Create, read, and edit Excel files in AWS Lambda
18 Dec 202516 minutes to read
Syncfusion® XlsIO is a .NET Core Excel library can be used to create, read, edit Excel files. This library supports manipulating Excel documents in Amazon Web Services (AWS) with the Lambda function.
Steps to create an Excel document in AWS Lambda
The below steps illustrates creating a simple Invoice formatted Excel document in AWS Lambda.
Step 1: Create a new AWS Lambda project as follows.

Step 2: Select Blueprint as Empty Function and click Finish.

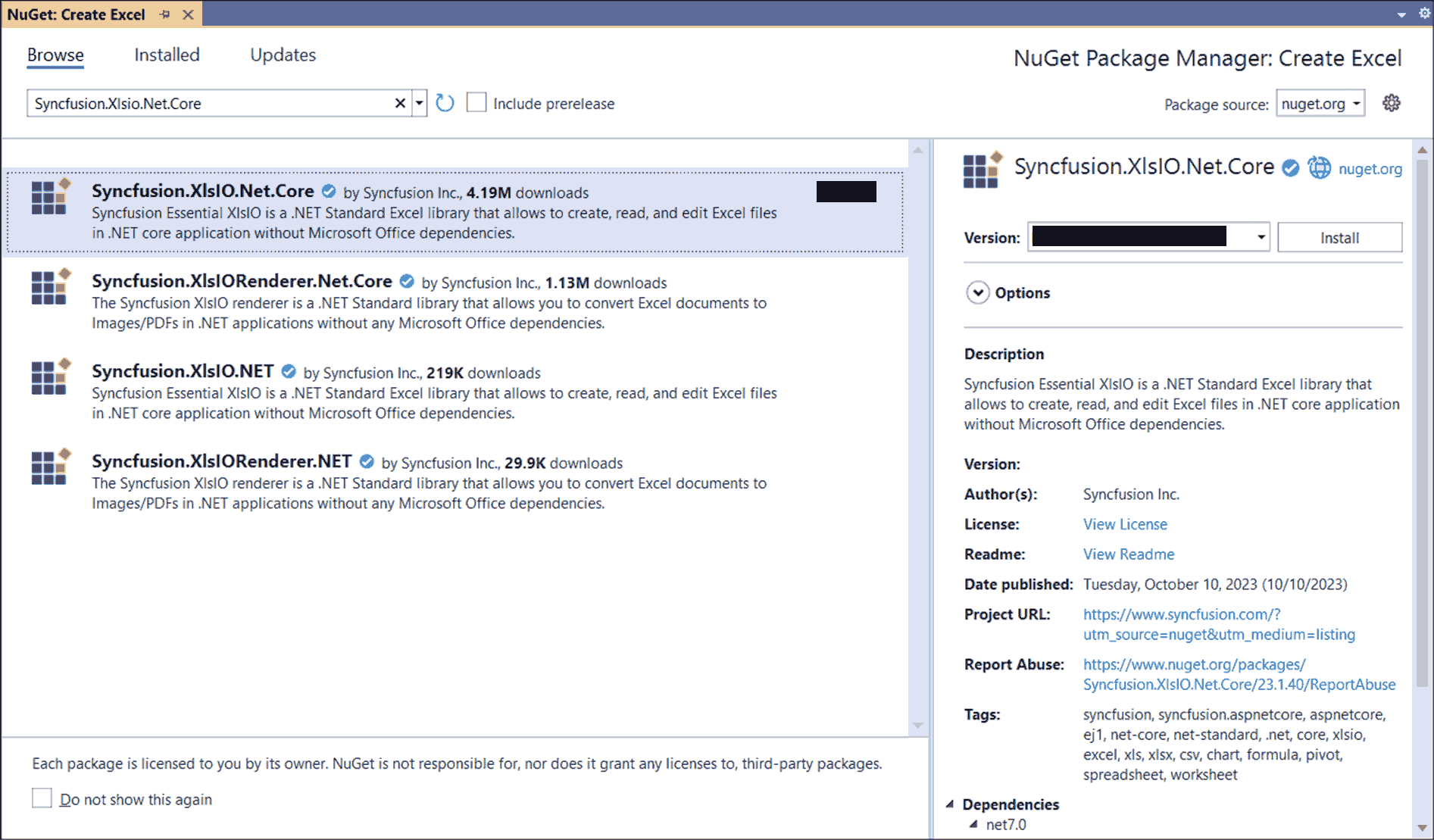
Step 3: Install the Syncfusion.XlsIO.Net.Core NuGet package as reference to your .NET Standard applications from NuGet.org.
NOTE
Starting with v16.2.0.x, if you reference Syncfusion® assemblies from trial setup or from the NuGet feed, you also have to add “Syncfusion.Licensing” assembly reference and include a license key in your projects. Please refer to this link to know about registering Syncfusion® license key in your applications to use our components.
Step 4: Create a folder and copy the required data files and include the files to the project.

Step 5: Set the copy to output directory to Copy if newer to all the data files.
Step 6: Include the following namespaces in Function.cs file.
using Syncfusion.XlsIO;step 7: Add the following code snippet in Function.cs to create an Excel document.
//Create an instance of ExcelEngine
using (ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine())
{
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
//Create a workbook
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Create(1);
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Adding a picture
FileStream imageStream = new FileStream("AdventureCycles-Logo.png", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
IPictureShape shape = worksheet.Pictures.AddPicture(1, 1, imageStream, 20, 20);
//Disable gridlines in the worksheet
worksheet.IsGridLinesVisible = false;
//Enter values to the cells from A3 to A5
worksheet.Range["A3"].Text = "46036 Michigan Ave";
worksheet.Range["A4"].Text = "Canton, USA";
worksheet.Range["A5"].Text = "Phone: +1 231-231-2310";
//Make the text bold
worksheet.Range["A3:A5"].CellStyle.Font.Bold = true;
//Merge cells
worksheet.Range["D1:E1"].Merge();
//Enter text to the cell D1 and apply formatting.
worksheet.Range["D1"].Text = "INVOICE";
worksheet.Range["D1"].CellStyle.Font.Bold = true;
worksheet.Range["D1"].CellStyle.Font.RGBColor = Color.FromArgb(42, 118, 189);
worksheet.Range["D1"].CellStyle.Font.Size = 35;
//Apply alignment in the cell D1
worksheet.Range["D1"].CellStyle.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHAlign.HAlignRight;
worksheet.Range["D1"].CellStyle.VerticalAlignment = ExcelVAlign.VAlignTop;
//Enter values to the cells from D5 to E8
worksheet.Range["D5"].Text = "INVOICE#";
worksheet.Range["E5"].Text = "DATE";
worksheet.Range["D6"].Number = 1028;
worksheet.Range["E6"].Value = "12/31/2018";
worksheet.Range["D7"].Text = "CUSTOMER ID";
worksheet.Range["E7"].Text = "TERMS";
worksheet.Range["D8"].Number = 564;
worksheet.Range["E8"].Text = "Due Upon Receipt";
//Apply RGB backcolor to the cells from D5 to E8
worksheet.Range["D5:E5"].CellStyle.Color = Color.FromArgb(42, 118, 189);
worksheet.Range["D7:E7"].CellStyle.Color = Color.FromArgb(42, 118, 189);
//Apply known colors to the text in cells D5 to E8
worksheet.Range["D5:E5"].CellStyle.Font.Color = ExcelKnownColors.White;
worksheet.Range["D7:E7"].CellStyle.Font.Color = ExcelKnownColors.White;
//Make the text as bold from D5 to E8
worksheet.Range["D5:E8"].CellStyle.Font.Bold = true;
//Apply alignment to the cells from D5 to E8
worksheet.Range["D5:E8"].CellStyle.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHAlign.HAlignCenter;
worksheet.Range["D5:E5"].CellStyle.VerticalAlignment = ExcelVAlign.VAlignCenter;
worksheet.Range["D7:E7"].CellStyle.VerticalAlignment = ExcelVAlign.VAlignCenter;
worksheet.Range["D6:E6"].CellStyle.VerticalAlignment = ExcelVAlign.VAlignTop;
//Enter value and applying formatting in the cell A7
worksheet.Range["A7"].Text = " BILL TO";
worksheet.Range["A7"].CellStyle.Color = Color.FromArgb(42, 118, 189);
worksheet.Range["A7"].CellStyle.Font.Bold = true;
worksheet.Range["A7"].CellStyle.Font.Color = ExcelKnownColors.White;
//Apply alignment
worksheet.Range["A7"].CellStyle.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHAlign.HAlignLeft;
worksheet.Range["A7"].CellStyle.VerticalAlignment = ExcelVAlign.VAlignCenter;
//Enter values in the cells A8 to A12
worksheet.Range["A8"].Text = "Steyn";
worksheet.Range["A9"].Text = "Great Lakes Food Market";
worksheet.Range["A10"].Text = "20 Whitehall Rd";
worksheet.Range["A11"].Text = "North Muskegon,USA";
worksheet.Range["A12"].Text = "+1 231-654-0000";
//Create a Hyperlink for e-mail in the cell A13
IHyperLink hyperlink = worksheet.HyperLinks.Add(worksheet.Range["A13"]);
hyperlink.Type = ExcelHyperLinkType.Url;
hyperlink.Address = "[email protected]";
hyperlink.ScreenTip = "Send Mail";
//Merge column A and B from row 15 to 22
worksheet.Range["A15:B15"].Merge();
worksheet.Range["A16:B16"].Merge();
worksheet.Range["A17:B17"].Merge();
worksheet.Range["A18:B18"].Merge();
worksheet.Range["A19:B19"].Merge();
worksheet.Range["A20:B20"].Merge();
worksheet.Range["A21:B21"].Merge();
worksheet.Range["A22:B22"].Merge();
//Enter details of products and prices
worksheet.Range["A15"].Text = " DESCRIPTION";
worksheet.Range["C15"].Text = "QTY";
worksheet.Range["D15"].Text = "UNIT PRICE";
worksheet.Range["E15"].Text = "AMOUNT";
worksheet.Range["A16"].Text = "Cabrales Cheese";
worksheet.Range["A17"].Text = "Chocos";
worksheet.Range["A18"].Text = "Pasta";
worksheet.Range["A19"].Text = "Cereals";
worksheet.Range["A20"].Text = "Ice Cream";
worksheet.Range["C16"].Number = 3;
worksheet.Range["C17"].Number = 2;
worksheet.Range["C18"].Number = 1;
worksheet.Range["C19"].Number = 4;
worksheet.Range["C20"].Number = 3;
worksheet.Range["D16"].Number = 21;
worksheet.Range["D17"].Number = 54;
worksheet.Range["D18"].Number = 10;
worksheet.Range["D19"].Number = 20;
worksheet.Range["D20"].Number = 30;
worksheet.Range["D23"].Text = "Total";
//Apply number format
worksheet.Range["D16:E22"].NumberFormat = "$0.00";
worksheet.Range["E23"].NumberFormat = "$0.00";
//Apply incremental formula for column Amount by multiplying Qty and UnitPrice
application.EnableIncrementalFormula = true;
worksheet.Range["E16:E20"].Formula = "=C16*D16";
//Formula for Sum the total
worksheet.Range["E23"].Formula = "=SUM(E16:E22)";
//Apply borders
worksheet.Range["A16:E22"].CellStyle.Borders[ExcelBordersIndex.EdgeTop].LineStyle = ExcelLineStyle.Thin;
worksheet.Range["A16:E22"].CellStyle.Borders[ExcelBordersIndex.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = ExcelLineStyle.Thin;
worksheet.Range["A16:E22"].CellStyle.Borders[ExcelBordersIndex.EdgeTop].Color = ExcelKnownColors.Grey_25_percent;
worksheet.Range["A16:E22"].CellStyle.Borders[ExcelBordersIndex.EdgeBottom].Color = ExcelKnownColors.Grey_25_percent;
worksheet.Range["A23:E23"].CellStyle.Borders[ExcelBordersIndex.EdgeTop].LineStyle = ExcelLineStyle.Thin;
worksheet.Range["A23:E23"].CellStyle.Borders[ExcelBordersIndex.EdgeBottom].LineStyle = ExcelLineStyle.Thin;
worksheet.Range["A23:E23"].CellStyle.Borders[ExcelBordersIndex.EdgeTop].Color = ExcelKnownColors.Black;
worksheet.Range["A23:E23"].CellStyle.Borders[ExcelBordersIndex.EdgeBottom].Color = ExcelKnownColors.Black;
//Apply font setting for cells with product details
worksheet.Range["A3:E23"].CellStyle.Font.FontName = "Arial";
worksheet.Range["A3:E23"].CellStyle.Font.Size = 10;
worksheet.Range["A15:E15"].CellStyle.Font.Color = ExcelKnownColors.White;
worksheet.Range["A15:E15"].CellStyle.Font.Bold = true;
worksheet.Range["D23:E23"].CellStyle.Font.Bold = true;
//Apply cell color
worksheet.Range["A15:E15"].CellStyle.Color = Color.FromArgb(42, 118, 189);
//Apply alignment to cells with product details
worksheet.Range["A15"].CellStyle.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHAlign.HAlignLeft;
worksheet.Range["C15:C22"].CellStyle.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHAlign.HAlignCenter;
worksheet.Range["D15:E15"].CellStyle.HorizontalAlignment = ExcelHAlign.HAlignCenter;
//Apply row height and column width to look good
worksheet.Range["A1"].ColumnWidth = 36;
worksheet.Range["B1"].ColumnWidth = 11;
worksheet.Range["C1"].ColumnWidth = 8;
worksheet.Range["D1:E1"].ColumnWidth = 18;
worksheet.Range["A1"].RowHeight = 47;
worksheet.Range["A2"].RowHeight = 15;
worksheet.Range["A3:A4"].RowHeight = 15;
worksheet.Range["A5"].RowHeight = 18;
worksheet.Range["A6"].RowHeight = 29;
worksheet.Range["A7"].RowHeight = 18;
worksheet.Range["A8"].RowHeight = 15;
worksheet.Range["A9:A14"].RowHeight = 15;
worksheet.Range["A15:A23"].RowHeight = 18;
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
workbook.SaveAs(stream);
return Convert.ToBase64String(stream.ToArray());
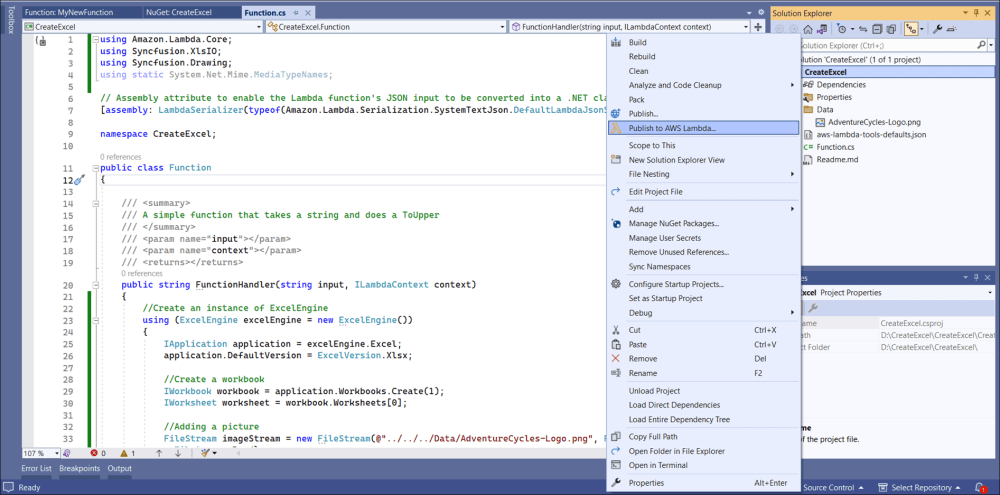
}Step 8: Right-click the project and select Publish to AWS Lambda.
Step 9: Create a new AWS profile in the Upload Lambda Function Window. After creating the profile, add a name for the Lambda function to publish. Then, click Next.

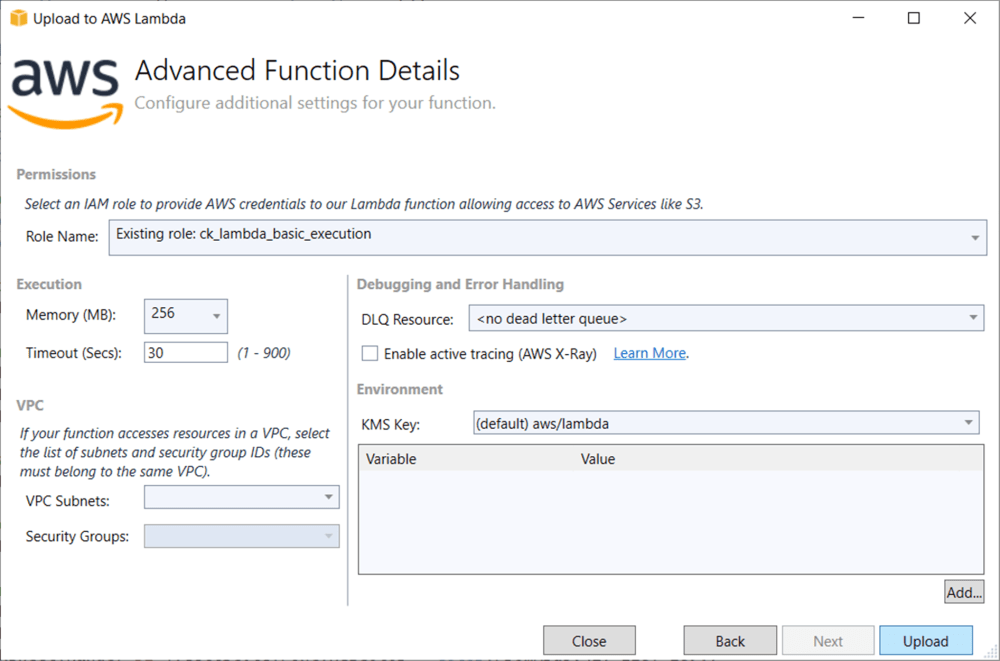
Step 10: In the Advanced Function Details window, specify the Role Name as based on AWS Managed policy. After selecting the role, click the Upload button to deploy your application.
Step 11: After deploying the application, you can see the published Lambda function in AWS console.

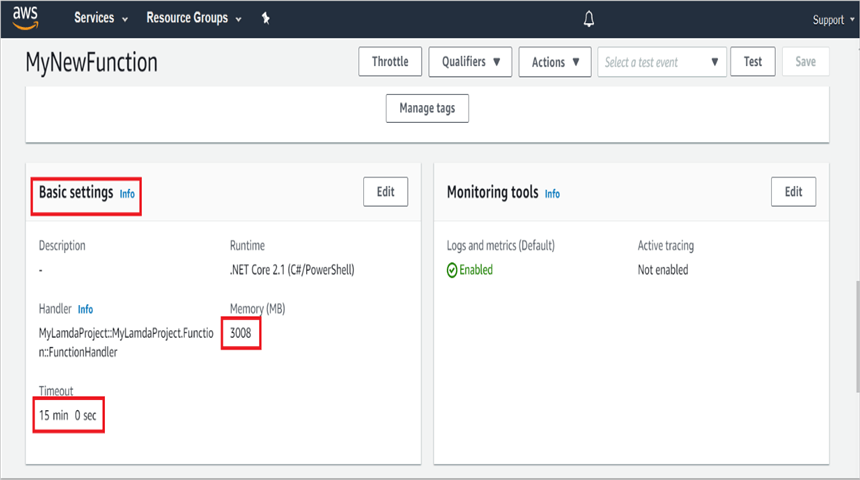
Step 12: Edit Memory size and Timeout as maximum in Basic settings of the AWS Lambda function.
Steps to post the request to AWS Lambda
Step 1: Create a new console project.

step 2: Install the following Nuget packages in your application from Nuget.org.



Step 3: Include the following namespaces in Program.cs file.
using Amazon;
using Amazon.Lambda;
using Amazon.Lambda.Model;
using Newtonsoft.Json;Step 4: Add the following code snippet in Program.cs to invoke the published AWS Lambda function using the function name and access keys.
//Create a new AmazonLambdaClient
AmazonLambdaClient client = new AmazonLambdaClient("awsaccessKeyID", "awsSecreteAccessKey", RegionEndpoint.USEast2);
//Create new InvokeRequest with published function name.
InvokeRequest invoke = new InvokeRequest
{
FunctionName = "MyNewFunction",
InvocationType = InvocationType.RequestResponse,
Payload = "\"Test\""
};
//Get the InvokeResponse from client InvokeRequest.
InvokeResponse response = client.Invoke(invoke);
//Read the response stream
var stream = new StreamReader(response.Payload);
JsonReader reader = new JsonTextReader(stream);
var serilizer = new JsonSerializer();
var responseText = serilizer.Deserialize(reader);
//Convert Base64String into Excel document
byte[] bytes = Convert.FromBase64String(responseText.ToString());
FileStream fileStream = new FileStream("Sample.xlsx", FileMode.Create);
BinaryWriter writer = new BinaryWriter(fileStream);
writer.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
writer.Close();
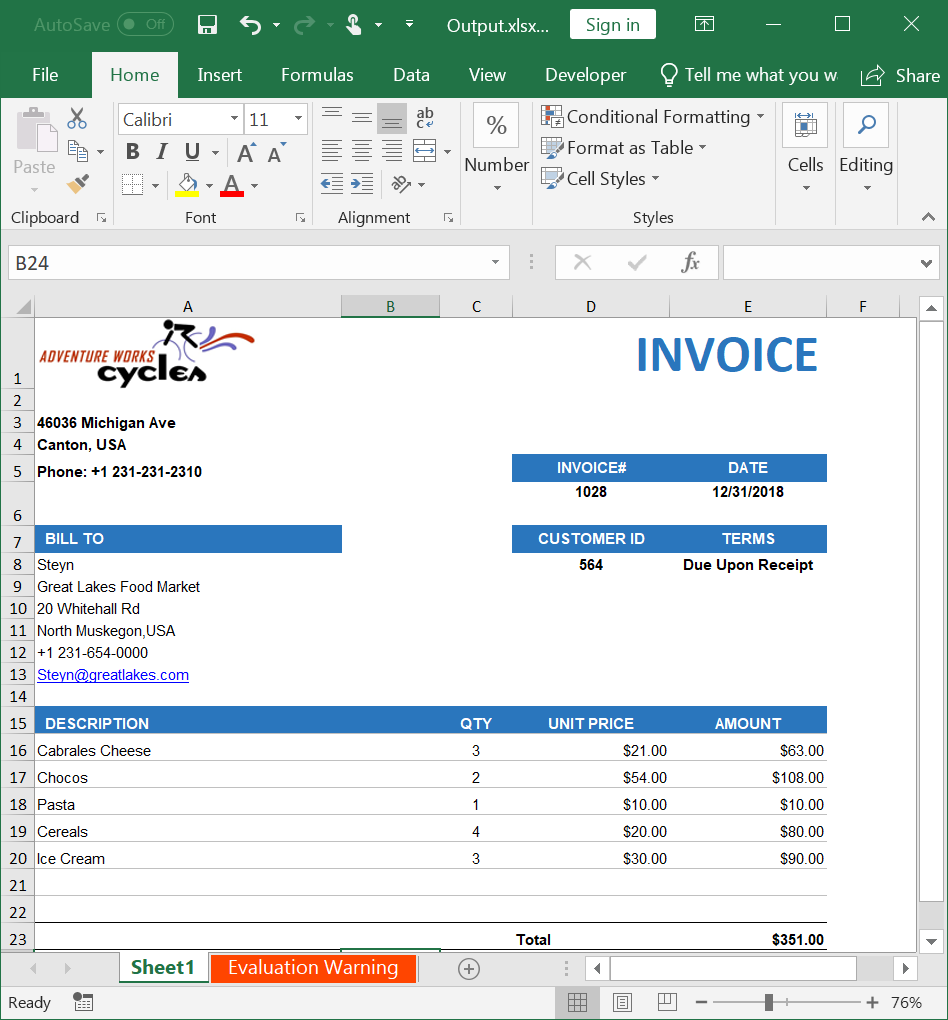
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start("Sample.xlsx");By executing the program, you will get the Excel document as follows.
A complete working example of how to create an Excel file in AWS Lambda is present on this GitHub page, you can download the console application project here.
Read and Edit Excel file
The below code snippet illustrates how to read and edit an Excel file in AWS Lambda.
//Create an instance of ExcelEngine
ExcelEngine excelEngine = new ExcelEngine();
//Instantiate the Excel application object
IApplication application = excelEngine.Excel;
//Assigns default application version
application.DefaultVersion = ExcelVersion.Xlsx;
//A existing workbook is opened.
IWorkbook workbook = application.Workbooks.Open("Sample.xlsx");
//Access first worksheet from the workbook.
IWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
//Set Text in cell A3.
worksheet.Range["A3"].Text ="Hello World";
//Creating stream object.
MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream();
workbook.SaveAs(stream);
return Convert.ToBase64String(stream.ToArray());A complete working example of how to read and edit an Excel file in AWS Lambda is present on this GitHub page, you can download the console application project here.
Click here to explore the rich set of Syncfusion® Excel library (XlsIO) features.
An online sample link to create an Excel document in ASP.NET Core.