How can I help you?
Summary
Summary is a key feature in DataManager that helps to aggregate any data. DataManager provides several summary type by default, they are as follows.
-
Sum
-
Average
-
Minimum
-
Maximum
-
Distinct
The ej provided several data utilization methods to achieve summary.
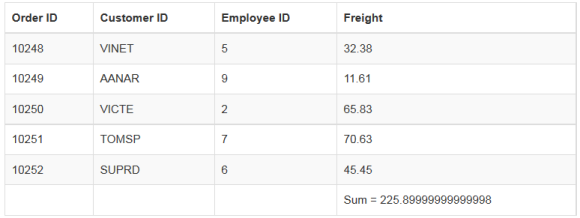
Sum
The Sum summary type provides the sum of the data. The Sum data utilization method accepts two parameters, they are JSON data and the field name where the sum is calculated. The following code example illustrates the Default Summary Types.
<div class="datatable" style="padding:10px">
<table id="table1" class="table table-striped table-bordered" style="width:700px">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Order ID</th>
<th>Customer ID</th>
<th>Employee ID</th>
<th>Freight</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody></tbody>
</table>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function () {
window.data = [{ OrderID: 10248, CustomerID: "VINET", EmployeeID: 5, Freight: 32.38 },
{ OrderID: 10249, CustomerID: "AANAR", EmployeeID: 9, Freight: 11.61 },
{ OrderID: 10250, CustomerID: "VICTE", EmployeeID: 2, Freight: 65.83 },
{ OrderID: 10251, CustomerID: "TOMSP", EmployeeID: 7, Freight: 70.63 },
{ OrderID: 10252, CustomerID: "SUPRD", EmployeeID: 6, Freight: 45.45 }];
var dataManager = ej.DataManager(data);
var query = new ej.Query();
var promise = dataManager.executeLocal(query);
var sum = ej.sum(data, "Freight"); //Calculates the sum Freight
$("#table1 tbody").html($("#tableTemplate").render(promise));
$("#table1 tbody").append("<tr><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>Sum = " + sum + "</td></tr>");
});
</script>
<script id="tableTemplate" type="text/x-jsrender">
<tr>
<td>{{>OrderID}}</td>
<td>{{>CustomerID}}</td>
<td>{{>EmployeeID}}</td>
<td>{{>Freight}}</td>
</tr>
</script>The result of the above code example is illustrated as follows.
Min
The Minimum of a particular field can be calculated using the ej.min data utilization method and this method accepts the arguments such as JSON data/array, field name and the comparer used for the comparison. When the data to the min method is a JSON array then the whole record is returned.
The minimum of particular field can be calculated as follows.
<div class="datatable" style="padding:10px">
<table id="table1" class="table table-striped table-bordered" style="width:700px">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Order ID</th>
<th>Customer ID</th>
<th>Employee ID</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody></tbody>
</table>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function () {
window.data = [{ OrderID: 10248, CustomerID: "VINET", EmployeeID: 5 },
{ OrderID: 10249, CustomerID: "AANAR", EmployeeID: 9 },
{ OrderID: 10250, CustomerID: "VICTE", EmployeeID: 2 },
{ OrderID: 10251, CustomerID: "TOMSP", EmployeeID: 7 },
{ OrderID: 10252, CustomerID: "SUPRD", EmployeeID: 6 }];
var dataManager = ej.DataManager(data);
var query = new ej.Query();
var promise = dataManager.executeLocal(query);
var min = ej.min(data, "EmployeeID"); //Calculates the minimum EmployeeID
$("#table1 tbody").html($("#tableTemplate").render(promise));
$("#table1 tbody").append("<tr><td></td><td></td><td>Minimum = " + min["EmployeeID"] + "</td></tr>");
});
</script>
<script id="tableTemplate" type="text/x-jsrender">
<tr>
<td>{{>OrderID}}</td>
<td>{{>CustomerID}}</td>
<td>{{>EmployeeID}}</td>
</tr>
</script>The result of the above code example is illustrated as follows.

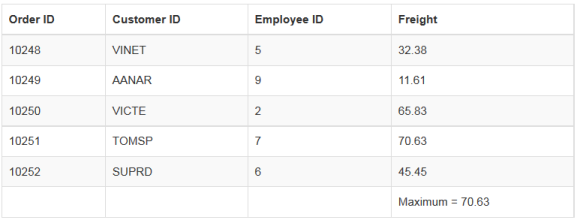
Max
The Maximum of a particular field can be calculated using the ej.max data utilization method and this method accepts the arguments such as JSON data/array, field name and the comparer used for the comparison. When the data to the max method is a JSON array then the whole record is returned.
The maximum of particular field can be calculated as follows.
<div class="datatable" style="padding:10px">
<table id="table1" class="table table-striped table-bordered" style="width:700px">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Order ID</th>
<th>Customer ID</th>
<th>Employee ID</th>
<th>Freight</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody></tbody>
</table>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function () {
window.data = [{ OrderID: 10248, CustomerID: "VINET", EmployeeID: 5, Freight: 32.38 },
{ OrderID: 10249, CustomerID: "AANAR", EmployeeID: 9, Freight: 11.61 },
{ OrderID: 10250, CustomerID: "VICTE", EmployeeID: 2, Freight: 65.83 },
{ OrderID: 10251, CustomerID: "TOMSP", EmployeeID: 7, Freight: 70.63 },
{ OrderID: 10252, CustomerID: "SUPRD", EmployeeID: 6, Freight: 45.45 }];
var dataManager = ej.DataManager(data);
var query = new ej.Query();
var promise = dataManager.executeLocal(query);
var max = ej.max(data, "Freight"); //Calculates the Maximum Freight value
$("#table1 tbody").html($("#tableTemplate").render(promise));
$("#table1 tbody").append("<tr><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>Maximum = " + max["Freight"] + "</td></tr>");
});
</script>
<script id="tableTemplate" type="text/x-jsrender">
<tr>
<td>{{>OrderID}}</td>
<td>{{>CustomerID}}</td>
<td>{{>EmployeeID}}</td>
<td>{{>Freight}}</td>
</tr>
</script>The result for the above code example is illustrated as follows.
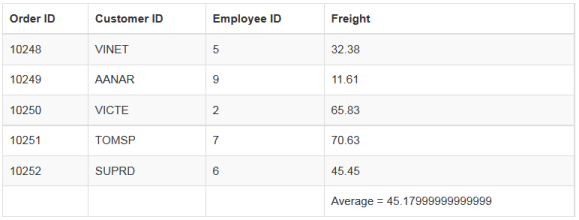
Avg
The Average summary type provides the average of the given data. The Average data utilization method accepts two parameters, they are JSON/Array data and the field name where the sum is calculated. Use the following code example for calculating the average of given JSON data.
<div class="datatable" style="padding:10px">
<table id="table1" class="table table-striped table-bordered" style="width:700px">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Order ID</th>
<th>Customer ID</th>
<th>Employee ID</th>
<th>Freight</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody></tbody>
</table>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function () {
window.data = [{ OrderID: 10248, CustomerID: "VINET", EmployeeID: 5, Freight: 32.38 },
{ OrderID: 10249, CustomerID: "AANAR", EmployeeID: 9, Freight: 11.61 },
{ OrderID: 10250, CustomerID: "VICTE", EmployeeID: 2, Freight: 65.83 },
{ OrderID: 10251, CustomerID: "TOMSP", EmployeeID: 7, Freight: 70.63 },
{ OrderID: 10252, CustomerID: "SUPRD", EmployeeID: 6, Freight: 45.45 }];
var dataManager = ej.DataManager(data);
var query = new ej.Query();
var promise = dataManager.executeLocal(query);
var avg = ej.avg(data, "Freight"); //Calculates the Average of Freight values
$("#table1 tbody").html($("#tableTemplate").render(promise));
$("#table1 tbody").append("<tr><td></td><td></td><td></td><td>Average = " + avg + "</td></tr>");
});
</script>
<script id="tableTemplate" type="text/x-jsrender">
<tr>
<td>{{>OrderID}}</td>
<td>{{>CustomerID}}</td>
<td>{{>EmployeeID}}</td>
<td>{{>Freight}}</td>
</tr>
</script>The result of the above code example is illustrated as follows.
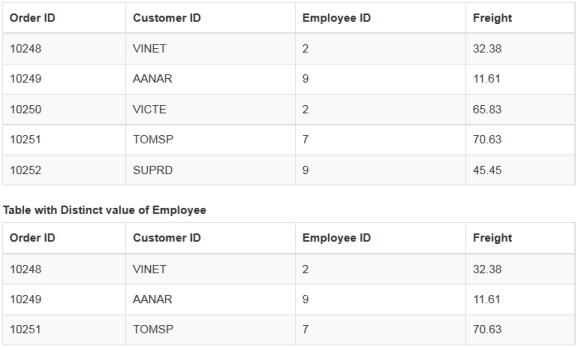
Distinct
In a data, a field may contain many duplicate values; and sometimes you only require to list the different (distinct) values. This can be achieved by using the ej.distinct method. This method accepts three parameters such as JSON/Array data, fieldname that you want to fetch as distinct and the third boolean parameter when set as true, returns the whole record when the data is a JSON array.
The following code example illustrates how to use the ej.distinct method. In the following code, the third param of distinct method is set as true and hence it fetches the whole record from the provided data.
<div class="datatable" style="padding:10px">
<table id="table1" class="table table-striped table-bordered" style="width:700px">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Order ID</th>
<th>Customer ID</th>
<th>Employee ID</th>
<th>Freight</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody></tbody>
</table>
<label>Table with Distinct value of Employee</label>
<table id="distinct" class="table table-striped table-bordered" style="width:700px">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Order ID</th>
<th>Customer ID</th>
<th>Employee ID</th>
<th>Freight</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody></tbody>
</table>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function () {
window.data = [{ OrderID: 10248, CustomerID: "VINET", EmployeeID: 2, Freight: 32.38 },
{ OrderID: 10249, CustomerID: "AANAR", EmployeeID: 9, Freight: 11.61 },
{ OrderID: 10250, CustomerID: "VICTE", EmployeeID: 2, Freight: 65.83 },
{ OrderID: 10251, CustomerID: "TOMSP", EmployeeID: 7, Freight: 70.63 },
{ OrderID: 10252, CustomerID: "SUPRD", EmployeeID: 9, Freight: 45.45 },];
var dataManager = ej.DataManager(data);
var query = new ej.Query();
var promise = dataManager.executeLocal(query);
var distinct = ej.distinct(data, "EmployeeID", true);
$("#table1 tbody").html($("#tableTemplate").render(promise));
$("#distinct tbody").html($("#tableTemplate").render(distinct));
});
</script>
<script id="tableTemplate" type="text/x-jsrender">
<tr>
<td>{{>OrderID}}</td>
<td>{{>CustomerID}}</td>
<td>{{>EmployeeID}}</td>
<td>{{>Freight}}</td>
</tr>
</script>The result for the above code example is illustrated as follows.