Getting started with JavaScript PivotGauge
3 May 202124 minutes to read
Creating a simple application with pivot gauge and relational data source (client mode)
This section covers the basic information required to populate a simple pivot gauge with Relational data completely on the client-side.
Scripts and CSS references
Create an HTML page and add scripts and style sheets that are required to render a pivot gauge widget which are highlighted below in an appropriate order:
- ej.web.all.min.css
- jQuery-3.0.0.min.js
- ej.web.all.min.js
Initialize pivot gauge
Place a “div” tag in the HTML page which acts as a container for the pivot gauge widget. Then, initialize the widget by using the “ejPivotGauge” method.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>PivotGauge - Getting Started</title>
<link href="http://cdn.syncfusion.com/32.1.19/js/web/flat-azure/ej.web.all.min.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<script src="http://cdn.syncfusion.com/js/assets/external/jquery-3.0.0.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="http://cdn.syncfusion.com/32.1.19/js/web/ej.web.all.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!--Create a tag which acts as a container for ejPivotGauge widget.-->
<div id="PivotGauge1"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function () {
//Initialize ejPivotGauge widget.
$("#PivotGauge1").ejPivotGauge();
});
</script>
</body>
</html>Populate pivot gauge With data
This section illustrates the steps to populate the pivot gauge control using a sample JSON data as shown below:
var pivotData = [
{ Amount: 100, Country: "Canada", Product: "Bike" },
{ Amount: 200, Country: "Germany", Product: "Van" },
{ Amount: 300, Country: "Germany", Product: "Car" },
{ Amount: 150, Country: "United Kingdom", Product: "Bike" },
{ Amount: 200, Country: "Canada", Product: "Car" }
];Now, set the JSON data to the “data” property available in the “dataSource” object. The “dataSource” object allows you to set the raw data input and fields in the rows, columns, values, and filters.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
//....
<body>
<div id="PivotGauge1"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
//Datasource
var pivotData = [
{ Amount: 100, Country: "Canada", Product: "Bike" },
{ Amount: 200, Country: "Germany", Product: "Van" },
{ Amount: 300, Country: "Germany", Product: "Car" },
{ Amount: 150, Country: "United Kingdom", Product: "Bike" },
{ Amount: 200, Country: "Canada", Product: "Car" }
]
$(function () {
$("#PivotGauge1").ejPivotGauge({
dataSource: {
data: pivotData,
rows: [
{
fieldName: "Country",
fieldCaption: "Country"
}
],
columns: [
{
fieldName: "Product",
fieldCaption: "Product"
}
],
values: [
{
fieldName: "Amount",
fieldCaption: "Amount"
}
]
},
scales: [
{
showRanges: true,
radius: 150, showScaleBar: true, size: 1,
border: {
width: 0.5
},
showIndicators: true, showLabels: true,
pointers: [
{
showBackNeedle: true,
backNeedleLength: 20,
length: 120,
width: 7
},
{
type: "marker",
markerType: "diamond",
distanceFromScale: 5,
placement: "center",
backgroundColor: "#29A4D9",
length: 25,
width: 15
}
],
ticks: [
{
type: "major",
distanceFromScale: 2,
height: 16,
width: 1,
color: "#8c8c8c"
},
{
type: "minor",
height: 6,
width: 1,
distanceFromScale: 2,
color: "#8c8c8c"
}
],
labels: [
{
color: "#8c8c8c"
}
],
ranges: [
{
distanceFromScale: -5,
backgroundColor: "#fc0606",
border: { color: "#fc0606" }
},
{
distanceFromScale: -5
}
],
customLabels: [
{
position: { x: 180, y: 290 },
font: { size: "10px", fontFamily: "Segoe UI", fontStyle: "Normal" }, color: "#666666"
},
{
position: { x: 180, y: 320 },
font: { size: "10px", fontFamily: "Segoe UI", fontStyle: "Normal" }, color: "#666666"
},
{
position: { x: 180, y: 150 },
font: { size: "12px", fontFamily: "Segoe UI", fontStyle: "Normal" }, color: "#666666"
}
]
}
]
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>The above code will generate a simple pivot gauge as shown in the below image:
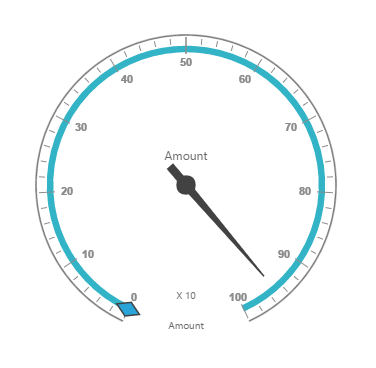
The following table will explain the relational datasource properties at client-side in detail:
| Properties | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Lists out the items to bind in columns section.
|
|||||||||||||
Lists out the items to bind in rows section.
|
|||||||||||||
Lists out the items supports calculation in pivot gauge.
|
|||||||||||||
Lists out the items which supports filtering of values without displaying the members in UI in PivotGauge.
|
Creating a simple application with pivot gauge and relational data source (server mode)
This section covers the information required to create a simple pivot gauge that is bound to the Relational data source from the server-side.
NOTE
This section is illustrated by creating a simple web application through the Visual Studio IDE, since the pivot gauge in server mode requires .NET dependency. The web application contains an HTML page and a service which will transfer the data to
server-side, process it, and return it to theclient-sidefor control rendering. The service utilized for communication can be a WebAPI controller class or a WCF service based on user requirement. Here, both are illustrated for user convenience.
Project initialization
Create a new ASP.NET Empty Web Application by using the Visual Studio IDE and name the project “PivotGaugeDemo”.
Next, you can add an HTML page. To add an HTML page in your web application, right-click the project in the solution explorer and select Add > New Item. In the Add New Item window, select HTML Page and name it “GettingStarted.html,” and then click Add.
Now, you can set the “GettingStarted.html” page as start-up page. To do so, right-click the “GettingStarted.html” page and select “Set As Start Page”.
Scripts and CSS initialization
The scripts and style sheets that are required to render a pivot gauge widget in the HTML page are highlighted below in an appropriate order:
- ej.web.all.min.css
- jQuery-3.0.0.min.js
- ej.web.all.min.js
The scripts and style sheets listed above can be found in any of the following locations:
Local disk: Click here to know more about script and style sheets installed on the local machine.
CDN link: Click here to know more about script and style sheets available in online.
NuGet package: Click here to know more about script and style sheets available in the NuGet package.
Control initialization
To initialize a pivot gauge widget, first you can define a “div” tag with an appropriate “id” attribute which acts as a container for the pivot gauge widget. Then, you can initialize the widget by using the ejPivotGauge method.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>PivotGauge - Getting Started</title>
<link href="http://cdn.syncfusion.com/32.1.19/js/web/flat-azure/ej.web.all.min.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<script src="http://cdn.syncfusion.com/js/assets/external/jquery-3.0.0.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="http://cdn.syncfusion.com/32.1.19/js/web/ej.web.all.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!--Create a tag which acts as a container for ejPivotGauge widget.-->
<div id="PivotGauge1"> </div>
<script type="text/javascript">
//Set properties and initialize ejPivotGauge widget.
$(function() {
$("#PivotGauge1").ejPivotGauge({
url: "/Relational",
scales: [
{
showRanges: true,
radius: 150, showScaleBar: true, size: 1,
border: {
width: 0.5
},
showIndicators: true, showLabels: true,
pointers: [
{
showBackNeedle: true,
backNeedleLength: 20,
length: 120,
width: 7
},
{
type: "marker",
markerType: "diamond",
distanceFromScale: 5,
placement: "center",
backgroundColor: "#29A4D9",
length: 25,
width: 15
}
],
ticks: [
{
type: "major",
distanceFromScale: 2,
height: 16,
width: 1,
color: "#8c8c8c"
},
{
type: "minor",
height: 6,
width: 1,
distanceFromScale: 2,
color: "#8c8c8c"
}
],
labels: [
{
color: "#8c8c8c"
}
],
ranges: [
{
distanceFromScale: -5,
backgroundColor: "#fc0606",
border: { color: "#fc0606" }
},
{
distanceFromScale: -5
}
],
customLabels: [
{
position: { x: 180, y: 290 },
font: { size: "10px", fontFamily: "Segoe UI", fontStyle: "Normal" },
color: "#666666"
},
{
position: { x: 180, y: 320 },
font: { size: "10px", fontFamily: "Segoe UI", fontStyle: "Normal" }, color: "#666666"
},
{
position: { x: 180, y: 150 },
font: { size: "12px", fontFamily: "Segoe UI", fontStyle: "Normal" }, color: "#666666"
}
]
}
]
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>The url property in the pivot gauge widget points the service endpoint, where the data is processed and fetched in the form of JSON. The services used for the pivot gauge widget as endpoint are WebAPI and WCF.
NOTE
The above “GettingStarted.html” contains WebAPI URL, which is “/Relational”. If you are using the WCF service, then the URL will look like “/RelationalService.svc”.
WebAPI
Adding a WebAPI controller
To add a WebAPI controller in your existing web application, right-click the project in the solution explorer and select Add > New Item. In the Add New Item window, select WebAPI Controller Class and name it “RelationalController.cs,” and then click Add.
The WebAPI controller is added to your application, which, in-turn, comprises the following file. The utilization of this file will be explained in the immediate sections.
- RelationalController.cs
NOTE
While adding the WebAPI controller class, add the mandatory suffix “Controller”. For example, in the demo, the controller is named “RelationalController”.
Next, remove all existing methods such as “Get”, “Post”, “Put”, and “Delete” present in the RelationalController.cs file.
namespace PivotGaugeDemo
{
public class RelationalController: ApiController
{
}
}List of dependency libraries
Next, you should add the below-mentioned dependency libraries to your web application. These libraries can be found in the GAC (Global Assembly Cache).
To add them to your web application, right-click References in the solution explorer and select Add Reference. In the Reference Manager dialog, under Assemblies > Extension, the following Syncfusion libraries are found.
NOTE
If you have installed any version of Essential Studio, then the location of Syncfusion libraries is [system drive:\Program Files (x86)\Syncfusion\Essential Studio\32.1.19\Assemblies].
- Syncfusion.Compression.Base
- Syncfusion.Linq.Base
- Syncfusion.Olap.Base
- Syncfusion.PivotAnalysis.Base
- Syncfusion.EJ
- Syncfusion.EJ.Export
- Syncfusion.EJ.Pivot
List of namespaces
Following is the list of namespaces to be added on top of the main class in the RelationalController.cs file.
using Syncfusion.JavaScript;
using Syncfusion.PivotAnalysis.Base;
namespace PivotGaugeDemo
{
public class RelationalController : ApiController
{
}
}Data source initialization
A simple collection is provided as a data source for the pivot gauge in this demo section. This data source is placed inside a separate class “ProductSales” in the RelationalController.cs file. Refer to the following code example:
namespace PivotGaugeDemo
{
//....
//....
internal class ProductSales
{
public string Product { get; set; }
public string Date { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; }
public string State { get; set; }
public int Quantity { get; set; }
public double Amount { get; set; }
public static ProductSalesCollection GetSalesData()
{
/// Geography
string[] countries = new string[] { "Australia", "Canada", "France", "Germany", "United Kingdom", "United States" };
string[] ausStates = new string[] { "New South Wales", "Queensland", "South Australia", "Tasmania", "Victoria" };
string[] canadaStates = new string[] { "Alberta", "British Columbia", "Brunswick", "Manitoba", "Ontario", "Quebec" };
string[] franceStates = new string[] { "Charente-Maritime", "Essonne", "Garonne (Haute)", "Gers", };
string[] germanyStates = new string[] { "Bayern", "Brandenburg", "Hamburg", "Hessen", "Nordrhein-Westfalen", "Saarland" };
string[] ukStates = new string[] { "England" };
string[] ussStates = new string[] { "New York", "North Carolina", "Alabama", "California", "Colorado", "New Mexico", "South Carolina" };
/// Time
string[] dates = new string[] { "FY 2005", "FY 2006", "FY 2007", "FY 2008", "FY 2009" };
/// Products
string[] products = new string[] { "Bike", "Van", "Car" };
Random r = new Random(123345345);
int numberOfRecords = 2000;
ProductSalesCollection listOfProductSales = new ProductSalesCollection();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfRecords; i++)
{
ProductSales sales = new ProductSales();
sales.Country = countries[r.Next(1, countries.GetLength(0))];
sales.Quantity = r.Next(1, 12);
/// 1 percent discount for 1 quantity
double discount = (30000 * sales.Quantity) * (double.Parse(sales.Quantity.ToString()) / 100);
sales.Amount = (30000 * sales.Quantity) - discount;
sales.Date = dates[r.Next(r.Next(dates.GetLength(0) + 1))];
sales.Product = products[r.Next(r.Next(products.GetLength(0) + 1))];
switch (sales.Product)
{
case "Car":
{
sales.Date = "FY 2005";
break;
}
}
switch (sales.Country)
{
case "Australia":
{
sales.State = ausStates[r.Next(ausStates.GetLength(0))];
break;
}
case "Canada":
{
sales.State = canadaStates[r.Next(canadaStates.GetLength(0))];
break;
}
case "France":
{
sales.State = franceStates[r.Next(franceStates.GetLength(0))];
break;
}
case "Germany":
{
sales.State = germanyStates[r.Next(germanyStates.GetLength(0))];
break;
}
case "United Kingdom":
{
sales.State = ukStates[r.Next(ukStates.GetLength(0))];
break;
}
case "United States":
{
sales.State = ussStates[r.Next(ussStates.GetLength(0))];
break;
}
}
listOfProductSales.Add(sales);
}
return listOfProductSales;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("{0}-{1}-{2}", this.Country, this.State, this.Product);
}
public class ProductSalesCollection : List<ProductSales>
{
}
}
}Service methods in WebAPI controller
Now, you can define the service methods in the RelationalController class. To do so, find the RelationalController.cs file which was created while adding the WebAPI controller class to your web application.
namespace PivotGaugeDemo
{
public class RelationalController : ApiController
{
PivotGauge pivotGauge = new PivotGauge();
[HttpPost]
[ActionName("InitializeGauge")]
public Dictionary<string, object> InitializeGauge(Dictionary<string, object> jsonResult)
{
pivotGauge.PivotReport = BindDefaultData();
return pivotGauge.GetJsonData(jsonResult["action"].ToString(), ProductSales.GetSalesData());
}
private PivotReport BindDefaultData()
{
PivotReport pivotSetting = new PivotReport();
pivotSetting.PivotRows.Add(new PivotItem { FieldMappingName = "Date", FieldHeader = "Date", TotalHeader = "Total" });
pivotSetting.PivotColumns.Add(new PivotItem { FieldMappingName = "Product", FieldHeader = "Product", TotalHeader = "Total" });
pivotSetting.PivotCalculations.Add(new PivotComputationInfo { CalculationName = "Amount", Description = "Amount", FieldHeader = "Amount", FieldName = "Amount", Format = "C", SummaryType = Syncfusion.PivotAnalysis.Base.SummaryType.DoubleTotalSum });
return pivotSetting;
}
}
.....
..... // Datasource initialization
.....
}Configure routing in global application class
To add a Global.asax in your existing web application, right-click the project in the solution explorer and select Add > New item. In the Add New Item window, select Global Application class and name it “Global.asax,” and then click Add.
After adding the Global.asax file, delete all methods in the Global class and add the namespace “using System.Web.Http;”, and then configure the routing as shown in the following code example:
public class Global : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
protected void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
GlobalConfiguration.Configuration.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional });
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.SetData("SQLServerCompactEditionUnderWebHosting", true);
}
}Now, the pivot gauge is rendered with sales amount as shown in the below image:
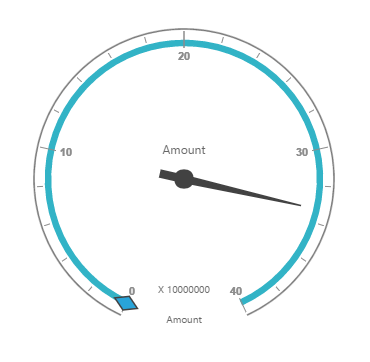
WCF
This section demonstrates the utilization of the WCF service as endpoint binding Relational data source to a simple pivot gauge. For more details on this topic, click here.