Data Binding
29 Jun 201816 minutes to read
Data Binding is the process that establishes a connection between the application and different kinds of data sources such as business objects. You can set the data source for TreeGrid control by using dataSource property.
Local Data Binding
In Local Data Binding, datasource for rendering the TreeGrid control is retrieved from the same application locally.
Two types of Data Binding are possible with the TreeGrid control.
- Hierarchical Datasource Binding
- Self-Referential Data Binding (Flat Data)
Hierarchy Datasource Binding
The childMapping property is used to map the child records in hierarchy data source.
The following code example shows you how to bind the hierarchical local data into the TreeGrid control.
var projectData = [
{
taskID: 1,
taskName:"Planning",
startDate:"02/03/2014",
endDate:"02/07/2014",
progress: 100,
duration:5,
subtasks: [
{
taskID: 2,
taskName:"Plan timeline",
startDate:"02/03/2014",
endDate:"02/07/2014",
duration: 5,
progress: 100
},
{
taskID: 3,
taskName:"Plan budget",
startDate:"02/03/2014",
endDate:"02/07/2014",
duration: 5,
progress: 100
},
//...
]},
//...
];
$(function() {
$("#TreeGridContainer").ejTreeGrid({
dataSource: projectData,
childMapping:"subtasks",
treeColumnIndex:1,
columns: [
{ field:"taskID", headerText:"Task Id", width:"45"},
{ field:"taskName", headerText:"Task Name"},
{ field:"startDate", headerText:"Start Date"},
{ field:"endDate", headerText:"End Date"},
]
})
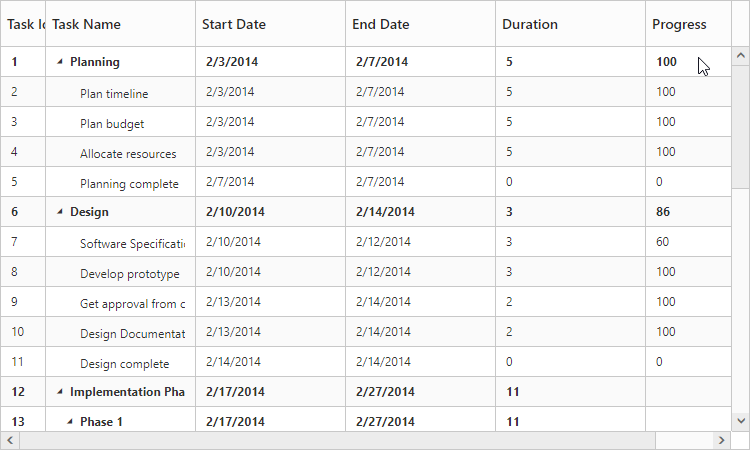
});The output of the above steps is as follows:
It is also possible to set the data source to TreeGrid using ejDataManager. And we can pass the query value to ejDataManager by using query property.
The following code example explains how to assign the ejDataManager instance to TreeGrid.
$("#TreeGridContainer").ejTreeGrid({
//...
dataSource: ej.DataManager(taskDetails),
query: ej.Query().select("taskID", "taskName", "startDate", "duration", "progress", "subtasks"),
//...
});Self-Referential Data Binding (Flat Data)
TreeGrid is rendered from Self-Referential data structures by providing two fields, ID field and parent ID field.
-
ID Field: This field contains unique values used to identify nodes. Its name is assigned to the
idMappingproperty. -
Parent ID Field: This field contains values that indicate parent nodes. Its name is assigned to the
parentIdMappingproperty.
var projectData = [{
"TaskID": 1,
"TaskName": "Parent Task 1",
"StartDate": new Date("02/23/2014"),
"EndDate": new Date("02/27/2014"),
"Progress": "40"
},
{
"TaskID": 2,
"TaskName": "Child Task 1",
"StartDate": new Date("02/23/2014"),
"EndDate": new Date("02/27/2014"),
"Progress": "40",
"parentID": 1
},
//...
];
$(function () {
$("#TreeGridContainer").ejTreeGrid({
dataSource: projectData,
treeColumnIndex:1,
idMapping:"TaskID",
parentIdMapping:"parentID",
columns: [
{ field: "TaskID", headerText: "Task Id", width: "45" },
{ field: "TaskName", headerText: "Task Name" },
{ field: "StartDate", headerText: "Start Date" },
{ field: "EndDate", headerText: "End Date" },
{ field: "Duration", headerText: "Duration" },
{ field: "Progress", headerText: "Progress" }
]
})
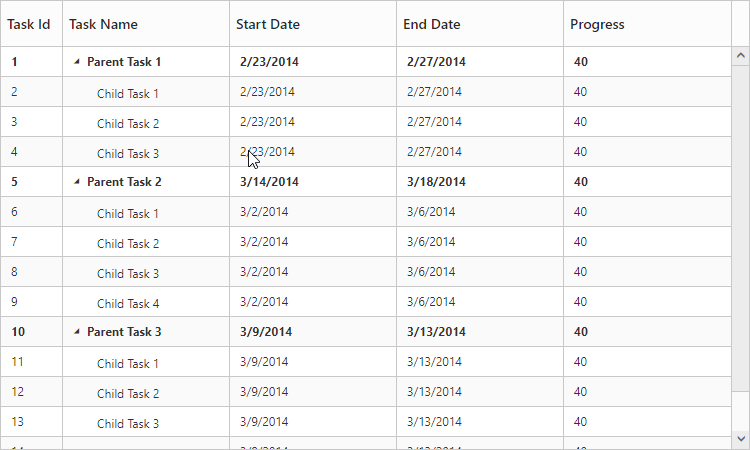
});The following screenshot shows the output of the above steps,
It is possible to the refresh the data source rendered in TreeGrid at run-time using the refresh method. The data source to be displayed and the query to render the data should be passed as the method parameters.
Remote data binding
Load on demand
The TreeGrid provides Load on Demand support for rendering remote data. The Load on demand is considered in TreeGrid for the following actions.
- Expanding root nodes.
- Navigating pages, with paging enabled in TreeGrid.
When load on demand is enabled, all the root nodes are rendered in collapsed state at initial load.
When load on demand support is enabled in TreeGrid with paging, the current or active page’s root node alone will be rendered in collapsed state. On expanding the root node, the child nodes will be loaded from the remote server.
When a root node is expanded, its child nodes are rendered and are cached locally, such that on consecutive expand/collapse actions on root node, the child nodes are loaded from the cache instead from the remote server.
Similarly, if the user navigates to a new page, the root nodes of that specific page, will be rendered with request to the remote server.
NOTE
- Load on demand support in TreeGrid can be enabled only for remote data.
- For better initial load time performance, we need to define the “hasChildMapping” property.
Load on demand support in TreeGrid can be enabled by using the property enableLoadOnDemand.
The following code explains how to use Load on Demand in TreeGrid Control.
$(function() {
var dataManager = ej.DataManager({
url: "http://js.syncfusion.com/demos/ejServices/Wcf/TreeGridGantt/TreeGantt.svc/SelfReferenceDatas",
crossDomain: true,
});
$("#TreeGridContainer").ejTreeGrid({
dataSource: dataManager,
idMapping: "TaskID",
parentIdMapping: "ParentID",
hasChildMapping: "isParent",
enableLoadOnDemand: true,
enableVirtualization: true,
columns: [{field: "TaskID", headerText: "Task Id", width: columnWidth},
{ field: "TaskName", headerText: "Task Name"},
{ field: "StartDate", headerText: "Start Date" },
{ field: "EndDate", headerText: "End Date” },
{ field: "Progress", headerText: "Progress" }],
})
});The output for load on demand support in TreeGrid:
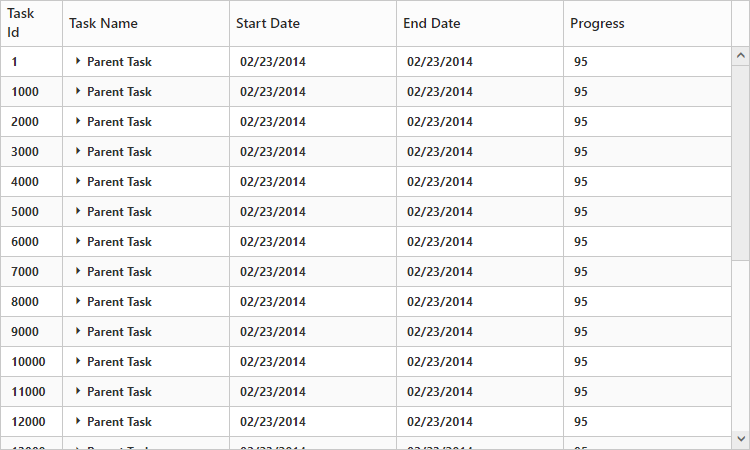
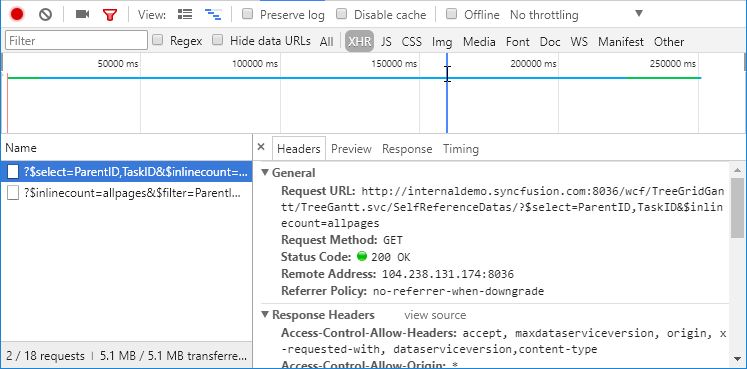
The following output shows how load on demand works for expanding action.
Load at once:
On remote data binding, for every action such as paging, sorting and filtering the data will be fetched from remote server each time. To avoid requesting the data from the remote server for each action, we can set TreeGrid to load all the data on initialization and make all the data operations in client-side. To enable this, we can use offline property of the ej.DataManager. The following code example explains this.
$(function() {
var dataManager = ej.DataManager({
url: "http://js.syncfusion.com/demos/ejServices/Wcf/TreeGridGantt/TreeGantt.svc/SelfReferenceDatas",
offline: true,
});
$("#TreeGridContainer").ejTreeGrid({
dataSource: dataManager,
idMapping: "TaskID",
parentIdMapping: "ParentID",
hasChildMapping: "isParent",
enableVirtualization: true,
columns: [{field: "TaskID", headerText: "Task Id", width: columnWidth},
{ field: "TaskName", headerText: "Task Name"},
{ field: "StartDate", headerText: "Start Date" },
{ field: "EndDate", headerText: "End Date” },
{ field: "Progress", headerText: "Progress" }],
})
});Please refer to this link for further reference on offline property.
Limitations:
- Mapping the expand state of a record using the
expandStateMappingproperty is not supported in load on demand feature. - If a root or parent node is in collapsed state (child nodes not yet loaded), then that parent node will not be expanded while inserting new child to that parent node using toolbar icon or drag and drop actions.
Virtual rendering
Virtualization support is used to render large number of records in TreeGrid with effective performance. In this mode all the records are fetched from data source initially, but only few records will be displayed in the document object model (DOM) which should be visible to the user. While scrolling, the visible records are updated in DOM as per the scrolled position. This mode can be enabled by setting enableVirtualization property as true.
The below code example shows how to use this property.
$("#TreeGrid").ejTreeGrid({
//...
enableVirtualization:true,
//...
});Setting scroll offset to the content
The TreeGrid by default without enabling paging, will render the contents with horizontal and vertical scrollbars. The method scrollOffset allows the user to scroll the content to the specified left and top offset values with custom actions at run-time.
It is also possible to get the scroll offsets of the content by the using the getScrollTopOffset and getScrollLeftOffset methods. At any instances, the user can scroll the TreeGrid content to the top most position and to the bottom position by using the scrollToTop and scrollToBottom methods.