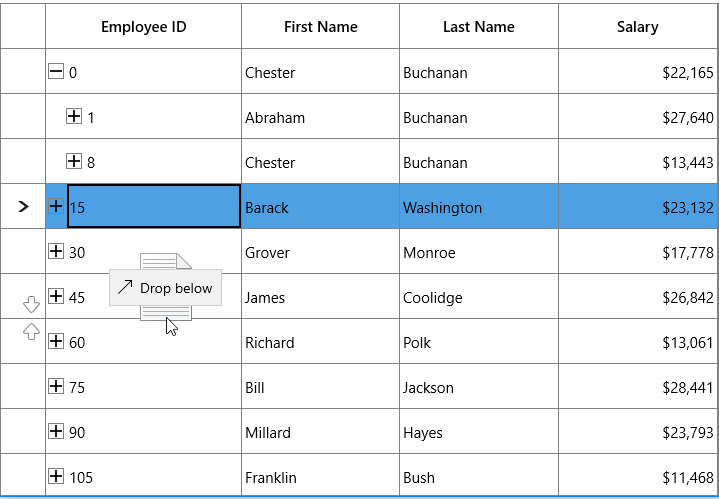
When dropping, the dragged node(s) can be added above or below as a child node based on its drop position. For example, if you drop at the bottom of node, it will be added below the node. If you are drop over the node, then it will be added as a child of that node.
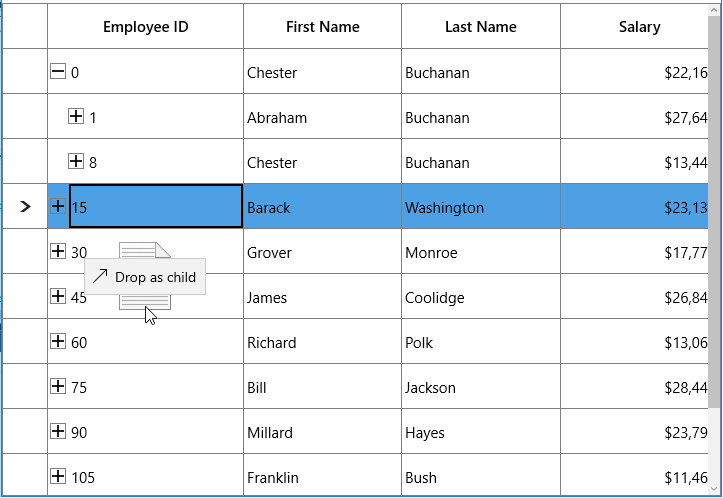
Auto expanding the node on drag over
When drag over the tree node, if drop position is “Drop as child”, then you can auto expand the corresponding tree node by setting the TreeGridRowDragDropController.CanAutoExpand as true. It is also possible to control the delay in expanding the node when drag over using TreeGridRowDragDropController.AutoExpandDelay property. Its default value in 3 sec.
treeGrid.RowDragDropController.CanAutoExpand = true;
treeGrid.RowDragDropController.AutoExpandDelay = new TimeSpan(0, 0, 2);NOTE
When drop position is “Drop as child”, drag indicators will not be shown.
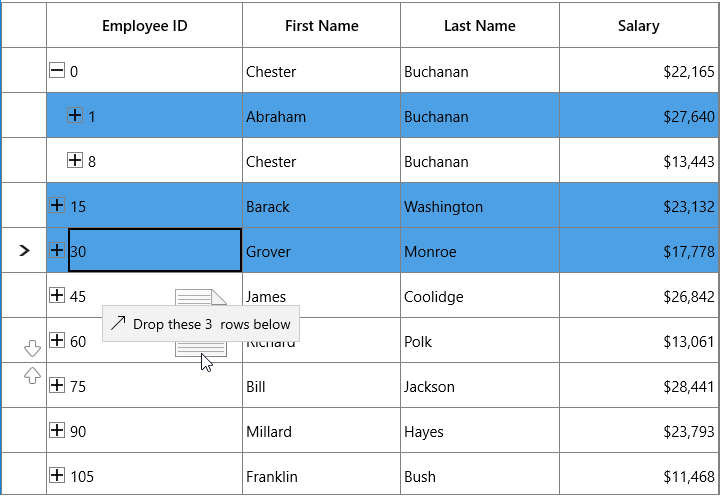
Dragging multiple nodes
SfTreeGrid allows user to drag multiple selected nodes. You can enable multiple selection by setting the SfTreeGrid.SelectionMode property to Multiple or Extended.
Drag and drop between TreeGrids
SfTreeGrid provides built-in support to drag and drop the nodes between SfTreeGrid.
Disabling drag and drop between SfTreeGrid
If SfTreeGrid.AllowDraggingRows is set to true, you can drag and drop nodes between TreeGrids and within TreeGrid. If you want to disable the drag-and-drop functionality from one TreeGrid to another TreeGrid, override the target TreeGrid’s GetDropPosition method in TreeGridRowDragDropController class.
public class TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt : TreeGridRowDragDropController
{
public TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt(SfTreeGrid treeGrid) : base(treeGrid)
{
}
protected override DropPosition GetDropPosition(DragEventArgs args, RowColumnIndex rowColumnIndex)
{
SfTreeGrid sourceTreeGrid = null;
if (args.DataView.Properties.ContainsKey("SourceTreeGrid"))
sourceTreeGrid = args.DataView.Properties["SourceTreeGrid"] as SfTreeGrid;
// Disable drop operation if source tree grid is different.
if (sourceTreeGrid != TreeGrid)
return DropPosition.None;
return base.GetDropPosition(args, rowColumnIndex);
}
}
treeGrid.RowDragDropController = new TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt(treeGrid);If source tree grid and target tree grid are different, drop operation will be disabled.
Customizing row drag and drop
SfTreeGrid processes row drag and drop operations in TreeGridRowDragDropController class. You can customize the row drag and drop operations by overriding TreeGridRowDragDropController and set it toSfTreeGrid.RowDragDropController.
Disable dragging of certain nodes
If you want to restrict the dragging for specific node, you need to override the ProcessOnDragStarting method in TreeGridRowDragDropController class.
Here, drag operation is disabled for root nodes.
public class TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt : TreeGridRowDragDropController
{
public TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt(SfTreeGrid treeGrid) : base(treeGrid)
{
}
protected override void ProcessOnDragStarting(DragStartingEventArgs args, RowColumnIndex rowColumnIndex)
{
base.ProcessOnDragStarting(args, rowColumnIndex);
// Skip dragging of root nodes.
if (args.Data.Properties.ContainsKey("Nodes"))
{
var nodes = args.Data.Properties["Nodes"] as ObservableCollection<TreeNode>;
var node = nodes.FirstOrDefault(n => n.Level == 0);
if (node != null)
args.Cancel = true;
}
}
}Disable drop over specific node
If you want to restrict the drop for specific nodes, you need to override the GetDropPosition method in TreeGridRowDragDropController class.
Here, the drop operation is disabled on leaf nodes.
public class TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt : TreeGridRowDragDropController
{
public TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt(SfTreeGrid treeGrid) : base(treeGrid)
{
}
protected override DropPosition GetDropPosition(DragEventArgs args, RowColumnIndex rowColumnIndex)
{
var nodeIndex = TreeGrid.ResolveToNodeIndex(rowColumnIndex.RowIndex);
var node = TreeGrid.View.GetNodeAt(nodeIndex);
// Disable drop on leaf nodes.
if (!node.HasChildNodes)
return DropPosition.None;
return base.GetDropPosition(args, rowColumnIndex);
}
}
treeGrid.RowDragDropController = new TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt(treeGrid);Customizing drag UI text
You can customize the drag UI text by overriding the ProcessOnDragOver method in TreeGridRowDragDropController class.
Here, the drag UI text is localized based to the German language.
public class TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt : TreeGridRowDragDropController
{
public TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt(SfTreeGrid treeGrid) : base(treeGrid)
{
}
protected override void ProcessOnDragOver(DragEventArgs args, RowColumnIndex rowColumnIndex)
{
base.ProcessOnDragOver(args, rowColumnIndex);
var dropPosition = GetDropPosition(args, rowColumnIndex);
if (dropPosition == DropPosition.DropAbove)
args.DragUIOverride.Caption = "rube fallen";
}
}
treeGrid.RowDragDropController = new TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt(treeGrid);Customizing dragging nodes
When dragging, all the selected nodes will be added to the dragging nodes collection. If you want to customize the dragging nodes collection, override the ProcessOnDragOver method in TreeGridRowDragDropController class.
public class TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt : TreeGridRowDragDropController
{
public TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt(SfTreeGrid treeGrid) : base(treeGrid)
{
}
protected override void ProcessOnDragStarting(DragStartingEventArgs args, RowColumnIndex rowColumnIndex)
{
var nodes = new ObservableCollection<TreeNode>();
var node = this.TreeGrid.GetNodeAtRowIndex(rowColumnIndex.RowIndex);
if (node == null)
return;
nodes.Add(node);
args.Data.Properties.Add("Nodes", nodes);
args.Data.Properties.Add("SourceTreeGrid", TreeGrid);
args.Data.SetText(StandardDataFormats.Text);
args.DragUI.SetContentFromDataPackage();
}
}
treeGrid.RowDragDropController = new TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt(treeGrid);Here, even multiple nodes had been selected, only the dragged node will be added to the dragging nodes collection.
Drag and drop between ListView and TreeGrid
You can drag the item from ListView and drop into TreeGrid by overriding the GetDropPosition, ProcessOnDragOver, and ProcessOnDrop methods in the TreeGridRowDragDropController class.
In ListView, use the DragItemsStarting event and add dragged item.
listView.CanDragItems = true;
listView.DragItemsStarting += ListView_DragItemsStarting;
listView.DragItemsCompleted += ListView_DragItemsCompleted;
private void ListView_DragItemsStarting(object sender, DragItemsStartingEventArgs e)
{
e.Data.Properties.Add("DraggedItem", listView.SelectedItem);
e.Data.SetText(StandardDataFormats.Text);
}
private void ListView_DragItemsCompleted(ListViewBase sender, DragItemsCompletedEventArgs args)
{
foreach (var item in args.Items)
{
(listView.ItemsSource as ObservableCollection<PersonInfo>).Remove(item as PersonInfo);
}
}public class TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt : TreeGridRowDragDropController
{
public TreeGridRowDragDropControllerExt(SfTreeGrid treeGrid) : base(treeGrid)
{
}
protected override void ProcessOnDrop(DragEventArgs args, RowColumnIndex rowColumnIndex)
{
this.TreeGrid.AutoScroller.AutoScrolling = AutoScrollOrientation.None;
var dropPosition = GetDropPosition(args, rowColumnIndex);
if (dropPosition != DropPosition.None && rowColumnIndex.RowIndex != -1)
{
var draggedItem = GetDraggedItem(args);
if (this.TreeGrid.View is TreeGridNestedView)
{
var treeNode = this.TreeGrid.GetNodeAtRowIndex(rowColumnIndex.RowIndex);
if (treeNode == null)
return;
var data = treeNode.Item;
TreeGrid.SelectionController.SuspendUpdates();
var itemIndex = -1;
TreeNode parentNode = null;
if (dropPosition == DropPosition.DropBelow || dropPosition == DropPosition.DropAbove)
parentNode = treeNode.ParentNode;
else if (dropPosition == DropPosition.DropAsChild)
{
if (!treeNode.IsExpanded)
TreeGrid.ExpandNode(treeNode);
parentNode = treeNode;
}
IList sourceCollection = null;
if (dropPosition == DropPosition.DropBelow || dropPosition == DropPosition.DropAbove)
{
if (treeNode.ParentNode != null)
{
var collection = TreeGrid.View.GetPropertyAccessProvider().GetValue(treeNode.ParentNode.Item, TreeGrid.ChildPropertyName) as IEnumerable;
sourceCollection = GetSourceListCollection(collection);
}
else
{
sourceCollection = GetSourceListCollection(TreeGrid.View.SourceCollection);
}
itemIndex = sourceCollection.IndexOf(data);
if (dropPosition == DropPosition.DropBelow)
{
itemIndex += 1;
}
}
else if (dropPosition == DropPosition.DropAsChild)
{
var collection = TreeGrid.View.GetPropertyAccessProvider().GetValue(data, TreeGrid.ChildPropertyName) as IEnumerable;
sourceCollection = GetSourceListCollection(collection);
if (sourceCollection == null)
{
var list = data.GetType().GetProperty(TreeGrid.ChildPropertyName).PropertyType.CreateNew() as IList;
if (list != null)
{
TreeGrid.View.GetPropertyAccessProvider().SetValue(treeNode.Item, TreeGrid.ChildPropertyName, list);
sourceCollection = list;
}
}
itemIndex = sourceCollection.Count;
}
sourceCollection.Insert(itemIndex, draggedItem);
TreeGrid.SelectionController.ResumeUpdates();
(TreeGrid.SelectionController as TreeGridRowSelectionController).RefreshSelection();
}
}
CloseDragIndicators();
}
protected override DropPosition GetDropPosition(DragEventArgs args, RowColumnIndex rowColumnIndex)
{
bool canDrop = true;
var p = args.GetPosition(this.TreeGrid);
var treeNode = this.TreeGrid.GetNodeAtRowIndex(rowColumnIndex.RowIndex);
ScrollAxisRegion columnRegion = ScrollAxisRegion.Body;
var treeGridPanel = TreeGrid.GetTreePanel();
if (treeGridPanel.FrozenColumns > 0)
columnRegion = ScrollAxisRegion.Header;
var rowRect = treeGridPanel.RangeToRect(ScrollAxisRegion.Body, columnRegion, rowColumnIndex, true, false);
var node = treeNode;
if (!canDrop)
return DropPosition.None;
else if (p.Y > rowRect.Y + 15 && p.Y < rowRect.Y + 35)
{
return DropPosition.DropAsChild;
}
else if (p.Y < rowRect.Y + 15)
{
return DropPosition.DropAbove;
}
else if (p.Y > rowRect.Y + 35)
{
return DropPosition.DropBelow;
}
else
return DropPosition.Default;
}
protected override void ProcessOnDragOver(DragEventArgs args, RowColumnIndex rowColumnIndex)
{
autoExpandNode = null;
var node = this.TreeGrid.GetNodeAtRowIndex(rowColumnIndex.RowIndex);
var draggedItem = GetDraggedItem(args);
var dropPosition = GetDropPosition(args, rowColumnIndex);
if (draggedItem == null)
return;
if (dropPosition == DropPosition.None || dropPosition == DropPosition.Default)
{
CloseDragIndicators();
args.AcceptedOperation = DataPackageOperation.None;
args.DragUIOverride.Caption = "Can't drop here";
return;
}
else if (dropPosition == DropPosition.DropAbove)
{
args.DragUIOverride.Caption = "Drop above";
}
else if (dropPosition == DropPosition.DropAsChild)
{
args.DragUIOverride.Caption = "Drop as child";
}
else
{
args.DragUIOverride.Caption = "Drop below";
}
args.AcceptedOperation = DataPackageOperation.Move;
ShowDragIndicators(dropPosition, rowColumnIndex);
args.Handled = true;
}
private object GetDraggedItem(DragEventArgs dragEventArgs)
{
if (dragEventArgs.DataView.Properties.ContainsKey("DraggedItem"))
return dragEventArgs.DataView.Properties["DraggedItem"];
else
return null;
}
internal IList GetSourceListCollection(IEnumerable collection = null)
{
IList list = null;
if (collection == null)
collection = TreeGrid.View.SourceCollection;
if ((collection as IList) != null)
{
list = collection as IList;
}
return list;
}
}After dropping in tree grid, the dragged item is added to TreeGrid based on the dropped position.
Sample for dragging the item from ListView and dropping into TreeGrid: Sample.