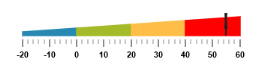
Ranges
17 Nov 201712 minutes to read
Ranges are used to specify or group the scale values. You can describe the values in the pointers using ranges.
Adding range collection
Range collection can be directly added to the scale object. Refer the following code example to add range collection in a Linear Gauge control.
@(Html.EJ().LinearGauge("LinearGauge1").EnableAnimation(false)
.Height(150).Width(600).Orientation(Orientation.Horizontal)
.LabelColor("Black").IsResponsive(true)
//Adding scale collection
.Scales(scale => {
scale.Width(0).BackgroundColor("transparent").Border(border => border.Color("transparent").Width(0)).ShowMarkerPointers(true)
.ShowBarPointers(false).ShowCustomLabels(true).Direction(Directions.Clockwise)
.ShowRanges(true).Minimum(-20).Maximum(60)
//Adding label collection
.Labels(label => { label.DistanceFromScale(distance => distance.X(0).Y(50)).Add(); })
//Adding tick collection
.Ticks(tic =>
{
tic.Type(TickType.MajorInterval).Width(2).Color("#8c8c8c")
.DistanceFromScale(distance => distance.X(25).Y(0)).Add();
tic.Type(TickType.MinorInterval).Color("#8c8c8c").Width(1)
.Height(6).DistanceFromScale(distance => distance.X(25).Y(0)).Add();
})
//Adding marker pointer collection
.MarkerPointers(mp =>
{
mp.Width(3).Length(30).MarkerBackgroundColor("#FE5C09")
.Type(MarkerType.Star).MarkerDistanceFromScale(20)
.Placement(PointerPlacement.Near).Value(55).Add();
})
//Adding range collection
.Ranges(range=>{
range.StartValue(-20).EndValue(60).StartWidth(0)
.EndWidth(20).RangeBackgroundColor("#FEBE48")
.Placement(RangePlacement.Near).DistanceFromScale(20).Add();
}).Add();
}))Execute the above code to render the following output.
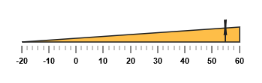
Range Customization
Appearance
The major attributes for ranges are startValue and endValue. The startValue defines the start position of the range and endValue defines the end position of the range. The startWidth and endWidth are used to specify the range width at the starting and ending position of the ranges.
@(Html.EJ().LinearGauge("LinearGauge1").Width(500)
.LabelColor("#8c8c8c")
//Adding scale collection
.Scales(scale => {
scale.Width(4).BackgroundColor("#10ADF5").ShowMarkerPointers(false)
.Border(border => border.Color("transparent").Width(0))
.ShowBarPointers(false).Length(310).ShowRanges(true)
//Adding label collection
.Labels(label => {
label.Font(font => font.Size("11px").FontStyle("Bold")
.FontFamily("Segoe UI")).Add(); })
//Adding ticks collection
.Ticks(tic =>
{
tic.Type(TickType.MajorInterval).Width(1).Color("#8c8c8c").Add();
})
//Adding range collection
.Ranges(range=>{
range.StartValue(0).EndValue(50).StartWidth(8)
.EndWidth(8).RangeBackgroundColor("#F6B53F").DistanceFromScale(5).Add();
range.StartValue(70).EndValue(100).StartWidth(8)
.EndWidth(8).RangeBackgroundColor("#E94649").DistanceFromScale(5).Add();
}).Add();
}))Execute the above code to render the following output.
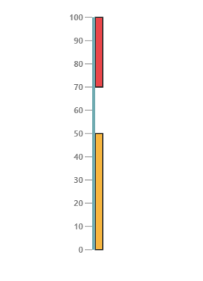
Colors and Border
- You can customize the ranges to improve the appearance of the Gauge. The range border is modified with the object called border. It has two border property such as
colorandwidthwhich are used to customize the border color of the ranges and border width of the ranges. - You can set the background color to improve the look and feel of the Linear Gauge. For customizing the background color of the ranges,
backgroundColoris used.You can add the gradient effects to the ranges by usinggradientobject.
@(Html.EJ().LinearGauge("LinearGauge1").Width(500)
.LabelColor("#8c8c8c")
//Adding scale collection
.Scales(scale => {
scale.Width(4).BackgroundColor("transparent").ShowMarkerPointers(false)
.Border(border => border.Color("transparent").Width(0))
.ShowBarPointers(false).Length(310).ShowRanges(true)
//Adding label collection
.Labels(label => {
label.Font(font => font.Size("11px").FontStyle("Bold")
.FontFamily("Segoe UI")).Add(); })
//Adding ticks collection
.Ticks(tic =>
{
tic.Type(TickType.MajorInterval).Width(1).Color("#8c8c8c").Add();
})
//Adding range collection
.Ranges(range=>{
range.StartValue(0).EndValue(50).StartWidth(18).Border(border => border.Color("Black").Width(2))
.EndWidth(3).RangeBackgroundColor("#F6B53F").DistanceFromScale(10).Add();
range.StartValue(70).EndValue(100).StartWidth(18).Border(border => border.Color("Black").Width(2))
.EndWidth(3).RangeBackgroundColor("#E94649").DistanceFromScale(10).Add();
}).Add();
}))Execute the above code to render the following output.
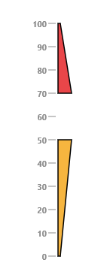
Positioning the ranges
- You can position ranges using two properties such as distanceFromScale and placement. The
distanceFromScaleproperty defines the distance between the scale and range. -
Placementproperty is used to locate the pointer with respect to scale either inside the scale or outside the scale or along the scale. It is an enumerable data type.
@(Html.EJ().LinearGauge("LinearGauge1").Width(500)
.LabelColor("#8c8c8c")
//Adding scale collection
.Scales(scale => {
scale.Width(4).BackgroundColor("transparent").ShowMarkerPointers(false)
.Border(border => border.Color("transparent").Width(0))
.ShowBarPointers(false).Length(310).ShowRanges(true)
//Adding label collection
.Labels(label => {
label.Font(font => font.Size("11px").FontStyle("Bold")
.FontFamily("Segoe UI")).Add(); })
//Adding Ticks collection
.Ticks(tic =>
{
tic.Type(TickType.MajorInterval).Width(1).Color("#8c8c8c").Add();
})
//Adding range collection
.Ranges(range=>{
range.StartValue(0).EndValue(50).StartWidth(18).Border(border=> border.Color("Black").Width(2))
.EndWidth(3).RangeBackgroundColor("#F6B53F").DistanceFromScale(10)
.Placement(RangePlacement.Near).DistanceFromScale(-30).Add();
range.StartValue(70).EndValue(100).StartWidth(18).Border(border=> border.Color("Black").Width(2))
.EndWidth(3).RangeBackgroundColor("#E94649").DistanceFromScale(10)
.Placement(RangePlacement.Near).DistanceFromScale(-30).Add();
}).Add();
}))Execute the above code to render the following output.
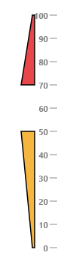
Multiple Ranges
You can set multiple ranges by adding an array of range objects. Refer the following code example for multiple range functionality.
@(Html.EJ().LinearGauge("LinearGauge1").EnableAnimation(false)
.Height(150).Width(600).Orientation(Orientation.Horizontal)
.LabelColor("Black").IsResponsive(true)
//Adding scale collection
.Scales(scale => {
scale.Width(0).BackgroundColor("transparent").Border(border=> border.Color("transparent").Width(0)).ShowMarkerPointers(true)
.ShowBarPointers(false).ShowCustomLabels(true).Direction(Directions.Clockwise)
.ShowRanges(true).Minimum(-20).Maximum(60)
//Adding label collection
.Labels(label => { label.DistanceFromScale(dc => dc.X(0).Y(50)).Add(); })
//Adding ticks collection
.Ticks(tic =>
{
tic.Type(TickType.MajorInterval).Width(2).Color("#8c8c8c")
.DistanceFromScale(distance => distance.X(-1).Y(20)).Add();
tic.Type(TickType.MinorInterval).Color("#8c8c8c").Width(1)
.Height(6).DistanceFromScale(distance => distance.X(-1).Y(20)).Add();
})
//Adding marker pointer collection
.MarkerPointers(mp =>
{
mp.Width(3).Length(30).MarkerBackgroundColor("#FE5C09")
.Type(MarkerType.Star).MarkerDistanceFromScale(20)
.Placement(PointerPlacement.Near).Value(55).Add();
})
//Adding range collection
.Ranges(range=>{
range.StartValue(-20).EndValue(0).StartWidth(5)
.EndWidth(10).RangeBackgroundColor("#2788B1")
.Border(border => border.Color("#2788B1"))
.Placement(RangePlacement.Near).DistanceFromScale(20).Add();
range.StartValue(0).EndValue(20).StartWidth(10)
.EndWidth(15).RangeBackgroundColor("#A5BA28")
.Border(border => border.Color("#A5BA28"))
.Placement(RangePlacement.Near).DistanceFromScale(20).Add();
range.StartValue(20).EndValue(40).StartWidth(15)
.EndWidth(20).RangeBackgroundColor("#FEBE48")
.Border(border => border.Color("#FEBE48"))
.Placement(RangePlacement.Near).DistanceFromScale(20).Add();
range.StartValue(40).EndValue(60).StartWidth(20)
.EndWidth(25).RangeBackgroundColor("Red")
.Border(border => border.Color("Red"))
.Placement(RangePlacement.Near).DistanceFromScale(20).Add();
}).Add();
}))Execute the above code to render the following output.