How can I help you?
Working with Macros in Syncfusion® Excel library
3 Nov 202524 minutes to read
Macro is a set of process that can be run repeatedly in Excel document.
Creating a Macro
XlsIO allows to create macros in Excel document through IVbaProject interface. The macro document can be saved into different formats such as XLS, XLTM and XLSM.
XlsIO supports creating macro in following types using VbaModuleType enum.
- Document
- StdModule
- Class
- MsForm
You can add a Vba module through IVbaModules interface in XlsIO.
Document
Document is the default module type which will be added for every worksheet and one for entire workbook while creating VbaProject.
//Adding Document to the workbook
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
IVbaModule module = project.Modules.Add("Document ", VbaModuleType. Document);//Adding Document to the workbook
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
IVbaModule module = project.Modules.Add("Document", VbaModuleType.Document);//Adding Document to the workbook
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
Dim [module] As IVbaModule = project.Modules.Add("Document ", VbaModuleType. Document)The following code illustrate how to use Document module in Excel document.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
// Accessing sheet module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules[sheet.CodeName];
//Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open\n MsgBox \" Workbook Opened \" \n End Sub";
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/MacroAsDocument.xlsm"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
//Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Creating new workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Accessing sheet module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules[sheet.CodeName];
//Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open\n MsgBox \"Workbook Opened\" \n End Sub";
//Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Creating new Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating Vba project
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
'Accessing vba modules collection
Dim vbaModules As IVbaModules = project.Modules
‘Accessing sheet module
Dim vbaModule As IVbaModule = vbaModules(sheet.CodeName)
'Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open" & vbLf & " MsgBox "" Workbook Opened "" " & vbLf & " End Sub"
'Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm")
End UsingA complete working example to create macro as document in C# is present on this GitHub page.
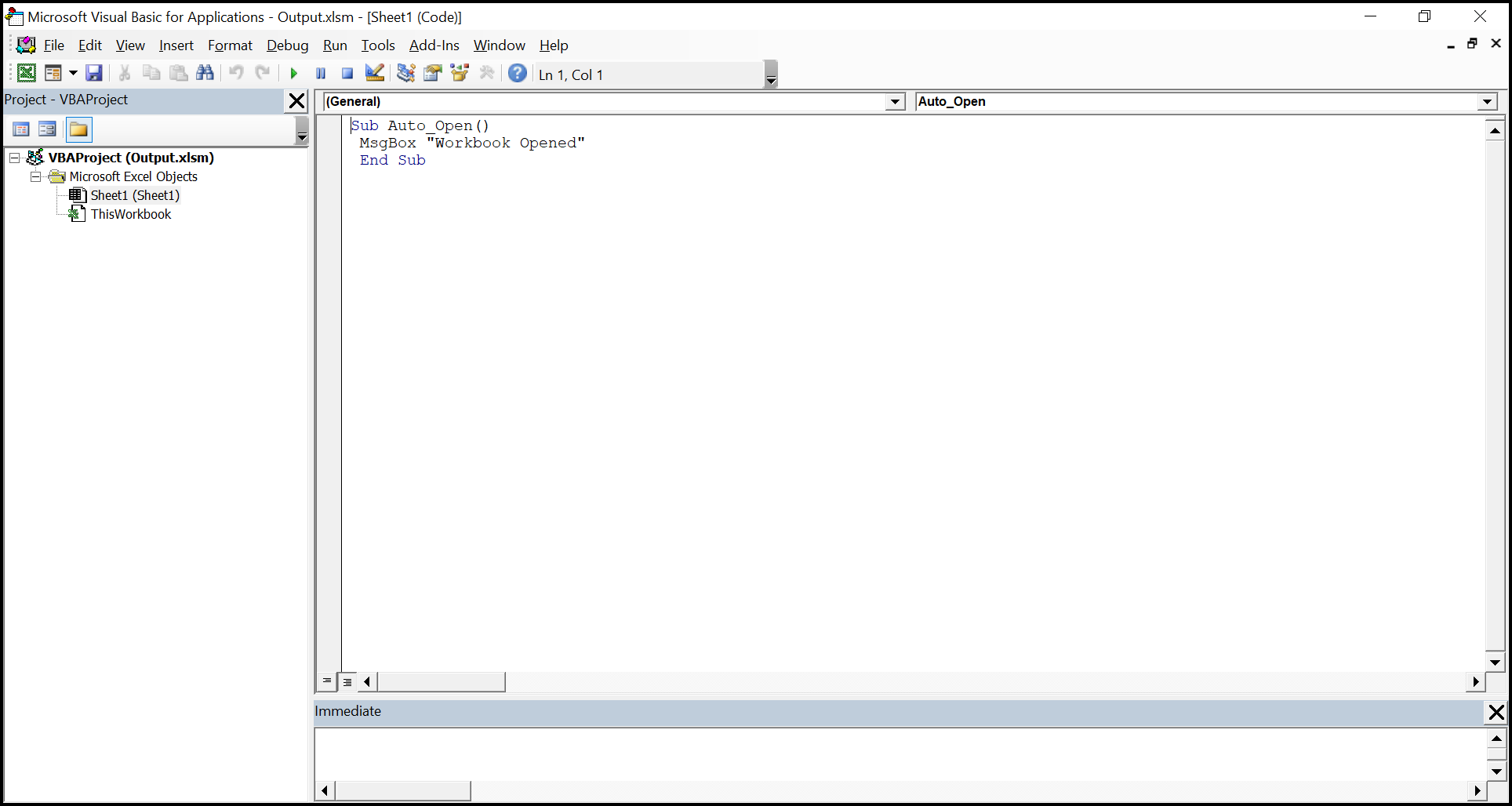
The Vba project in the output looks like below.
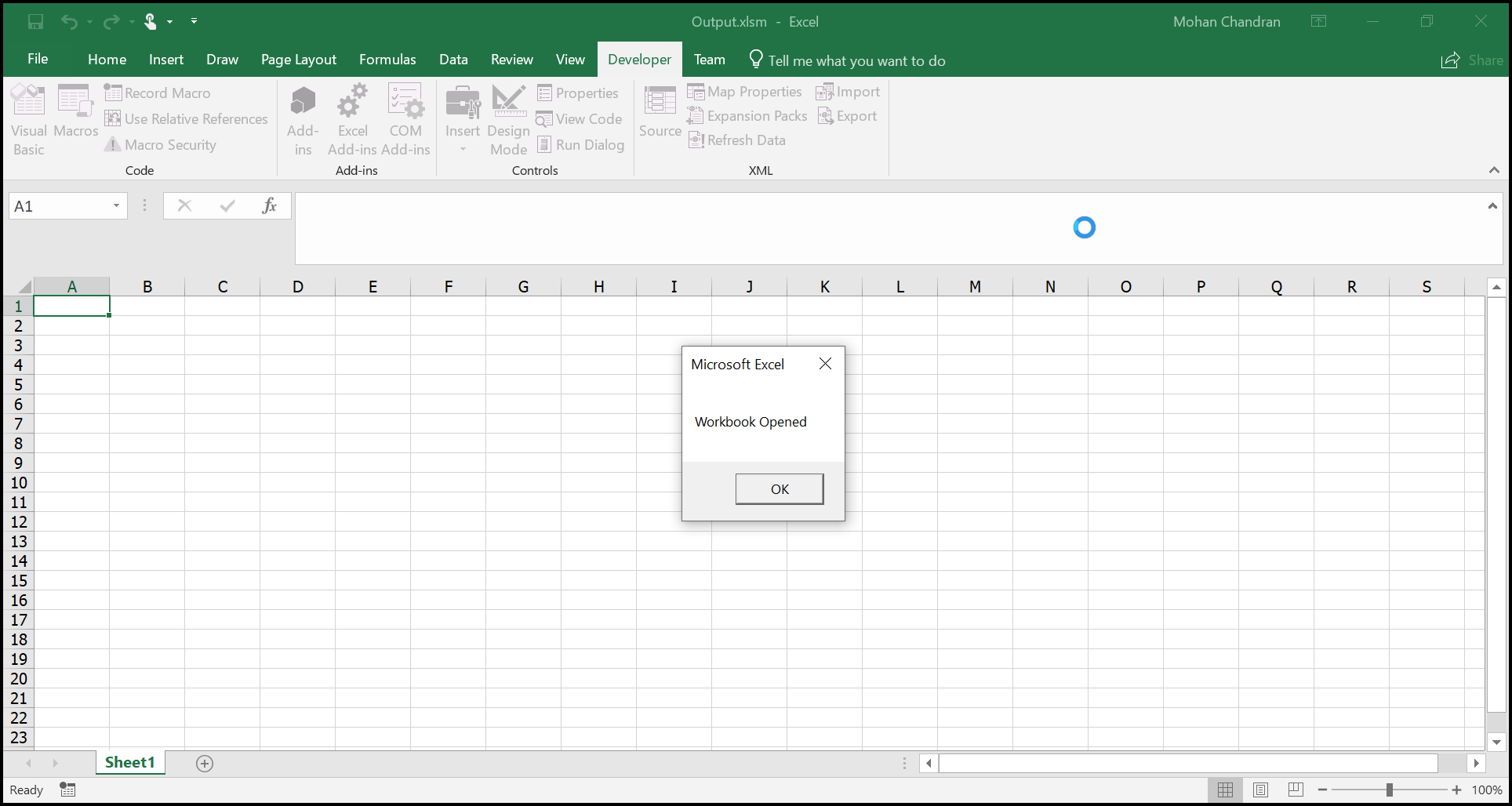
The macro output in the Excel document looks like below.
StdModule
StdModule is the module created for whenever a macro process is recorded in Excel document.
The following code illustrate how to add a StdModule using Add method. Here, the parameters name and VbaModuleType enum value is used.
- Test – Macro module name added to the Vba project.
- StdModule – Type of the Vba module.
//Adding StdModule to the workbook
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
IVbaModule module = project.Modules.Add("Test", VbaModuleType.StdModule);//Adding StdModule to the workbook
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
IVbaModule module = project.Modules.Add("Test", VbaModuleType.StdModule);//Adding StdModule to the workbook
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
Dim [module] As IVbaModule = project.Modules.Add("Test", VbaModuleType.StdModule)The following code illustrate how to create a macro using StdModule in Excel document.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Adding a vba module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules.Add("StdModule", VbaModuleType.StdModule);
//Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open\n MsgBox \"Macro Added\" \n End Sub";
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/MacroAsStdModule.xlsm"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
//Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Creating new workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Adding a vba module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules.Add("StdModule", VbaModuleType.StdModule);
//Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open\n MsgBox \"Macro Added\" \n End Sub";
//Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Creating new Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating Vba project
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
'Accessing vba modules collection
Dim vbaModules As IVbaModules = project.Modules
'Adding a vba module
Dim vbaModule As IVbaModule = vbaModules.Add("StdModule", VbaModuleType.StdModule)
'Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open" & vbLf & " MsgBox ""Macro Added"" " & vbLf & " End Sub"
'Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm")
End UsingA complete working example to create macro as standard module in C# is present on this GitHub page.
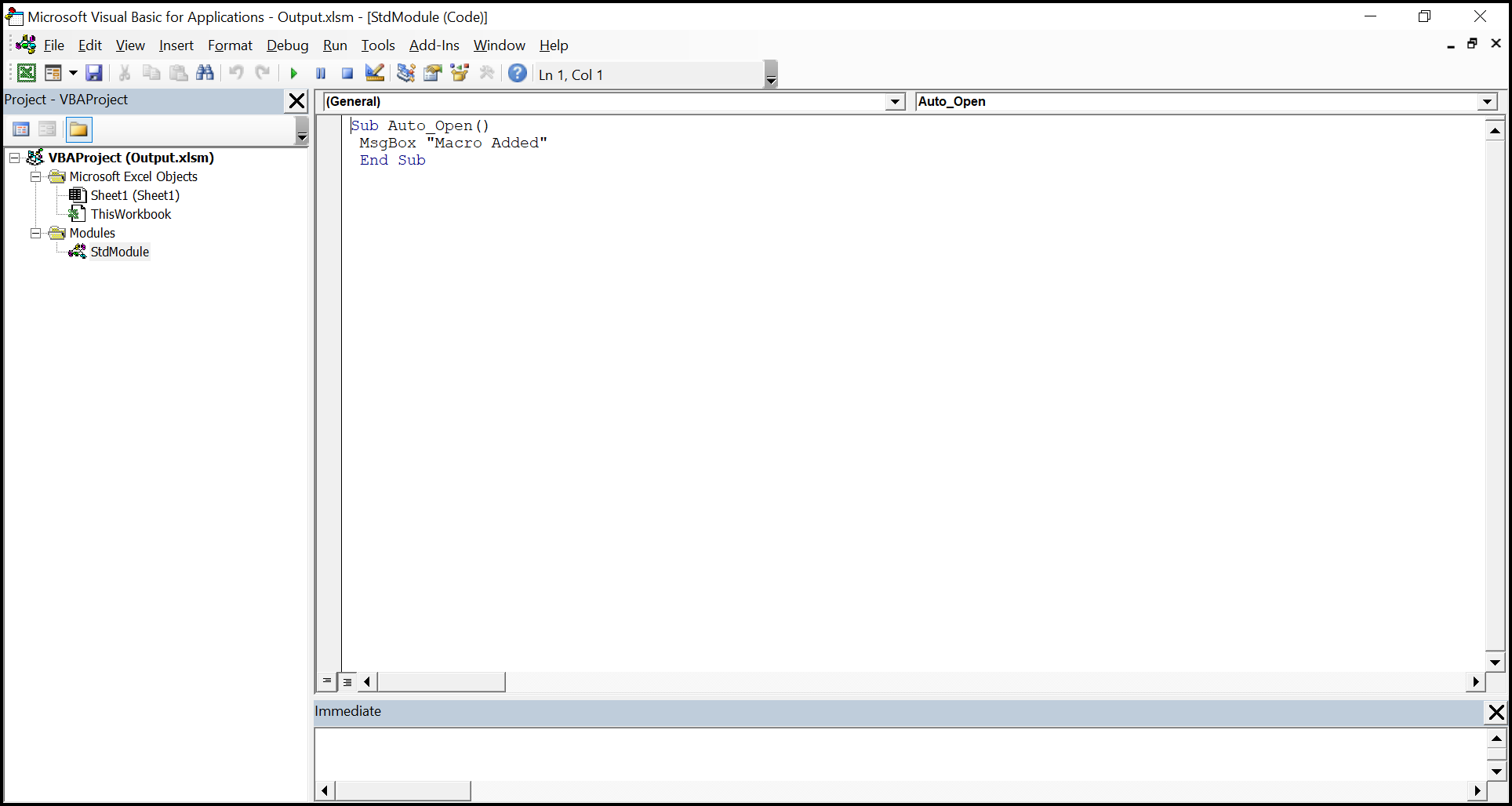
The Vba project in the output Excel document looks like below.
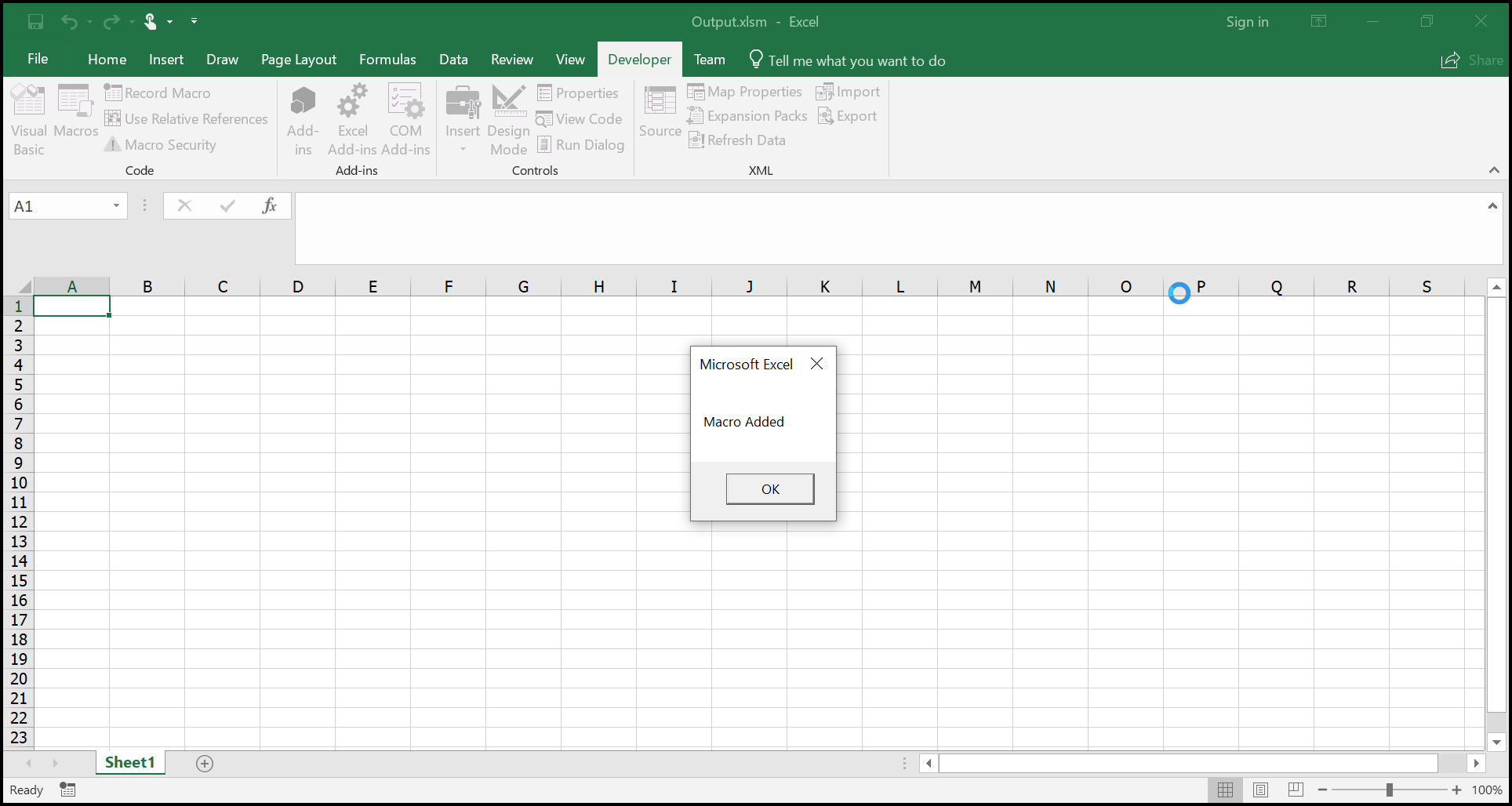
The Macro output in the Excel document looks like below.
Class
Class module allows us to create our own object model to use it where same kind of objects needs to be added with different values such as creating the employee information list. XlsIO supports creating a class module in Excel document.
The following code illustrate how to add a class in XlsIO. Here, the parameters name and VbaModuleType enum value is used.
- Test – Class name used in the Vba project
- ClassModule – Type of Vba module
//Adding class module to the workbook
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
IVbaModule module = project.Modules.Add("Test", VbaModuleType.ClassModule);//Adding class module to the workbook
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
IVbaModule module = project.Modules.Add("Test", VbaModuleType.ClassModule);//Adding class module to the workbook
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
Dim [module] As IVbaModule = project.Modules.Add("Test", VbaModuleType.ClassModule)The following code illustrate how to use class module to run a macro with another module in Excel document.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Adding a class module
IVbaModule clsModule = vbaModules.Add("Test", VbaModuleType.ClassModule);
clsModule.Code = "Public Sub Create()\n MsgBox \"Created a class module\" \n End Sub";
//Adding a vba module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules.Add("Module1", VbaModuleType.StdModule);
//Using class in StdModule
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open()\n Dim obj As New test \n obj.Create \n End Sub";
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/MacroAsClass.xlsm"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
//Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Creating new workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Adding a class module
IVbaModule clsModule = vbaModules.Add("Test", VbaModuleType.ClassModule);
clsModule.Code = "Public Sub Create()\n MsgBox \"Created a class module\" \n End Sub";
//Adding a vba module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules.Add("Module1", VbaModuleType.StdModule);
//Using class in StdModule
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open()\n Dim obj As New test \n obj.Create \n End Sub";
//Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Creating new Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating Vba project
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
'Accessing vba modules collection
Dim vbaModules As IVbaModules = project.Modules
'Adding a vba module
Dim vbaModule As IVbaModule = vbaModules.Add("StdModule", VbaModuleType.StdModule)
'Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open" & vbLf & " MsgBox ""Macro Added"" " & vbLf & " End Sub"
'Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm")
End UsingA complete working example to create macro as class in C# is present on this GitHub page.
The Vba project in the output Excel document looks like below.
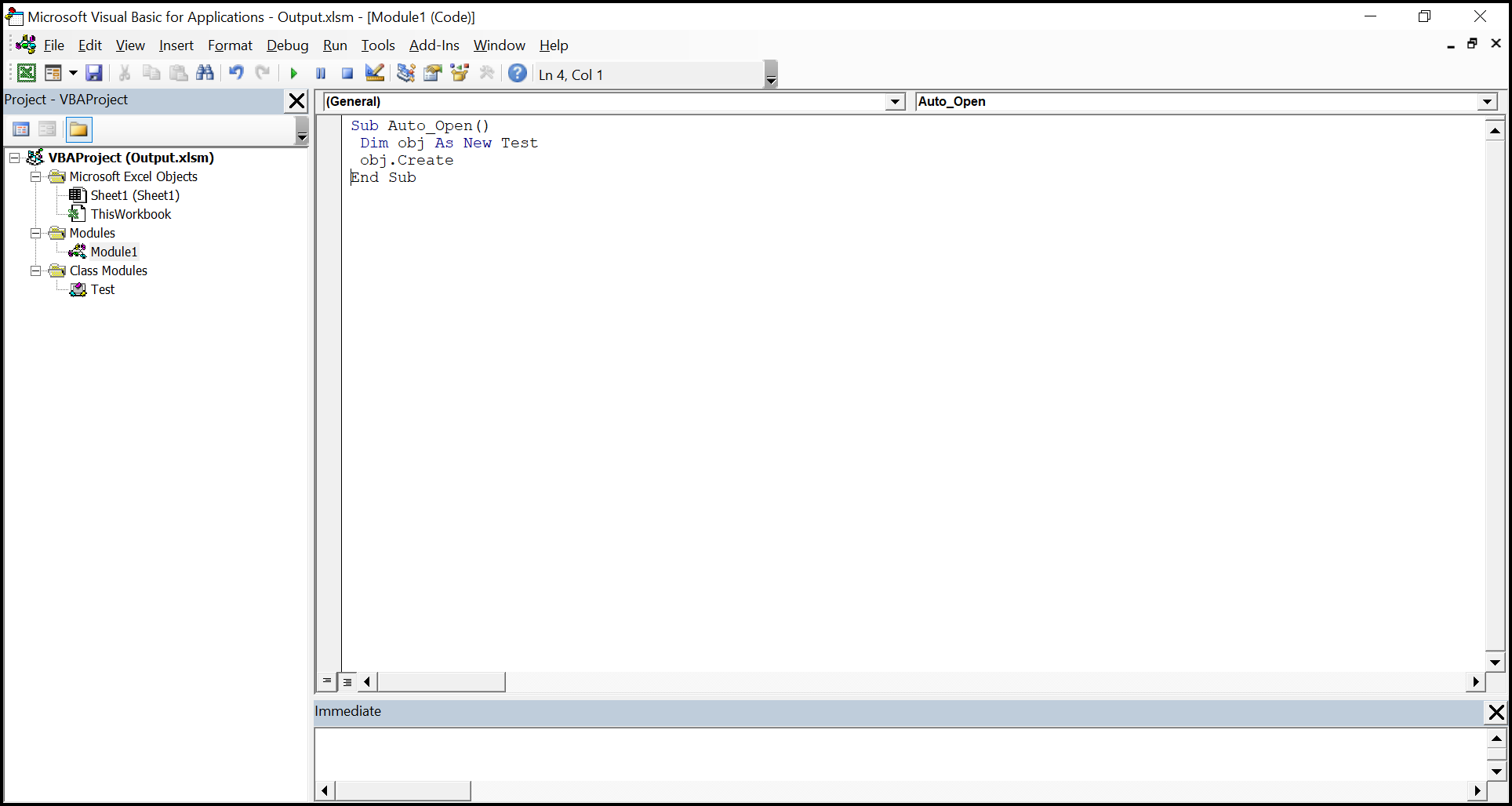
The Macro output in the Excel document looks like below.
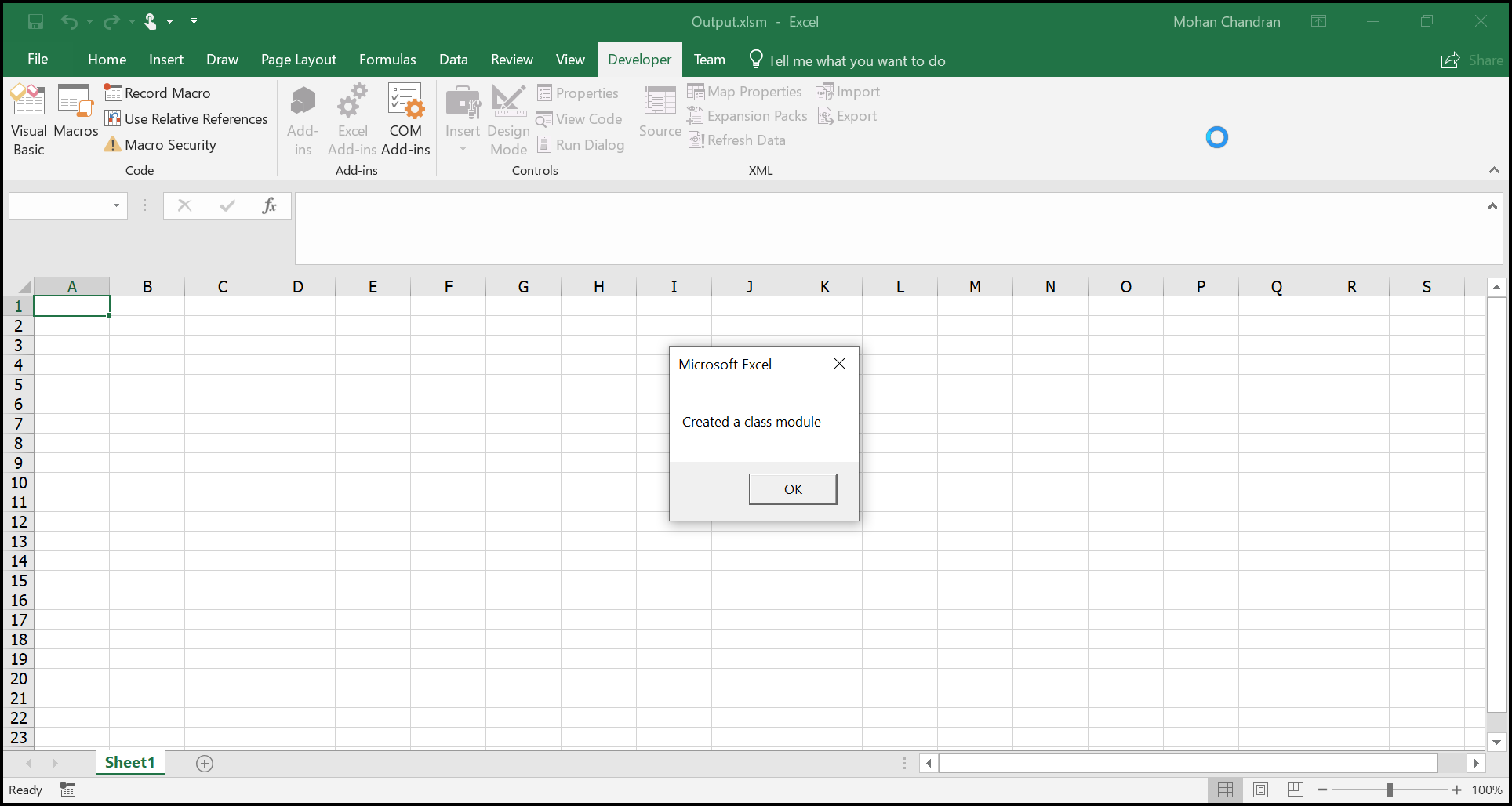
MsForm
MsForm is the form module in which we can have form controls such as textbox, label, buttons etc. Form module cannot be created by XlsIO, but it allows to copy from a form module existing another workbook to new workbook.
The following code illustrate how to add a class in XlsIO. Here, the parameters name and VbaModuleType enum value is used.
- UserForm – Class name used in the Vba project
- MsForm – Type of Vba module
//Adding class module to the workbook
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
IVbaModule module = project.Modules.Add("UserForm", VbaModuleType.MsForm);//Adding class module to the workbook
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
IVbaModule module = project.Modules.Add("UserForm", VbaModuleType.MsForm);//Adding class module to the workbook
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
Dim [module] As IVbaModule = project.Modules.Add("UserForm", VbaModuleType.MsForm)The following code illustrate how to copy a form from another workbook to new workbook.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Opening form module existing workbook
IWorkbook newBook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xls"));
IVbaProject newProject = newBook.VbaProject;
//Accessing existing form module
IVbaModule form = newProject.Modules["UserForm1"];
//Adding a form module in new workbook
IVbaModule formModule = project.Modules.Add(form.Name, VbaModuleType.MsForm);
//Copying the form code behind
formModule.Code = form.Code;
//Copying the designer of the form
formModule.DesignerStorage = form.DesignerStorage;
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/MacroAsMSForm.xlsm"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
//Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Creating new workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Opening form module existing workbook
IWorkbook newBook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls");
IVbaProject newProject = newBook.VbaProject;
//Accessing existing form module
IVbaModule form = newProject.Modules["UserForm1"];
//Adding a form module in new workbook
IVbaModule formModule = project.Modules.Add(form.Name, VbaModuleType.MsForm);
//Copying the form code behind
formModule.Code = form.Code;
//Copying the designer of the form
formModule.DesignerStorage = form.DesignerStorage;
//Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Creating new Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating Vba project
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
'Accessing vba modules collection
Dim vbaModules As IVbaModules = project.Modules
'Open form existing workbook
Dim newBook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls")
Dim newProject As IVbaProject = newBook.VbaProject
'Accessing existing form module
Dim form As IVbaModule = newProject.Modules("UserForm1")
'Adding a form module in new workbook
Dim formModule As IVbaModule = project.Modules.Add(form.Name, VbaModuleType.MsForm)
'Copying the form code behind
formModule.Code = form.Code
'Copying the designer of the form
formModule.DesignerStorage = form.DesignerStorage
'Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm")
End UsingA complete working example to create macro as MS Form in C# is present on this GitHub page.
The Vba project in the output Excel document looks like below.
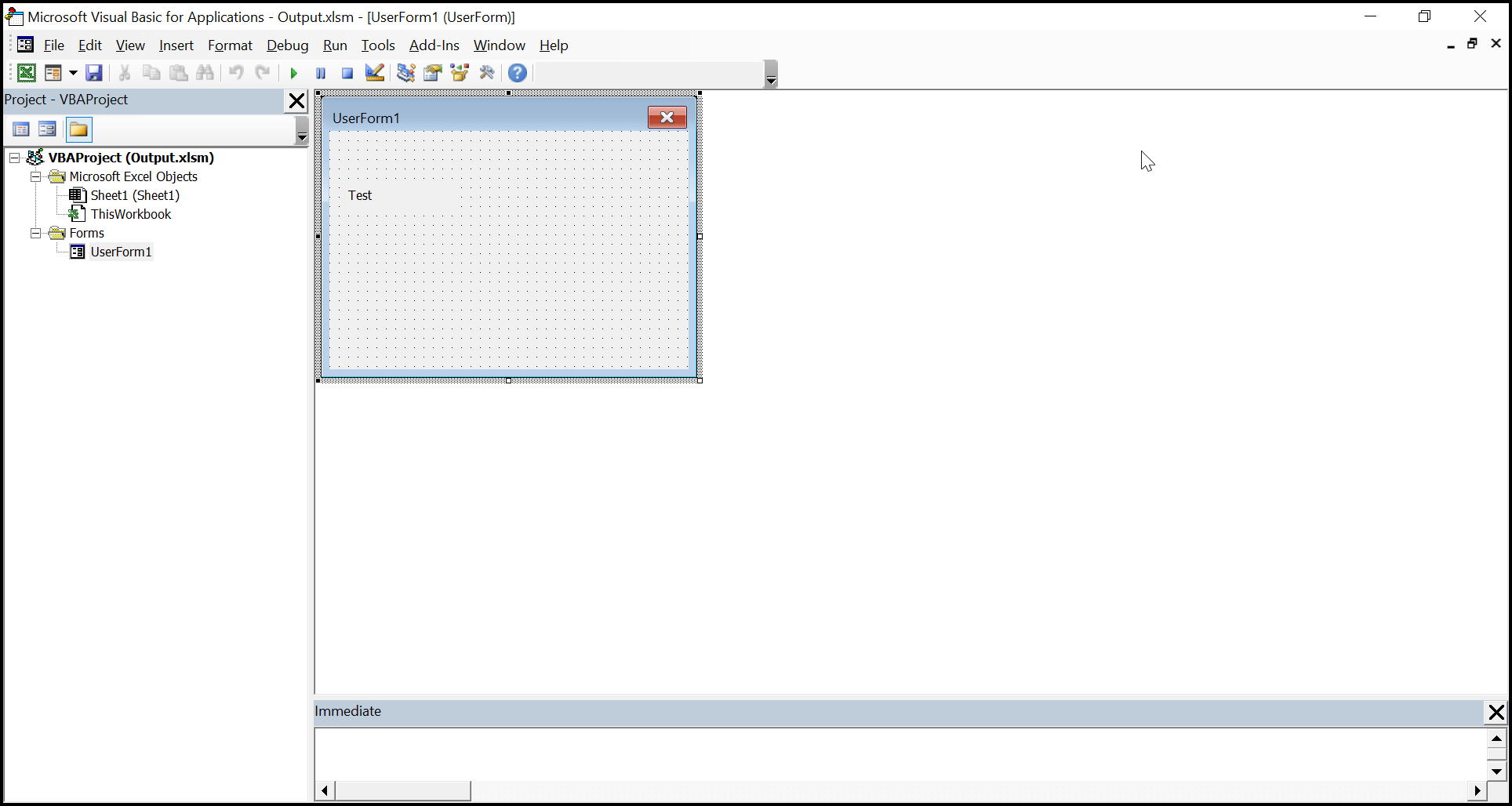
Assigning Macro to Shapes
XlsIO supports assigning macros to the shape controls in the Excel document through OnAction property.
The following code illustrate how to assign macros to shapes in Excel document.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Adding a vba module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules.Add("StdModule", VbaModuleType.StdModule);
//Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Invoke()\n MsgBox \"Macro Added\" \n End Sub";
//Adding a auto shape
IShape shape = sheet.Shapes.AddAutoShapes(AutoShapeType.Rectangle, 1, 2, 60, 70);
shape.Name = "Shape1";
//Assigning a Macro to shape
shape.OnAction = "StdModule.Invoke";
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ShapesWithMacro.xlsm"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
//Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Creating new workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Adding a vba module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules.Add("StdModule", VbaModuleType.StdModule);
//Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Invoke()\n MsgBox \"Macro Added\" \n End Sub";
//Adding a auto shape
IShape shape = sheet.Shapes.AddAutoShapes(AutoShapeType.Rectangle, 1, 2, 60, 70);
shape.Name = "Shape1";
//Assigning a Macro to shape
shape.OnAction = "StdModule.Invoke";
//Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Creating new Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating Vba project
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
'Accessing vba modules collection
Dim vbaModules As IVbaModules = project.Modules
'Adding a vba module
Dim vbaModule As IVbaModule = vbaModules.Add("StdModule", VbaModuleType.StdModule)
'Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Invoke()" & vbLf & " MsgBox ""Macro Added"" " & vbLf & " End Sub"
'Adding a auto shape
Dim shape As IShape = sheet.Shapes.AddAutoShapes(AutoShapeType.Rectangle, 1, 2, 60, 70)
shape.Name = "Shape1"
'Assigning a Macro to shape
shape.OnAction = "StdModule.Invoke"
'Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm")
End UsingA complete working example to assign macro to shape in C# is present on this GitHub page.
When the shape is clicked, the output looks like below.
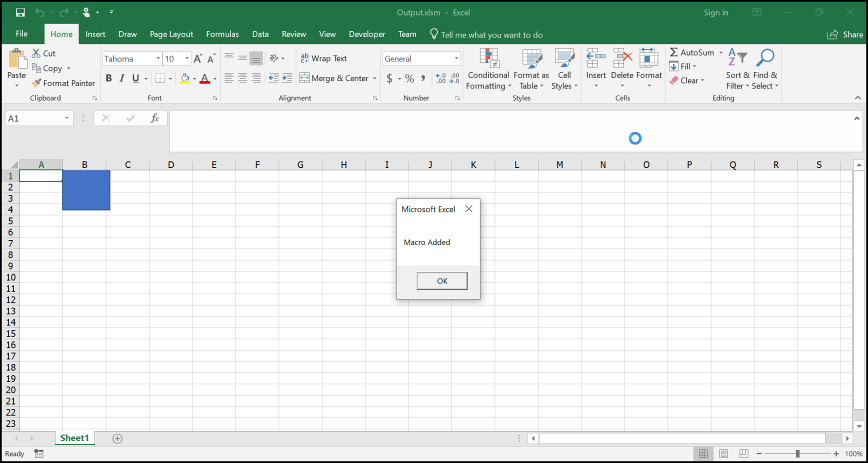
Saving macro enabled document into stream
By default, while saving the Excel workbook into stream, the file type will be based on the Excel version used. For Excel97to2003 version, the file format will be XLS type. Above this version, the document will be saved as XLSX format. So, while saving the macro enabled documents into XLSM and XLTM formats into stream, the ExcelSaveType should be provided as SaveAsMacro and SaveAsMacroTemplate.
The following code illustrate how to save macro-enabled documents into stream.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Adding a vba module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules.Add("StdModule", VbaModuleType.StdModule);
//Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open\n MsgBox \"Macro Added\" \n End Sub";
#region Save
//Saving the workbook Macro in XLTM format
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/SaveAsStream.xltm"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacroTemplate);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
//Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Creating new workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Creating Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Adding a vba module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules.Add("StdModule", VbaModuleType.StdModule);
//Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open\n MsgBox \"Macro Added\" \n End Sub";
//Saving as Macro in XLSM format
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
workbook.SaveAs(stream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro);
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Creating new Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1)
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating Vba project
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
'Accessing vba modules collection
Dim vbaModules As IVbaModules = project.Modules
'Adding a vba module
Dim vbaModule As IVbaModule = vbaModules.Add("StdModule", VbaModuleType.StdModule)
'Adding vba code to the module
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open" & vbLf & " MsgBox ""Macro Added"" " & vbLf & " End Sub"
‘Saving as Macro in XLSM format
Dim stream As MemoryStream = New MemoryStream()
workbook.SaveAs(stream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro)
End UsingA complete working example to save macro enabled document into stream in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Editing a Macro
XlsIO allows to edit the existing macros in the Excel documents. To edit macros in Excel document, the module containing the macro code needs to be modified. By using the name of the module, it can be accessed and edited in XlsIO.
The following code illustrate how to edit existing macro in Excel document.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xls"), ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Access a Vba Module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules["Module1"];
//Edit the macro
vbaModule.Name = "Module1";
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open()\n MsgBox \"Macro is edited\" \n End Sub ";
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/EditMacro.xlsm"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
// Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Opening a workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls");
workbook.Version = ExcelVersion.Excel2016;
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Access a Vba Module
IVbaModule vbaModule = vbaModules["Module1"];
//Edit the macro
vbaModule.Name = "CreateData";
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open()\n MsgBox \"Macro is edited\" \n End Sub ";
//Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Opening a Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls")
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating Vba project
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
'Accessing vba modules collection
Dim vbaModules As IVbaModules = project.Modules
'Accessing a vba module
Dim vbaModule As IVbaModule = vbaModules("Module1")
'Editing a module
vbaModule.Name = "CreateData"
vbaModule.Code = "Sub Auto_Open()" & vbLf & " MsgBox ""Macro is edited"" " & vbLf & " End Sub "
'Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm")
End UsingA complete working example to edit macro in C# is present on this GitHub page.
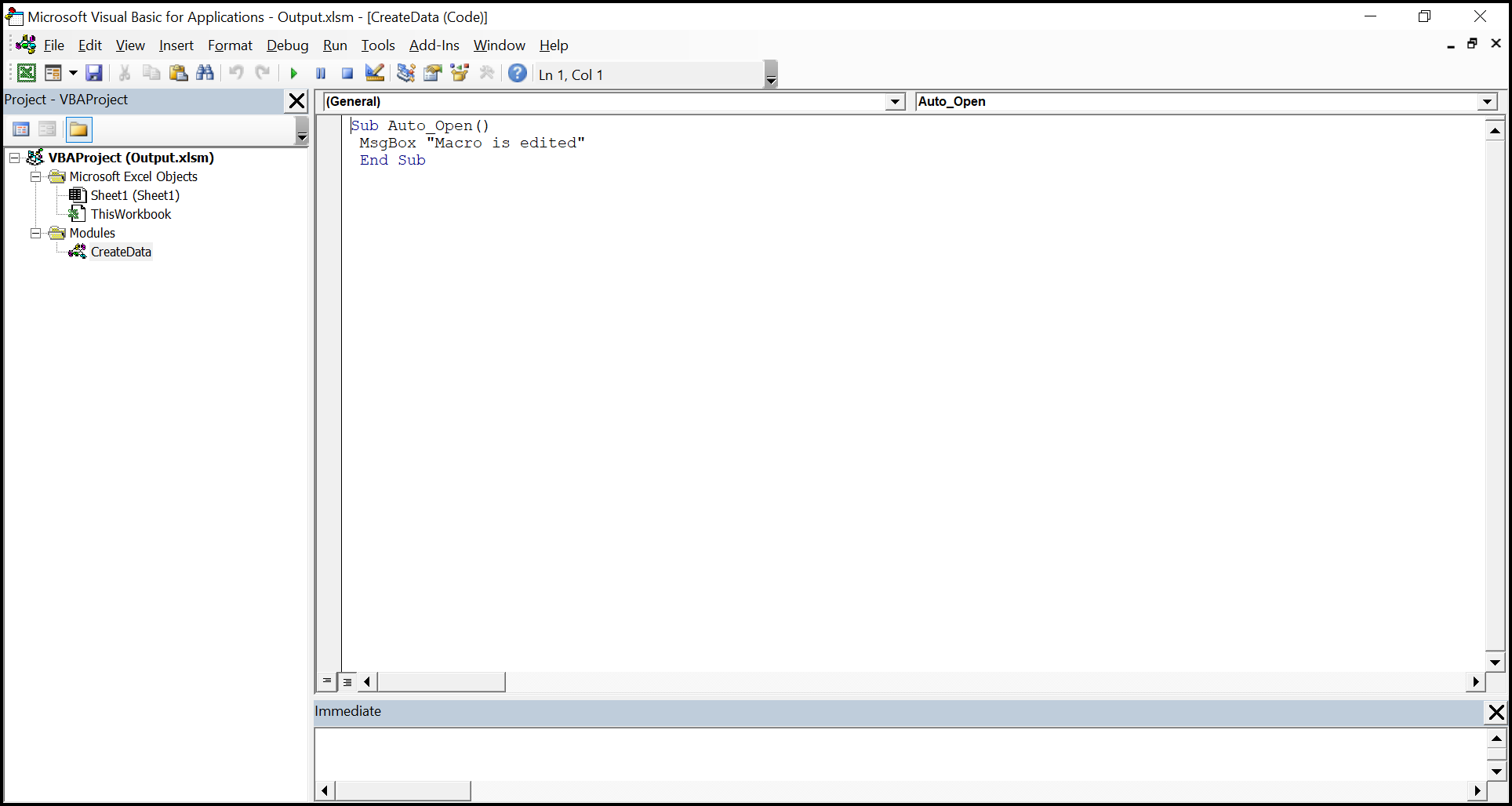
The Vba project in the output Excel document looks like below.
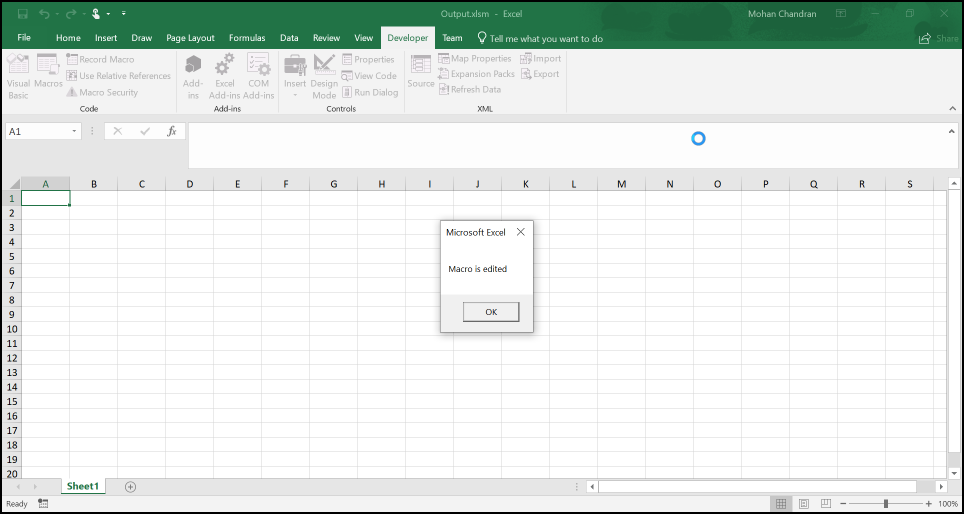
The Macro output in the Excel document looks like below.
NOTE
Macros are parsed only when accessed. By default, opening and saving a macro file will preserve its macros.
Removing Macros
Excel macro-enabled documents can be saved as normal documents where the macro process is not necessary. XlsIO supports saving the macro-enabled documents such as XLS, XLSM, XLTM without macros and normal documents such as XLSX and XLS. For that, macro in the Excel documents needs to be removed.
Macro in the Excel document can be removed in the following ways.
- Remove(String name)
- RemoveAt(int index)
- Clear()
- SkipOnSave
Remove(string name)
Macro process exist in the Vba project’s code modules. To remove a macro, the Vba modules needs to be removed.
- name – Name of the Vba module needs to be removed.
The following code illustrate how to remove a module using Remove method.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xls"), ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Remove macro module
vbaModules.Remove("Module1");
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/RemoveMacroWithName.xlsm"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
// Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Opening a workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls");
workbook.Version = ExcelVersion.Excel2016;
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Remove macro module
vbaModules.Remove("Module1");
//Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Opening a Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls")
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating Vba project
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
'Accessing vba modules collection
Dim vbaModules As IVbaModules = project.Modules
//Remove macro module
vbaModules.Remove("Module1")
'Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm")
End UsingA complete working example to remove macro using name in C# is present on this GitHub page.
RemoveAt(int index)
Vba module can be removed using the position from the IVbaModules collection.
- Index – Position of the Vba module in the modules collection.
The following code illustrate how to remove a macro using module index.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xls"), ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Remove macro module
vbaModules.RemoveAt(2);
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/RemoveMacroWithIndex.xlsm"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
// Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Opening a workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls");
workbook.Version = ExcelVersion.Excel2016;
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Remove macro module
vbaModules.RemoveAt(0);
//Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Opening a Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls")
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating Vba project
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
'Accessing vba modules collection
Dim vbaModules As IVbaModules = project.Modules
//Remove macro module
vbaModules.RemoveAt(0)
'Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm")
End UsingA complete working example to remove macro using index in C# is present on this GitHub page.
Clear()
Clear() method removes all the Vba modules at once by clearing the module collection.
The following code illustrate how to remove all macros using Clear method.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xls"), ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Remove all macros
vbaModules.Clear();
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/ClearAllMacro.xlsm"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsMacro);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
// Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Opening a workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls");
workbook.Version = ExcelVersion.Excel2016;
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Accessing Vba project
IVbaProject project = workbook.VbaProject;
//Accessing vba modules collection
IVbaModules vbaModules = project.Modules;
//Remove all macros
vbaModules.Clear();
//Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Opening a Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls")
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
'Creating Vba project
Dim project As IVbaProject = workbook.VbaProject
'Accessing vba modules collection
Dim vbaModules As IVbaModules = project.Modules
//Remove all macros
vbaModules.Clear()
'Saving as macro document
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsm")
End UsingA complete working example to remove all macros in C# is present on this GitHub page.
SkipOnSave
SkipOnSave allows to resave the Excel document into normal XLSX and XLS documents.
The following code illustrate how to save the macro-enabled document into normal Excel document.
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open(Path.GetFullPath(@"Data/InputTemplate.xls"), ExcelOpenType.Automatic);
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Skip Macros while saving
application.SkipOnSave = SkipExtRecords.Macros;
#region Save
//Saving the workbook
FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(Path.GetFullPath("Output/SkipMacroAndSave.xlsx"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
workbook.SaveAs(outputStream, ExcelSaveType.SaveAsXLS);
#endregion
//Dispose streams
outputStream.Dispose();
}using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
// Instantiate the excel application object.
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
// Opening a workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls");
workbook.Version = ExcelVersion.Excel2016;
IWorksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Skip Macros while saving
application.SkipOnSave = SkipExtRecords.Macros;
//Saving as Excel without macro
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx");
}Using excelEngine As ExcelEngine = New ExcelEngine()
'Instantiate the excel application object.
Dim application As IApplication = excelEngine.Excel
'Opening a Workbook
Dim workbook As IWorkbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Test.xls")
Dim sheet As IWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
//Skip Macros while saving
application.SkipOnSave = SkipExtRecords.Macros
'Saving as Excel without macro
workbook.SaveAs("Output.xlsx")
End UsingA complete working example to skip macro on save in C# is present on this GitHub page.