Getting Started
3 Sep 20207 minutes to read
This section explains the steps required to configure a SfLinearGauge control in a real-time scenario and also provides a walk-through on some of the customization features available in SfLinearGauge control.
Adding namespace for the added assemblies
using Com.Syncfusion.Gauges.SfLinearGauge;Initialize gauge
You can initialize the SfLinearGauge control with a required optimal name by using the included namespace.
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle bundle)
{
base.OnCreate(bundle);
SfLinearGauge linearGauge = new SfLinearGauge(this);
SetContentView(linearGauge);
}Initialize gauge in axml:
SfLinearGauge allows users to drag the control from toolbox to designer window. The properties window will be displayed where you change the necessary functionalities to customize the linear gauge in designer.
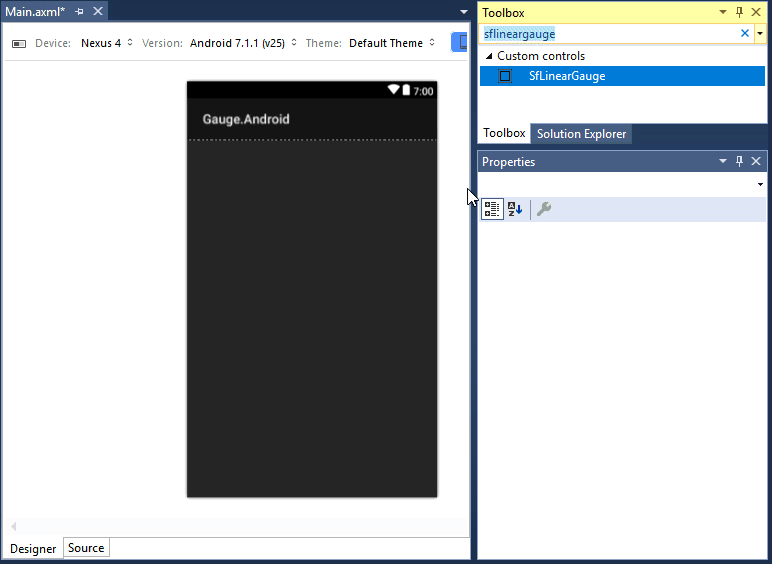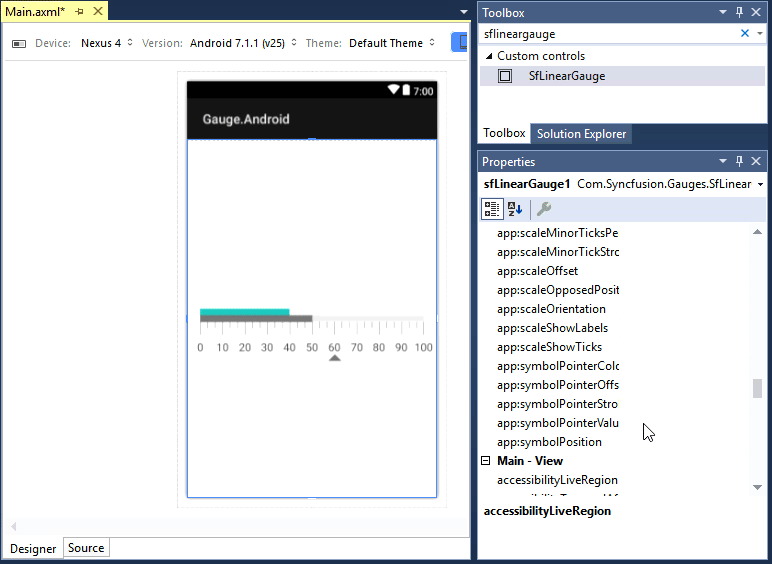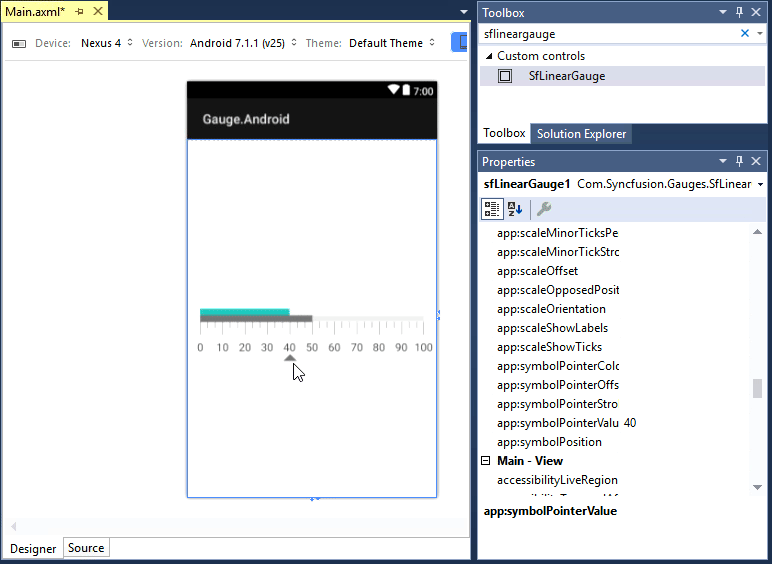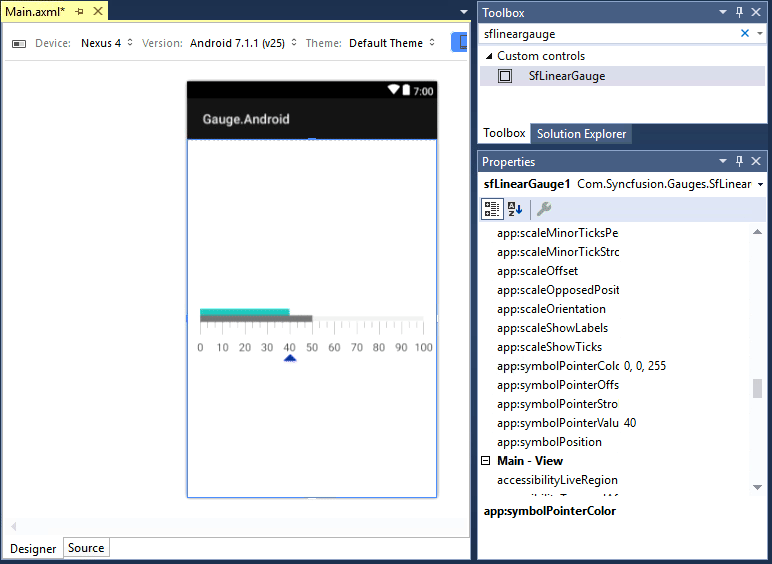
In MainActivity, you can access the linear gauge instance defined in axml page using the following code.
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
base.OnCreate(savedInstanceState);
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.activity_main);
SfLinearGauge linearGauge = FindViewById<SfLinearGauge>(Resource.Id.sfLinearGauge1);
}You can create linear gauge using code behind also. The following steps help to add linear gauge using code behind.
Adding header
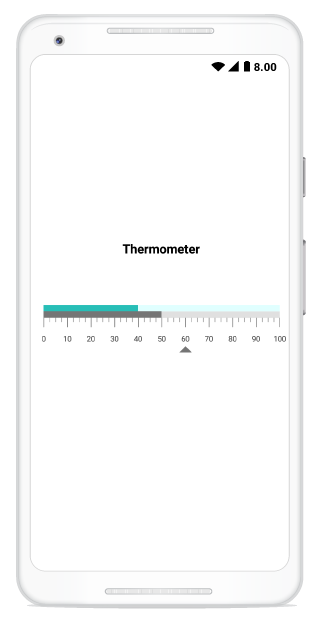
You can assign a unique header to SfLinearGauge by using the LinearLabel property and position it wherever as you desired by using the Offset property.
SfLinearGauge linearGauge = new SfLinearGauge(this);
linearGauge.SetBackgroundColor(Color.White);
LinearLabel linearHeader = new LinearLabel();
linearHeader.Text = "Thermometer";
linearHeader.TextSize = 20;
linearHeader.FontStyle = Typeface.Create("Helvetica", TypefaceStyle.Bold);
linearHeader.TextColor = Color.Black;
linearHeader.Offset = new PointF((float)0.35,(float) 0.35);
linearGauge.Header = linearHeader;Configuring scales
Scales is a collection of LinearScale, which is used to indicate the numeric values. Scale bar, ticks, labels, ranges, and pointers are the sub elements of a scale.
The Minimum and Maximum properties allow you to set the scale range.
LinearScale linearScale = new LinearScale();
linearScale.ScaleBarColor = Color.ParseColor("#e0e0e0");
linearScale.LabelColor = Color.ParseColor("#424242");
linearScale.MajorTickSettings.StrokeWidth = 1;
linearScale.MinorTickSettings.StrokeWidth = 1;
linearScale.MajorTickSettings.Length = 20;
linearScale.MajorTickSettings.Color = Color.Gray;
linearScale.MinorTickSettings.Color = Color.Gray;
linearScale.MinorTickSettings.Length = 10;
linearGauge.Scales.Add(linearScale);Adding a symbol pointer
SymbolPointer is a shape that can be placed to mark the pointer value in gauge.
SymbolPointer symbolPointer = new SymbolPointer();
symbolPointer.Value = 60;
symbolPointer.Offset = 50;
symbolPointer.Color = Color.ParseColor("#757575");
linearScale.Pointers.Add(symbolPointer);Adding a bar pointer
BarPointer is used to mark the scale values. It starts at the beginning of gauge and ends at the pointer value.
BarPointer barPointer = new BarPointer();
barPointer.Value = 50;
barPointer.Color = Color.ParseColor("#757575");
linearScale.Pointers.Add(barPointer);Adding ranges
You can categorize the scale values using the start and end values properties in LinearRange. You can add multiple ranges for a scale using the ranges property.
LinearRange linearRange = new LinearRange();
linearRange.StartValue = 0;
linearRange.EndValue = 40;
linearRange.Color = Color.ParseColor("#27beb7");
linearRange.Offset = -20;
linearRange.StartWidth = 10;
linearRange.EndWidth = 10;
linearScale.Ranges.Add(linearRange);
LinearRange linearRange1 = new LinearRange();
linearRange1.StartValue = 40;
linearRange1.EndValue = 100;
linearRange1.Color = Color.LightCyan;
linearRange1.Offset = -20;
linearRange1.StartWidth = 10;
linearRange1.EndWidth = 10;
linearScale.Ranges.Add(linearRange1);
linearGauge.Scales.Add(linearScale);