How can I help you?
Data binding
Data binding enables you to synchronize the elements with different sources of data. You can bind data using two ways, Local data and remote data.
Field Members
Field is a property that includes the object type. Fields are used to bind the data source and it includes following field members to make binding easier.
List of Field members
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| dataSource | datasource receives Essential DataManager object and JSON object. |
| Query | It receives query to retrieve data from the table (query is same as SQL). Example: ej.Query().from("Categories").select("CategoryID,CategoryName").take(3); |
| tableName | It receives table name to execute query on the corresponding table |
| Id | Specifies the id to menu items list |
| parentId | Specifies the parent id of the table. |
| Text | Specifies the text of menu items list |
| spriteCssClass | Specifies the sprite CSS class to “li” item list |
| linkAttribute | Specifies the link attribute to “a” tag in item list |
| imageAttribute | Specifies the image attribute to “img” tag inside items list |
| htmlAttribute | Specifies the HTML attributes to “li” item list |
| imageUrl | Specifies the image URL to “img” tag inside item list. |
Local data
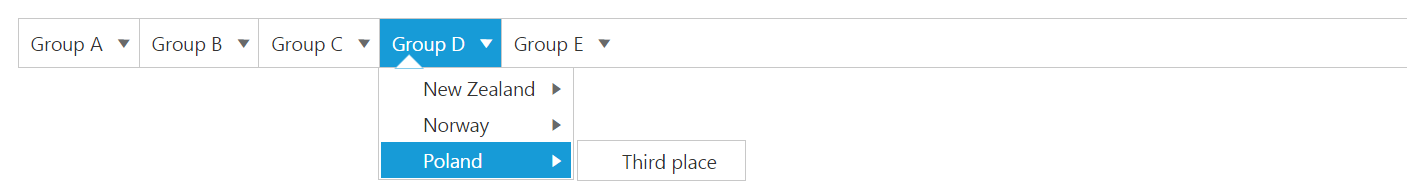
To define the local data to the Menu control, map the user-defined JSON data names with its appropriate dataSource column names.
Add the following code in your HTML page.
<div class="content-container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="cols-sample-area">
<ul id="menujson" ej-menu e-fields-datasource="dataList" e-id="id" e-parentid="parentid" e-text="text"></ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>var data = [
{ id: 1, text: "Group A", parentId: null },
{ id: 2, text: "Group B", parentId: null },
{ id: 3, text: "Group C", parentId: null },
{ id: 4, text: "Group D", parentId: null },
{ id: 5, text: "Group E", parentId: null },
//first level child
{ id: 11, parentId: 1, text: "Algeria" },
{ id: 12, parentId: 1, text: "Armenia" },
{ id: 13, parentId: 1, text: "Bangladesh" },
{ id: 14, parentId: 1, text: "Cuba" },
{ id: 15, parentId: 2, text: "Denmark" },
{ id: 16, parentId: 2, text: "Egypt" },
{ id: 17, parentId: 3, text: "Finland" },
{ id: 18, parentId: 3, text: "India" },
{ id: 19, parentId: 3, text: "Malaysia" },
{ id: 20, parentId: 4, text: "New Zealand" },
{ id: 21, parentId: 4, text: "Norway" },
{ id: 22, parentId: 4, text: "Poland" },
{ id: 23, parentId: 5, text: "Romania" },
{ id: 24, parentId: 5, text: "Singapore" },
{ id: 25, parentId: 5, text: "Thailand" },
{ id: 26, parentId: 5, text: "Ukraine" },
//second level child
{ id: 111, parentId: 11, text: "First Place" },
{ id: 112, parentId: 12, text: "Second Place" },
{ id: 113, parentId: 13, text: "Third place" },
{ id: 114, parentId: 14, text: "Fourth Place" },
{ id: 115, parentId: 15, text: "First Place" },
{ id: 116, parentId: 16, text: "Second Place" },
{ id: 117, parentId: 17, text: "Third Place" },
{ id: 118, parentId: 18, text: "First Place" },
{ id: 119, parentId: 19, text: "Second Place" },
{ id: 120, parentId: 20, text: "First Place" },
{ id: 121, parentId: 21, text: "Second Place" },
{ id: 122, parentId: 22, text: "Third place" },
{ id: 123, parentId: 23, text: "Fourth Place" },
{ id: 120, parentId: 24, text: "First Place" },
{ id: 121, parentId: 25, text: "Second Place" },
{ id: 122, parentId: 26, text: "Third place" }
];
angular.module('MenuApp', ['ejangular'])
.controller('MenuCtrl', function ($scope) {
$scope.dataList = data;
});The following screenshot displays the output of the above code.